Cardiovascular function (Patho physiology)
1/93
Earn XP
Description and Tags
By Fooz
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
94 Terms
What are the four main components of the cardiovascular system?
The heart, blood vessels, lymphatic system, and blood
What is the primary function of arteries in the cardiovascular system?
To carry oxygenated blood away from the heart
What is the primary function of capillaries in the cardiovascular system?
Site of exchange between blood and tissues
Name the three layers of blood vessels, from innermost to outermost
Tunica intima, Tunica media, Tunica adventitia
What is the exception to the general rule of artery and vein function in the pulmonary system?
The pulmonary artery carries deoxygenated blood away from the heart, while the pulmonary vein carries oxygenated blood to the heart
What are the three main layers of the heart wall?
Pericardium, Myocardium, Endocardium
What are the four chambers of the heart?
Two atria (receiving chambers) and two ventricles (pumping chambers)
Which heart chamber has the thickest walls and why?
The left ventricle, because it needs to pump blood throughout the entire body
What is the main function of the systemic circulation?
To carry blood throughout the body to meet the body's needs and remove waste products
What is the main function of the pulmonary circulation?
To carry blood to and from the lungs for gas exchange
The cardiovascular system is composed of the
{c1:heart}, {c2:blood vessels}, {c3:lymphatic system}, and {c4:blood}.
The three layers of blood vessels are
{c1:Tunica intima} (inner layer), {c2:Tunica media} (middle muscular layer), and {c3:Tunica adventitia} (outer elastic layer).
The heart wall consists of three layers:
{c1:Pericardium} (surrounds the heart for protection and support), {c2:Myocardium} (cardiac muscle), and {c3:Endocardium} (inner structures, including valves).
The four chambers of the heart are two
{c1:atria} (receiving chambers) and two {c2:ventricles} (pumping chambers).
Systemic circulation And pulmonary circulation
carries blood throughout the body, while {c2:pulmonary circulation} carries blood to and from the lungs for gas exchange.
The walls of blood vessels are composed of three layers of tissue
the {c1:endothelium}, {c2:elastic tissue}, and the {c3:connective tissue}.
In the pulmonary system
the {c1:pulmonary artery} carries deoxygenated blood away from the heart, while the {c2:pulmonary vein} carries oxygenated blood to the heart.
What are the two major veins that bring deoxygenated blood from the systemic circulation to the right atrium?
The superior vena cava and the inferior vena cava
What is the path of blood flow through the right side of the heart?
Right atrium → Tricuspid valve → Right ventricle → Pulmonic valve → Pulmonary arteries
What is the path of blood flow through the left side of the heart?
Pulmonary veins → Left atrium → Mitral valve → Left ventricle → Aortic valve → Aorta
What is the primary function of the cardiac conduction system?
To organize electrical impulses in cardiac cells, controlling automaticity, conductivity, and excitability
Where do cardiac impulses originate, and at what rate?
In the sinoatrial (SA) node, high in the right atrium, at a rate of 60-100 bpm
What is the function of the atrioventricular (AV) node?
To delay impulses, allowing for complete ventricular filling, and to initiate impulses if the SA node fails
What is the rate of impulses generated by the AV node if the SA node fails?
40-60 bpm
What structures do impulses pass through after the AV node?
Bundle of His, right and left bundle branches, and Purkinje network of fibers
What is depolarization in the context of cardiac electrical activity?
An increase in electrical charge accomplished through cellular ion exchange, generating cardiac contraction
What is repolarization in the context of cardiac electrical activity?
