microevolutions
1/9
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
10 Terms
Microevolution
is change in the frequency of a gene pool on a small scale
Happens from one generation to the next
Gene Flow (migration)
Description: Gene flow is the movement of alleles between two interbreeding populations with different allele frequencies.
Effect: It changes allele frequencies in one or both populations as genes move between them.
Example: Prairie dog colonies are normally closed, but in summer mature males can enter new colonies, introducing new genes and altering the gene pool.
Non-random Mating
Description: During non-random mating, individuals in a population select mates, often on the basis of their phenotypes.
Effect: Non-random mating increases the proportion of homozygous individuals in a population.
GENETIC DRIFT
Description: random change in genetic variation from generation to generation due to chance.
Effect: Genetic drift changes allele frequencies
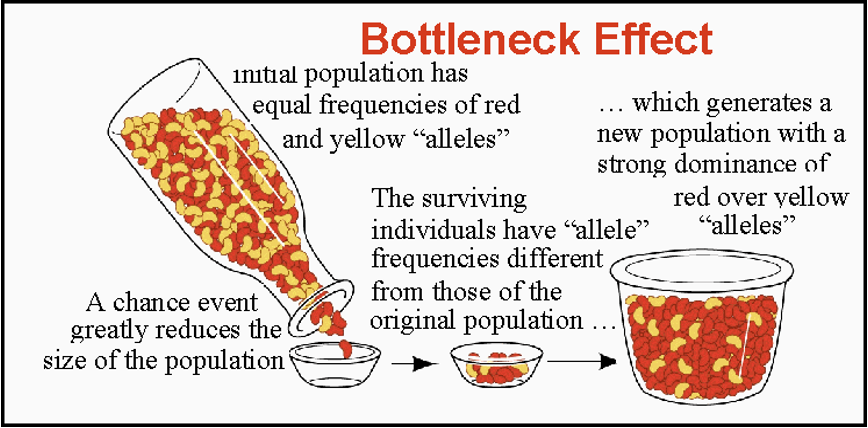
GENETIC DRIFT: THE BOTTLENECK EFFECT
When a severe event results in a drastic reduction in numbers, a population may experience a bottleneck effect.
A very small sample of alleles survives to establish a new population.
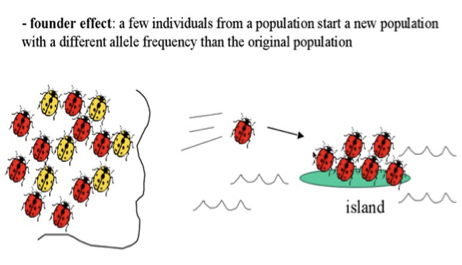
GENETIC DRIFT: THE FOUNDER EFFECT
When a few individuals from a large population leave to establish a new population
1. SEXUAL SELECTION
Favours the selection of any trait that influences the mating success of the individual.
Process by which individuals compete for the chance for a mate.
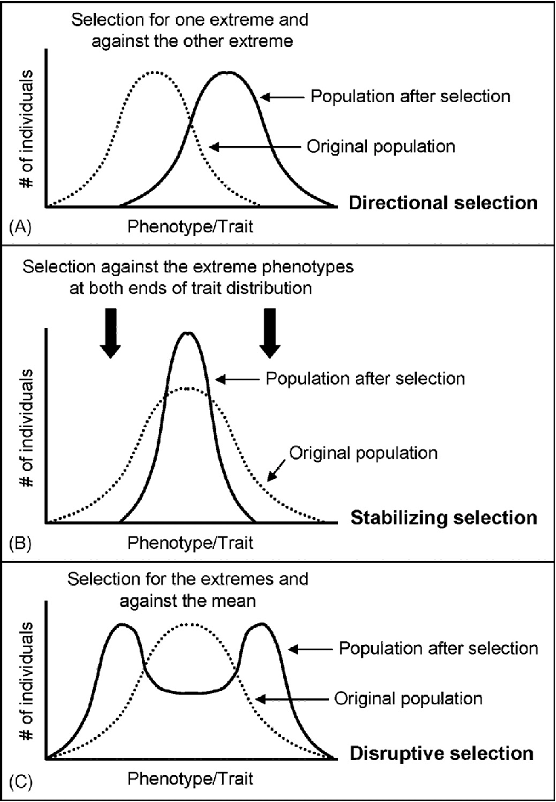
2. Stabilizing selection
It favors the intermediate variants.
