Sleep and Dreams
1/22
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Exam 3, neuro 101, WVU fall '25
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
23 Terms
Stochastic/asynchronous fire
found in REM and nREM 1
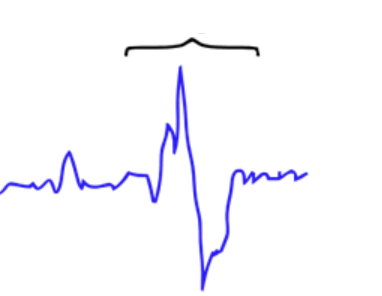
K complex
one sudden spike in neural activity
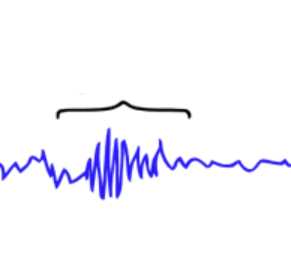
Sleep spindle
brief burst of neural activity
N1
irregular, jagged, low-voltage waves (alpha to theta waves); short period of first falling asleep
N2
light sleep, similar to N1 but has k complexes and sleep spindles
Dreams in SWS are often ___
replays of recent events
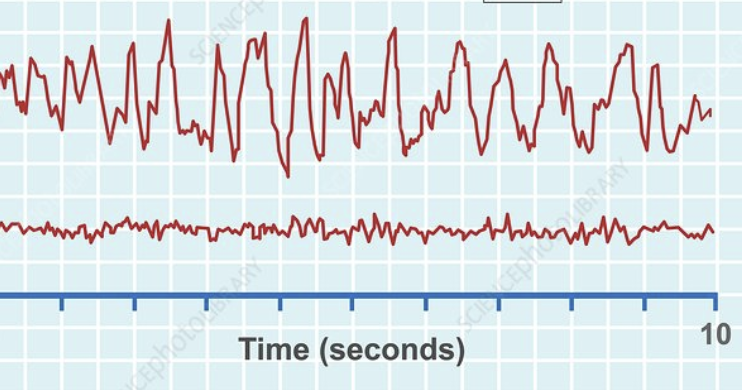
Slow wave sleep (SWS)
high amplitude, low frequency waves, deep sleep, reduced blood flow, paralysis
Slow wave sleep is important for consolidation of ___
explicit/declarative memories
REM sleep is important for consolidation of ___
nondeclarative memories
REM sleep
stochastic/desynchronized waves, dreams, blood flow to higher-order visual and auditory cortices
Systems consolidation occurs in ___
slow wave sleep
Superchiasmatic nucleus (SCN)
regulates circadian rhythm
The ___ secretes melatonin
pineal gland
Cortisol levels ___ to help you wake up
rise
Melatonin levels ___ to help you wake up
fall
During sleep, the brain exhibits high motor activity, but this is stopped by ___
the brainstem
Activation synthesis theory
dreams are interpretations of random neural firing that occurs during sleep
Expectation-fulfillment theory
your brain discharges pent-up emotions from the day to prevent them from interfering with memory
Threat-simulation theory
you have nightmares to prepare you for real-life threats
Manifest content
events in your dreams
Latent content
meanings of your dreams
Caffeine is an ____
adenosine antagonist
Adenosine makes you feel ___
relaxed and sleepy