Fluids and Electrolytes
1/123
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
124 Terms
total body water account for _______% of body weight
60
which amout of fluid does a healthy adult typically consume each day?
2 L/day
2.3 L/day
2.6 L /day
2.9 L/day
2.3 L/day
which electrolyte deficiency results in reduced excitable membrane depolarization and increased cellular swelling?
sodium
calcium
potassium
magnesium
sodium
which fluid is critical to prevent death?
urine
perspiration
blood volume
interstitial fluid
what are the factors to which TBW (total body water) depends on?
age - the elderly are more at risk for dehydration due to declining bodily functions as the kidneys is not cycling the sodium efficiently, and baby or younger kids as their systems are not as developed to keep the water
body compositions - someone with more lean muscle (e.g., atheletes) has more water compared to individual who has more fat content
nutritional status - hydrated/dehydrated? → eating food high in sodium also increased TBW due to increased water retention
comorbidities - heart failure, kidney dysfunction, etc
what are the two category that TBW (total body weight are split into)?
intracellular fluid (2/3)
extracellular fluid (1/3)
intracellular fluid comprised of ________ TBW and extracellular fluid comprised of _________ TBW
2/3; 1/3 respectively
what is the intracellular fluid and what are the main electrolytes that are present?
fluid contained within the cells
the main electrolytes that are present are potassium, phosphate, and sulfate (PPS Kids!)
what is the extracellular fluid and what are the main electrolytes that are present?
fluid outside of the cells in the nooks and crannies :) (e.g., intravascular, interstitial, and transcellular)
the main electrolytes that are present are sodium, chloride, and bicarbonate (SCB - salty cold beverage)
what is the transcellular fluid?
specialized extracellular fluids located in epithelial-lined body cavities (e.g., CSF, GI juices, etc)
intracellular fluid have the ________ (same/different) as extracellular fluid (why?)
osmolarity; as there are shifting of electrolyte back and forth constantly so the concentration of the particles are relatively the same and balanced
what are the functions of nephron inside our kidneys?
filter blood plasma
reabsorbs water and solutes as needed
maintain fluid and electrolyte balance
true or false: the kidney absorbs about 99% of the sodium present in the blood (only about 1% are excreted in the urine)
true
what is the glomerular filtration rate (GFR)?
basically it is how well/fast the kidney is filtering stuff out of the blood
what are the two lows that would decrease the GFR?
low blood pressure
low blood volume
how can the body response to increase GFR when there are low blood pressure and low blood volume?
retain sodium → release renin → angioteniogogen → angiotensin I → angiotensin II → increases blood pressure by causing vasocontriction and stimulate the release of aldosterone & antidiuretic hormone → which increase the retention of sodium and excretion of potassium (aldosterone) and decrease urine formation (antidiuretic)
what is the role of aldosterone in hormonal regulation of volume?
stimulate the retention of sodiym while increasing the excretion of potassium (potassium need to be excreted in order to reabsorp sodium) which increase water retention
true or false: aldosterone is a mineral corticoid (and that basically mean that…)
means it acts to regulate the balance of water and salt in the body, primarily by promoting sodium and water reabsorption and potassium excretion in the kidneys
what is the role of ADH (antidiuretic hormone) in term of hormonal regulaton of volume?
no pee hormone
stimulate the body retention of water without directly controlling the flow or any hormone (e.g., aldosterone) or electrolyte (e.g., potassium, sodium, etc)
they control the retention of water inside the body by contorlling the movement of water channels at each cells of the kidney called aquapoint
when the body is high in ADH, the patient is at risk for ___________
hyponatremia because the high concentration of water in the body dilutes the sodium concentration prsent
when is aldosterone and ADH released?
both of these hormone are release when angiotensin II is released which would indicate that the blood pressure and blood volume is low and there need to be retention of sodium and water!
where is aldosterone & ADH produced and stored?
aldosterone is produced and stored in the adrenal gladn
ADH is produced by the hypothalamus but is store din the posterior pituitary gland
what is diffusion?