Stabilizing selection tends to remove the more severe phenotypes, resulting in the reproductive success of the norm or average phenotypes.
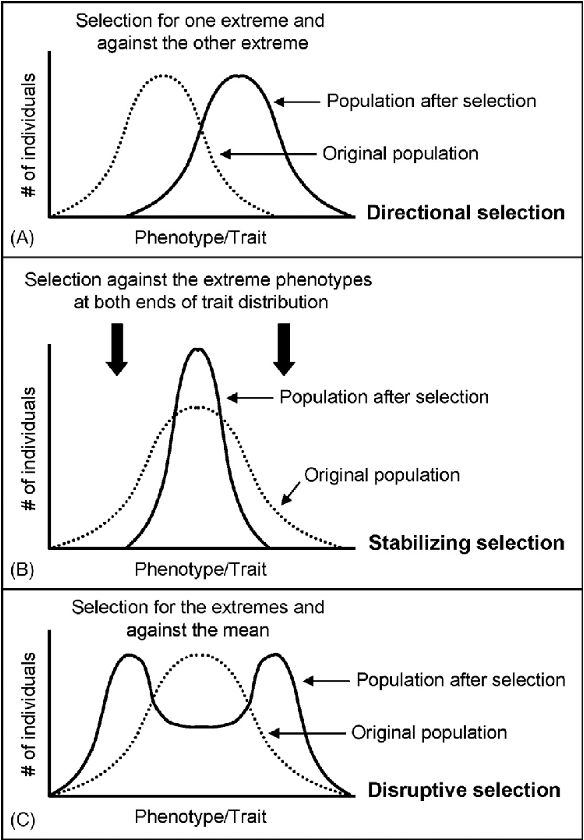
3. Directional selection
is a mode of negative natural selection in which an extreme phenotype is favored over other phenotypes.
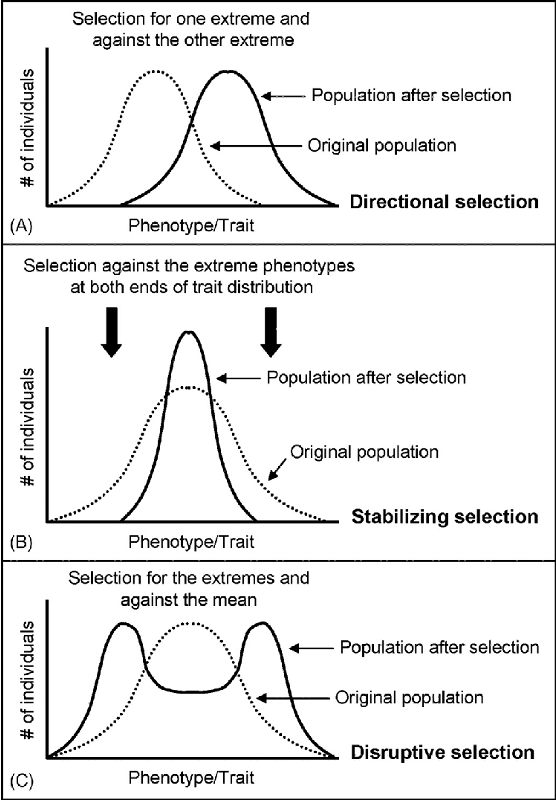
4. Disruptive selection
Describes changes in population genetics in which extreme values for a trait are favored over intermediate values. In this case, the variance of the trait increases, and the population is divided into two distinct groups.