account review: chapter 1-4
1/57
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
58 Terms
Ethics in Acounting
Pressure
Rationalization
Opportunity
Users of Accounting: Internal Users
Senior Management
Purchasing Managers
Production Managers
Marketing Managers
R&D Managers
HR Managers
Users of Accounting: External Users
Shareholders
Lenders/Creditors
External Auditors
Board of Directors
Regulators - ex. IRS, SEC
Suppliers
Customers
Non-managerial Employees
Nonexecutive Employees
Donors to Non-Profit Organizations
Revenue Recognition Principle
Recognize revenue when goods or services are provided at the amount expected
Expense Recognition (Matching) Principle
Report expenses in the same period as the revenue they generate
Types of Business Entities
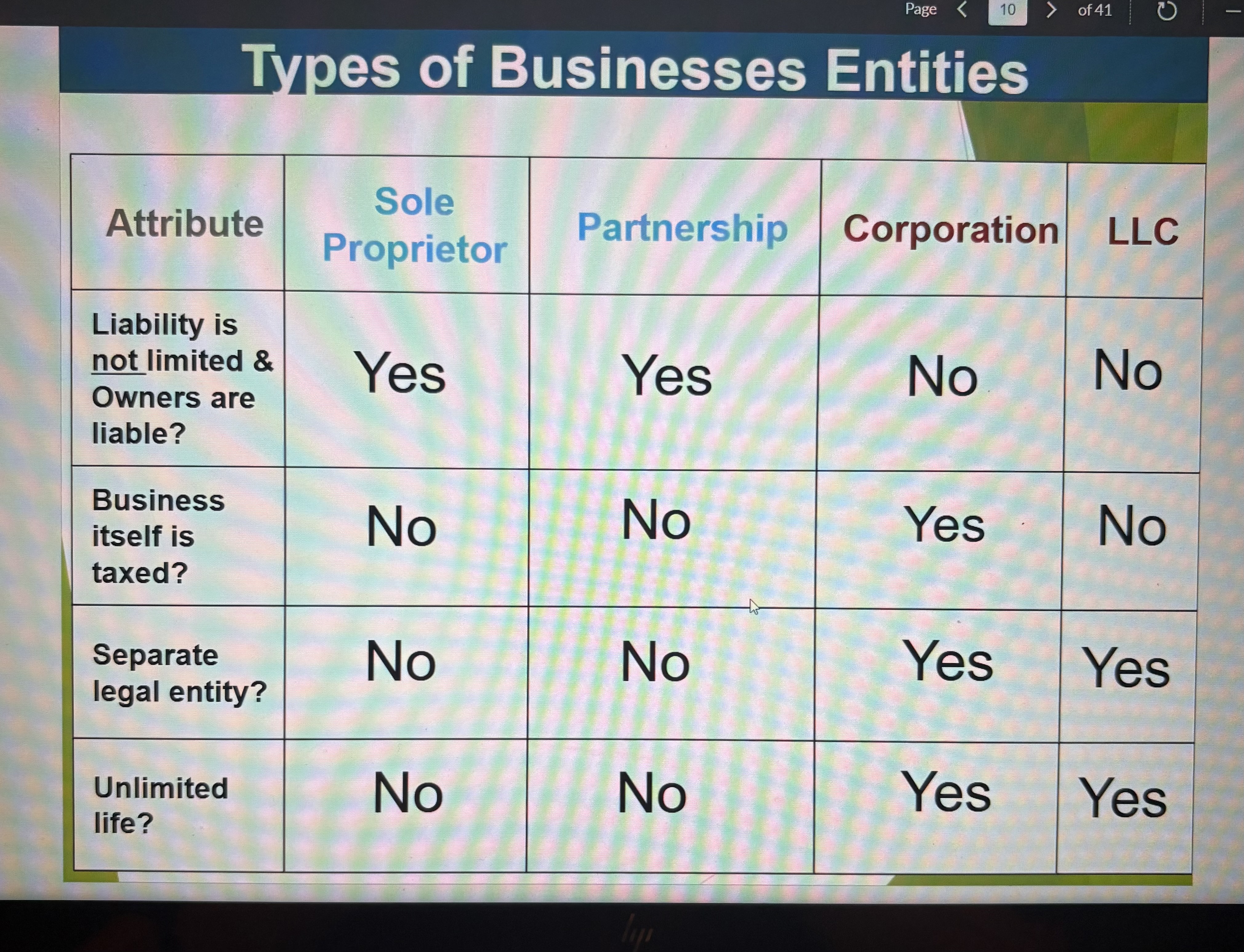
Chart of Accounts
A LIST of all accounts with their account #s
General Ledger
Is a collection of ALL accounts with their balances
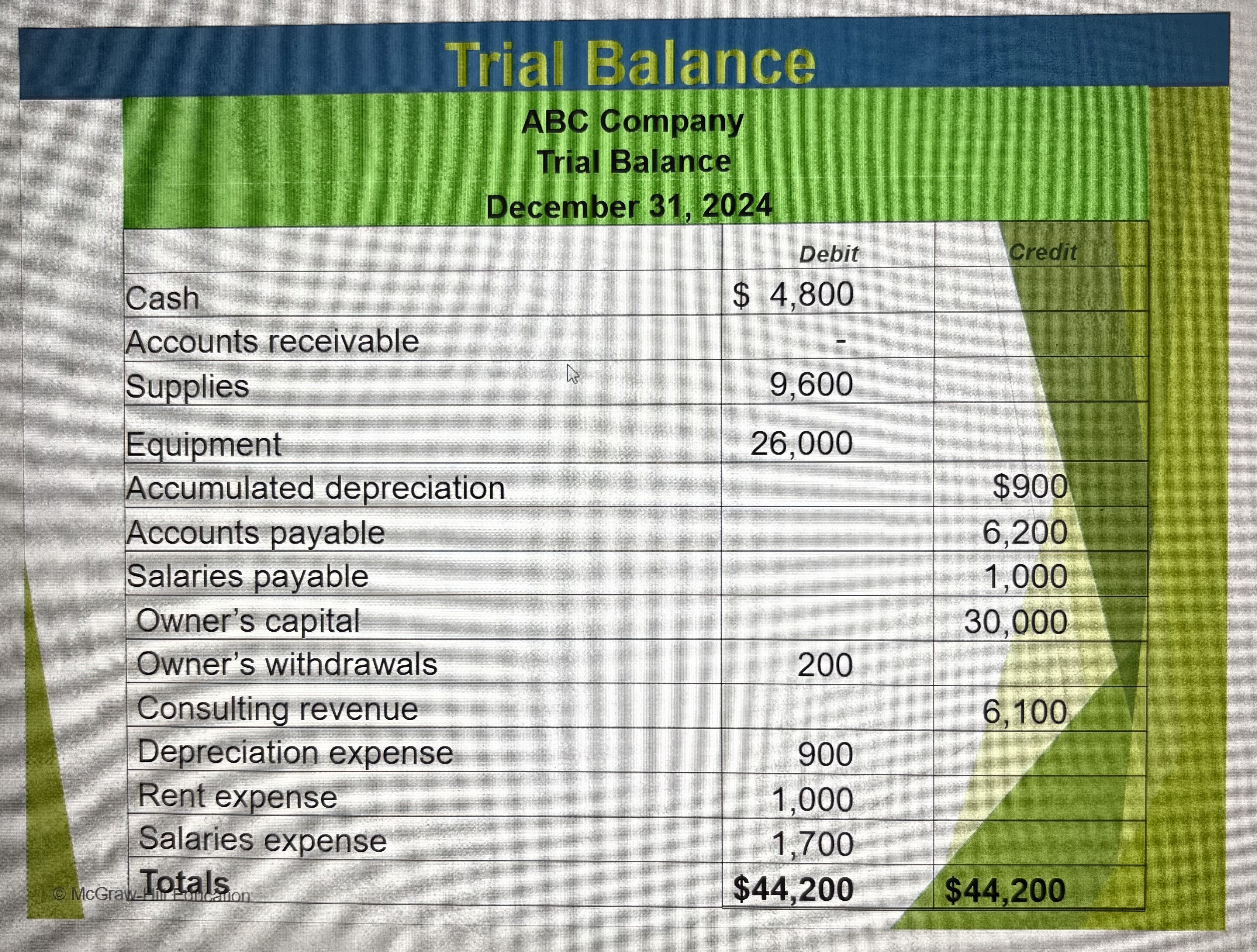
Trial Balance
A list of all ledger accounts & their balance at a point in time; total DR balances = total CR balances
Account Balance
Is the difference between DRs & CRs with including the beginning balance
Asset Accounts (Balance Sheet - Permanent Accounts)
Cash
land
buildings
equipment
supplies
prepaid rent
notes receivable
accounts receivable
Current Assets
Current assets are expected to be sold, collected, or used within one year ( or the companies operating cycle, whichever is longer)
Ex: cash
short-term investments
account receivable
