AP Human Geography: Types of Maps, AP Human Geography Types of Map Projections
1/27
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
28 Terms
Winkel Tripel
It's a compromise projection that's neither conformal, equal area, nor equidistant, but it minimizes all three types of geometric distortion
reference map
map type that shows reference information for a particular place, making it useful for finding landmarks and for navigating. emphasis on location
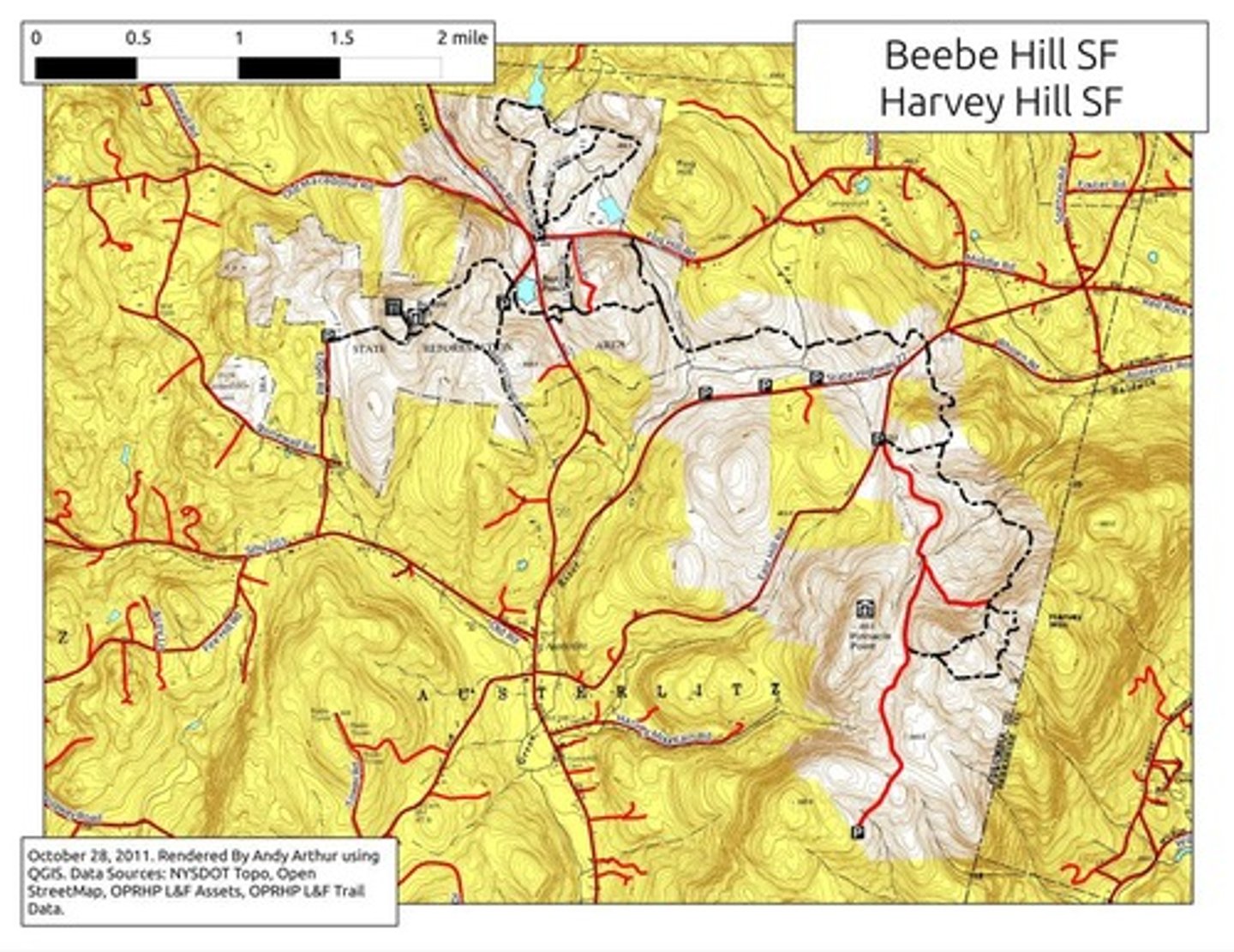
topographic maps
maps that use isolines to represent elevations, shows artificial and natural landscape markings
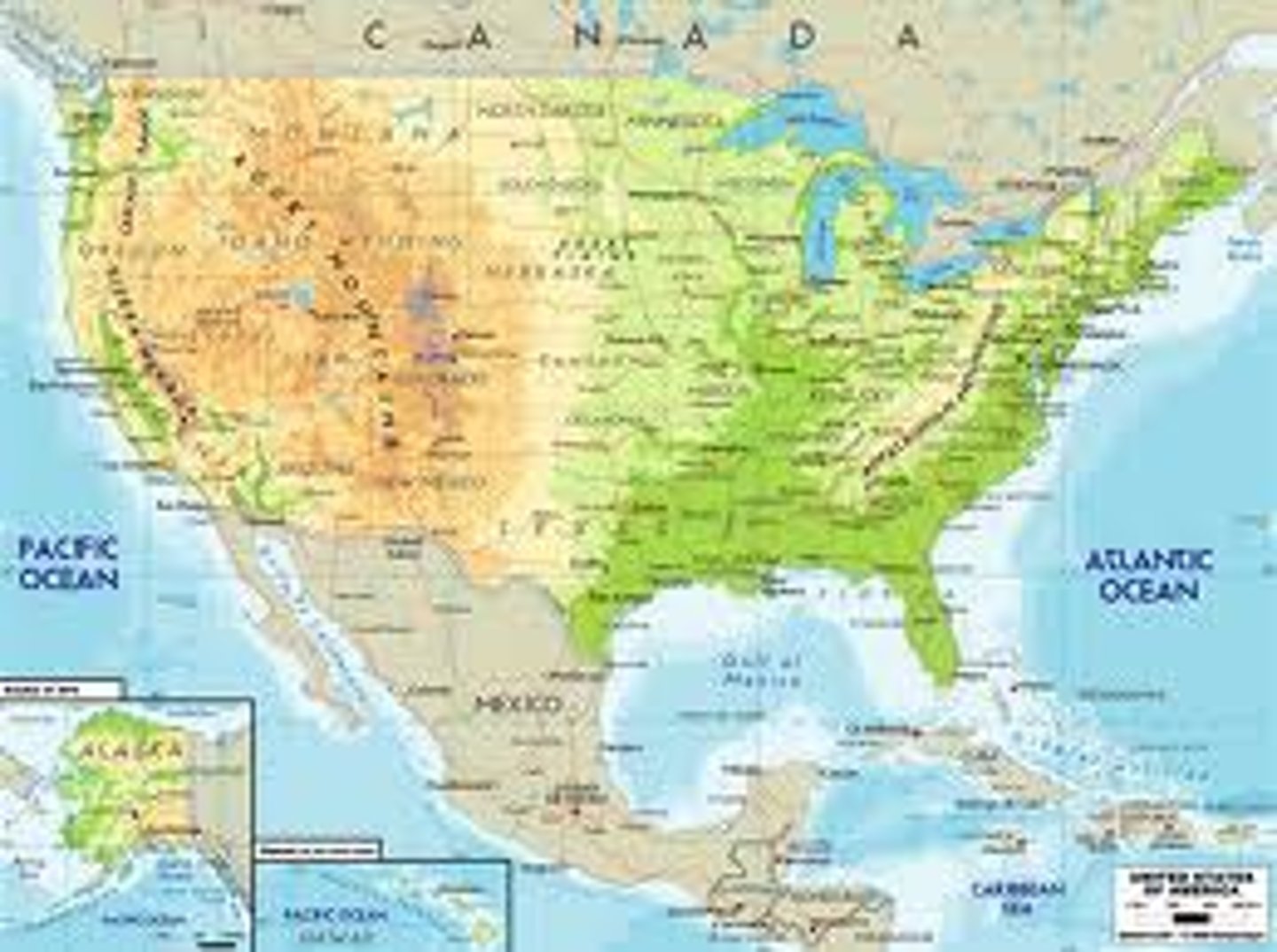
atlas/physical maps
maps that often include much of the same data found on a political map, but their primary purpose is to show landforms like deserts, mountains, and plains. their topography style presents an overall better picture of local terrain.
