lenses and the self
1/47
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
48 Terms
Rubber hand illusion
The brain maps the visual and sensory signals onto the rubber hand
Actual pain can be felt in the rubber hand because it is experienced as part of the self
Associated with gestalt cortex TPJ and somatosensory cortex
He tried to find a way to measure psychological lenses that didn't involve neuroimaging by assessing
the extent to which people see through lenses, noticing power dynamics, who needs help, all through asking questions.
what are some examples of lenses?
Analytic Connection Negativity Nurturing Openness Positivity Safety Hedonism Social Justice Social Awareness Self-reliance Tradition
we can imagine a person in our life based on their
lenses which affects how they experience the world.
sensory inputs from the world get
modified or superseded by nonsensory inputs in our head.
The way we see the world is driven by the past experiences we've had that formed
Attitudes, Beliefs, Knowledge, Theories, personality, schemas, Culture, Worldviews etc...
we use lenses to talk about
long term things such as beliefs or culture that are not present among most people's lenses.
landscapes are initially
neutral with no strong connection weights, experiences carve out the landscape and slowly change the model.
attractor states are not carved by objective truths but rather
our associations that get stronger through experiences. your enduring non sensory inputs
as attractor states get bigger, it causes you to
see new ambiguous experiences in terms of what's already in your attractor state which gives you more evidence of the attractor state being a good one.
different lenses can cause different
lanscapes
Most of the time when we see things differently from one another, its because
for the last couple decades, we have lived experiences that have carved out different landscapes that will change how we pre reflectively see the world
lenses are driven by
enduring non sensory influences on pre-reflective CEEing
lenses are
Idiosyncratic aspects of your attractor state landscape
Lenses are
personalized head-up displays (HUDs) that someone else does not have
schemas are the best proxy for
lenses
schemas are
a network of associations of things that go together in a certain domain.
Hypothetical structures that organize information in memory and knowledge.
Cognitive structures organized prior knowledge, abstracted experience with specific instances, schemas guide the processing of new information and the retrieval of stored information. They fill gaps
Your past experiences build up these schemas, the schemas have a lot of information that have elements that are associated with eachother, and we use this to make sense of new information and the retrieval of old information.
These are hypothetical structures. They are a network of associations in a domain that help you generalize statistically things that should go together more than other things
Lenses are about CEEing (social/semantic) not
thinking. more malleable than schemas. We can try on lenses temporarily, whereas you cant really try on schemas
schemas are more about
memory, judgment, & decision making. You have x, y, and z concept that youve been exposed to, and youve learned to associate or link those concepts with eachother, whereas lenses are the weights that change over time through training.
Lenses are more like weights given to parameters in an AI model. They are not about an aggregation of discrete facts, but
the effect of these facts on molding the landscape over time.
Pros of schemas
fast and efficient enhance memory for schema-consistent info Can fill gaps with accurate information
Self-schema (Markus, 1977)
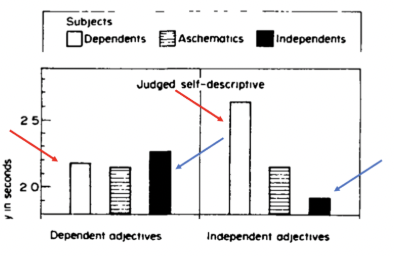
Schema for self as independent or dependent. the way you answered questions would tell you if you had a independent vs dependent schema.
Self-schema (Markus, 1977) cognitive task
shown one word at a time on a screen and as quickly as possible would answer does this word describe you.
Some words shown were related to independence or dependence
what was the reaction time to responding to the self schema?
responded faster to when the adjective matched their schema.
Schemas make us faster for schema-relevant information.
if you had a dependent self schema:
They said yes to both but were able to process the dependent trait faster than the independent trait
Schemas enhance memory for schema consistent info: Paragraph about washing clothes
Had people read passage with or without schema (the title), or schema given after.
Few minutes after they read the passage, they were asked to recall everything they remembered about the passage. how did people who saw the schema before do?
Remembered more than twice as much info from passage than the people from the other 2 categories.
schemas act as
hooks to put elements of a story onto that otherwise wouldn't make sense without.
schemas can fill gaps with accurate information.
tells us a story of a man who ordered a burger at a restaurant, sat for 45 min, and tipped generously. did he eat the burger? of course he did. we infer information and fill in gaps without thinking.
Deese paradigm 1995
read a list of words that are the schema for sleep. asked if the word sleep was said. 55% of participants reported hearing sleep in the list when probed afterwards even though sleep was not on the list.
Cons of schemas
can fill gaps with inaccurate information
schemas distort memory for inconsistent information
schemas produce biased assimilation of ambiguous info
effects are invisible to us
Kleider, Pezdek, Goldinger, & Kirk (2008): People shown series of pictures of men or women doing gender stereotypical or gender non stereotypical behaviors. for example:
Folding baby clothes
Woman- schema consistent
man - schema inconsistent
vice versa with plumbing equipment
study showed the participant a pic of a male or female in a given behavior afterwards shown list of behaviors and you had to indicate whether a man or woman was in the picture doing that behavior. what were some of the errors?
People much more likely to convert a stereotype inconsistent image to a stereotype consistent memory. Would see a pic of a man folding baby clothes and alter that image in head as a memory thinking that a woman was folding the clothes
Much less common that they took something schema consistent and
misremembered something as schema inconsistent
Can produce biased assimilation of ambiguous info:
If there is ambiguous info i will understand that info in terms of schema even when I shouldnt
Green study 2001: divide group into independent vs dependent schema
Then read a long passage about chris → tells you a lot about chris, organized, etc... what you dont learn about chris is whether he is more independent or dependent, totally ambiguous dont know if Chris is male or female. After read passage, asked to rate chris on a variety of traits. how did they rate chris on how organized he is?
both dependent and independent groups rated him highly. as if it was an objective trait of his.
If you have a big atractor state for independence, youre going to fall into that attractor state if its remotely plausible.
then they asked the groups how independent or dependent chris is, what were the responses?
If you have independent self schema, see chris as independent and if you have a dependent self schema, see chris as dependent.
If you only have a single dominant self-schema attractor state, then lots of things will fall into the one attractor state compared to if you didn't have a self-schema.
Someone without a self schema would have a bunch of little attractor states
If sensory input is clear then that will dominate over
self schema
If input is ambiguous than
self schema will dominate
schemas/lenses
describe who we are
schemas effects are invisible to us
even though they are very fast, we don't know they are operating.
the perceived effects of lenses
People said my lenses help me focus and other peoples lenses distort how they see
In reality, safer to say, lenses both focus and distort at different times and different ways
pros of schema
focusing (what you see) get us closer to reality with greater clarity
cons of schema
distorting (what you see)
My lenses/identities will help me see instances of antiSemitism that others might miss but my lenses/identities will also
bias my interpretation of ambiguous events to see anti-Semitism where is does not exist
therefore I am both the
best and worst person to identify anti-semitism
Like an illusion, even when I logically know I am biased,
that doesn't change what I see in the moment