Nursing Care of the Child with Infection
1/62
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
63 Terms
What are the five types of infections?
•Bacterial (septic)
•Viral
•Zoonotic & Vector-Borne
•Parasitic & helminthic
•Sexually transmitted
Infection prevention
What is the most effective method?
Hand washing
Infection prevention
What are the different methods?
•Handwashing
•Immunizations
•Proper food handling and preparation
•Judicious antibiotic use
Immunizations are an effective method for infection prevention in children. What needs to be promoted?
Ensure parents are properly educated regarding vaccine -schedule and boosters
What is judicious antibiotic use?
Ensuring the whole course of antibiotics is completed
Chain of infection
Infectious agent -> Reservoir -> Portal of Exit -> Modes of Transmission -> Portal of Entry -> Susceptible Host
Any agent capable of causing infection
Infectious agent
A place where the pathogen can thrive and reproduce
Reservoir
A way for the pathogen to exit the reservoir
Portal of exit
Two types of transmission
Direct and indirect
A way for the pathogen to enter the host
Portal of entry
Any person who cannot resist the pathogen
Susceptible host
Portal of exit/entry
What are examples?
•Skin and mucous membranes
•Respiratory tract
•Urinary tract
•GI tract
Infectious agent
How do you control or eliminate them?
•Handwashing
•Wearing gloves
•Cleaning, disinfecting, or sterilizing equipment
Reservoir
How do we break the chain?
•Control or eliminate reservoirs
•Control sources of body fluids that may harbor pathogens
•Provide provide proper wound care by changing soiled dressings
•Keep linens clean and dry
Provide provide proper wound care by changing soiled dressing
Which chain of infection are we breaking?
Reservoir
Portal of exit
How do we break the chain?
•Cover mouth and nose when sneezing
•Avoid talking over open wounds or sterile fields
•Use PPE
Avoid talking over open wounds or sterile fields
Which chain of infection are we breaking?
Portal of exit
Modes of Transmission
How do we break the chain?
•Wash hands before and after invasive procedures
•Use PPE
•Urge children and family to wash hands frequently, before eating, after eliminating, and touching infectious material
Urging children and family to wash hands frequently before eating is an example of breaking what chain?
Modes of Transmission
Portal of Entry
How do we break the chain?
•Use proper sterile technique during procedures
•Provide appropriate wound care
•Dispose of needles and sharps in containers
•Provide children with their own personal care items
Provide children with their own personal care items
Which chain of infection are we breaking?
Portal of Entry
Susceptible host
How do we break the chain?
•Protect susceptible host by promoting normal body defenses against infection
•Maintain integrity of child's skin and mucous membranes
Susceptible host
How do you protect normal defenses?
•Regular bathing and oral care
•Adequate fluid & food intake
•Proper immunizations
What are the reasons why infants can't fight off organisms naturally?
•Decreased inflammatory response
•Immature immune response
•Limited exposure to disease
•Loss of passive immunity from mothers antibodies
What is cellular immunity?
Immunity that we are born with
When does humoral immunity occur?
When the body encounters new disease and develop antibodies
Infants have humoral immunity T/F
False.
Common laboratory tests for infectious disease
•Complete Blood Count (CBC)
•Erythrocyte Sedimentation Rate (ESR)
•C-reactive protein (CRP)
•Blood Culture and Sensitivity
•Stool, urine, wound, throat, nasal cultures
What two laboratory tests will identify inflammatory markers?
•Erythrocyte Sedimentation Rate (ESR)
•C-reactive protein (CRP)
When should you take cultures?
Before giving antibiotics
What are the treatments for Infectious Disorders?
•Hydration
•Fever reduction
•Medications
Course of treatments for Infectious Disorders
What medications are used?
•Antibiotics (bacteria)
•Antivirals (viruses)
•Antipyretics (fever)
•Antipruritics (itching)
How will an infection cause a fever?
It will stimulate the release of endogenous pyrogens, these pyrogens act on the hypothalamus, releasing prostaglandins which increase body temperature, this triggers the cold response (shivering) in order to decrease heat loss and reset the body temperature
Fever with a stiff neck is a sign of what?
A more emergent illness (meningitis, lyme, tetanus)
Lyme disease
Tick-borne disease
What will educate parents about when their child has a fever?
If it's a low grade fever, let it ride out because it will help fight the infection
If it becomes a high grade fever, it must be treated immediately with antipyretics
Bacterial infections
What are the common symptoms?