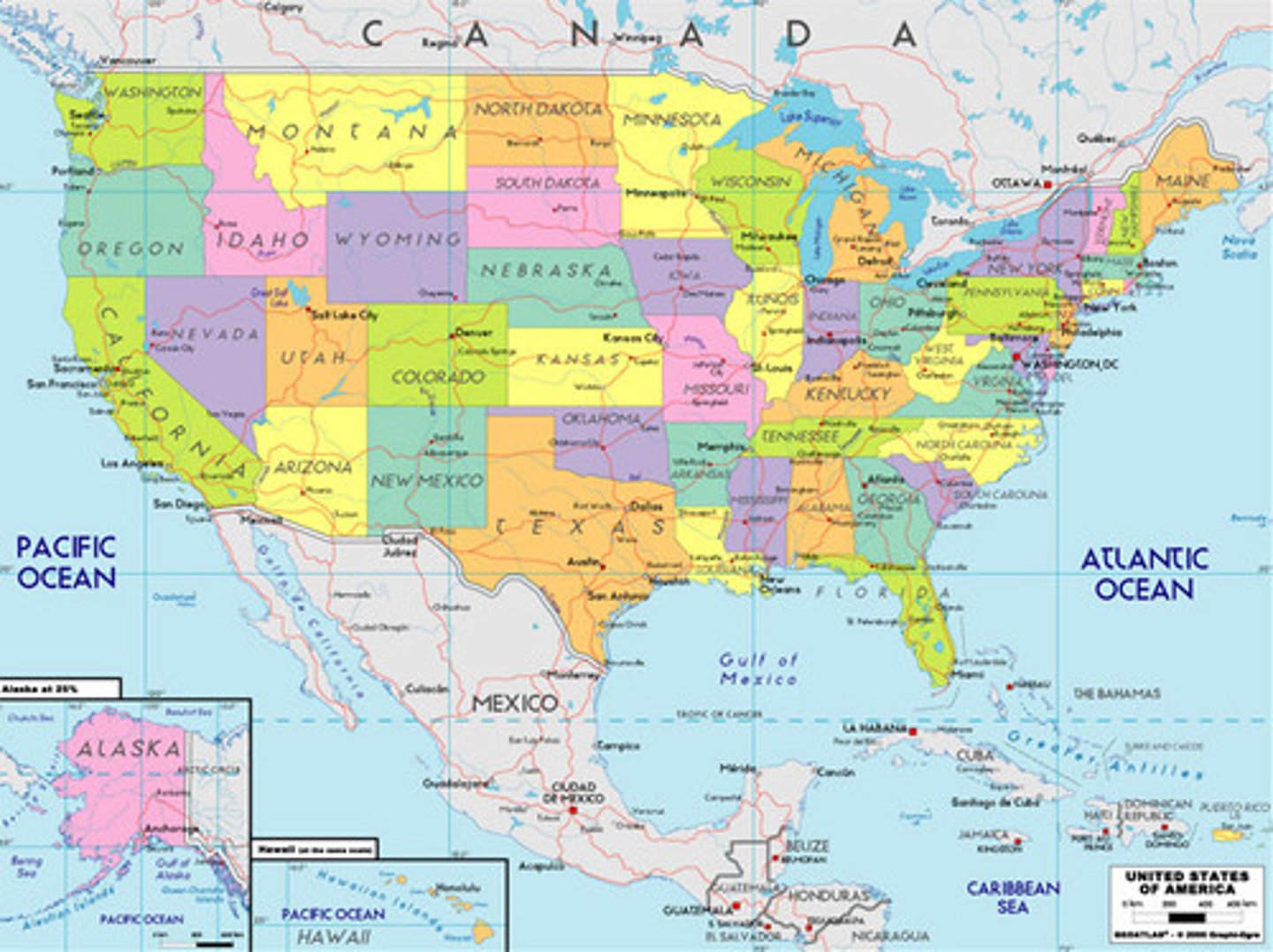
political map
maps that are designed to show governmental boundaries of countries and states
thematic map
type of map that displays one or more variables such as population, or income level- within a specific area
choropleth map
thematic map that uses tones or colors to represent spatial data as average values per unit of data
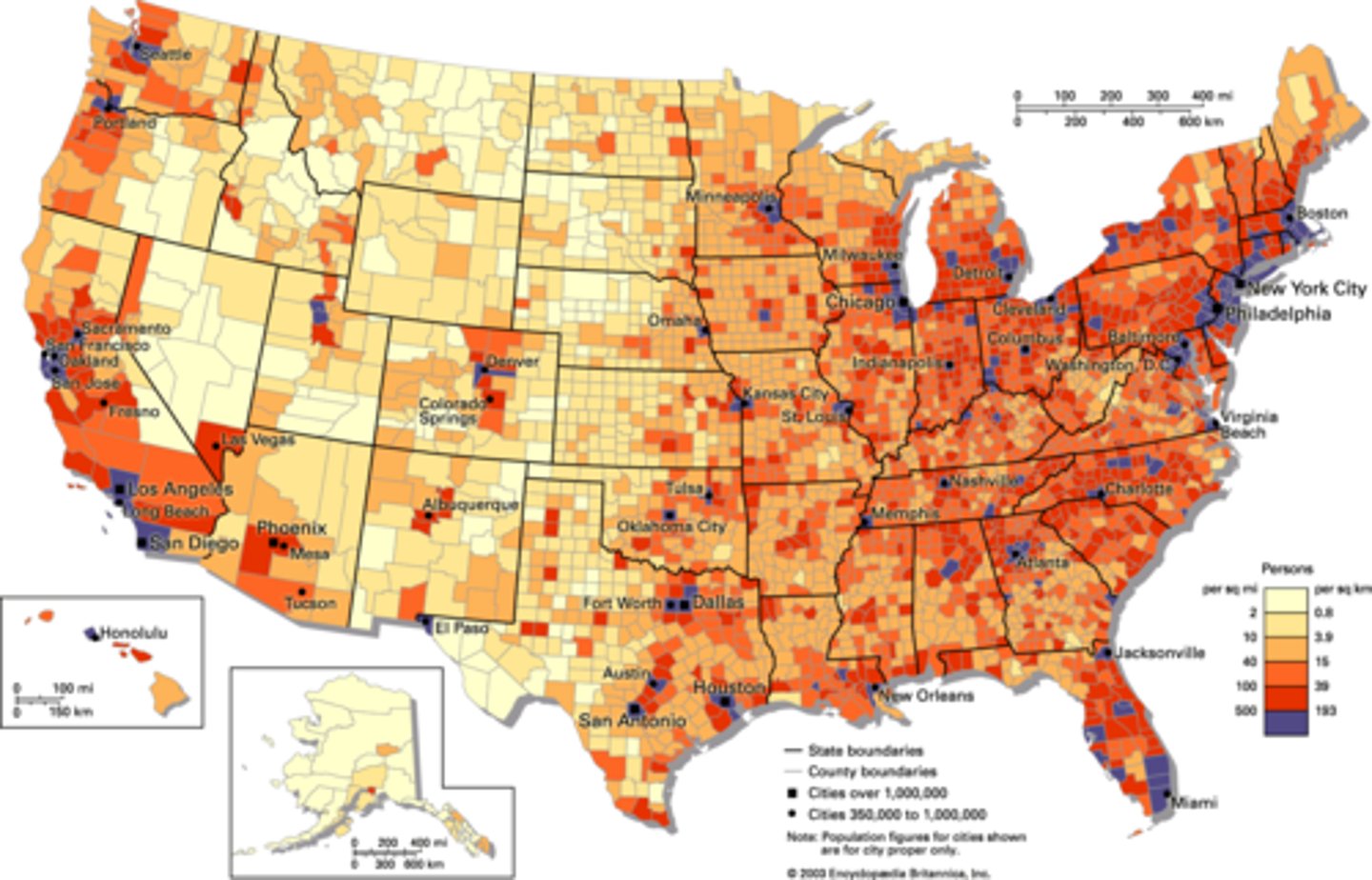
dot maps
