CKD and ESRD - Clin Med
1/31
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
32 Terms
What does this refer to
Kidneys are damaged and can't filter blood the way they should
Encompasses all degrees of decreased renal function
Chronic = progressive functional decline > months
Chronic Kidney Disease
What does this refer to
More prevalent in the elderly significantly increases with age
Stable kidney disease 30% of patients > 65yo
Younger patients have progressive loss of kidney function
Overall AA > Caucasian (4 : 1)
Peds → M > F
Posterior urethral valves (MC birth defect) found only in boys
Epidemiology Chronic Kidney Disease
What does this refer to
Risk factors for developing kidney disease
Diabetes
HTN
CAD
Family history of kidney failure
Risk factors of Chronic Kidney Disease
What does this refer to
Diabetic kidney disease
Hypertension
Vascular disease
Glomerular disease (primary or secondary)
Cystic kidney diseases
Tubulointerstitial disease
Urinary tract obstruction or dysfunction
Recurrent kidney stone disease
Congenital (birth) defects of the kidney or bladder
Unrecovered acute kidney injury
Etiology Causes of ckd
What does this refer to
Renal artery stenosis
Cytoplasmic pattern antineutrophil cytoplasmic antibody (C-ANCA)–positive and perinuclear pattern antineutrophil cytoplasmic antibody (P-ANCA)–positive vasculitides
ANCA-negative vasculitides
Atheroemboli
Hypertensive nephrosclerosis
Renal vein thrombosis
Etiology vascular
What does this refer to
Membranous nephropathy
Alport syndrome
Immunoglobulin A (IgA) nephropathy
Focal and segmental glomerulosclerosis (FSGS)
Minimal change disease
Membranoproliferative glomerulonephritis (MPGN)
Complement-related diseases (e.g., atypical hemolytic-uremic syndrome [HUS], dense deposit disease)
Rapidly progressive (crescentic) glomerulonephritis
Etiology primary glomerular disease
What does this refer to

Etiology of Secondary Glomerular Diseas
What does this refer to

Etiology causes of Tubulointerstitial disease
What does this refer to
Benign prostatic hypertrophy
Urolithiasis (kidney stones)
Urethral stricture
Tumors
Neurogenic bladder
Congenital (birth) defects of the kidney or bladder
Retroperitoneal fibrosis
Etiology urinary tract obstruction
What does this refer to
CKD stages 1-3 may be asx
Usually sx with stage 4
Metabolic Acidosis
Peripheral edema
Pulmonary edema
HTN
Anemia due ↓ renal synthesis of erythropoietin
Fatigue
Reduced exercise capacity
New onset HF, worsening of HF & ↑ risk of CV disease
Clinical History Chronic Kidney Disease
What does this refer to
Pericarditis
Encephalopathy
Peripheral Neuropathy
RLS
GI sx → N/V/D/loss of appetite
Skin – dry, pruritic, ecchymosis
Malnutrition
Platelet dysfunction ( ↑ bleeding)
ED/decreased libido/amenorrhea
Less common Clinical history Chronic Kidney Disease
What does this refer to
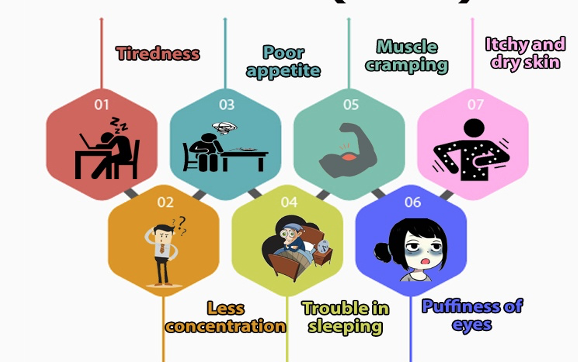
How to detect chronic kidney disease
What does this refer to
Findings characteristic of disease that cause CKD
Lupus, severe arteriosclerosis, HTN
Peripheral edema
Pulmonary edema
HTN
Dry, pruritic skin +/- ecchymosis
Clinical Presentation Chronic Kidney Disease
What does this refer to
Findings characteristic of disease that cause CKD
Lupus, severe arteriosclerosis, HTN
Peripheral edema
Pulmonary edema
HTN
Dry, pruritic skin +/- ecchymosis
Clinical Presentation Chronic Kidney Disease
What does this refer to
AKI
Alport Syndrome
Antiglomerular Basement Membrane Disease
Chronic Glomerulonephritis
Diabetic Nephropathy
Multiple Myeloma
Nephrolithiasis
Rapidly Progressive Glomerulonephritis
Differential Diagnosis Chronic Kidney Disease
What does this refer to
Proteinuria
Abnormal urine sediment
Abnormal serum/urine chemistries
Abnormal imaging studies
Inability to buffer pH
Inability to make urine
Inability to excrete nitrogen waste
↓ synthesis of vitamin D/erythropoietin
Characteristics Chronic Kidney Disease
What does this refer to

