Electrochemistry ⚡️
1/20
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
21 Terms
definition of electrolysis
the breakdown of a molten or aqueous ionic compound by the passage of electricity through it
charge formula
Q = I t
Q: charge / coulombs
I: current / amperes
t: time / seconds
Faraday's Constant formula
F = le
F: charge carried by one mole of electrons
l: Avogadro's constant
e: electronic charge
*All values given in the data booklet
electrode potential
numerical value that shows the ease of reduction for metals as well as non-metals
higher positive/less negative E° value
more reduction
higher negative/more negative E° value
more oxidation
salt bridge
maintains the ionic balance at 1 moldm⁻³, any excess of ions is absorbed by the salt bridge
standard electrode potential (E°)
emf of an electrode which is connected to a standard hydrogen half cell at 298K, 1 atm and concentration 1 moldm-3
standard cell potential (E°cell)
voltage produced under standard conditions when 2 half cells are connected and none of them is a reference half cell
E°cell =
E°reduced − E°oxidised
prove Cl oxidises Fe²⁺ to Fe³⁺ using E° values
½Cl₂ + e ⇌ Cl⁻ (E°= +1.36V)
Fe³⁺ + e ⇌ Fe²⁺ (E°= +0.77V)
Cl⁻ has a more positive E° value meaning it's reduced so the reaction is feasible
Predict if Fe³⁺ can oxidise Cl⁻ to Cl₂ by calculation
1) Change the sign of E° for the substance that's being oxidised
2) Add the 2 E° values
3) If the final answer is positive, it's a feasible reaction. If it's negative, the reaction does not occur.
½Cl₂ + e ⇌ Cl⁻ (E°= +1.36V)
Fe³⁺ + e ⇌ Fe²⁺ (E°= +0.77V)
-1.36 + 0.77 = -0.59 (negative so reaction does not occur)
a substance with a high positive E°
is a strong oxidising agent
a substance with a high negative E°
is a strong reducing agent
Fe³⁺ + e ⇌ Fe²⁺ (E°= +0.77V)
If Fe³⁺ > 1 moldm⁻³, what happens to the E° value?
- equilibrium shifts to the RHS
- more reduction occurs
- E° becomes more positive
Fe³⁺ + e ⇌ Fe²⁺ (E°= +0.77V)
If Fe²⁺ > 1 moldm⁻³, what happens to the E° value?
- equilibrium shifts to the LHS
- more oxidation occurs
- E° becomes more negative
disadvantages of hydrogen fuel cell
1. water freezes at low temp
2. expensive
3. hydrogen storage is difficult
4. producing the hydrogen fuel cell itself is bad for the environment
half equations of hydrogen fuel cell
cathode: O₂ + 2H₂O + 4e⁻ → 4OH⁻
anode: 2H₂ + 4OH⁻ → 4H₂O + 4e⁻
overall: 2H₂ + O₂ → 2H₂O
half equations of hydrogen fuel cell under acidic conditions
reduction: O₂ + 4H⁺ + 4e⁻ ⇌ 2H₂O
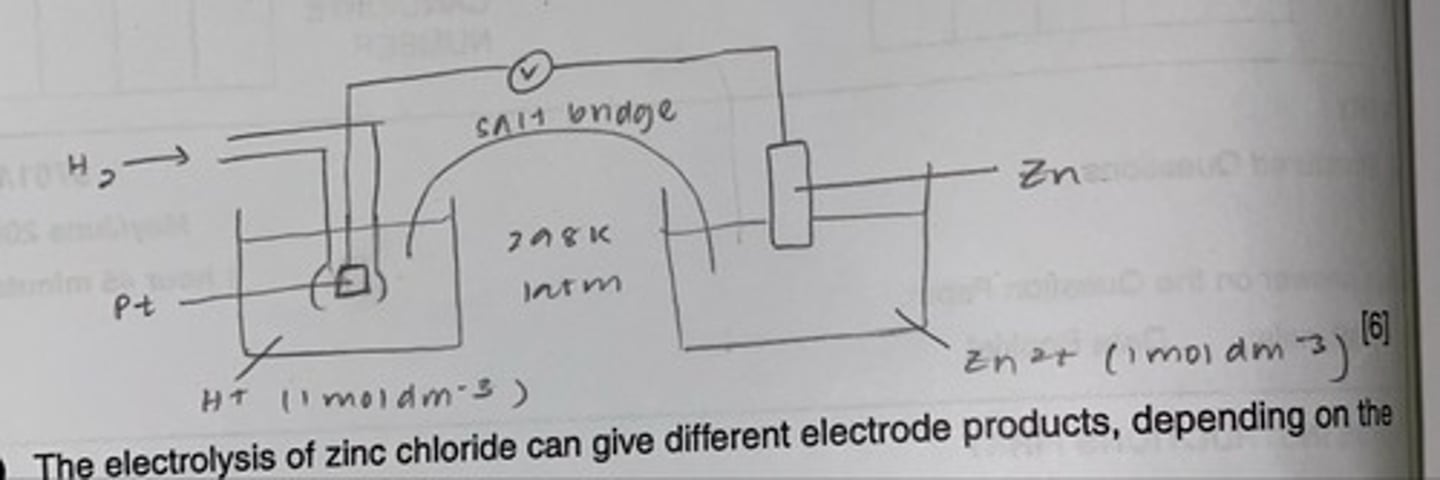
draw a fully labelled diagram to show how you could use a standard hydrogen electrode to measure the standard electrode potential of zinc
.
In the alkaline hydrogen-oxygen fuel cell, H₂(g) and O₂(g) are passed over two inert electrodes immersed in an alkaline solution.
Write the half-equations for the reactions taking place at each of these electrodes.
hydrogen electrode: H₂ + 2OH⁻ → 2H₂O + 2e⁻
oxygen electrode: O₂ + 2H₂O + 4e⁻ → 4OH⁻
overall: 2H₂ + O₂ → 2H₂O