short-term notes receivable
Merchandise inventory
prepaid expense
Plant Assets
Plant assets are tangible, long-lived assets used to produce or sell products and services
Ex: equipment, machinery, buildings, land
Also called property, plant, and equipment (PP&E) or fixed assets
Liabilities Accounts
Balance sheet = Permanent Accounts
Wages payable
Accounts payable
Accrued Liabilities ( aka Accrued Expense)
Unearned Revenue
Notes Payable
Current Liabilities
Current liabilities are liabilities due within one year ( or the company’s operating cycle if longer)
Ex: accounts payable
wages payable
taxes payable
interest, payable
unearned revenues
Equity Accounts
Balance Sheet Accounts = Permanent Accounts
Owner’s capital
Revenues
Owners withdraws
Expenses
All Balance Sheets are __1__ accounts and are __2__ at the end of the period ( expect for __3__)
Permanent
Not closed
Owners withdrawals
Typical B/S accounts
Cash
accounts receivable
prepaid expenses
inventory
supplies
equipment
land
accounts payable
accrued liabilities
notes payable
deferred revenue
wages payable
taxes payable
owner’s capital
All income statement accounts are __1__ and are __2__ at the end of the period
Temporary
Closed
Income statement
Temporary account
CLOSED
Revenues
Expenses
Income summary
Withdrawals
Balance Sheet
Permanent account
NOT CLOSED
Assets
Liabilities
Owner’s equity
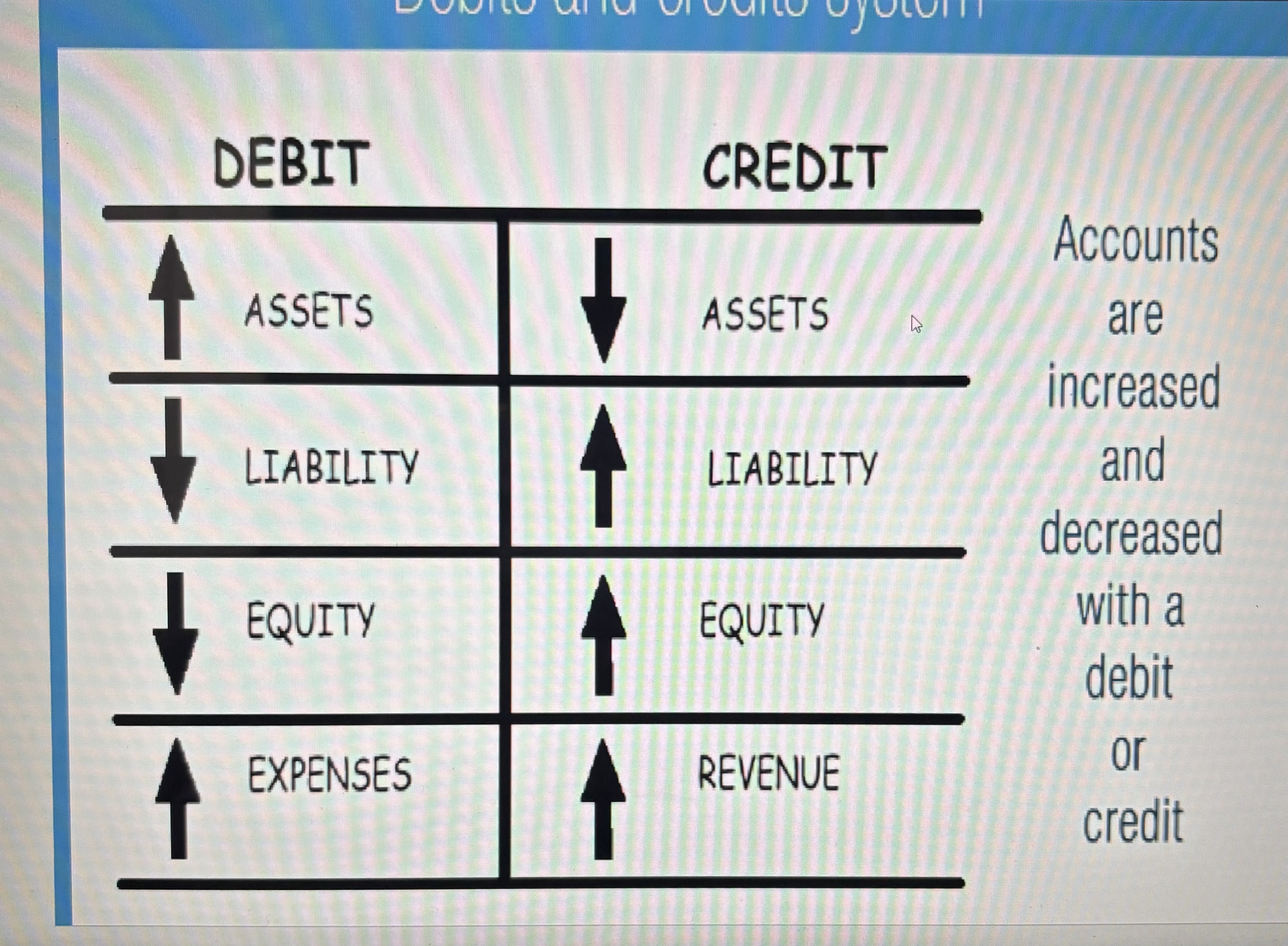
Debits and Credits system
Accounting equation
Assets = Liabilities + Owners Equity - Owners Withdrawals + Revenue - Expenses
Net income = ?
