microlab midterms
1/73
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
74 Terms
streaking method
simplest method for bacterial isolation
> involves bacterial sample mixed with melted agar medium
size of microbial colonies
<1mm - 3cm
color of microbial colonies
absolutely white
various degrees of pigmentation
texture of microbial colonies
determined by touching the colony with a needle
smooth texture
buttery
dry texture
granular
mucoid texture
slimy
appearance of microbial colonies are judged by the manner in which the
colony refracts light
appearances (5)
clear
glistening
dense
opaque
translucent
form
shape of colony
circular
irregular
filamentous
rhizoid
elevation (4)
degree where colony growth is raised
flat
raised
convex
umbonate
margin (5)
shape of edge / margin of colony
entire
undulate
fusiform
curled
lobate
bacteria grow in collections of cells on agar called
colonies
can be an aid in identification of microorganisms
colony morphology
method of transferring growing organisms from a pure culture to a sterile medium
inoculum
method of preventing UNWANTED microorganisms from gaining access to pure culture (gate)
aseptic technique
purposeful intro of bacteria into a sterile growth medium
inoculation
how to know if the material is sterile
when it has no living organisms present
presence of unwanted microorganisms
contamination
practices that prevent contamination of growth media
aseptic techniques
basic bacterial reqs in nutrition
• water
• carbon
• nitrogen
streaking method
most widely used method for isolating pure culture
spreading method
mixed culture or microorganisms is not diluted in melted agar medium
> diluted in a series of tubes containing water or saline
used to dissolve materials to be transported across cytoplasmic membrane
water
required for construction of all organic molecules & source of energy
carbon
photoautotrophs
energy source: use radiant energy or light
chemotrophs
source of energy: microbes use chemical compunds:
iron
sulfur
autotrophs
sole source of energy: use inorganic carbon (co2)
heterotrophs
source of energy: use organic substances
obligate
source of energy: living form that strictly requires host
nitrogen
obtained from inorganic source & organic source
> many organisms use nitrogen gas by nitrogen fixation to produce ammonia
inorganic source
nitrogen gas (n2)
nitrate (no3)
nitrite (no2)
ammonia (nh3)
required in small amounts
iron
sulfur
phosphorus
optimal growth temperature
temp range at which the highest rate of reproduction occurs
psychrophiles otr:
5-30ºc
mesophiles otr:
30-60ºc
thermophiles otr:
45-90ºc
most bacteria are pathogens that require
37ºc
temp: psychrophiles
some will exist below 0ºc if liquid’s available
• oceans
• ref
• freezers
temperature: mesophiles
most human flora & pathogens
temperature: thermophiles
• hot springs
• effluents from laundromat
• deep ocean thermal vents
oxygen
required for aerobic respiration & energy production
oxygen: obligate aerobic
grow only when oxygen is available
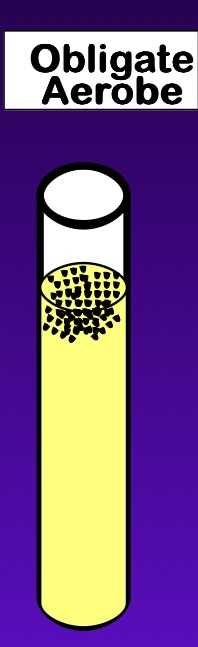
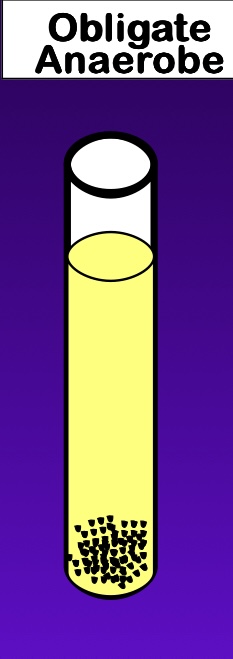
oxygen: obligate anaerobic
grow in the absence of oxygen
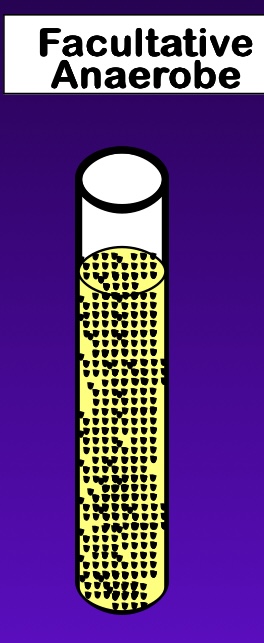
oxygen: facultative anaerobe
require oxygen but exhibit maximal growth rates at reduced oxygen concentrations
halophiles
bacteria that specifically require NaCl for growth
moderates
grow best at 3% NaCl solution
> many ocean dwelling bacteria
extreme
grow well at NaCl concentrations > 15% salt lakes, pickle barrels
in salinity, halophiles growing within salt lakes often
turn the water pink
Great Salt Lake, Utah
in salinity, staphy are salt tolerant up to
concentrations of 10% NaCl
• grown on surface of skin
bacterial pH reqs
microbes have different optimum pH reqs
acidophiles
some bacteria can grow in acid substrates
neutrophiles
most microbes prefer a pH near neutrality
alkalinophiles
microbes grow in very alkaline substrates
osmotic pressure
exerted on plasma m. due to solute concentrations of a solution
osmotolerant
bacteria able to grow in solutions w high solute concentration
hydrostatic pressure
exerted by the weight of water
barotolerant
bacteria able to grow at deep ocean depths
photosynthetic microorganisms
require light at min. lvls of intensity & proper wavelengths
• exposure to light causes death of some
some bacteria will produce pigments, protecting them from exposure to lethal effects of light
ultraviolet radiation is harmful to
dna of bacteria
causes abnormalities in cell growth & division
oxygen: microaerophiles
microbes that utilize low oxygen tension
serial dilution method
developed by joseph lister
> known for isolation & culturing of bacteria
> isolation technique, specific microorganism isolated form mixed culture
Biological Safety Levels
series of protection relegated to autoclave-related activities
> individual safeguards designed to protect lab personnel
BSL-1
lowest biosafety lab
> microbes not known to consistently cause disease in immunocompetent adult humans
risk lvl: minimal
BSL-2
microbes pose moderate potential hazard to ppl
> personnel are expected to take greater care
risk lvl: moderate
BSL-3
yellow fever, west nile virus
bacteria: yersinia pestis
agents: indigenous/exotic microbes that may cause serious or potentially lethal disease via inhalation
risk lvl: serious
BSL-4
pose a high risk of aerosol-transmitted lab infections & life threatening disease
e.g. Ebola & Margburg viruses
risk lvl: high
Centers for Disease Control & Prevention (CDC)
sets BSL lab lvls