movement of molecules from an area of higher concentrationt oa na rea of lower concentration
what is osmosis?
movement of fluid (e.g., water) through a semi-permeable membrane (e.g., capillary & cell walls)
what is active transport?
a type of cellular transport that require input of energy to move molecules across a membrane from an area of lesser concentration to an areas of higher concentration
what is filtration?
the transfer of water and dissolved substances through a permeable membrane froma n area of high pressure to an area of low pressure
what are the source of output that the nurse can and would need to assess for fluid balance?
urine
stool
bleeding
emesis (vomitting)
what is obligatory urine ‘output’?
the minimum amount of urine the body need to make to get rid of the toxin that build up in the body throughout one whole day
what is isotonic fluid volume deficit (FVD)? are there any changes in osmolarity?
the loss of water equal to the loss of sodium
no changes in the osmolarity
what is hypertonic fluid volume deficit (FVD)? are there any changes in osmolarity?
the loss of water is greater than the loss of sodium
there are changes in osmolarity as the fluid shift from intracellular to extracellular leading the cells to shrink
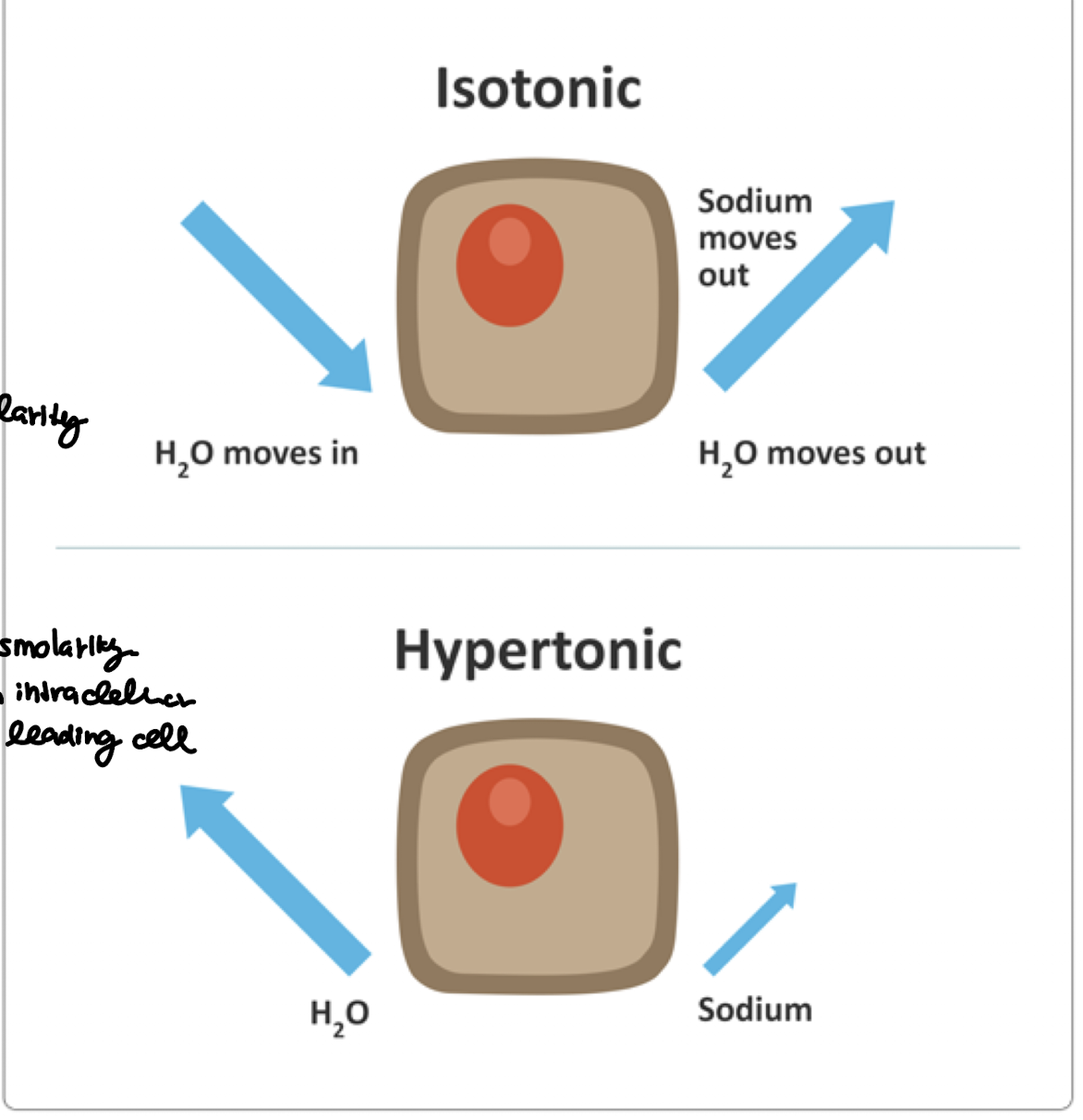
what are some of the common causes of isotonic fluid volume deficit (iFVD)?