thematic maps that use points to show the precise locations of specific observations or occurrences, such as crimes, car accidents, or births
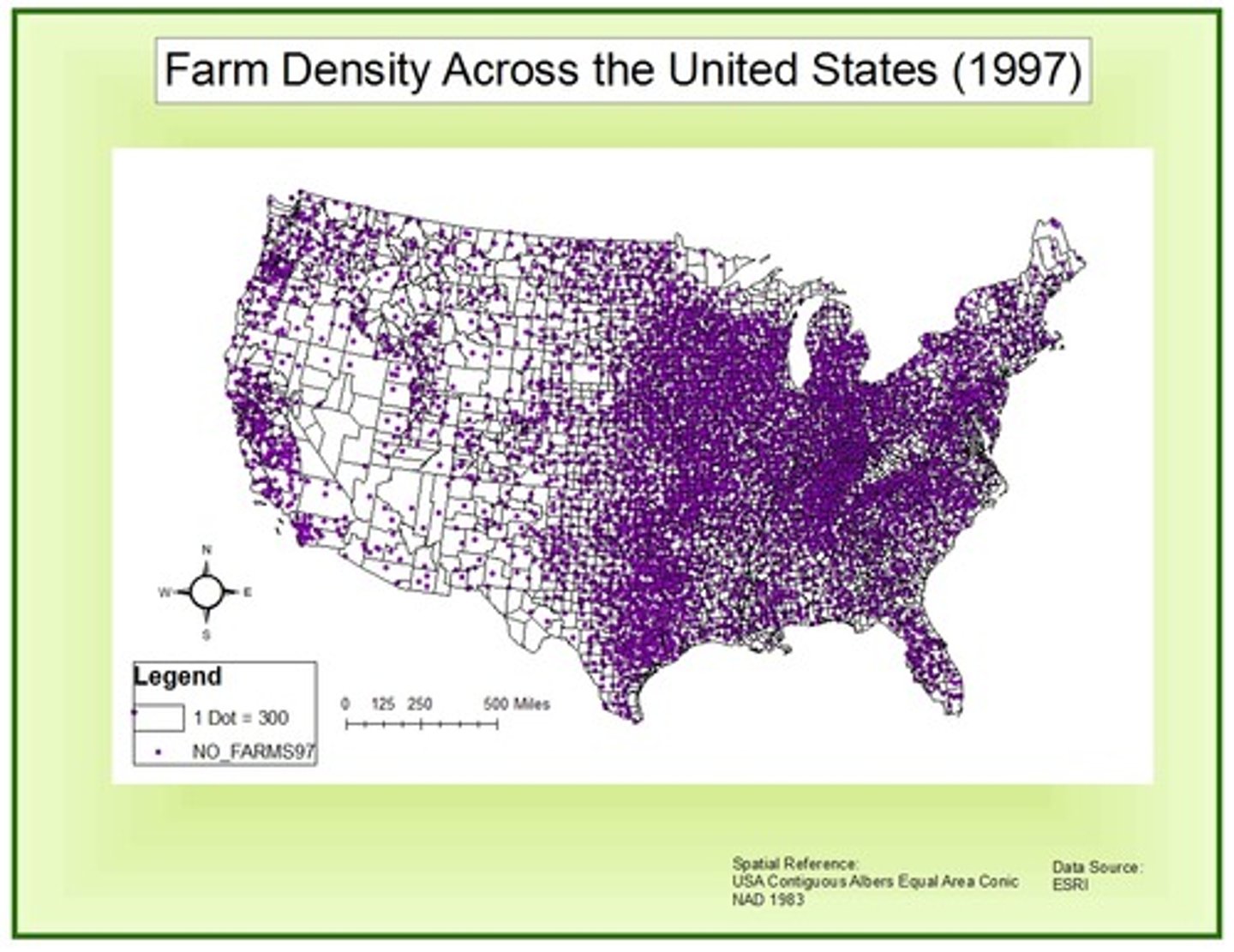
graduated symbol map
a map with symbols that change in size according to the value of the attribute they represent
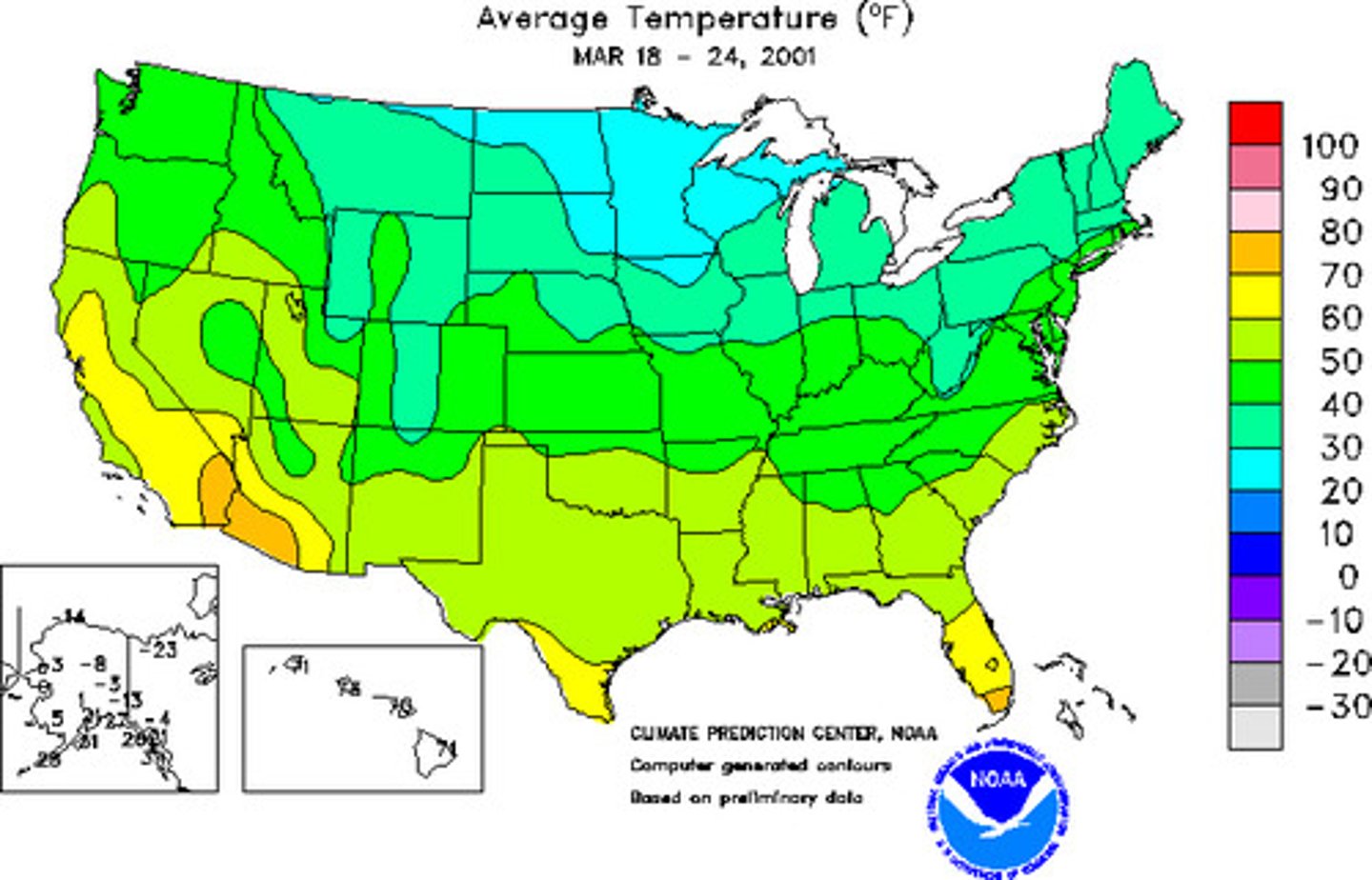
isoline map
map with continuous lines joining points of the same value examples would be equal altitude (contour lines), temperature (isotherms), barometric pressure (isobars), etc.