Net loss = ?
Credit
Debit
Accounts with normal balance of Debits
Assets
Expenses
Owners withdrawals
Accounts with normal balance of credit
Liabilities
Owners Equity
Revenue
Prepaid rent is considered an …
ASSET
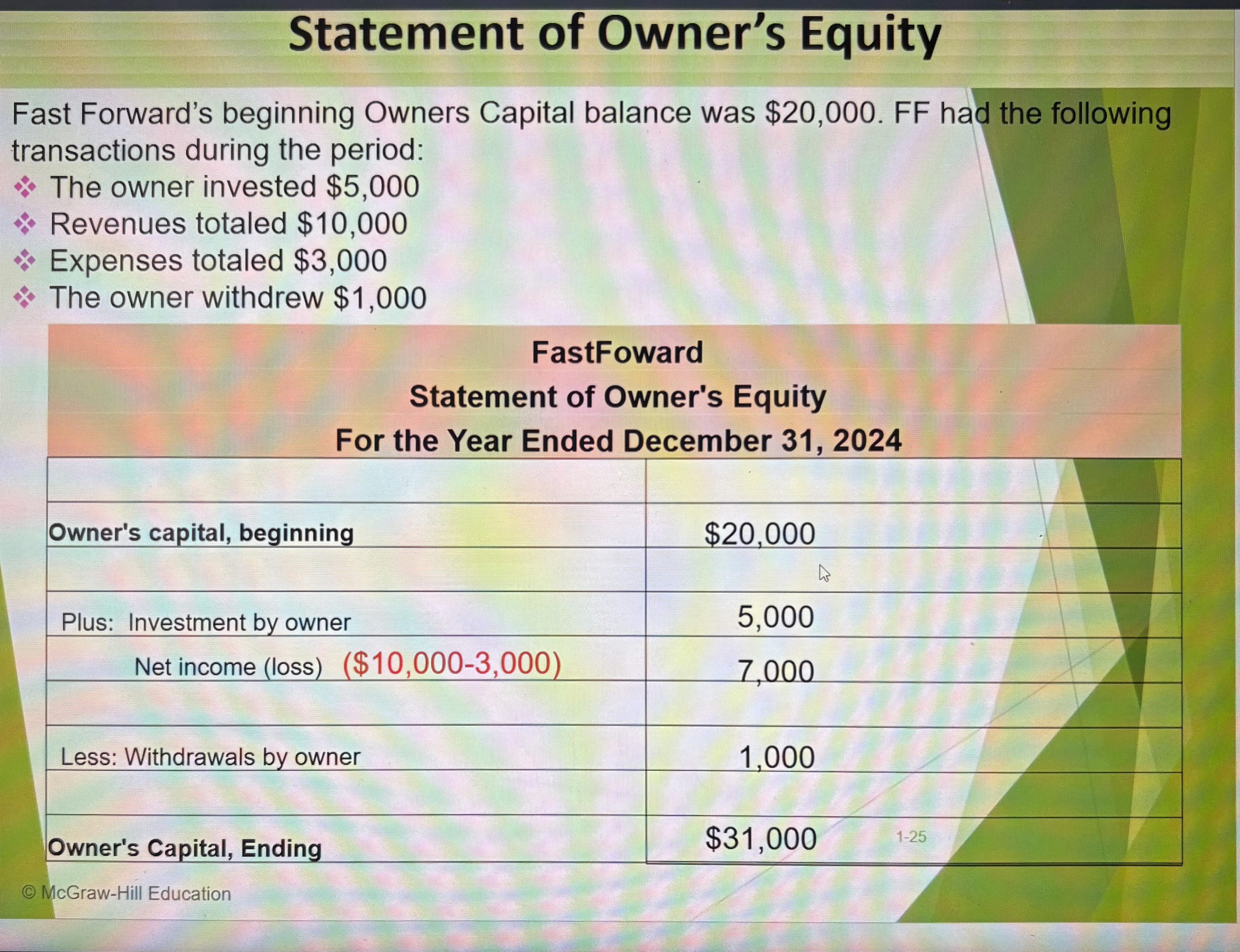
