DNAP Chem/Physics Exam 1
1/130
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
131 Terms
Accuracy
refers to how close experimental data is to the actual “true” data. For example, pulse ox correlating with the ABG.
Precision
represents agreement between repeated measures of the same target measure.
Baracity
The ratio of the density of a local anesesthetic to the density of cerebral spinal fluid (CSF). Correlates with specific gravity. One of the most important factors that determine the spread of a local anesthetic in the subarachnoid space.
Hypobaric Solution
will rise, less dense than CSF, usually local anesthetic and sterile water
Isobaric Solution
spread is minimal, 1:1 ratio of CSF to local anesthetic
Hyperbaric Solution
will sink, more dense than CSF, usually local anesthetic and dextrose
Halogens
highly reactive, have 7 valence electrons, easier to gain 1 to make 8 than remove 7
Alkali Metals
highly reactive, valence shell only contains 1 electron, easy to remove/share (low ionization energy)
nonmetals
will gain electrons when reacting with metals, but will share electrons when reacting with other nonmetals
Noble Gases
Group 18; lack of chemical reactivity, extremely high ionization energy due to complete valence shells (octet rule)
3 primary particles from which atoms are built?
neutrons, protons, electrons
Neutron
neutral charge, in the nucleus, help stabilize the repulsive forces in the nucleus of the positively charged protons and negatively charged electrons
Protons
positive charge, in the nucleus, larger/heavier than electrons, carry an equal but opposite charge to electrons
Electrons
negative charge, form a “cloud” around the nucleus, organized into “fixed” energy levels
meter (m)
International System (SI) unit for distance
kilogram (kg)
International System (SI) unit for weight
second (sec)
International System (SI) unit for time
ampere (A or amp)
International System (SI) unit for electrical current
kelvin (K)
International System (SI) unit for temperature
mole (mol)
International System (SI) unit for amount of substance
candela (cd)
International System (SI) unit for light intensity
newton (N)
International System (SI) unit for force
pascal (Pa)
International System (SI) unit for pressure
joule (J)
International System (SI) unit for energy or work
watt (W)
International System (SI) unit for power
specific gravity
the ratio of an object’s density to that of a reference, usually water
matter
object or material that has both mass and occupies space
Standard Temperature and Pressure (STP): Temperature
273 kelvin
Standard Temperature and Pressure (STP): Pressure
1 atm
what makes up all matter?
atoms
What states can matter exist in?
liquid, solid, gaseous, plasma
Liquid
state of matter that has definite volume and assumes shape of container
Solid
state of matter that has both shape and volume
Gas
state of matter that has neither definite shape or volume, will easily change volume with changes in temperature and pressure
Plasma
state of matter that is a mixture of ionized gas and free-floating electrons
Enthalpy
measure of the amount of energy associated with substances in a reaction
Examples of endothermic changes of state
sublimation (dry ice to CO2), melting (ice to water), vaporization (water to steam)
Examples of exothermic changes of stae
condensation (steam to water), freezing/crystallization (ice formation)
Physical properties
color or odor
Chemical properties
flammability
pure substance
matter that can’t be separated physically and the chemical and physical properties are uniform throughout with regard to chemical and physical properties are classified as:
mixture
matter that contains two or more pure substances is classified as:
homogeneous
mixture that is uniform throughout and can’t be separated
heterogeneous
mixture that is non-uniform and may be separated into component parts
Atomic number
the number of protons in the nucleus
Mass number
total number of protons + neutrons in the nucleus
Isotopes
atoms with identical atomic numbers but different mass numbers & different number of neutrons. how most elements in nature occur
horizontal rows on periodic table
periods (1-7)
vertical columns on periodic table
groups (18)
Cation
a positively charged ion due to the loss of electron(s)
-will be smaller than the parent atom because the excessive positive charge "pulls" the electrons closer to the nucleus (there is no longer a balance between attractive and repulsive forces)
Anion
-negatively charged ion due to the gain of electron(s)
-larger than the parent atom since the "pull" of the nucleus on any given electron is reduced
Monoatomic gases
completely full valence shells, most stable
halogens and alkali metals
the halogens (F, Cl, Br, I…) have 7 valence electrons, so it is much easier to gain 1 electron to make 8 rather than remove 7; this is why they are highly reactive. The alkali metals are similarly highly reactive as their valence shell only contains 1 electron, making it easy to remove/share.