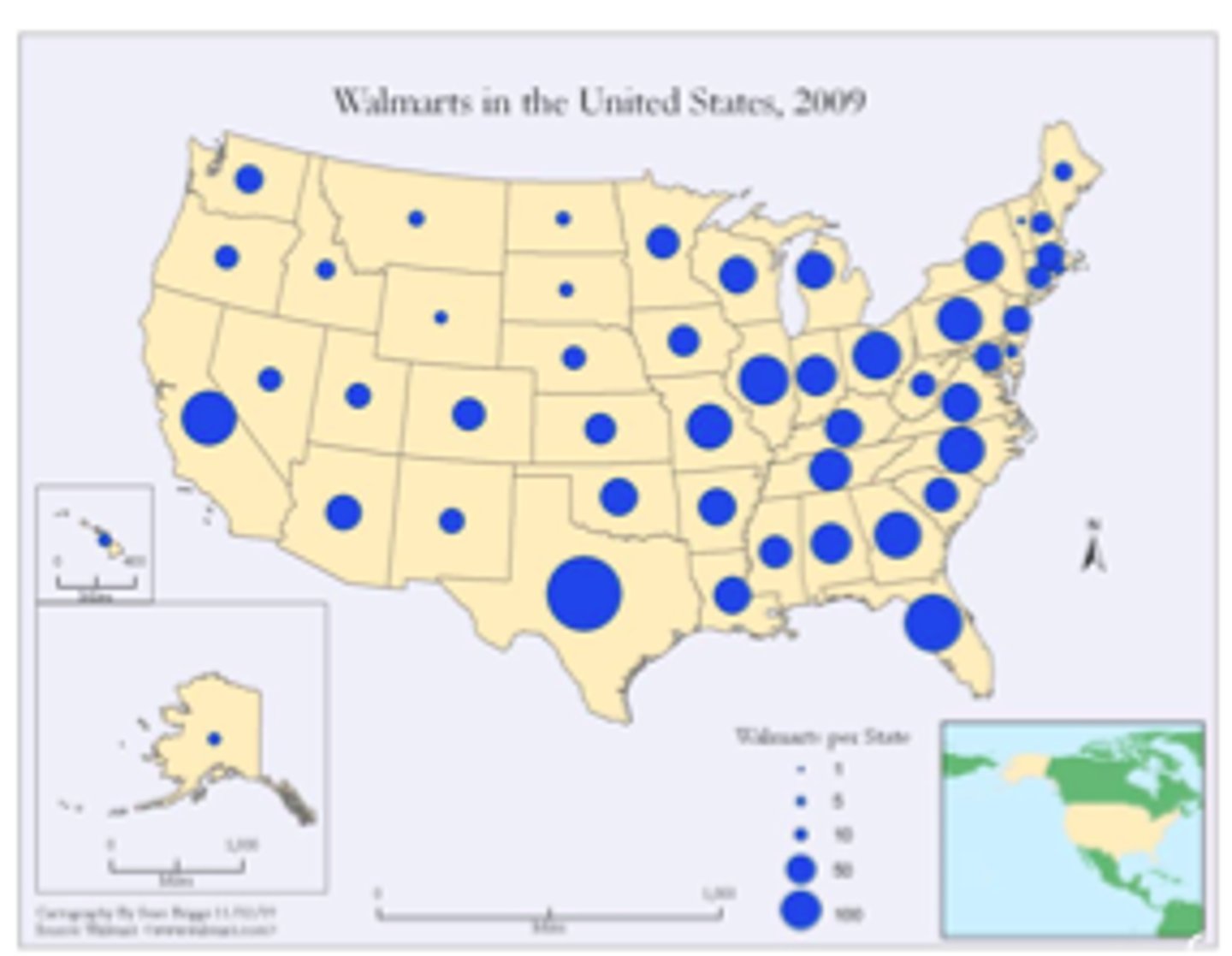
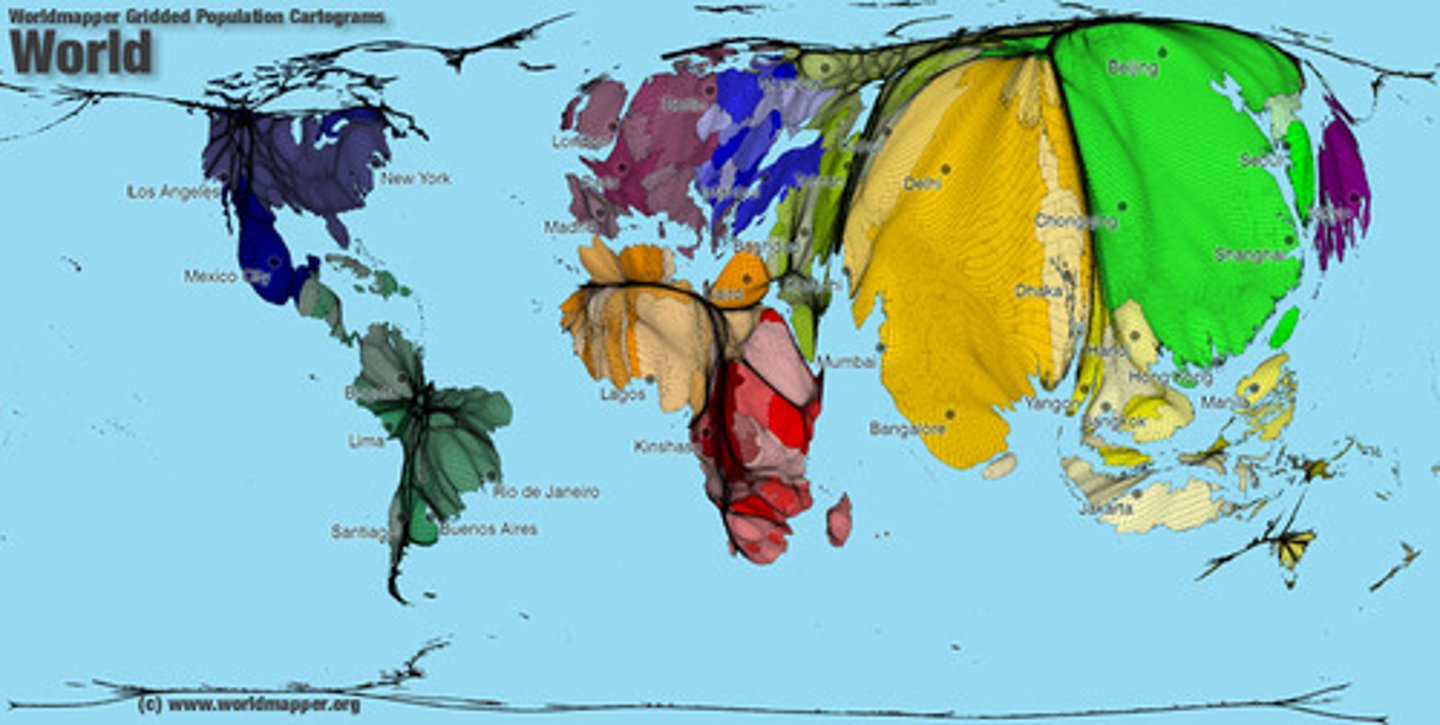
cartogram map
map in which some thematic mapping variable- such as travel time, population, gross national product, is substituted for land area or distance. the geometry or space of the map is distorted in order to convey the information of this alternate variable