Statement of Owners Equity Ex
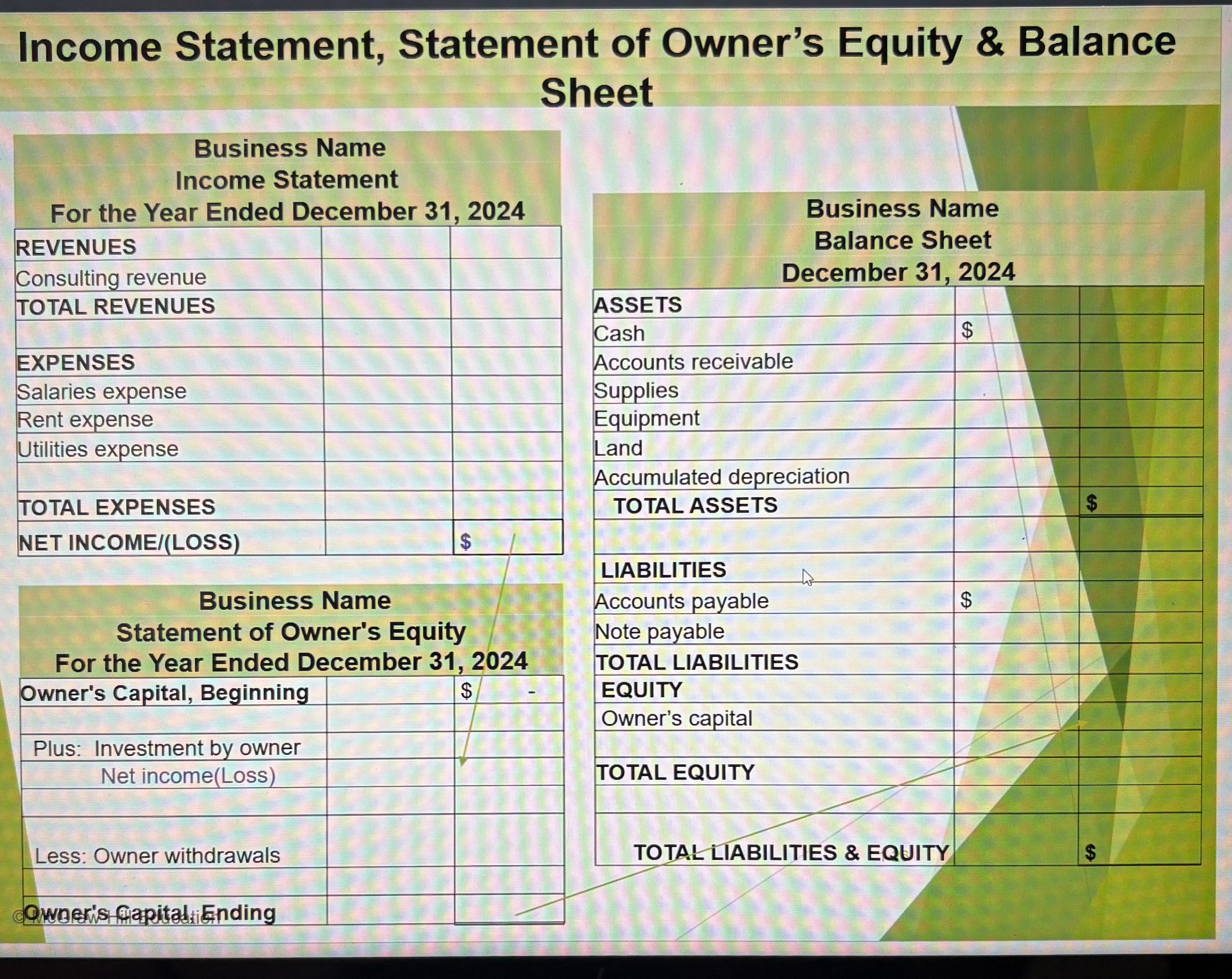
Income Statement, Statement of Owner’s Equity & Balance Sheet
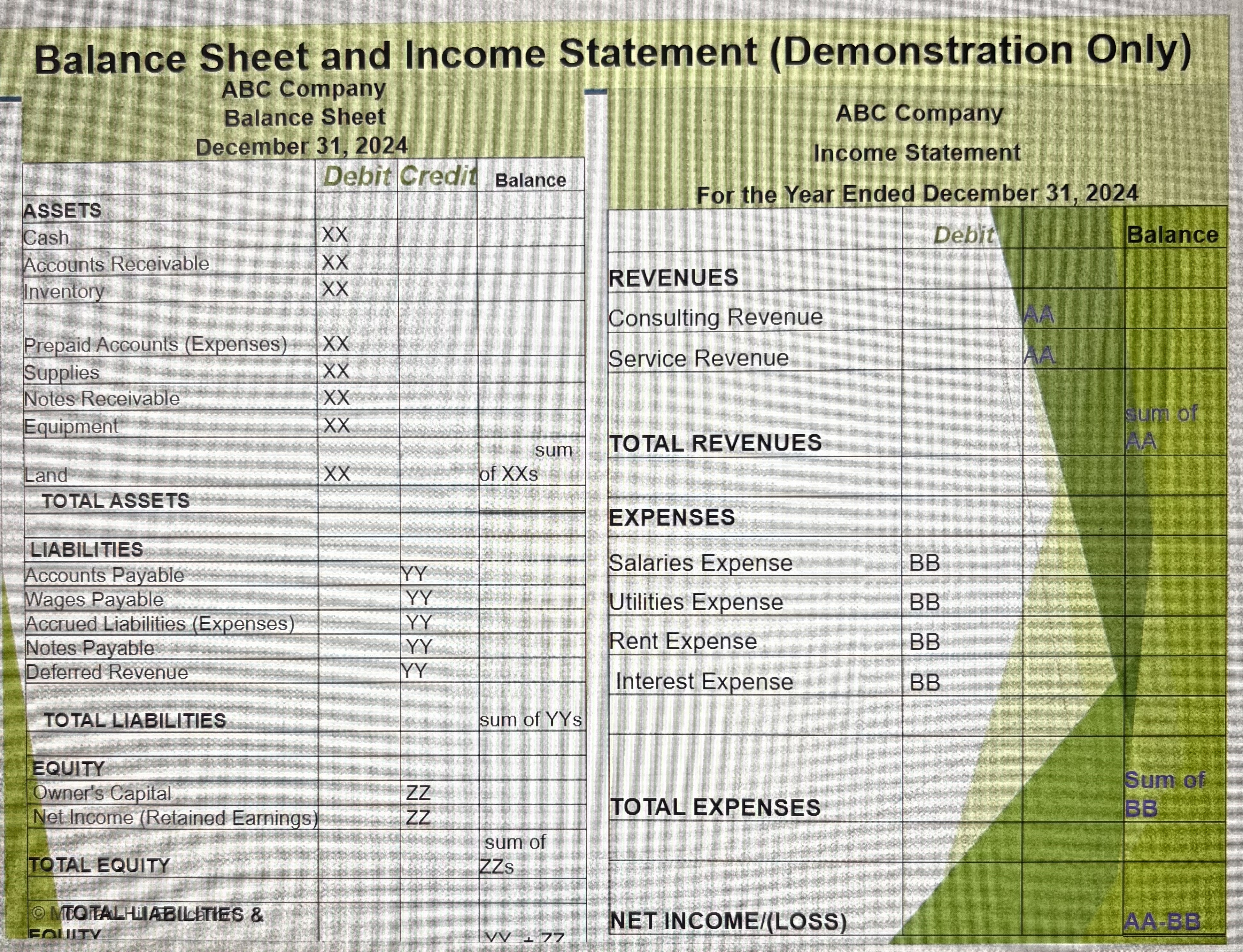
Balance Sheet and Income Statement (demonstration only)
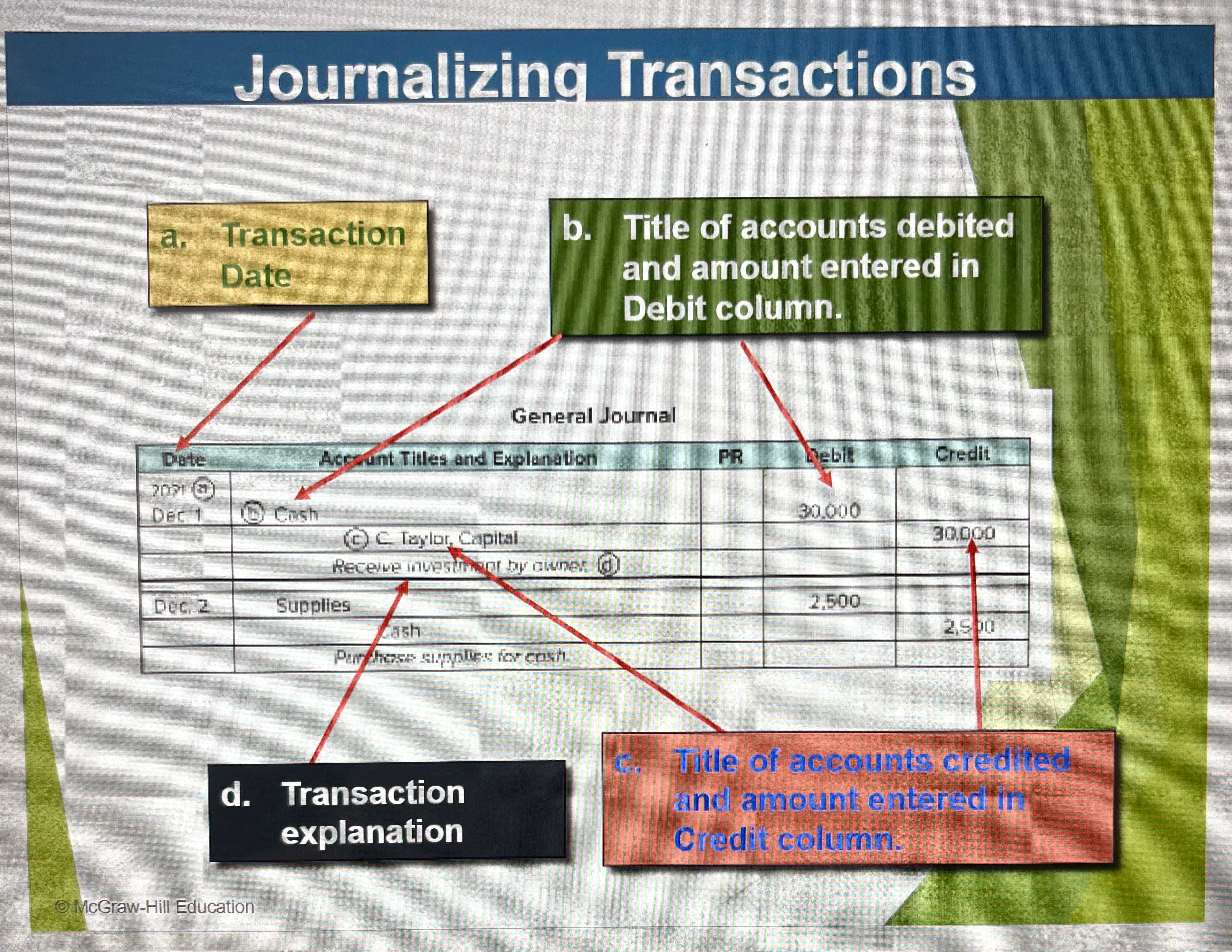