Workup Chronic Kidney Disease
What does this refer to
Serum Cr 1 mg/dL is normal GFR
Serum Cr 2 mg/dL 50% ↓ in GFR
Serum Cr 4 mg/dL 70-85% ↓ in GFR
Serum Cr 8 mg/dL 90-95% in ↓ GFR
Workup (Cr and GFR Correlation) Chronic Kidney Disease
What does this refer to
What is creatinine clearance?
Creatinine Clearance
Approximation of residual renal fxn in all patients with CKD
CrCl (male) = ([140-age in years] × weight in kg)/(serum creatinine × 72)
CrCl (female) = CrCl (male) × 0.85
eGFR
Included on the CMP
Workup - renal function studies Chronic Kidney Disease
What does this refer to
Renal US
Hydronephrosis
Retroperitoneal involvement in fibrosis tumor or diffuse adenopathy
Initial imaging study of choice for pediatric patients
CT/MRI/Radionuclide scans can better define renal masses/cysts on US
CT most sensitive for renal stones (NO CONTRAST)
MRI
MRA – renal artery stenosis
US guided transcutaneous renal bx (if imaging unclear + massive proteinuria)
Workup – imaging Chronic Kidney Disease
What does this refer to
Low protein
Low salt
Phosphate restriction
Potassium restriction
Plant based diet
DASH diet (HTN)
Clinical intervention – diet Chronic Kidney Disease
What does this refer to
Treat underlying disease(s)
Aggressive BP control
Glycemic control A1C < 7%
Avoidance of nephrotoxic meds
Monitor urine protein
Treat fluid/electrolyte & endocrine imbalances
Hyperlipidemia goals
LDL < 100mg/dL
TG < 150mg/dL
HDL > 50mg/dL
Clinical management Chronic Kidney Disease
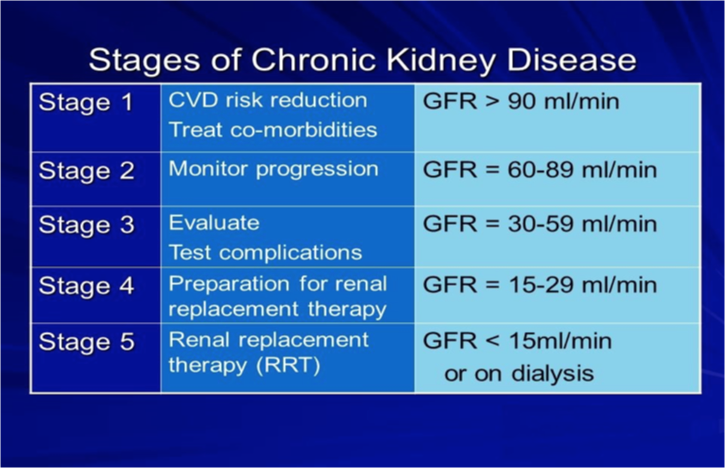
What does this refer to
Know this (u can change this slide later)
What does this refer to
Indications for dialysis (non-diabetic)
GFR < 10mL/min
Serum creatinine > 8mg/dL
Indications for dialysis (diabetic)
GFR < 15mL/min
Serum creatinine > 6mg/dL
Clinical management Chronic Kidney Disease
What does this refer to
At initiation of dialysis → MH screening
Depression
Sleep disturbance
Fatigue
Anorexia—that can coexist with chronic disease symptoms
Do not screen for CKD in asx adults without CKD risk factors
Prevention Chronic Kidney Disease
What does this refer to
Consult/referral Nephrology
Renal dietitian
Surgery for permanent vascular access or peritoneal catheter placement
Referral to renal transplant center
Consults Chronic Kidney Disease
What does this refer to
Progressive loss of renal function ↑ risk for ESRD
Rate of progression depends on age & underlying ds
Lower eGFR ↑ Albuminuria younger age & male sex = faster progression of kidney failure
Lower serum albumin, calcium, and bicarbonate level and a higher serum phosphate level predict an ↑ risk of kidney failure
Adjusted mortality rate for stage 4-5 CKD mortality is 76%
Prognosis Chronic Kidney Disease
What does this refer to
Last stage (5) of chronic kidney disease
Kidney failure
Dialysis
Renal transplant
eGFR < 15mL/min (diabetics)
eGFR < 10mL/min (non-diabetics)
End Stage Renal Disease (ESRD)
What does this refer to
Glomerular filtration rate (GFR) - flow rate of filtered fluid through the kidney
eGFR → estimate of renal function
Creatinine clearance → estimate of actual GFR
Workup End Stage Renal Disease (ESRD)
What does this refer to
Dialysis
Renal transplant
Treatment of End Stage Renal Disease (ERSD)
Whats the left box

Hemodialysis
Whats the right box

Peritoneal Dialysis