Cellular recovery, with ions returning to the cell membrane in preparation for depolarization
The path of blood through the right side of the heart:
{c1:Right atrium} → {c2:Tricuspid valve} → {c3:Right ventricle} → {c4:Pulmonic valve} → {c5:Pulmonary arteries}
The path of blood through the left side of the heart
{c1:Pulmonary veins} → {c2:Left atrium} → {c3:Mitral valve} → {c4:Left ventricle} → {c5:Aortic valve} → {c6:Aorta}
The cardiac conduction system controls three main aspects
{c1:Automaticity}, {c2:Conductivity}, and {c3:Excitability}
The conduction pathway
{c1:SA node} (60-100 bpm) → {c2:Atria} → {c3:AV node} (40-60 bpm if SA node fails) → {c4:Bundle of His} → {c5:Right and left bundle branches} → {c6:Purkinje network}
Depolarization and Repolarization
{c1:Depolarization} increases electrical charge and generates cardiac contraction, while {c2:Repolarization} involves cellular recovery and preparation for the next depolarization.
SA AND AV
The {c1:sinoatrial (SA) node} initiates impulses at 60-100 bpm, the {c2:atrioventricular (AV) node} can initiate at 40-60 bpm, and the {c3:ventricles} can initiate at 20-40 bpm if both nodes fail.
electrocardiogram (EKG)
is produced by reading the electric current generated by cardiac impulse conduction using {c2:electrodes attached to the skin}.
What are the three main electrolytes involved in cardiac conduction control?
Sodium, potassium, and calcium
What are the three main functions controlled by the medulla in cardiac function?
Chronotropic (rate of contraction), Dromotropic (rate of electrical conduction), and Inotropic (strength of contraction)
What is an action potential in the context of the nervous system?
Small ionic changes (e.g., potassium and sodium moving across cell membranes) that generate neural impulses
What does the P wave represent on an electrocardiogram?
Atrial depolarization
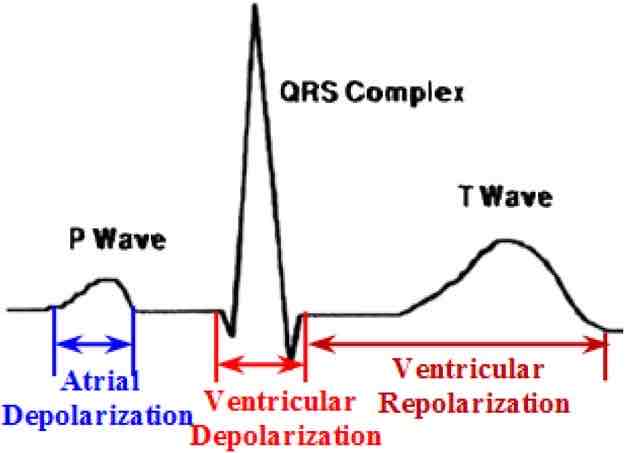
What does the QRS complex represent on an electrocardiogram?
Ventricular depolarization
What does the T wave represent on an electrocardiogram?
Ventricular repolarization
What is the formula for calculating blood pressure?
BP = CO × PVR (Cardiac Output × Peripheral Vascular Resistance)
What is the formula for calculating cardiac output?
CO = SV × HR (Stroke Volume × Heart Rate)
What is pulse pressure and what does it reflect?
The difference between systolic and diastolic blood pressure (usually ~40 mmHg); it reflects the force the heart generates each time it contracts
What are the main functions of the lymphatic system?
To return excess interstitial fluid (lymph) to the circulation, play a role in immunity, and provide a medium for nutrient, gas, and waste exchange between capillaries and cells
The medulla monitors and controls cardiac function through the
{c1:Autonomic nervous system}, {c2:Endocrine system}, and {c3:Cardiac tissue}.
Chemoreceptors detect
{c1:chemical changes in the blood}, while baroreceptors detect {c2:pressure in the heart and arteries}.
An electrocardiogram shows three main components
{c1:P wave} (atrial depolarization), {c2:QRS complex} (ventricular depolarization), and {c3:T wave} (ventricular repolarization).
Blood pressure is represented as a fraction, with
{c1:systolic} pressure (cardiac work phase) as the top number and {c2:diastolic} pressure (cardiac rest phase) as the bottom number.
Normal blood pressure according to the AHA is less than
{c1:120}/{c2:80} mmHg.