calcium (Ca)2+
blood clotting, muscle contraction, nerve impulse transmission
Iron (Fe)2+
oxygen transport
Potassium (K+)
regulate cellular ion concentrations
Sodium (Na+)
muscle contraction, nerve impulse transmission
Hydrogen carbonate (bicarbonate) (HCO3)-
acid-base balance
Hydrogen Phospate (HPO4)2-
acid-base balance
Ionization potential
the energy required to removal an electron from a neutral atom. the stronger the bond, the higher the ionization potential
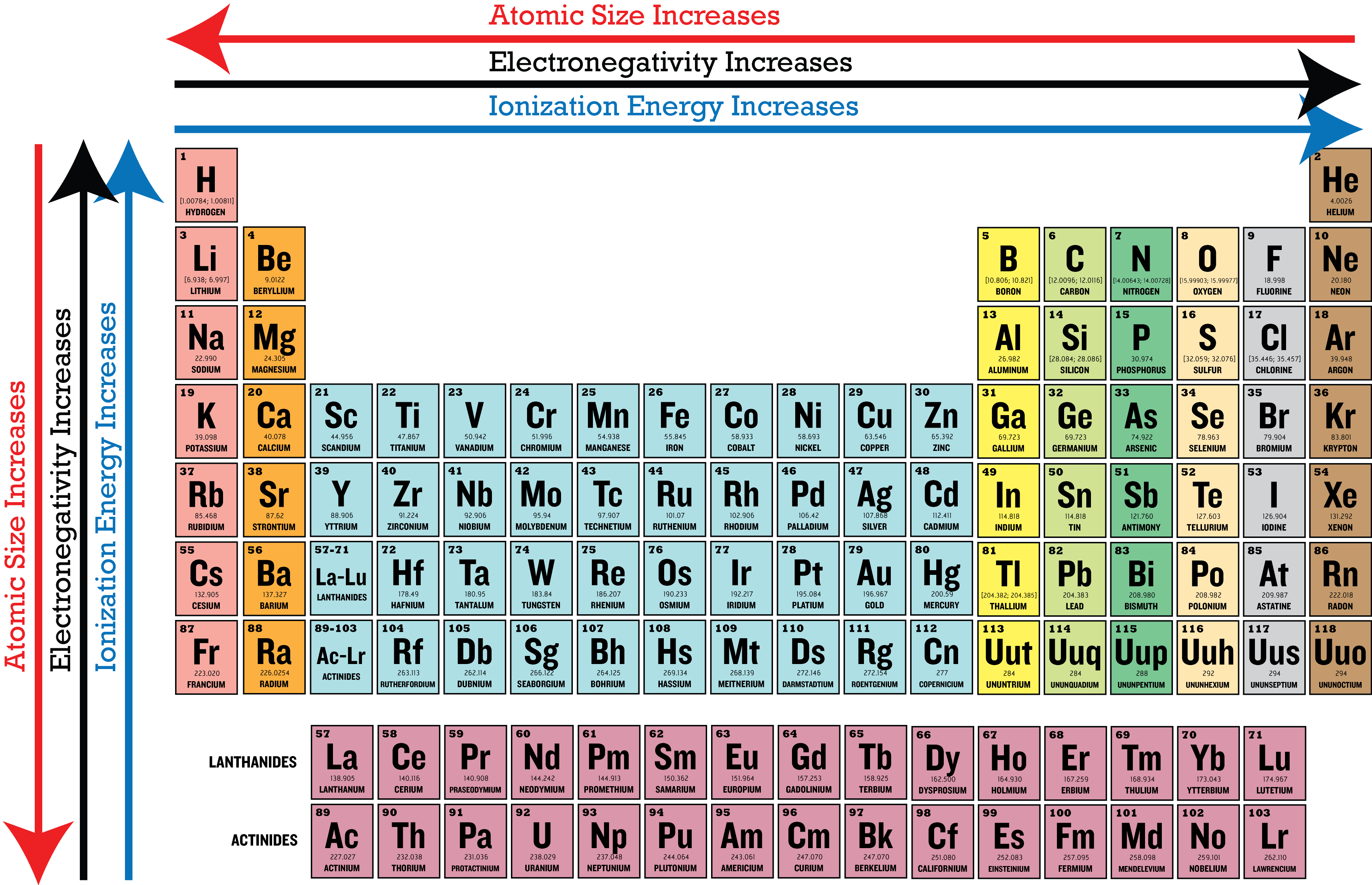
Ionization potential
as you move down in a particular group on the periodic table, the atom size increases, so the outer most electron is progressively further and further away from the nucleus and the ionization energy decreases. It will require less and less energy to remove the outermost electron(s) (low hanging fruit kind of thing) As you move across the table in periods, the atom size decreases, the outermost electrons are therefore closer to the nucleus and harder to remove, so the ionization energy increases. (more tightly held by nucleus) This energy is low for the alkali metals that have one valence electron and extremely high for the noble gases that have complete valence shells. Remember, the removal of an electron results in a positive ion.