proportionate loss of sodium and water
vomiting - since the stomach contents contain water, sodium, chloride, and potassium, vomiting would make you lose both fluid and electrolytes
diarrhea - intestinal fluid is rich in water and sodium, so when you are having diarrhea, you are losing both of those
excessive sweating - even though sweat is mostly water but does conain sodium, heavy sweeting will cause you to lose both water and sodium in an equal amount
fever - increased metabolic rate → more water and sodium loss via sweat and srespiratory secretions
severe bleeding (e.g., hemmorrhage, etc) - blood plasma is isotonic so bleeding will cause you to lose equal amount
burn - since burns damage capillaries leading plasma to leak into interstitial tissues or out of the body and since plasma is istonic, then ….
dehydration - since “dehydration is often refers to overall fluid volume loss,
why is hypertonic dehydration?
losing more water than sodium (e.g., prolonged fever, hyperventilation, watery diarrhea, inadequate water intake)
what is hypotonic dehydration?
losing more sodium than water (e.g., severe vomitting, diuretic use)
what are the signs and symptoms of isotonic volume deficit?
low blood pressure
increase heart rate to over compensate for low blood pressure
increased respiratory rate to overcompensate for decrease blood volume and pressure by increasing oxygen delivery
weak/not patent pulse due to low blood pressure/volume
low capillary refill due to weak perfusion
hypoactive bowel sounds because blood is diverted away from the system that is considered non-essential at the moment
isotonic volume deficit is also known as ___________
hypovolemia
what would be the nursing diagnosis and related fators for isotonic fluid volume deficit?
nursing diagnosis: deficient fluid volume
related factors: prolonged or marked loss of body fluids, prolonged or marked decreased in fluid intake, and diuretic use
what is the similarities etween isotonic fluid volume excess and hypotonic fluid volume excess?
increased circulating volume
what is isotonic volume excess and is there a change in osmolarity?
equal retention of both water and sodium - an increase in circulating volume
no change in serum osmolarity
what is hypotonic fluid volume excess and is there a change in osmolarity?
there is a higher rention of water at a greater rate than sodium leading to an increase in circulating volume with decrease in serum osmolarity
what is hemodilutions?
a process that decreases the concentration of blood components, such as red blood cells, plasma proteins, and electrolytes, by increasing the volume of blood
hypertonic causes the cell to _________ while hypotonic causes the cell to ________
shrink; swell
does hypotonic fluid volume excess cause the cell to swell or shrink?
swell
can hypotonic fluid volume excess be fatal if untreated?
