Recombinant DNA technologies
1/34
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
35 Terms
How is rDNA made
Cutting: restriction enzymes
Pasting: Ligase
How are restriction enzymes be used for cloning
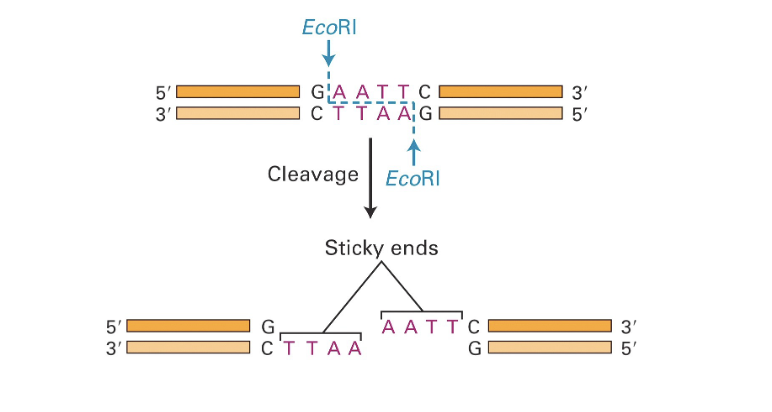
Recognise palindromic sequences aka restriction sites
restriction sites for cloning usually are 4 or 6 nucleotides
How do restriction enzymes cut
Cut both DNA strands creating sticky or blunt ends
Palindrome
A-T
C-G
C,D,F

Agarose gel electrophoresis
Load on agrose gel
Run with some voltage
stain with fluorescent dye and visualise
UV light
Size can be calculated from position of known molecular weight marker bands
DNA - negatively charged
Small= moves quickly
What is DNA ligase
Used for sticking back together: repair and replication
ATP dependent enzyme that links DNA strands
Ligates compatible sticky ends (more efficient) and blunt ends
What are selection markers
Cells that have the plasmid
Genes for antibiotic resistance or growth on specific media
What do plasmids need for cloning
Selection marker
Region where DNA can be inserted
Cloning workflow: Vector preparation
Restrcition digest at 27 dgerees
purify
Insert prepation
PCR 2-3 HOURS
Restriction digest at 37
purfication
Ligation
T4 DNA Ligase at 20 degrees
Optional purfication
Transformation
Prepare compentent cells
transformation of cells and plating
Cloning screening
Blue-white screening
restriction digest colony PCR sequencing
Insert ligates into vector
Vector may also ligate back onto itself
What is blue-white screening
A plasmid that contains LacZ gene, which encodes the enzyme b-galactosidase
If LacZ gene intact = Blue dye , B-gal active
If DNA insert disrupts LacZ gene= white, B-gal inactive
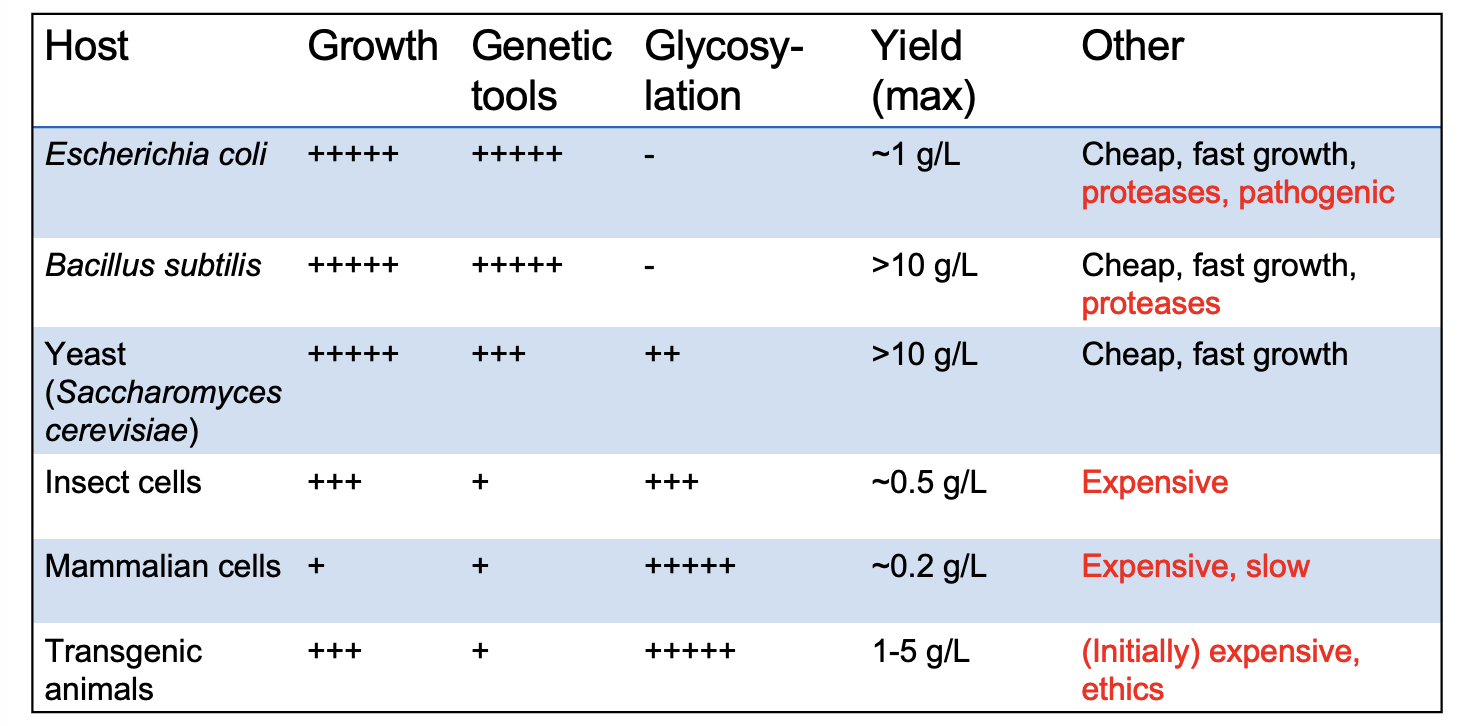
What properties do we want for hosts of cloning and expression
Grows rapidly in inexpensive medium
Non pathogenic
Generally stable
Has many tools for genetic manipulation
Allow high level of expression of genes
Difference between hosts and clones
Hosts for cloning and expression are not the same
What are some hosts for cloning and expression
Where does protein synthesis begin in the cell?
Any enzyme that needs to be secreted with come from endoplasmic reticulum