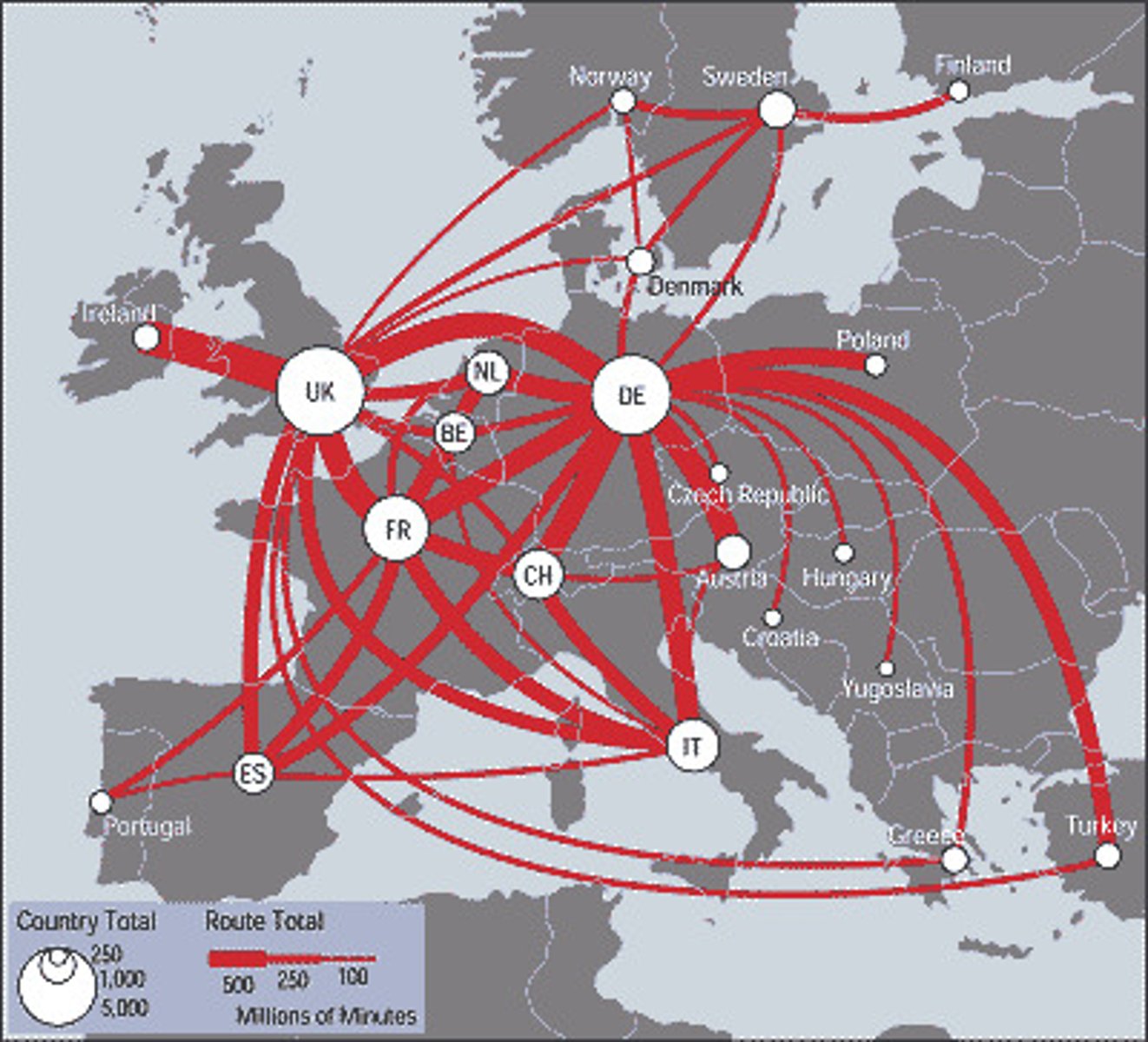
flow map
mix of maps and flow charts that show the movement of objects from one location to another
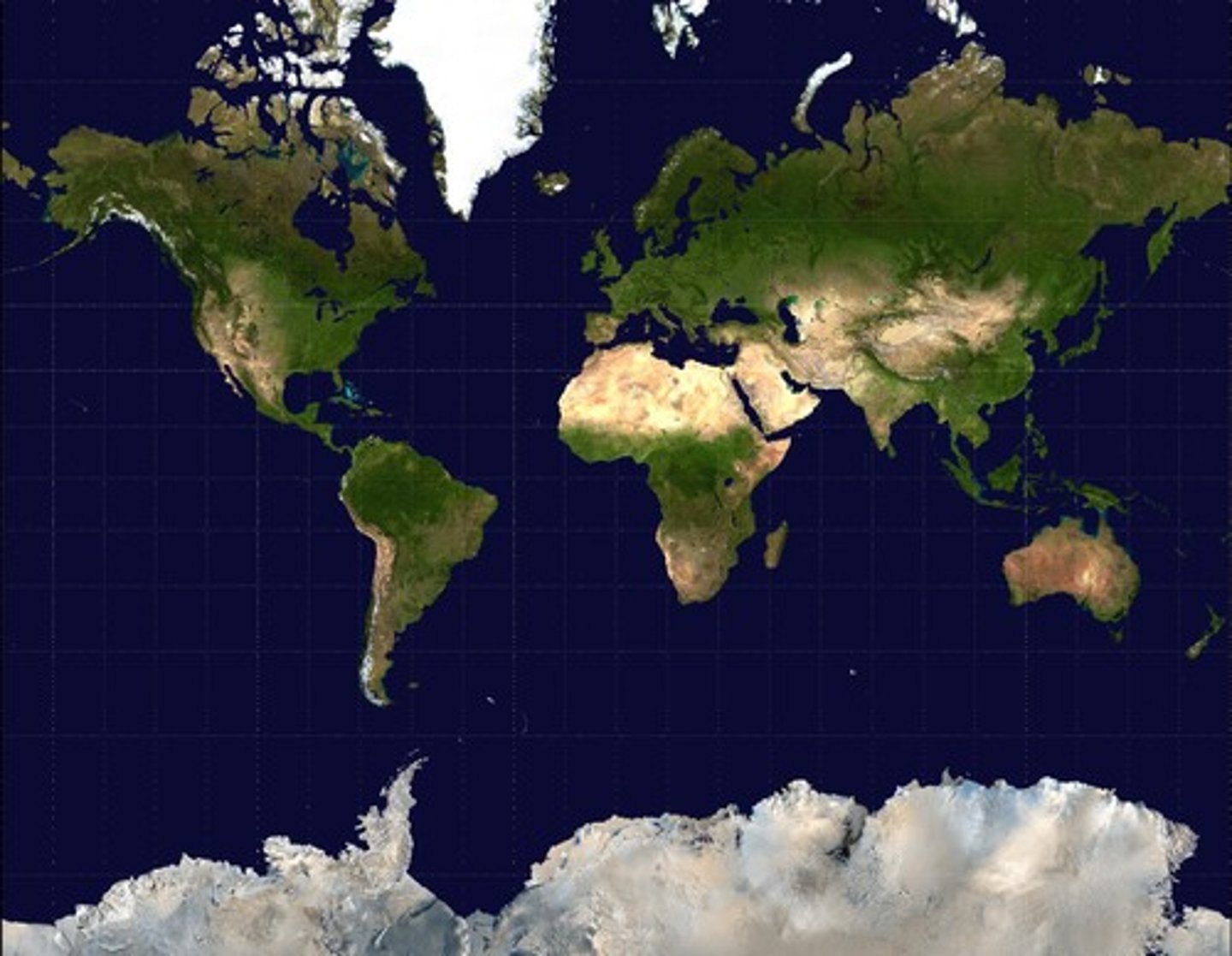
Mercator
a map projection that fairly accurately shows shape and direction, but distorts distance and size of land masses.