YES! it can lead to pulmonary and cerebral edema
what causes isotonic fluid volume excess?
heart failures - the heart pumps less effectively → kidney sense low perfusion → renin-agiotensin-aldosterone system (RAAS) activates → sodium and water are retained
kidney failure → kidney can’t excrete both sodium and water properly - fluid and sodium accumulate in the body in equal amounts
cirrhosis - low albumin → causing fluid to leak into tissues (ascites, edema) - kidney detect low circulating volume → RAAS activate → retain sodium and waer proportionally
excessive administration of isotonic IV solutions
high-sodium diet - extra sodium → leading to waer retention
use of certain medication like corticosteroids - croticosteroids can cause sodium retention
isotonic fluid volume excess is also known as ___________
hypervolemia
what are the signs and symptoms of hypotonic fluid volume excess?
too much water relative to sodium (ECF becomes hypotonic compared to ICF)
rapid weight gain
edema
increased blood pressure
increased heart rate to try to compensate for the increase blood volume which the heart try to maintain adequate circulation
mental status changes (e.g., confusion & lethargy)
headaches
nausea
seizures
shortness of breath (due to pulmonary edema)
what are the treatment for hypotonic fluid volume excess (what is it)?
when the body is retaining way more water relative to the sodium concentration → causes water to shift from the ECF to the ICF causing cell swelling which can be dangerous in dcases of cerebral edema
use diuretic to remove excess fluid
a low-sodium diet to decrease the rate of water retention
fluid restriction to help the body eliminate the excess fluid
dialysis or paracentesis if needed
what is the difference between osmolarity and osmolality?
osmolarity: number of solute in a L of water
osmolality: number of solute in a Kg of water
what is the WDL range of serum osmolarity?
270-300 mOsm/L
what is specific gravity?
basically how concentrated a fluid is (the more concentrated a fluid is, the higher its specific gravity)
what is the WDL range of specific gravity?
1.010-1.025
what is the WDL range of creatinine for men?
0.6-1.2 mg/dL
what is the WDL range of creatinine for women?
0.5-1.1 mg/dL
what is the WDL GFR (glomerular filtration rate)
more than 90 mL/min/1.73m² (>90)