Protein synthesis begins in the Endoplasmic Reticulum (ER), where ribosomes translate mRNA into a preprohormone.
What is a "preprohormone"?
A preprohormone is the initial, inactive form of a hormone that includes a signal sequence directing it to the ER. The signal sequence is cleaved off, transforming it into a prohormone.
How is the prohormone processed in the cell?
The prohormone is packaged into transport vesicles and sent to the Golgi complex, where it undergoes further modification and becomes an active hormone.
What role does the Golgi complex play in hormone activation?
How is recombinant insulin made
Short peptides such as insulin not stable
peptides stablaised by fusion into large protein
Sequence of insulin can be modified
How can we module insulin-release profile
Mix with protein to slow release
Introduce amino acid changes
Chemical modification
Describe the process of insulin synthesis.
Preproinsulin (inactive form) has a signal sequence and three chains (A, B, C).
The signal sequence is removed, creating proinsulin.
In the Golgi, the C chain is removed, leaving only the A and B chains connected by disulfide bonds, forming active insulin.
What are the A and B chains in insulin?
The A chain has 21 amino acids, and the B chain has 30 amino acids. They are connected by disulfide bonds, forming the structure of active insulin.
Release profile of insulin
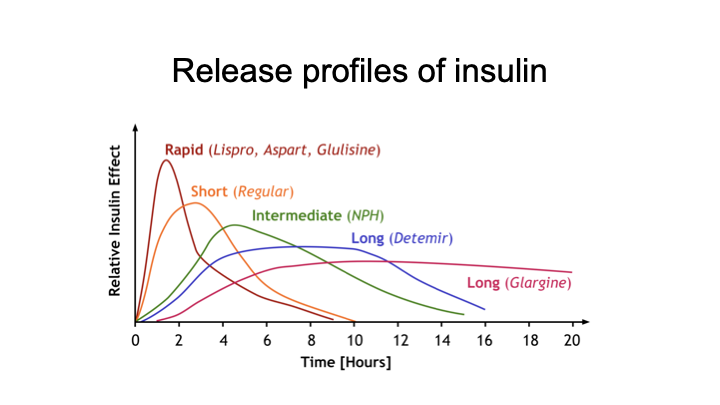
Lispro
Reversal of Lys/Pro in B chain
Forms dimers very ineffciently
rapid release
Glargine
Lantus
One deletion and 3 additions
PI: Isoelectric point
Slow release
PI value
proteins around PI value tend to precipitate
Detemere
Thr30 deleted
fatty acid is added on Lys29
causes it to bind very well to albumin
Slow release
What is Factor VIII
Blood clotting factor
Used for treatment of haemophilia
Very large protein
Glycosylated- can’t be made in bacteria
Cloning of factor VIII
Contains several introns
requires copies to be made from mRNA
Plasmid with gene used to transfect mammalian cells
Plasmid integrates with genome: copies amplified and cell line with highest number of copies used for production
How can Factor VIII be made
Batch culture
Continuous culture
purified from culture medium