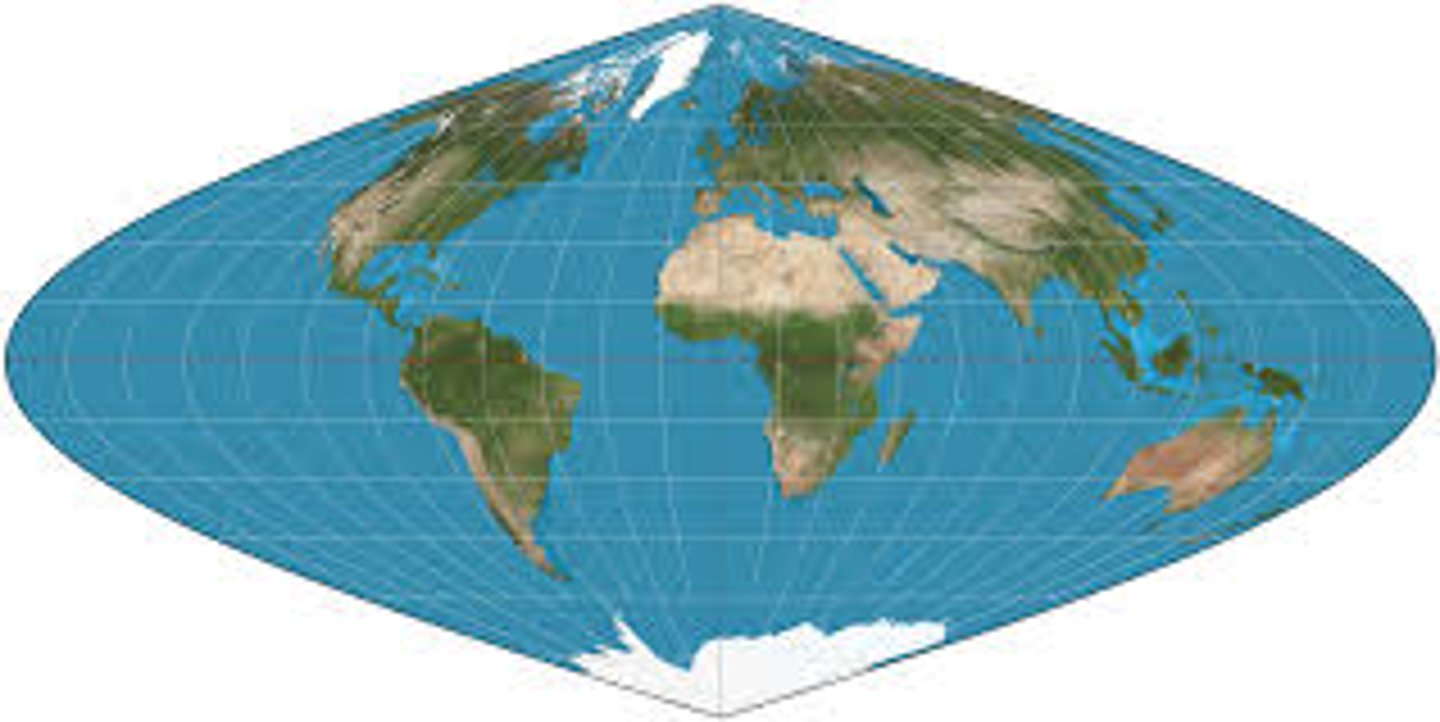
Sinusoidal
smoothly curving map that accurately presents the center of the map but the remaining is distorted.
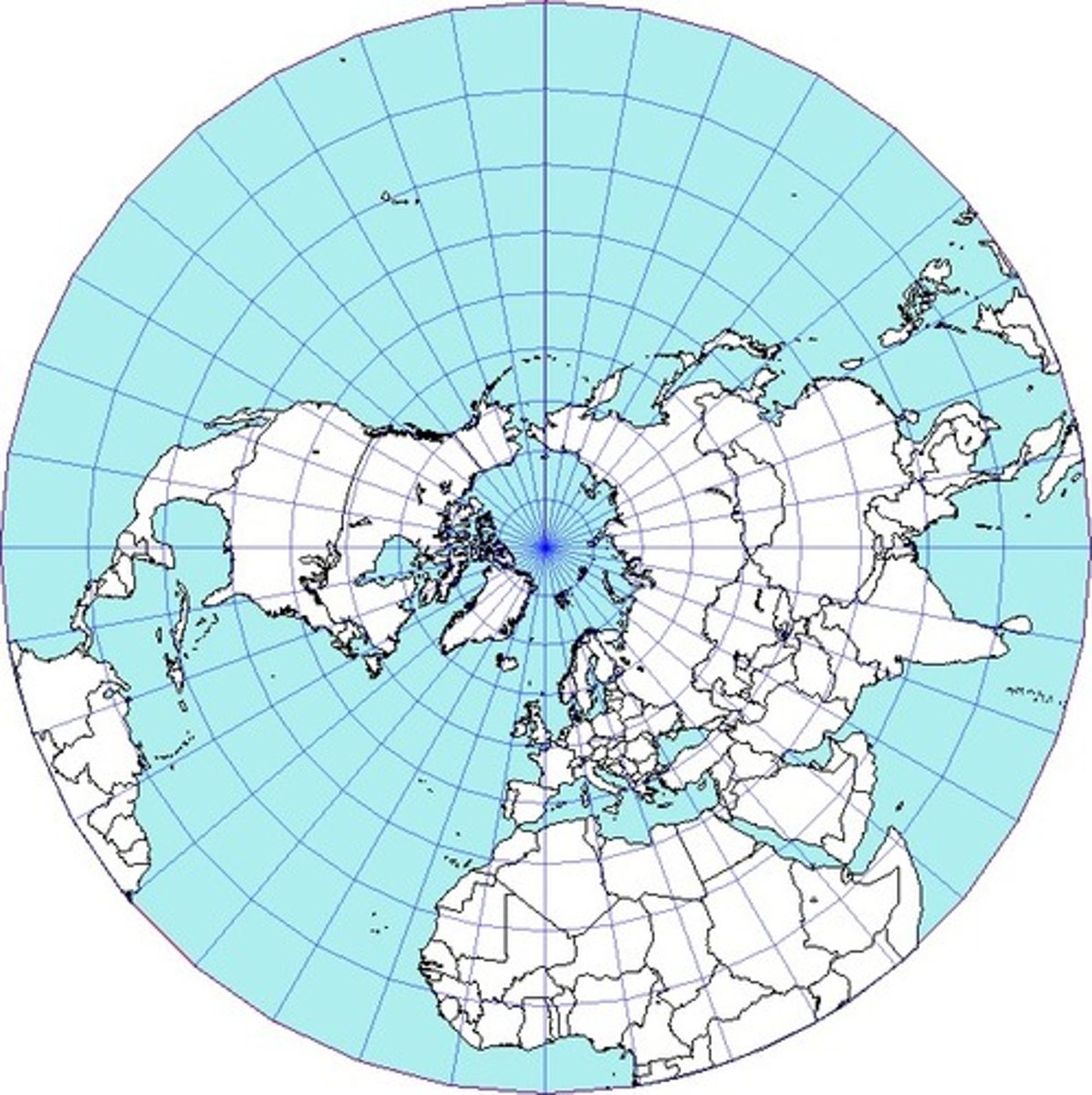
Azimuthal (polar)
a map which shows true compass directions; longitude lines are straight and latitude lines are circles; distorts shape and size more toward the outer edges.
Goode's Interrupted Equal Area
Area Projection; shows true size and shape of earth's landmasses
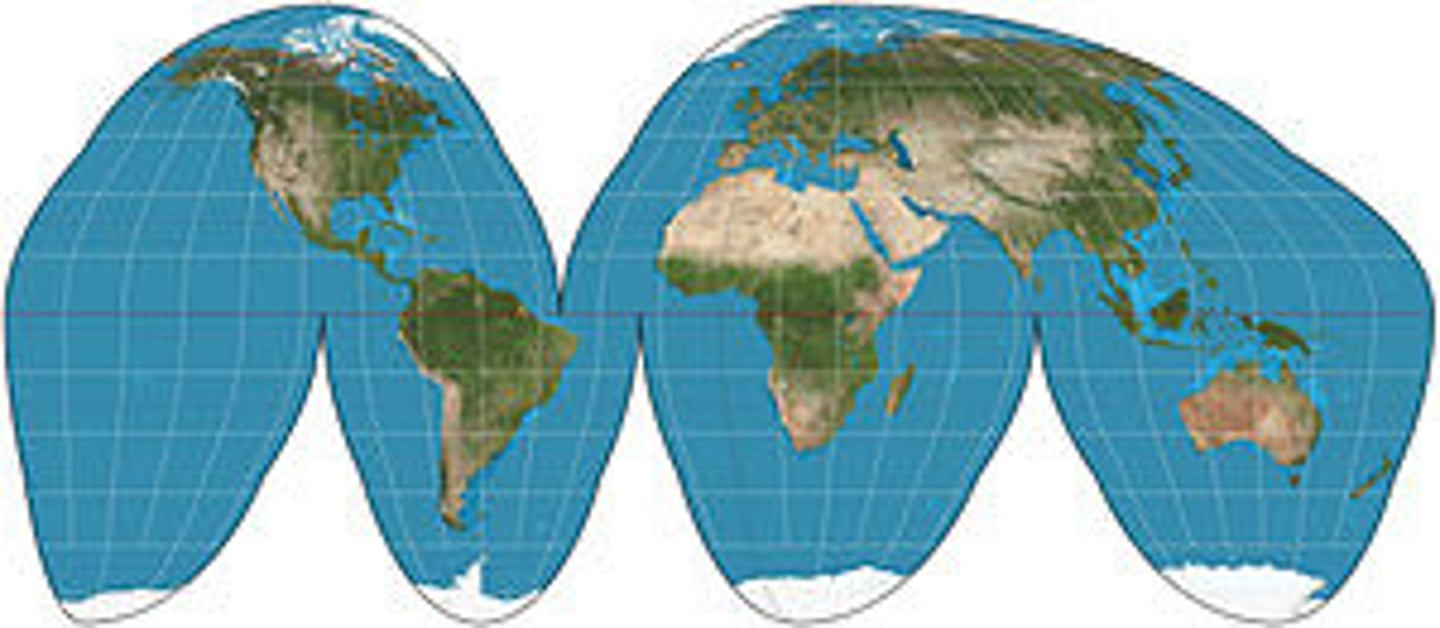
Fuller-Dymaxion
displays the entire world at once with minimal distortion. It looks like a bunch of triangles put together.