isotonic: ________ osmolality ________ net change in fluid movement
equal; no
hypertonic: ___________ osmolality: water moves from ____________ & __________ to ______________ and the cells ____________
increased (due to the increased osmolality, meaning there is a higher solute concentration outside of the cell, the water is being drawn out of the cell; cells; interstitial fluid; intravascular space
true or false: for a hypertonic solution, there is more solute outside of the cell than inside the cells
true
true or false: for a hypotonic solution, there is more solute inside the cell than outside of the cell
true
hypotonic: ___________ osmolality: water moves from ____________ & __________ to ______________ and the cells ____________
decreased (because there is more solute inside the cell than outside of the cell); intravascular; interstitial
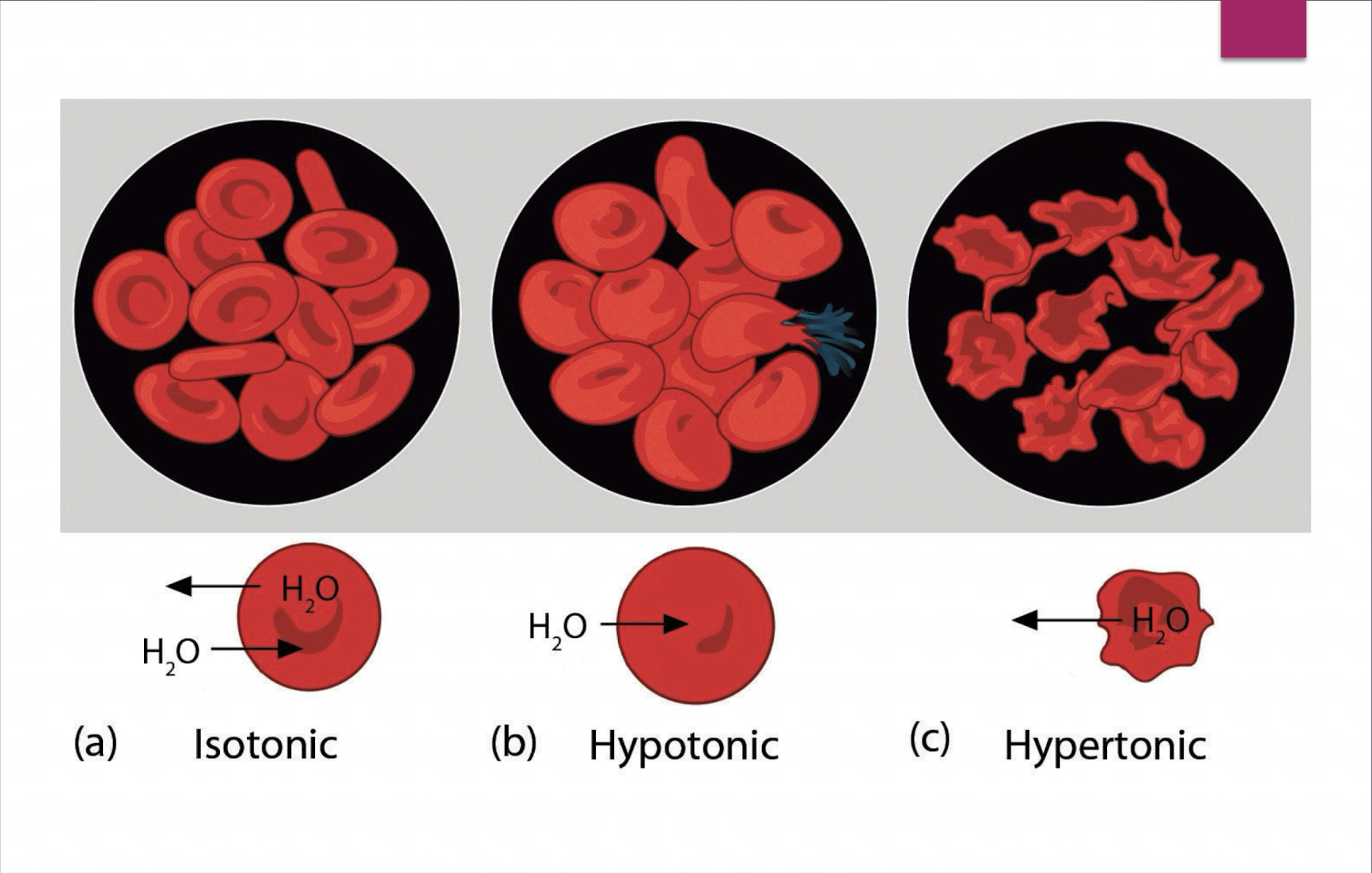
if the patient is isotonic fluid loss, what are some of the treatment for that?
the mainstay of treatment is to replace the volume with isotonic cyrstalloids which allow you to replenish the volume while not changes the osmolality
0.9% NaCL or Normal Saline (NS)
Lactated ringers (LR)
true or false: since normal saline have a slightly higher chrolide load compared to lactated ringer, giving too much can cause hyperchlomeric metabolic acidosis
true
what is lactated ringers (LR)?
a solution of sodium, chloride, potassium, calcium, and lactate (which is metabolized to bicarbonate)
it is more “balanced” (compared to normal saline) and is closer to the plasma composition
what is the main differences between normal saline and lactated ringer?
normal saline - “salt water only” - contain just Na+ and Cl- (in higher chloride than plasma) - best for hyponatremia, metabolic alkalosis, shock/trauma, blood transfusion (since no calcium to clot citrate)
lactated ringer “plasma-like” (contained electrolytes found in the plasma) - contain Na+, Cl-, K+, Ca2+, and lactate (metabolized into bicarbonate to help buffer acidosis) → best for surgery, burns, dehydration, metabolic acidosis (except lactic acidosis or liver failure)
why is lactated ringer not ideal for blood transfusion?
because calcium may bind citrate in stored blood which can clot the IV line or bag and block the transfusion
if the patient is experiencing a hypotonic fluid loss, what is the treatment for that?
