Need to Know
1/267
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
268 Terms
Homeostasis
maintaining a relatively constant internal environment in the presence of changing external conditions
Homeostasis is maintained by
negative feedback loops
Even in the presence of a changing environment
the inside of the body stays relatively constant or within a tight range by changing.
Homeostasis does not involve
keeping conditions static but rather within a tightly regulated range
Most diseases involve the
disruption of normal homeostasis
When a disease or virus, such as the flu
causes the body to lose its ability to maintain homeostasis, leading to symptoms such as fever and fatigue.
When you are thrown off
a 4is set in motion to get you back to equilibrium
Set Point
The optimal condition or range in which a physiological system operates, maintaining stability and homeostasis.
Sensor
• something that detects stimulus
• signals the control center
Control Center
• processing center (nervous system)
• triggers a response
Effector
• a cell (muscle or gland) that performs the body’s response
IF you go outside in the summer, it might be above your body temperature
This may cause you to start sweating if you stay outside for awhile. Evaporating cools your body.
If this did not happen, its dangerous and even deadly, and you might end up in the hospital
Feedback Loop
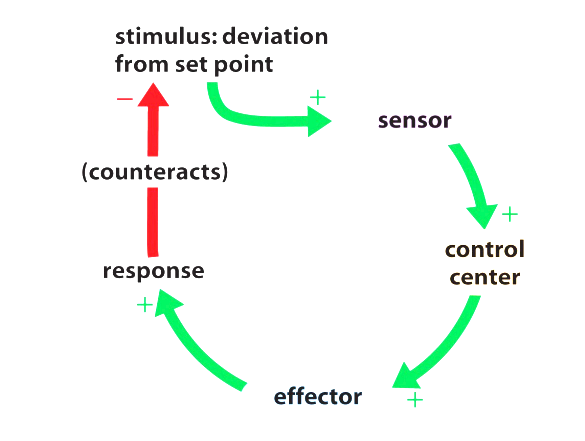
Negative Feedback Loop
A change in a variable triggers a response that counteracts that change and maintains homeostasis
When the response opposes (or reduces) the stimulus
Positive Feedback Loop
A change in a variable triggers a response that amplifies that change
When the response enhances the stimulus
Example of Negative Feedback Loop
Homeostasis
Example of Positive Feedback Loop
Childbirth and Blood Clotting
Thermoregulation
how animals maintain an internal temperature within an acceptable range
REGULATORS
generate their own heat internally (river otter)
CONFORMERS
warmed by heat from an external source or other ways (bass)
Humans are
regulators that maintain a stable internal body temperature
Endotherms
generate heat INTERNALLY
Regulation of body temperature through metabolism, body
response system (and behaviorally)
Mammals and birds
Ectotherms
gain most of their heat from the external environment
Regulation of body temperature MOSTLY through behavior
Amphibians, fish, reptiles, invertebrates
Ectotherms DO
regulate body temperature by behavior but NOT internally through metabolism
Example in butterflies
warming up flight muscles
This does not happen in birds and mammals! Why? They are endotherms.
Cost of thermoregulating
More energy is expended due to need for more metabolism to keep body regulated
Four processes regulate body temperature in ectotherms
conduction, convection, radiation, and evaporation
Radiation
heat transfer from a warmer object to a cooler one
Example: Absorbing heat from the sun --> warming
Evaporation
vaporization of water from a surface (heat is released)
Example: Sweat evaporating from skin --> cooling
Conduction
heat transfer between two objects by direct contact
Example: Sitting on a warm rock --> warming
Example: Sitting on cool concrete --> cooling
Convection
heat transfer through movement of air or liquid (not direct contact)
Example: Feeling a cool breeze (fan) on a hot day --> cooling (pushes heat away from body)
Example: Blood moves heat from the body core to extremities
endotherm and ectotherm are not
mutually exclusive
•Insulation in endotherms
reduces the flow of heat between the body and environment. Hair & layers of adipose (fat) in mammals
Feathers in birds
Vasodilation
widening of blood vessels near surface of body; enhances heat loss
Vasoconstriction
decrease in diameter of blood vessels reduces blood flow and heat loss
Types of Thermoregulation
Insulation, Evaporation, Behavioral, and Circulatory
Nerve cells in the hypothalamus
serve as a thermostat
How can a fever be maintained for hours to days?