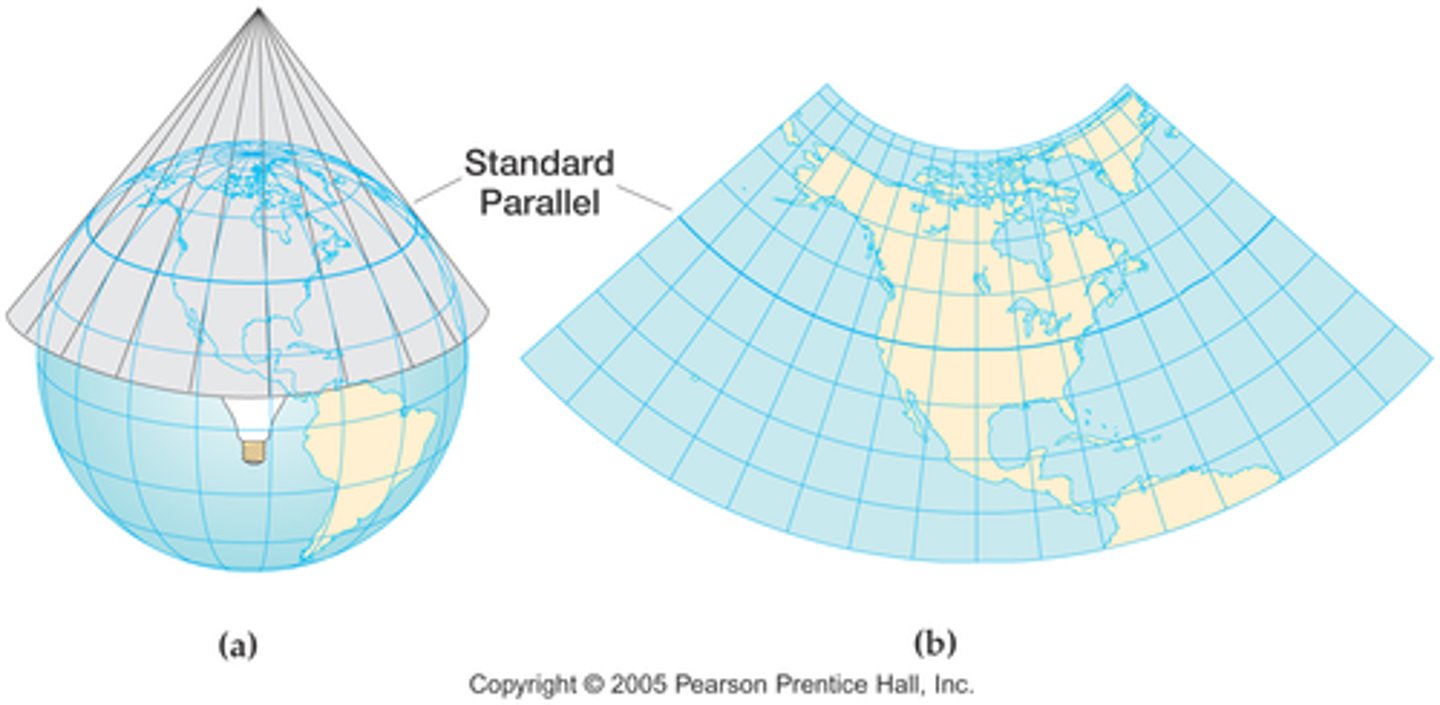
Conic
a map projection of the globe onto a cone with its point over one of the earth's poles
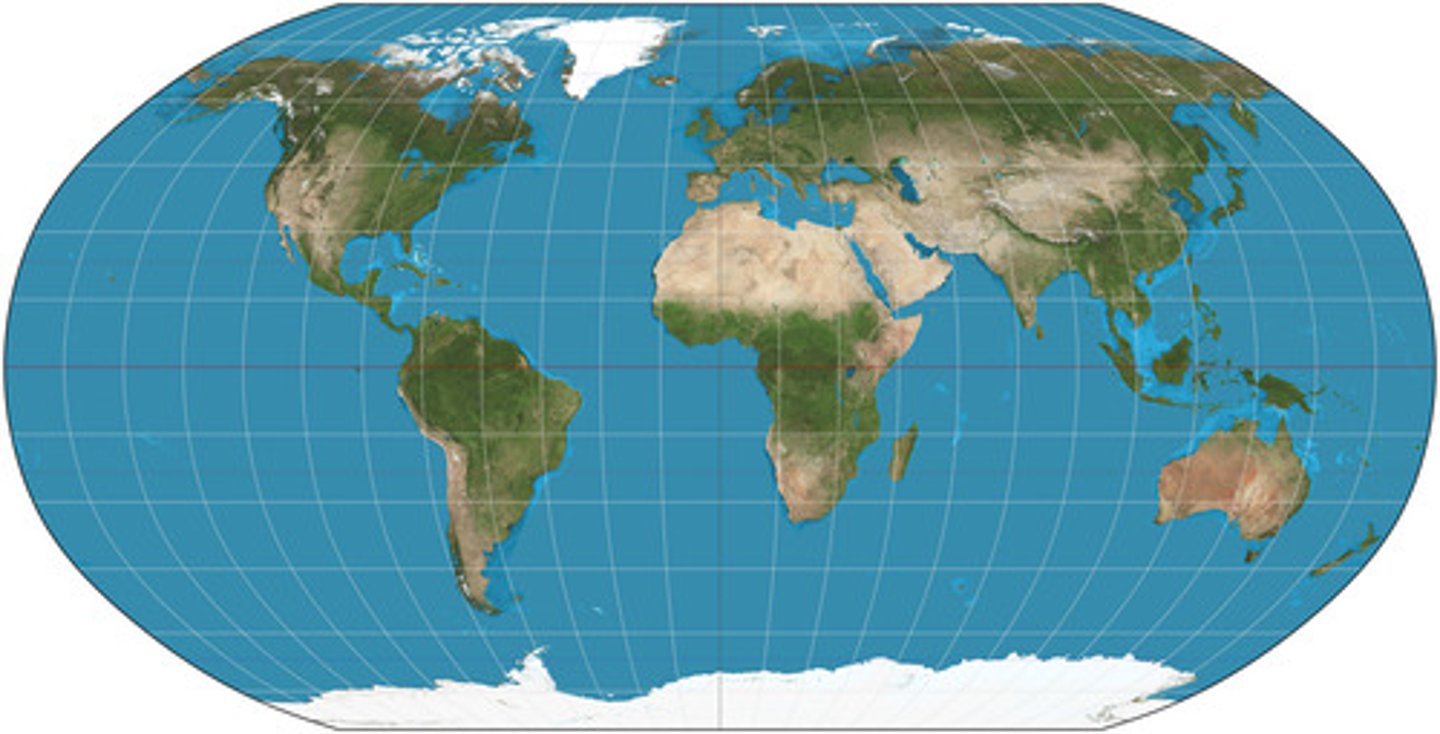
Robinson
a projection that maintains overall shapes and relative positions without extreme distortion.
