ATP & Respiration
1/34
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
35 Terms
Word equation of aerobic respiration
Oxygen + Glucose —> Water + Carbon dioxide
Word equation for anaerobic respiration?
Glucose —> Lactic acid
What is adenosine triphosphate made of?
Adenine, ribose (adenosine) & 3 phosphate
How is energy transferred?
Energy is converted from one form to another, food contains chemical energy where respiration breaks down glucose C-H C-C C-O bonds, and energy is transferred from respiration to ATP and heat
Why is ATP described as a universal energy currency?
Used for all living organisms and used to provide energy for all cell reactions
How is ATP synthesised and broken down
Synthesise ( ADP + Pi → ATP) Breakdown ( ATP → ADP + Pi)
Advantages of using ATP as an energy carrier (not store)
Only 1 enzyme needed in the breakdown of ATP, releases small amounts of energy so less energy wasted.
How much energy does ATP breakdown release?
30.6 KJ mol-1
What enzyme catalyses ATP? What’s the process?
ATPase catalyses ATP 3rd Phosphate (dephosphorylation)
TASK - draw and label both mitochondria and chloroplast as well as respiratory enzyme ( show direction)
Mitochondria - matrix, loop of DNA, Cristae, inner membrane, inter membrane space, outer membrane, 70s ribosomes, direction of stalked particle into matrix
Chloroplast - outer membrane, inter membrane space, inner membrane, stroma, thylakoid (membrane, space), granum, direction of stalked particle out of thylakoid into stroma
What enzyme do stalked particles contain?
ATP synthetase
What are the stages of aerobic respiration in order
Glycolysis, Link reaction, Kreb cycle, electron transport chain
Draw a labelled diagram of Glycolysis
Where does glycolysis take place
In cytosol
How much ATP is used, produced and net yield?
2, 4, 2
What type of phosphorylation is used in glycolysis and the kreb cycle?
Substrate level phosphorylation?
How many dehydrogenation reactions are in glycolysis
makes 2 reduced NAD
What does glycolysis produce?
produces 2 pyruvate
What is the equation for glycolysis?
Glucose + 2NAD + 2ADP + 2pi → 2 pyruvate + 2 NADH2 + 2 ATP + heat energy
Draw and label a diagram of the link reaction
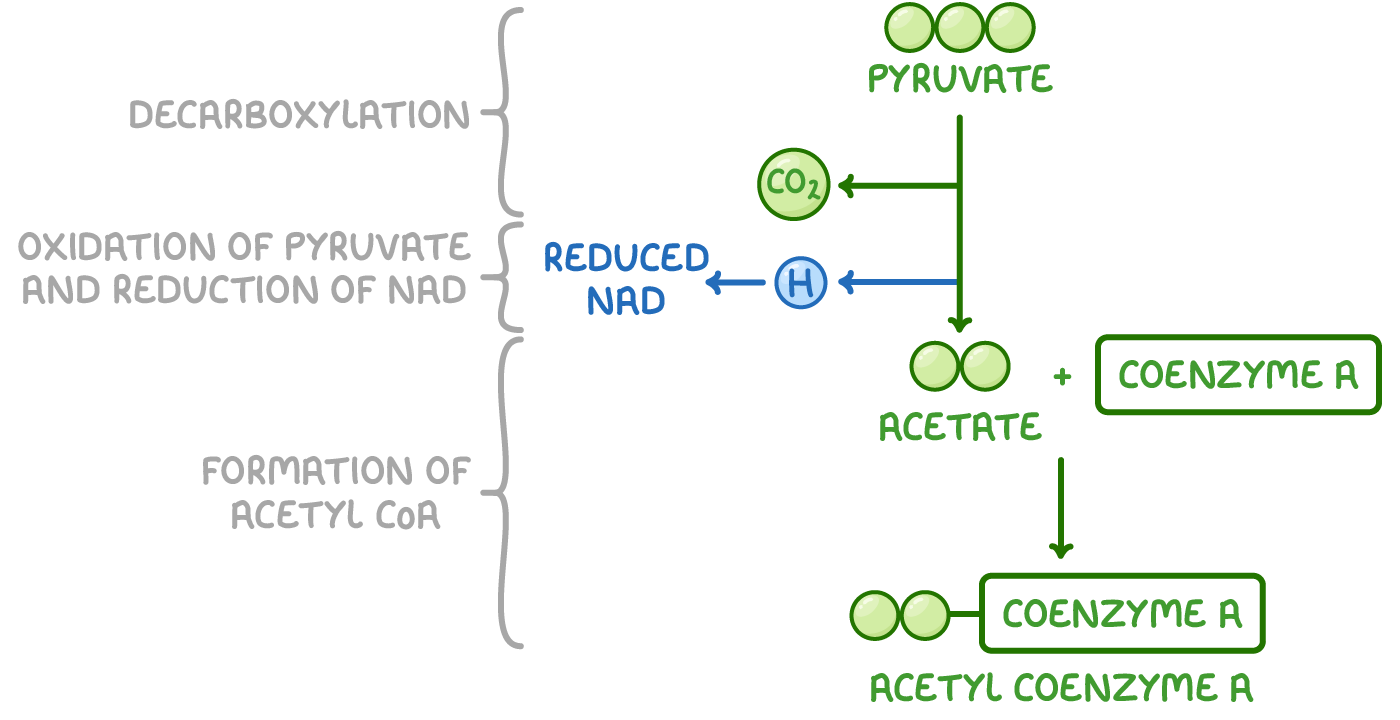
Where does the link reaction take place?
