Week 3: Transcription & Translation
1/11
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
12 Terms
bases
CG - 3 H+ bonds & AT(U) - 2 H+ bonds
pyrimidine: C & T (one ring), purine: A & G (two rings)
stacking interaction
backbone
nucleotide (sugar-phosphate) attaches bases
polar H+ bonds
major & minor to keep nonpolar groups from water
DNA vs RNA
U not T
double stranded helix vs single
at 2` deoxy has H & ribose has OH-
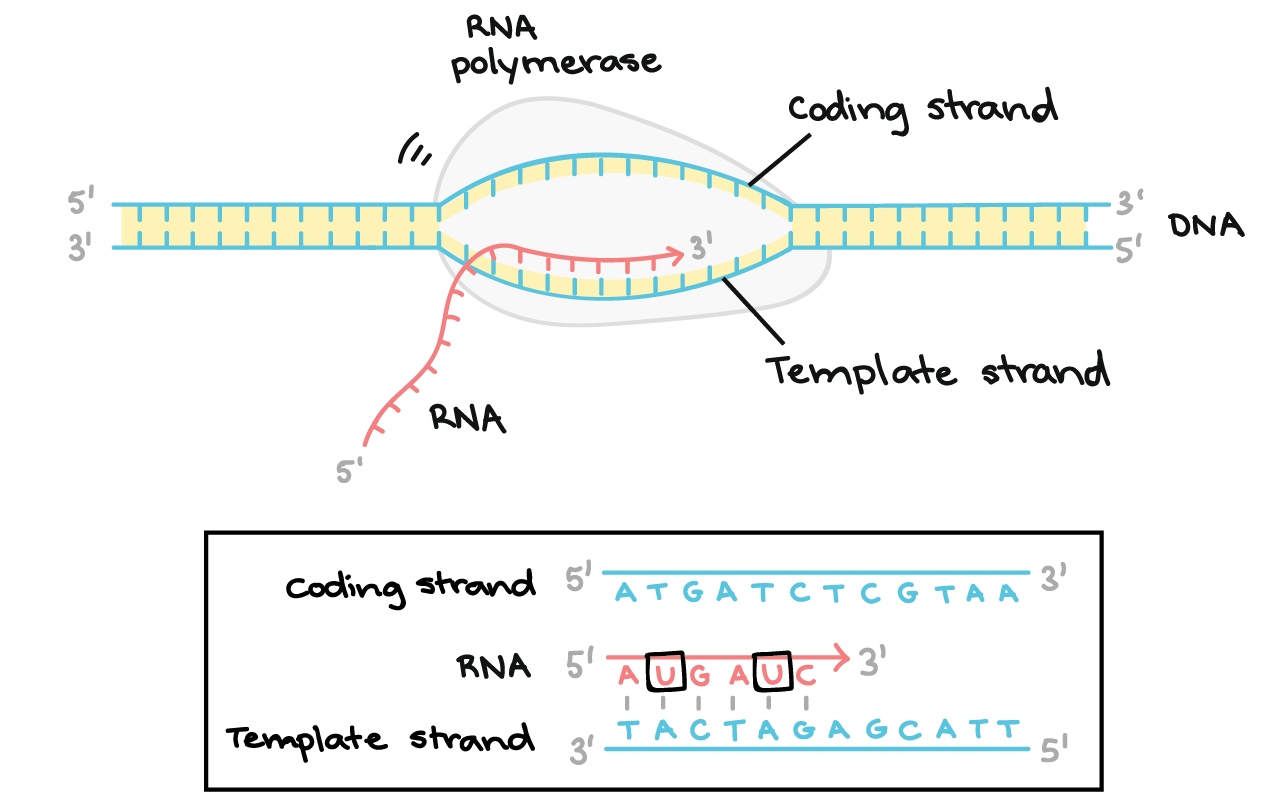
transcription stages
initiation - RNA pol binds to promoter to start at +1 site, ribonucleotides enter active site through template strand
elongation - nucleotides grow from 3` to continue RNA chain
termination - RNA folds back and is separated when encounter termination signal
transcription purpose
uses DNA to make RNA strands for gene expression or protein
transcription strands
template: complementary to bases on RNA, synthesized by RNA pol - RNA strand is made here
coding: matches RNA transcribed
*made 5`-3`
translation stages
initiation - start codon w/ ribosome subunits & aminoaxcyl tRNA
elongation - amino acid sequence grows polypeptide chain w/ peptide bonds
termination - reaches stop codon, ribosome subunits dissociate
codon vs anti
3 mRNA to specify amino acid
3 tRNA to base pair with mRNA
translation components
ribosomes: large & small subunits
mRNA & tRNA: instruction template & binds
aminoaxcyl tRNA: charged w amino acid
stage factors & energy sources (ATP to supply PE)
primary vs mature mRNA
primary - introns & exons (non-coding strands)
mature - only exons (introns removed from splicing)
directionality
5`cap - recognition & 3` poly(A)tail - prevent degradation
RNA synthesized 5`-3`
nucleotides add to 3`, read from 5`
bacterial vs eukaryotic
bacterial
1 RNA pol guided to promoter
-35 box & -10 box directly to mature mRNA
transcription & translation occur simeltaneously
eukaryotic
3 RNA pol recruited to promoter
TATA box, splicing
transcription in nucleus & translation in cytoplasm