hypotonic fluid loss - losing more sodium compared to water
treatment - isotonic fluid (in most cases) to store both sodium and water but in severe cases, hypertonic solution can be used
isotonic sale (0.9% NaCl) - the common treatmenr for hypotonic fluid loss where the body is losing more sodium compared to water
→ replaces ECF volume and sodium in a near-physiologic ratio
if hyponatremia is severe/symptomatic (e.g., seizures, neuro signs - confusion, agitation, mental status change)
→ hypertonic saline (3% NaCl) may be used cautiously in the ICU
if the patient is experiencing a hypertonic fluid loss, then what treatment is needed for that?
hypertonic fluid loss - losing more water than sodium
treatment = hyptonic solution - meaning the solution has fewer solutes compared to the plasma → since the cell is already shrinking, the solution won’t cause the cell to swell
0.45% NaCl because the NaCl concentration is a hypotonic solution relative to plasma (meaning there is less salt in the solution compared to the body cell) which would provide free water to correct the hypernatremia and lower the osmolality while still giving some sodium and chloride to avoid dropping osmolalilty too quick due to dilution if we just give straight water if the solution is hypertonic than it would cause cell to shrink that is why we went with the hypotonic
D5W (5% dextrose in water): the solution starts isotonic in the bag but once the dextrose is metabolized then it is essentially just free water that acts as a hypotonic solution to prevent the cell from shrinking but still supplies the loss water → dextrose is used because the dextrose made the solution isotonic so the solution won’t instantly hemolyze the blood cells when its enter the ven
true or false: normal saline is the same as 0.9% NaCl
true
what are the differen type of isotonic crystalloids?
0.9% NaCl
lactated ringer [LR]
what is a 0.45% NaCl solution and why is it a hypotonic solution?
it is basically normal saline at half strength
0.45% NaCl is a hypotonic solution relative to plasma (meaning there is less salt in the solution compared to the body cell) which would provide free water to replenish the body with water that does not cause a spike in blood sodium
why do we need to include sodium or dextrose in our solution to fix fluid loss when we could just infuse plain sterile water?
No! We cannot infuse plain sterile water into the bloodstream because that would immediately cause the blood to hemolyze - dextrose and sodium mixed in the solution is a critical part to prevent that from happening
what are the different hypertonic crystalloids IV infusions?
D5 NS
D5 1/2NS
D5LR
3% NaCl
what is a 0.9% NaCl solution and why is it an isotonic solution?
it is basically salt water (AKA normal saline) and is used when the body is experiencing isotonic fluid loss where the loss of sodium and water is equal so since normal saline isotonic (meaning it have an equal osmolarity of water and sodium), it would help the body replenish the water and sodium supplies without spiking the sodium concentration or put the water out of balance
why is D5NS considered hypertonic instead of isotonic when dextrose typically get metabolize pretty quickly and what is left is 0.9% NaCl?
Because the added dextrose raises the solution’s osmolarity above plasma (≈560 mOsm/L). However, once infused, the dextrose is metabolized, leaving isotonic 0.9% NaCl in the body.
when to use isotonic solution like 0.9% NaCl and hypertonic solution like D5NS when both can be use to treat isotonic fluid loss?
NS/LR = purely hydration & electrolytes; D5NS/D5LR = hydration + sugar.
dextrose is added when the patient needs __________ in addition to fluids and electrolytes replacement
calories (sugar) for energy
what are the different type of hypertonic cystalloids IV infusions?
D5NS
D51/2NS
D5LR
3% NaCl
what is D5W and what type of crystalloids IV infusion is it?
it is 5% dextrose in water
it is isotonic in the bag but acts like a hypotonic solution in the body
essentially acts like 0.45 NaCl but instead of giving the body water and a little bit of salt, D5W give the body free water and a bit og sugar for those that needs the calorie for energy
what are the only case where 3% NaCl would make sense to be used?
when the patient is severely lacking in sodium; but even then it is still used very cautiously
what are the conditions that hypotonic fluids is usually given for?
hypotonic fluid loss (when the body is losing more water than sodium)
hypernatremia (the solution is given to dilute the salt without spiking the salt level at the same time)
intracellular dehydration (DKA, HHS)
what happens to water when hypotonic fluids are infused?