Your body changes its set point if you have an infection.
It reprograms its thermostat to stay at a higher temperature to possibly slow down pathogens. Scientists are not sure why
What happens when your fever breaks?
You sweat to cool down. (negative feedback!)
Two major systems coordinate and control responses to stimuli and maintain homeostasis (Mind/Brain-Body connection!)
The endocrine and nervous systems
Endocrine system
Signaling molecules travel directly via blood affecting
various cells with receptors
Acts “globally”
Slower, but long-lasting
Nervous system
Electrochemical signaling travels to a specific location
affecting neurons or muscle/gland cells
Acts “specifically”, along dedicated routes
Faster, but fleeting
Endocrine and Nervous System can
work together
SIGNALING MOLECULES
Endocrine System - Hormones
Nervous System - Neurotransmitters and Neurohormones
Hormones
Released by cells of the endocrine system
Travel in the bloodstream and affect target cells
Neurotransmitters
Act on other neurons, muscles or glands.
Travel very short distance across a synapse
Neurohormones
Released by neurosecretory cells
Travel in the bloodstream
TWO TYPES: HORMONE SIGNALING MOLECULES
Peptide and Steroid
Peptide hormones (amino acid based)
Water soluble
• Cannot travel through plasma membrane
Bind to the receptor in the membrane of the target cell
Triggers signal transduction (second messenger, kinases, etc)
Steroid hormones (lipids)
Lipid soluble
Travel through the plasma membrane into the target cell
Bind to the receptors in the cytoplasm or inside the nucleus
Acts as transcription factor
signal transduction
It is a chain reaction from one protein to another to convert an extracellular signal to an intracellular one….turn on a gene inside the cell
Which kind of molecules will go more easily through the cell membrane?
Small and Hydrophobic Molecules
Is the blood hydrophilic or hydrophobic?
75% water-hydrophilic
Which type of hormone travel easier into the bloodstream?
Peptide hormones flow directly in bloodstream.
Steroid binds to a carrier protein that
escorts them through the blood
A single hormone can create different responses in different cells, based on
1. The receptor it interacts with
2. The relay proteins involved in the
signaling pathway.
Ex: Epinephrine (Adrenaline)
Elicits the Fight-or-Flight Response
Fight or flight is not good for diabetics. Think about that and let me know why?
Likely not a good thing. Epinephrine increase blood glucose
Are you hungry when you are stressed or running from a predator?
No
Simple endocrine pathway
•A stimuli causes endocrine cells and
glands to release a peptide hormone
(secretin).
•Digestion: Partially processed food
(highly acidic juices) triggers this
Steps of Secretin Signaling
1. Low pH on duodenum
2. Secretin is release from your
duodenum (of small intestine)
3. Secretin target pancreatic cells to
release bicarbonate to neutralize
the pH in the intestines.
4. This is negative feedback to keep
your small intestine the right pH!
alpha cells secrete
glucagon in response to low blood sugar levels.
beta cells secrete
insulin in response to high blood sugar levels.