•High fever
•Green/yellow nasal discharge
What are the different types of bacterial infections?
•Community acquired MRSA
•Pertussis
•Tetanus
•Botulism
•Osteomyelitis
•Septic arthritis
Pertussis
Tetanus
Botulism
Osteomyelitis
Septic arthritis
Identify each one
Pertussis - Whooping cough
Tetanus - Rusty nails
Botulism - Food borne illness (most common)
Osteomyelitis - Bone infection (hard to treat)
Septic arthritis - Fluid around joints (post-injury)
What type of infections are children at high risk for?
Bacterial infections
What type of infections cannot be treated with medications and must run their course naturally?
Viral infections
Vaccines prevent what type of illnesses?
Viral infections
Symptoms of Viral Exanthem
Rashes that starts in the face or trunk and continue to spread
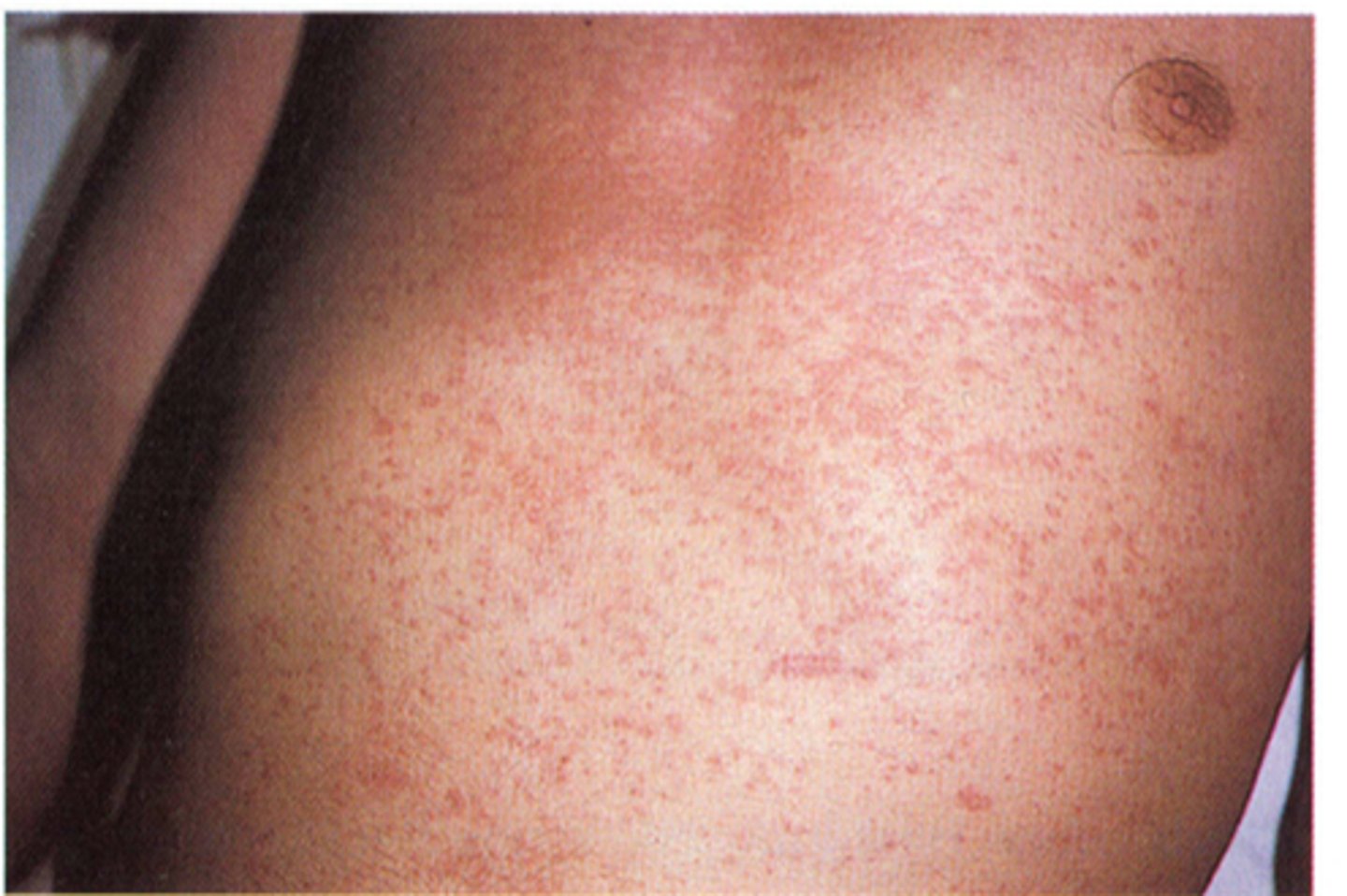
Characteristic rashes that emerge from viral illnesses
What is this called?