Journalized Transactions
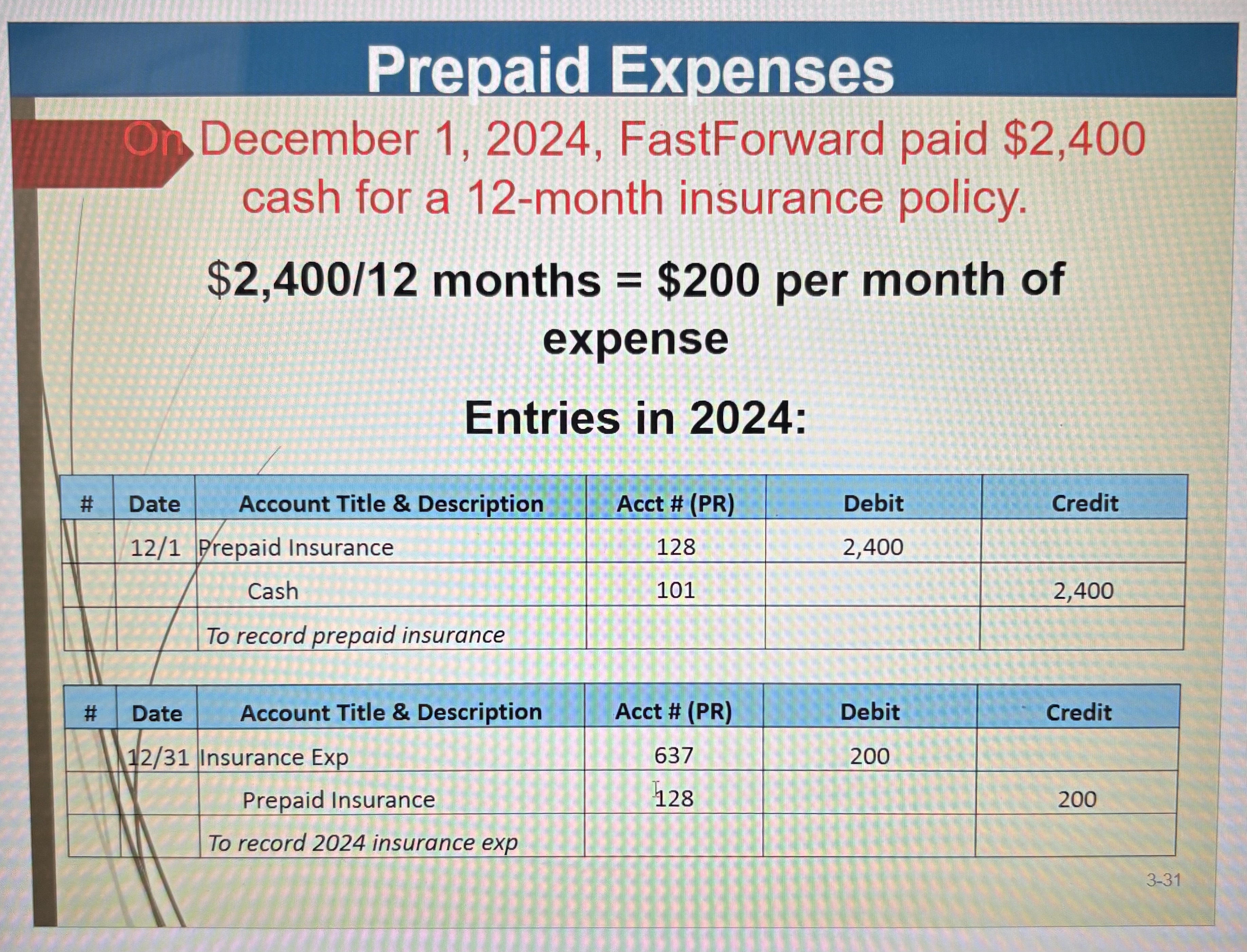
Prepaid Insurance

Prepaid Expenses
Adjusting for Supplies - Part 1

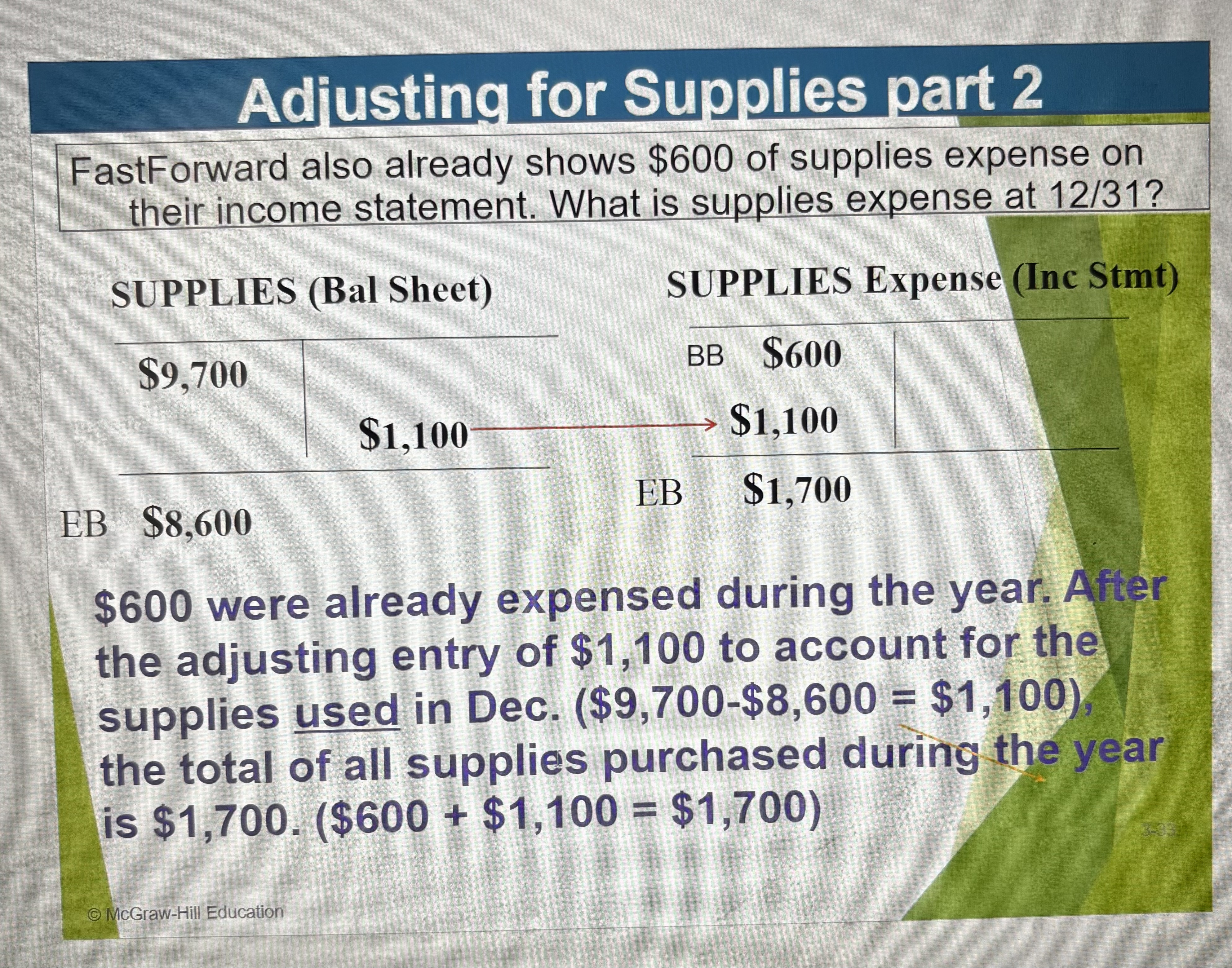
Adjusting for Supplies - part 2
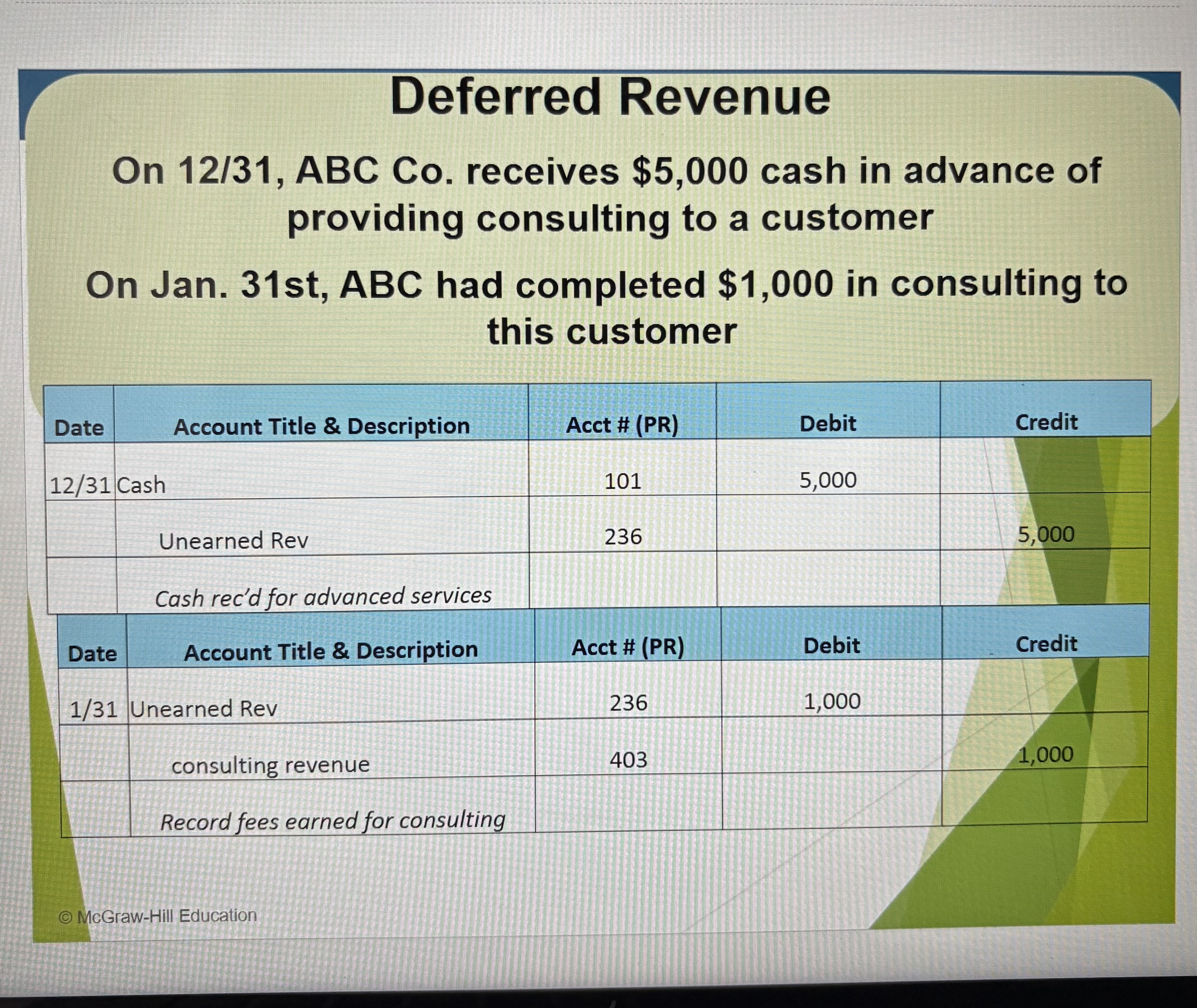
Deferral of Revenue