When hypotonic fluids are infused, they lower the osmolarity of the extracellular fluid (ECF) compared to the intracellular fluid (ICF). Because water moves from areas of lower solute concentration to higher solute concentration, water shifts out of the ECF and into the ICF. This influx of water causes cells to swell. The key point is that hypotonic solutions dilute plasma, so the osmotic gradient drives water into cells.”
why can hypotonic fluids worsen hypovolemia and hypotension?
since hypotonic solution causes the water to shift into the cells, only a small fraction stays in the ECF as the body is experiencing hypotonic fluid loss and there is a high concentration of sodium in the cell → this mean that the plasma volume isn’t effectively expanded or mediated, and hypotension may persist or worsen
why are hypotonic fluids dangerous in patients with increased intracranial pressure (ICP)?
since hypotonic fluid causes water to shift into the cell, water can start shifting into the brain cells, increasing the brain volume, and worsening cerebral edema, which can lead to brain herniation in severe cases
what type of fluids should be used for volume resuscitation in hypovolemic or hypotensive patients?
isotonic fluids (0.9% NaCl ringers) because since the solution is isotonic, they would stay in the ECF and effective expand plasma volume
true or false: hypertonic saline should only be administered in high acuity areas with constant surveillance because the hypertonic solution could promote severe edema as its pull water out of cells and lead to cell shrinkage
why can hypertonic fluid causes fluid overload and pulmonary edema?
since hypertonic fluid pull the water out of the cell, too many can cause a fluid overload and since the plasma volumje would expand, causing an increased in hydrostatic pressurte in the capillaries, increasing the risk of fluid leaking from pulmonary capillaries into the alveoli, causing pulmonary edema
what is the WDL range for serum sodium?
Na+: 135-145 mEq/L
what is the WDL range for serum chloride (does not need to know for the first exam)
Cl-: 97-107 mEq/L
what is the WDL range of serum potassium (K+)?
K+: 3.5-5.0 mEq/L
what is the WDL range for serum calcium Ca2+? (does nto need to know for the first exam?
8.5-10.5 mg/dL
what is the WDL range of magnesium (Mg2+)? (does not need to know for the first exam)
1.8-3 mEq/L
whic electrolytes is the main cation in the ECF?
sodium
sodium is regulated by ____________, __________, __________. and ADH
renal blood blow (on the slides - but why not ANP)
RAAS - (renin → angiotensin → aldosterone)
ADH
how do kidney tubules maintain electrolytes and acid-base balance?
by exchanging sodium and potassium with hydrogen ions - sodium is reabsorbed while hydrogen or potassiuym is secreted—helping regulate plasma electrolytes and blood pH
what is hyponatremia?
a decreased level of sodium in the blood plasma
diagnosed when the serum of sodium concentration is less than 135 mEq/L
what are the two basic types of hyponatremia and how are they characterized?
hypovelimic hyponatremia - both sodium and water are lost but sodium lost is greater than water loss leading to low sodium concentration
→ lost both Na+ & water → dry
hypervolemic hyponatremia - sodium is increased or retained but water retention is even greater leading to the sodium being dilutes, causing hyponatremia
→ water > Na+ → swollen
what are the general causes of hypovolemic hyponatremia?
low water volume and low salt concentration
salt-wasting diuretics
GI fluid loss (e.g., prolonged vomiting, diarrhea, suctioning)
replacing fluid loss with only water
what are the general causes hypervolemic hyponatremia?
a lot of water and low sodium (the water probs dilutes the sodium by a lot)
water intoxication
excessive fluid intake
prolonged use of hypotonic travenous solutions
SIADH (syndrome of inapproriate antidiuretic hormone secretion)
what are the clinical manifestation for neurology when the patient is experiencing hyponatremia?
irritability
confusion
lethargy
weakness
tremors
myoclonus
seizures
what are the clinical manifestation for GI when the patient is experiencing hyponatremia?
hyperactive bowel sounds
diarrhea
nausea
ABD cramping
what are the clinical signs of hypovolemic hyponatremia?
postural hypotension (BP drops when standing)
weak/thready pulse
tachycardia
decreased urine output