Viral exanthems
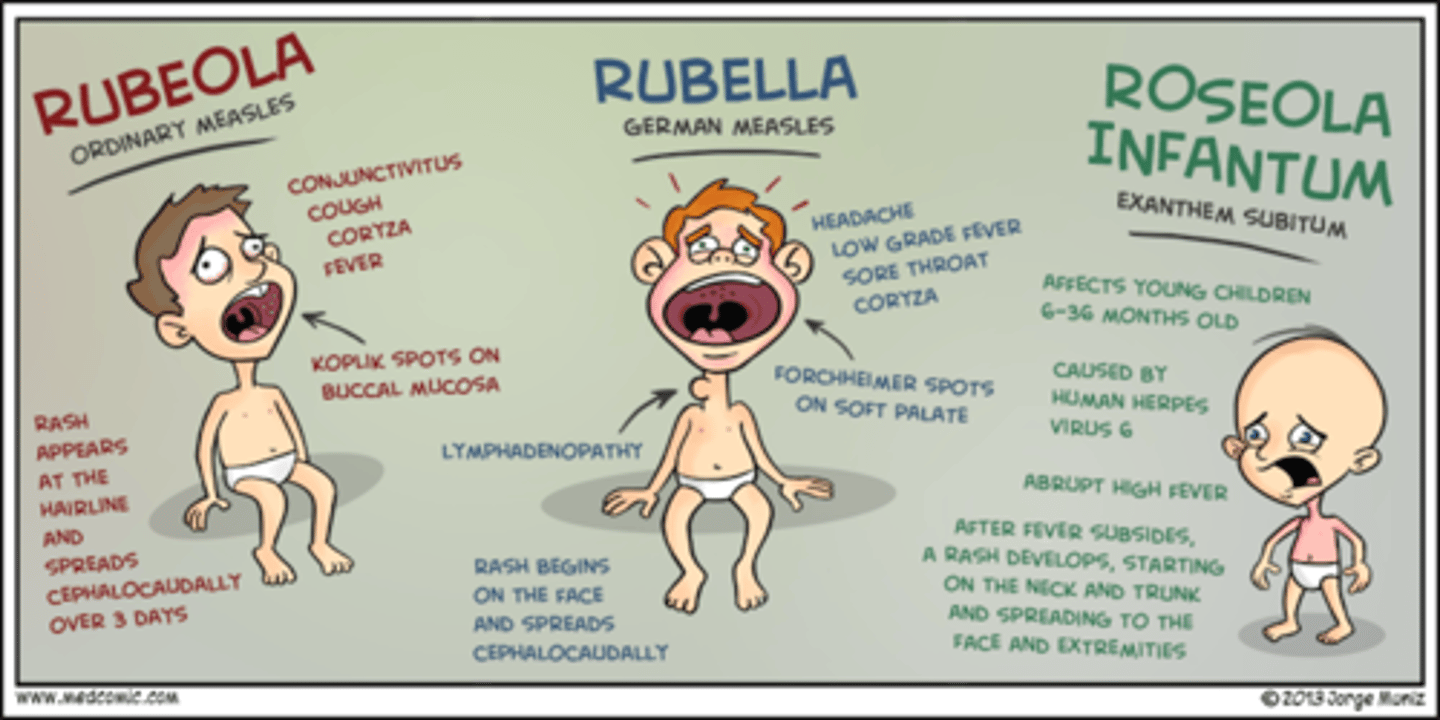
Rubella vs. Rubeola
Rubella (German measles) and Rubeola (Measles)
Parvovirus (fifth disease)
"Slapped cheeks" rash
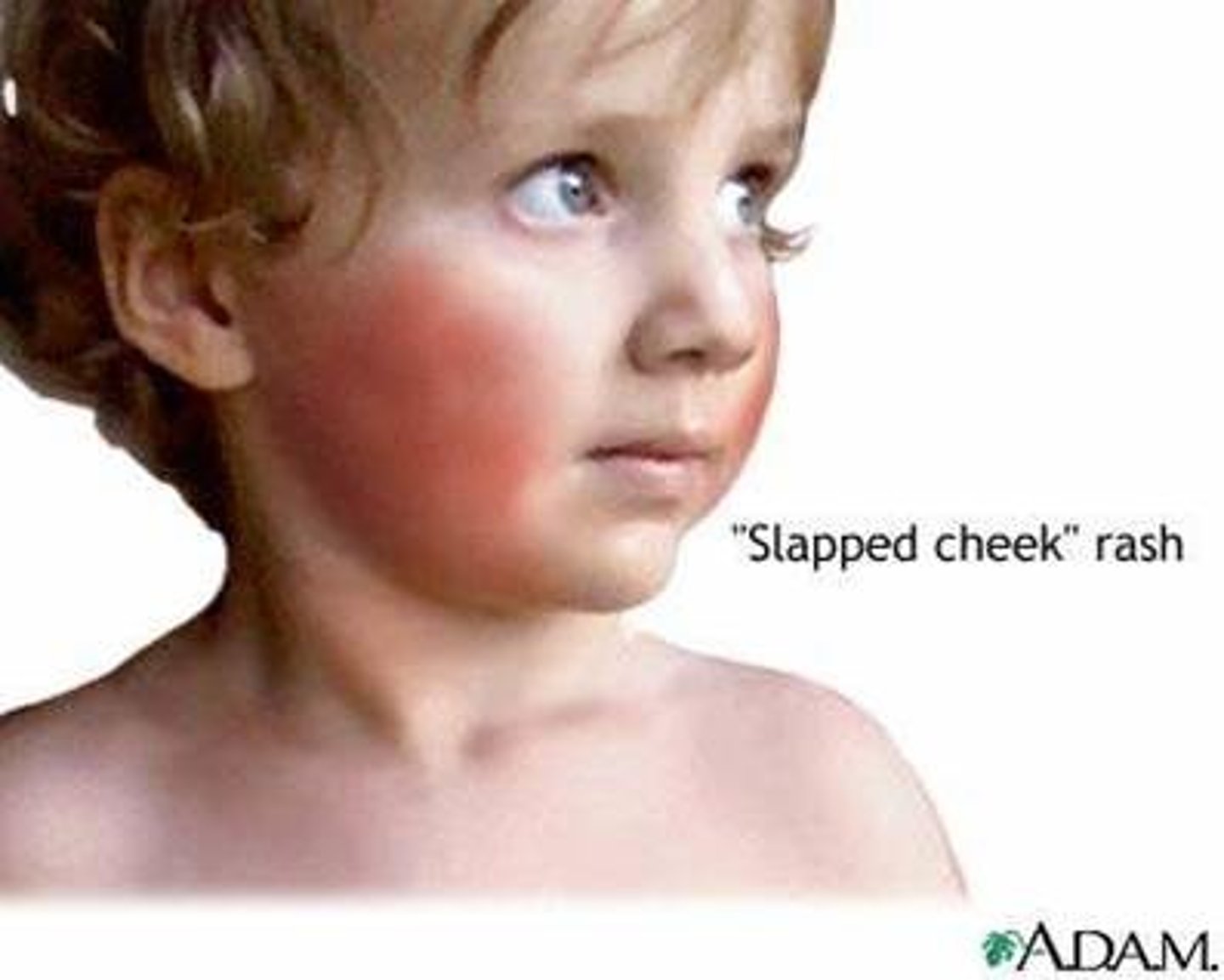

Parvovirus (fifth disease)
What should you be cautious about with this infection?
It can easily be mistaken for child abuse
What are the viral infections?
•Rubella (german measle)
•Rubeola (measles)
•Varicella
•Shingles
•Roseola infantum
Varicella zoster
This virus is contagious until when?
