proximity measure
1/23
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
24 Terms
similarity
numerical measure of the degree to which two objects are alike
dissimilarity
another alternative or opposite measure of the degree to which objects are different
proximity
both dissimilarity and similarity are also termed as _, ranges from zero to come finite or infinite value
distance
synonym or special case for dissimilarity; estimate similarity between two objects defined with interval-scaled attributes
similarity measure
higher when objects are more alike
dissimilarity measure
lower when objects are more alike, minimum dissimilarity is often 0 and upper limit varies
binary
for nominal variables, measures are _, indicating whether two values are equal or not
1
similarity value is _ if the two objects contains the same attribute value
0
similarity value is _ implies objects are not at all similar
proximity calculation for nominal data
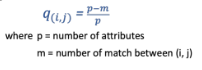
symmetric binary coefficient
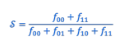
asymmetric binary or jaccard coefficient
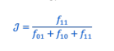
minkowski disatnce
generalization of euclidean and manhattan distance, identity condition, order is not important, triangle inequality
triangle inequality
the least distance between objects x and z is always less than or equal to the sum of the distance between objects x and y, and between y and z
manhattan distance
sum of the absolute value of the difference between x and y, also known as taxicals metric, city-block metric
hamming distance
special instance of manhattan distance when values are either 0 or 1 (binary vectors)
euclidean distance
square root of the sum of the squared difference of x and y
chebychev distance
maximum absolute value between the differences of x and y
numerical data normalization
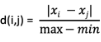
ordinal data normalization

cosine similarity
essentially a measure of the (_ of the) angle between x and y
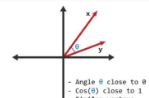
similar vectors
angle close to 0, cosine close to 1
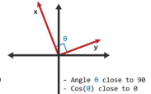
orthogonal vectors
angle close to 90, cosine close to 0
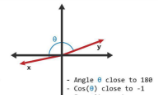
opposite vectors
angle close to 180, cosine close to -1