Unearned revenue, aka deferred revenue is cash received in advance of providing products for services
As products or services are provided, unearned revenue becomes earned (regular) revenues on the income statement
Deferred Revenue Ex
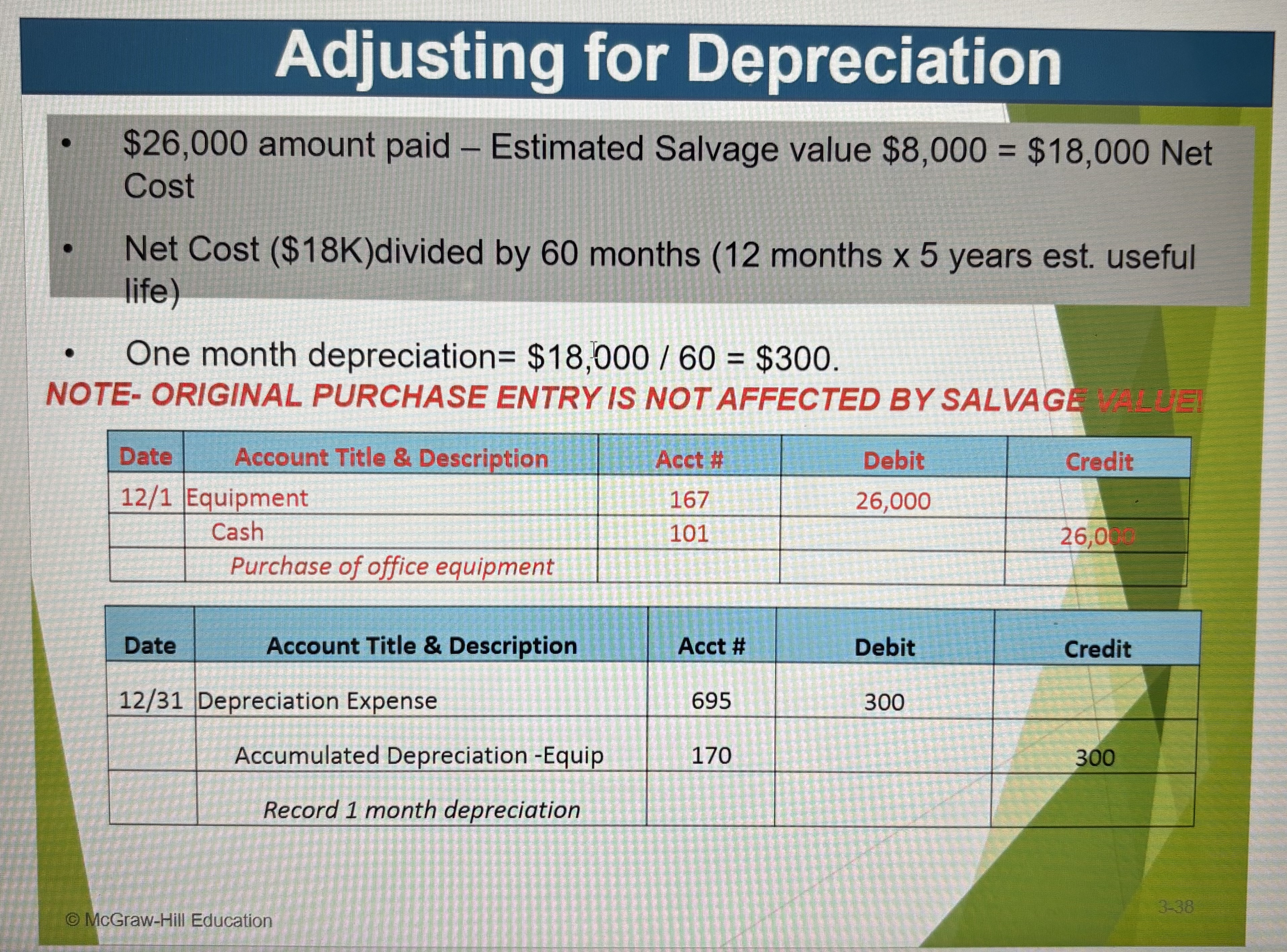