Factors influencing blood pressure include
{c1:Cardiac output}, {c2:Peripheral vascular resistance}, {c3:Sympathetic nervous system}, {c4:Parasympathetic nervous system}, {c5:Arterial elasticity}, {c6:Blood viscosity}, {c7:Preload}, and {c8:Hormones}.
The lymphatic system includes
{c1:lymph nodes}, {c2:spleen}, {c3:thymus}, and {c4:tonsils}.
Antidiuretic hormone Vs Renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system
increases water reabsorption in the kidney and acts as a vasoconstrictor, while the {c2:Renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system} plays a role in blood pressure regulation.
What are the two main categories of alterations in cardiovascular conditions?
Alterations resulting in decreased cardiac output and alterations resulting in altered tissue perfusion
Name three conditions that can result in both decreased cardiac output and altered tissue perfusion
Hypertension and shock
What is hypertension?
Prolonged elevation in blood pressure
What is the primary cause of excessive cardiac workload in hypertension?
Vasoconstriction, which leads to increased afterload
What are the two main types of hypertension?
Primary (Essential) hypertension and Secondary hypertension
What is pregnancy-induced hypertension (PIH)?
Hypertension first seen in pregnancy, characterized by high blood pressure, proteinuria, and edema
Why is hypertension often called the "silent killer"?::
Because it often has no symptoms
What is an aneurysm?
Dilatation and weakening of an artery
What are the three types of true aneurysms?
Saccular aneurysm, Fusiform aneurysm, and Dissecting aneurysm
Alterations resulting in decreased cardiac output include:
{c1:pericarditis}, {c2:infective endocarditis}, {c3:myocarditis}, {c4:valvular disorders}, {c5:cardiomyopathy}, {c6:electrical alterations}, {c7:heart failure}, and {c8:congenital heart defects}.
Alterations resulting in altered tissue perfusion include:
{c1:aneurysm}, {c2:dyslipidemia}, {c3:atherosclerosis}, {c4:peripheral vascular disease}, {c5:coronary artery disease}, {c6:thrombi and emboli}, {c7:varicose veins}, {c8:lymphedema}, and {c9:myocardial infarction}.
Risk factors for hypertension include:
{c1:advancing age}, {c2:family history}, {c3:obesity}, {c4:physical inactivity}, {c5:tobacco use}, {c6:high-sodium diet}, {c7:low-potassium diet}, {c8:high vitamin D intake}, {c9:excessive alcohol intake}, and {c10:stress}.
Primary hypertension Vs Secondary hypertension
{c1:Primary hypertension} is the most common form and develops gradually over time, while {c2:secondary hypertension} tends to appear suddenly and cause higher blood pressure.
Complications of hypertension include
{c1:atherosclerosis}, {c2:aneurysms}, {c3:heart failure}, {c4:stroke}, {c5:hypertensive crisis}, {c6:renal damage}, {c7:vision loss}, {c8:metabolic syndrome}, and {c9:memory problems}.
Risk factors for aneurysms include
{c1:congenital defect}, {c2:atherosclerosis}, {c3:hypertension}, {c4:dyslipidemia}, {c5:diabetes mellitus}, {c6:tobacco use}, {c7:advanced age}, {c8:trauma}, and {c9:infection}.
The three main types of true aneurysms are
{c1:Saccular aneurysm} (bulge on the side), {c2:Fusiform aneurysm} (affects the entire circumference), and {c3:Dissecting aneurysm} (weakening occurs in the inner layers).
What is dyslipidemia?
::A condition characterized by abnormal levels of cholesterol and triglycerides in the blood
What are the four key types of dyslipidemia?
Hypercholesterolemia, Hypertriglyceridemia, Combined hyperlipidemia, and Low HDL cholesterol
What is atherosclerosis?
A chronic inflammatory disease characterized by thickening and hardening of the arterial wall
What is Virchow's triad?
Three factors that contribute to thrombosis: endothelial injury, sluggish blood flow, and increased coagulopathy
What is a pulmonary embolism?