In the mitochondrial matrix
how much ATP is used, produced and net yield
0, 0, 0
How many dehydrogenation reactions take place in the link reaction?
produces 2 reduced NAD, 1 per pyruvate
How many decarboxylation reactions take place in link reaction?
2 carbons are removed, 1 per pyruvate which produces acetate
What does the link reaction produce?
2 acetyl CoA, 1 per pyruvate
What is the equation for the link reaction?
pyruvate + NAD + CoA → Acetyl coA + Co2 + NADH2
Draw and label a diagram of the Kreb cycle
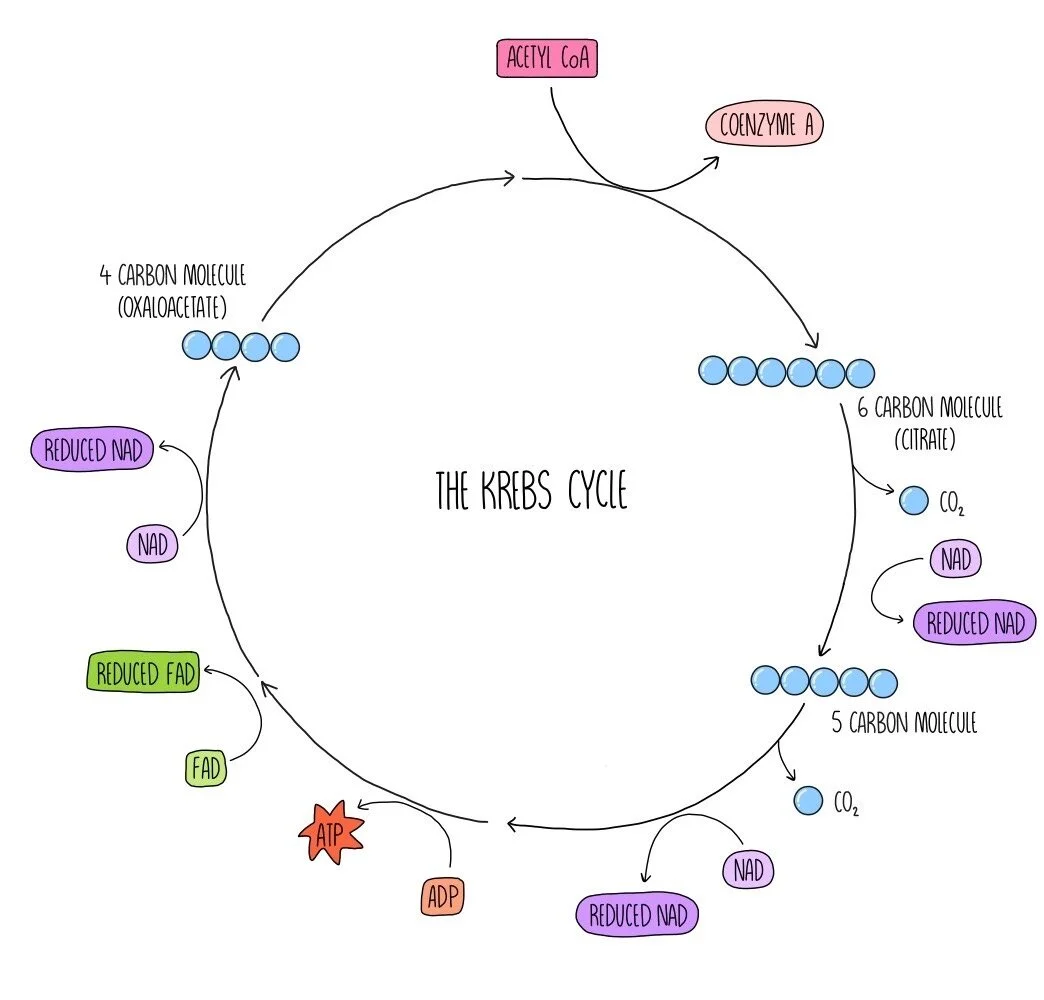
Where does the Kreb cycle take place?
In mitochondrial matrix
How much ATP is used, produced and net yield
0, 2, 2 per glucose
How many dehydrogenation reactions are in the Kreb cycle
8 per glucose, 4 per acetate (3 NADH2, 1 FADH2)
How many decarboxylation reactions take place in Kreb cycle?
4 per glucose , 2 per acetate
What is the equation for the kreb cycle
acetyl CoA + 4C Compound + 3NAD + 1FAD + ADP + pi → ATP + 3 NADH2 + 1 FADH2 + 2CO2 + 4C compound + CoA
Draw and label the process of electron transport chain
What type of phosphorylation is involved in electron transport chain?
oxidative phosphorylation
How much ATP does one NADH2 make?
makes 3 ATP