Depreciation
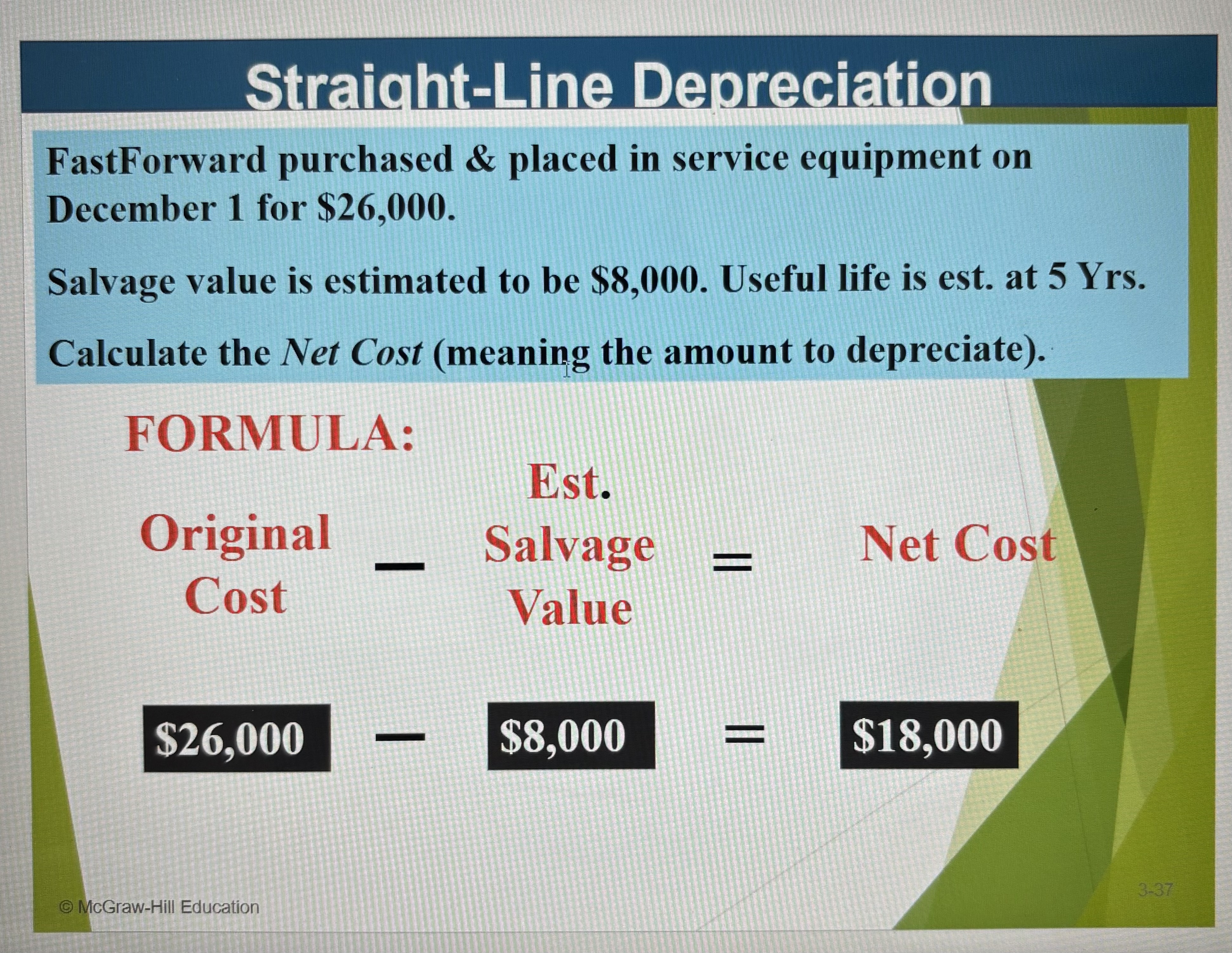
Instead of expensing the cost of a plant asset (equipment, buildings, vehicles, etc.) in the year it is purchased we spread out the cost of their expected useful lives. This is called depreciation.