electron affinity
the ease with which a neutral atom gains an electron, represents the energy released when a single electron is added to a neutral atom in the gaseous state resulting in a negative ion
Electronegativity
the ability of an atom in a molecule to attract electrons to itself in a chemical bond (how strongly the atoms pull on the electons in a bond)
electron affinity & electronegativity
both generally decrease as you move down a group on the table and increase as you move left to right across periods
First Law of Therodynamics
(the law of conservation of energy): energy is not created or destroyed, just converted to another form or transferred to another part of the system
Second Law of Thermodynamics
A system and its surroundings tend towards increasing disorder or randomness
Entropy
The measure of disorder or randomness (think second law of thermodynamics)
catalyst
presence of this will increase the rate of reaction
Kids Have Dropped Over Dead Converting Metrics
K=Kilo, H=Hecto, D=Deca, O= Base Unit (Liter, Meter, or Gram), D=Deci, C=Centi, M=Milli
percent concentrations
X amount % concentration = X g/100mL
To easily convert X% concentration to mg/mL simply move the decimal point to the right one spot (i.e 0.9% NaCl = 9mg NaCl/mL)
1% Lidocaine
10mg/ml
2% Lidocaine
20mg/ml
0.5% Bupivacaine
5mg/ml
3% Nesocaine
30mg/ml
7.5% Bupivacaine
75mg/ml
¼ or .25
2.5mg/ml
1/8 or 0.125
1.25mg/ml
1/10 or 0.1
1mg/ml
1/16 or 0.0625
0.625mg/ml
1/32 or 0.03125
0.3125mg/ml
Epi 1:1000 (most common preparation)
1mg/ml or 1000mcg/ml
Epi 1:10,000 (ACLS dose)
100mcg/ml
Epi 1:100,000
10mcg/m
Epi 1:200,000
5mcg/ml
Epi 1:400,000
2.5mcg/ml
Epi 1:500,000
2mcg/ml
Lidocaine with epi max dose
7 mg/kg (300mg max single dose)
Lidocaine without epi max dose
4.5mg/kg (300mg max single dose)
Mepivacaine with epi max dose
7mg/kg (400mg max single dose)
Mepivacaine without epi max dose
5mg/kg (400mg max single dose)
Chloroprocaine with epi max dose
14mg/kg (1000mg max single dose)
Chloroprocaine without epi max dose
11mg/kg (800mg max single dose)
Bupivacaine with epi max dose
2.5mg/kg (225mg max single dose)
Bupivacaine without epi max dose
2mg/kg (175mg max single dose)
Levobupivacaine with epi max dose
3.2mg/kg (no max single dose)
Levobupivacaine without epi max dose
2.5mg/kg (no max single dose)
Ropivacaine with epi max dose
3.5mg/kg (no max single dose)
Ropivacaine without epi max dose
3mg/kg (no max single dose)
Tetracaine with epi max dose
3mg/kg (200mg max single dose)
Tetracaine without epi max dose
1-2mg/kg (200mg max single dose)