Until all lesions are gone
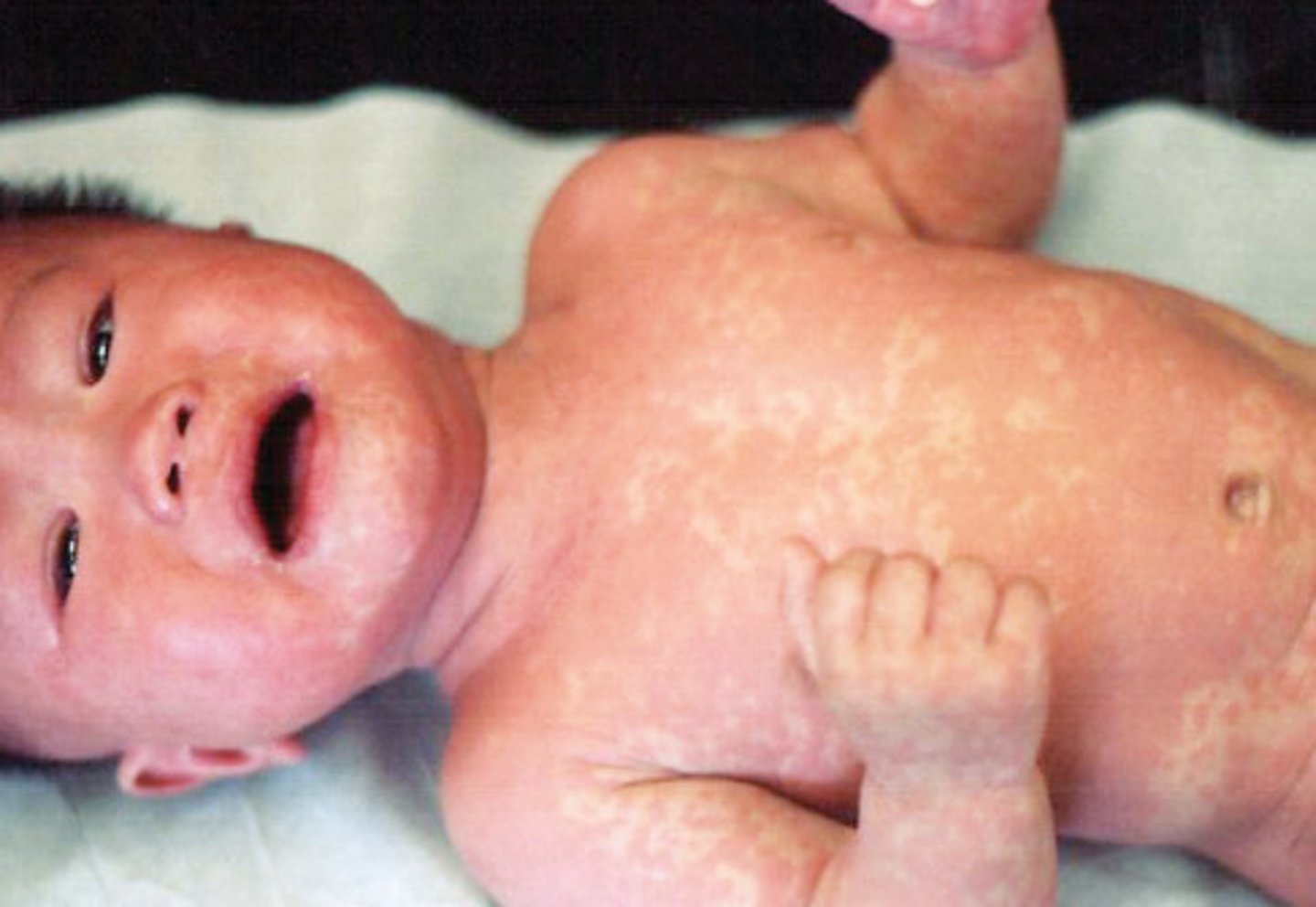
Roseola infantum
Rash starts on the trunk and goes to the extremities
Disease caused by infectious agents that are transmitted directly or indirectly from animals or vectors
Zoonotic and Vector-Borne Illnesses
Examples of vectors
Ticks, mosquitos, or other insects
What illnesses are derived from mosquito bites?
•West Nile virus
•Dengue fever
•Zika
What illnesses are derived from tick bites?
•Anaplasmosis
•Ehrlichiosis
•Lyme disease
What illness is derived from anopheles mosquitoes?
Malaria
What illness is derived from mammals?
Rabies
Parasitic and Helminthic Infections
How do they spread?
Through direct and indirect contact
Name the parasitic infections
•Pediculosis capitis (head lice)
•Pediculosis pubis (pubic lice)
•Scabies (most common)
Name the helminthic infections
•Ascariasis (round worm)
•Hook worm
•Pin worm
How can a new born or infant become infected with STIs?
If the mother is untreated during pregnancy and delivery
Why are adolescents commonly infected with STIs?
Lack of education and resources
Nursing interventions to promote comfort
•Assess pain and response to interventions frequently
•Administer analgesics and antipruritics
•Apply cool compresses or bathe areas with itching
•Provide fluids frequently
•Cool mist humidification
•Dress child in light clothing if febrile
•Use diversion and distraction