Straight-Line Depreciation Ex & Formula
Adjusting for Depreciation Ex
Trial Balance Ex
All the debits and all the credits should equal each other
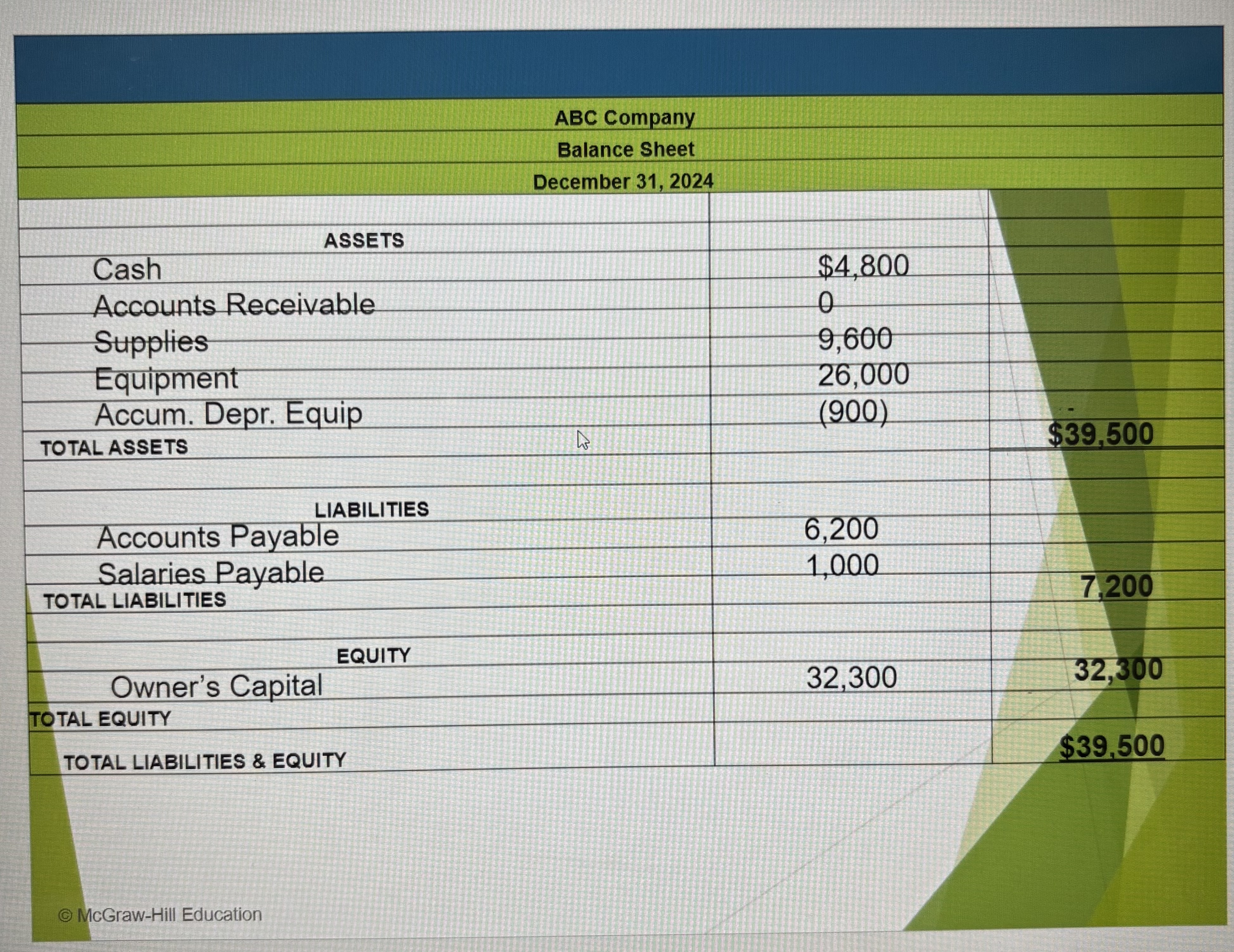
Balance Sheet Ex
The collection of all accounts and their balances is called a(n)
Ledger (general ledger)
A company’s list of all ledger accounts with an identification number assigned to each account is called a …
chart of accounts
True/ false
Income summary is a temporary account only used for the closing process
True
True/false
revenue and expense accounts are temporary accounts that begin each accounting period with zero balance
True
True/false
closing entries result in permanent account balances being transferred into net income or net loss for the period ending
False
True/false
Closing entries are only required when a business is shutting down
False
True/false
Plant assets are tangible assets that are both long lived and used to produce or sell products and services
True
True/false
the worksheet is a required report made available to external decision makers
False
True/False
on a worksheet, if the debit total exceeds the credit total of the income statement columns, a net loss is indicated
True
True/ false
an expense account is normally closed by debiting income, summary and crediting the expense account
True
True/false
the account receivable account is normally closed by debiting it
False
revenue and expense account, which are closed at the end of which counting period, are …
Temporary accounts
how to find net income (loss)
Revenue - expense = net income (loss)
On a classified balance sheet in order to find Equity:
Capital = o.w capital + revenue - W.D. - expenses
Balance sheet TIP
All the numbers go in the left column expect for the TOTALS