Insulin
is a peptide hormone secreted by the beta cells of the pancreas. It is in a control system that helps keep blood glucose from rising too high
GLUCOSE REGULATION
• Controlled by 2
different hormones (Alpha and Beta Cells)
• Both produced in the
pancreas
You can breakdown fat to
live without food for weeks
Diabetes mellitus
blood glucose levels too high
Type I Diabetes
Loss of insulin-producing cells (autoiummune disease or viral
infection)
Insulin shots required & diet must be monitored
Type II Diabetes
Cells resist the influence of insulin & do not take up glucose
Pancreas overproduces insulin and becomes desensitized
Diet change, weight loss, exercise can reverse (but may be
genetic)
7th most common cause of death in the US
Exchange processes between organisms and their environment often occur
passively (or actively) through the physical process of diffusion. This does not require an energy input
Substances move from high concentration to lower concentration by
passive diffusion until they reach equilibrium. (e.g., oxygen diffusing into a cell)
SLOW PROCESS. How do we maximize diffusion overall?
• shorten the diffusion distance
• have a steeper concentration gradient
• increase in surface area
Basal Metabolic Rate
the amount of energy an animal uses in a unit of time (base level to stay alive). This is the rate when you are not exercising or stressed out
An ectotherm requires
much less energy per kilogram than does an endotherm of equivalent size
A small endotherm has a much greater energy demand per kilogram than does a
large animal of the same class (e.g., hummingbird vs hawk). due to a higher surface : volume ratio (hummingbird loses heat faster)
Ectotherms have a much lower metabolic rate than
endotherms of comparable size
Chemoheterotrophs
Organisms that depend on organic chemicals to generate energy/ATP
Food processing involves
Ingestion, Digestion, Absorption (Transport), and Elimination
Ingestion
the act of eating or feeding
Digestion
when food is broken down into small molecules (mechanical and chemical)
Absorption (Transport)
when cells take up small molecules (and deliver to body cells)
Elimination
passing of undigested material out of the digestive system
If a person is on life support receiving food intravenously, which of the 4 steps are skipped?
Ingestion, Digestion, and Absorption
Two Types of Digestion
Mechanical and Chemical
Four basic ways to ingest
• Substrate feeding-live in or
on their food source
• Suspension feeding-filter,
capture or trap food
• Fluid feeding-suck fluid
nutrients from a host
• Bulk feeding-consume large
pieces of food (most)
Humans are what type of feeders
Bulk feeders, consuming large pieces of food.
Chemical digestion is known as
Hydrolysis
Mechanical digestion
breaks food into smaller pieces, increasing surface area exposes surfaces to chemical digestion
Chemical digestion
cleaves large molecules into smaller molecules (protein-→amino acids) using enzymes (enzymatic hydrolysis)
How Do We Safely Eat?
• Compartmentalization: Processing food within
intracellular or extracellular compartments.
• Food vacuoles are an example of intracellular
digestion. Food vacuoles plus digestive enzymes
break the food down safely. (Ex. Sponges)
• Most animals have extracellular digestion using a
long alimentary canal with compartments.
• Or BOTH (Ex. Hydra)
Simple body plans have a
gastrovascular cavity with a single opening
• Single opening EITHER takes in food OR expels waste
• Ex: Hydra uses tentacles, 2 specialized cells, enzymes, and food vacuoles
Complex body plans have an
alimentary canal with two separate openings
• One opening takes in food (mouth) and the other expels waste (anus)
• They can eat and digest at the same time.
• Ex: Earthworms, grasshoppers, birds, us
Most animals use an
alimentary canal with compartments that are continuous with the outside of the animals’ body
Digestion Begins in the
Oral Cavity
Teeth & tongue
• Chewing increases surface area for
enzymatic hydrolysis
• Tongue facilitates swallowing by forming and
pushing back the bolus
• Mechanical Digestion
Carnivores have
large, pointed incisors and canines to kill, rip, cut, etc
• Jagged premolars and molars crush and shred meat to digest it

Herbivores have
broad, ridged premolars to grind up plants
• Incisors and canines (if present) to bite
plants
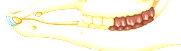
Omnivores (US!) have
incisors for biting, canines for tearing, premolars for grinding, and molars for crushing
Salivary glands do
Chemical Digestion
Mucus (component of saliva)
lubricates food for swallowing & protects gums from abrasion