::A condition where a blood clot (thrombus) travels from a vein, typically in the legs, to the lungs
The three main types of lipoproteins based on density are:
{c1:Very-low-density lipoproteins}, {c2:Low-density lipoproteins} ("bad" cholesterol), and {c3:High-density lipoproteins} ("good" cholesterol).
Manifestations of aneurysms depend on
{c1:location and size}, and may include {c2:pulsating mass}, {c3:pain}, {c4:respiratory difficulty}, and {c5:neurologic decline}.
Complications of atherosclerosis include
{c1:peripheral vascular disease}, {c2:coronary artery disease}, {c3:thrombi}, {c4:hypertension}, and {c5:stroke}.
Peripheral Vascular Disease (PVD) can be caused by:
{c1:atherosclerosis}, {c2:thrombus}, {c3:inflammation}, and {c4:vasospasms}.
Manifestations of Peripheral Vascular Disease include
: {c1:pain}, {c2:intermittent claudication}, {c3:numbness}, {c4:burning}, {c5:nonhealing wounds}, {c6:skin color changes}, {c7:hair loss}, and {c8:impotency}.
The two main types of angina are:
{c1:Stable angina} (goes away with demand reduction) and {c2:Unstable angina} (increased intensity or frequency, does not go away with demand reduction, or occurs at rest).
Causes of Coronary Artery Disease include
{c1:atherosclerosis}, {c2:vasospasms}, {c3:thrombus}, and {c4:cardiomyopathy}.
The key steps in the pathophysiology of pulmonary embolism are:
{c1:Thrombus Formation}, {c2:Thrombus Detachment}, {c3:Embolization}, {c4:Pulmonary Arterial Occlusion}, and {c5:Consequences of Occlusion}.
What are the main complications that varicose veins can cause?
Stasis pigmentation, subcutaneous induration, dermatitis, and thrombophlebitis
What are the two main types of lymphedema?
Primary lymphedema (usually congenital) and secondary lymphedema
What is myocardial infarction?
Death of the myocardium, commonly known as a heart attack, where blood supply to the heart muscle is abruptly cut off
What are the three types of angina?
Stable angina, unstable angina, and variant angina (Prinzmetal's angina)
What are the three stages of shock?
Compensatory, progressive, and irreversible
Risk factors for varicose veins include
{c1:genetic predisposition}, {c2:pregnancy & obesity}, {c3:prolonged sitting or standing}, {c4:alcohol abuse and liver disorders}, and {c5:constipation}.
Manifestations of varicose veins include
{c1:irregular, purplish, bulging veins}, {c2:pedal edema}, {c3:fatigue}, {c4:aching in the legs}, {c5:shiny, pigmented, hairless skin on the legs and feet}, and {c6:skin ulcer formation}.
Clinical manifestations of lymphedema include
{c1:edema}, {c2:skin changes}, {c3:hyperpigmentation}, {c4:ulceration}, and {c5:thickening (brawny edema)}.
Symptoms of myocardial infarction include
{c1:chest pain or discomfort}, {c2:pain spreading to shoulder, arm, neck, jaw, or back}, {c3:fatigue}, {c4:nausea}, {c5:vomiting}, {c6:shortness of breath}, {c7:diaphoresis}, and {c8:anxiety}.
Causes of heart failure include:
{c1:congenital heart defects}, {c2:myocardial infarction}, {c3:heart valve disease}, {c4:dysrhythmias}, and {c5:thyroid disease}.
The three types of heart failure based on dysfunction are:
: {c1:systolic dysfunction}, {c2:diastolic dysfunction}, and {c3:mixed dysfunction}.
Manifestations of shock include:
{c1:thirst}, {c2:tachycardia}, {c3:restlessness}, {c4:irritability}, {c5:tachypnea}, {c6:cool and pale skin}, {c7:hypotension}, {c8:cyanosis}, and {c9:decreasing urinary output}.