Gall Peters
a projection that displays accurate axes, but shapes are distorted. They are hard to navigate when the shapes are not accurate
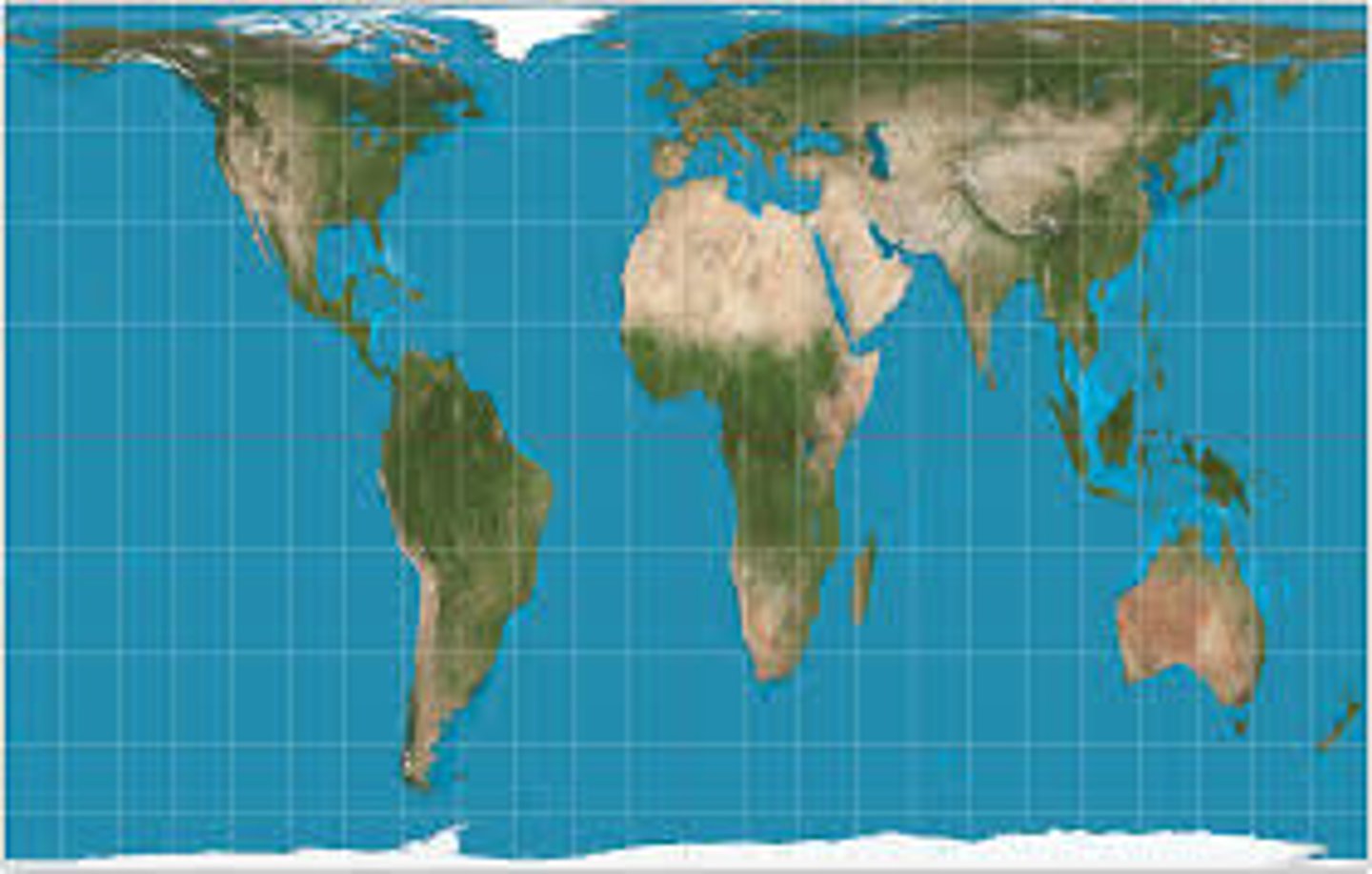
Miller
Similar to Mercator projection, but spacing between parallels stops growing after 55 degrees.
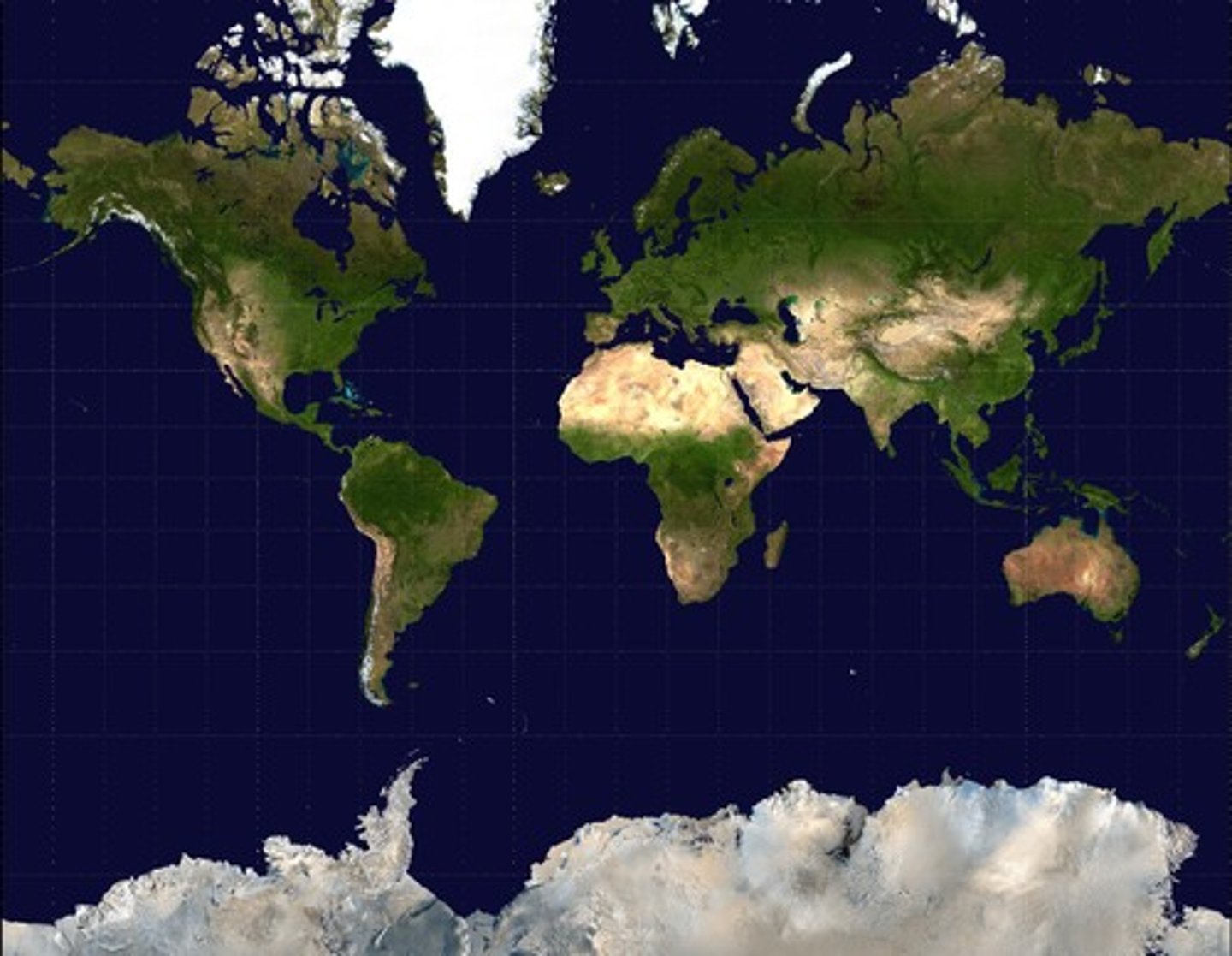
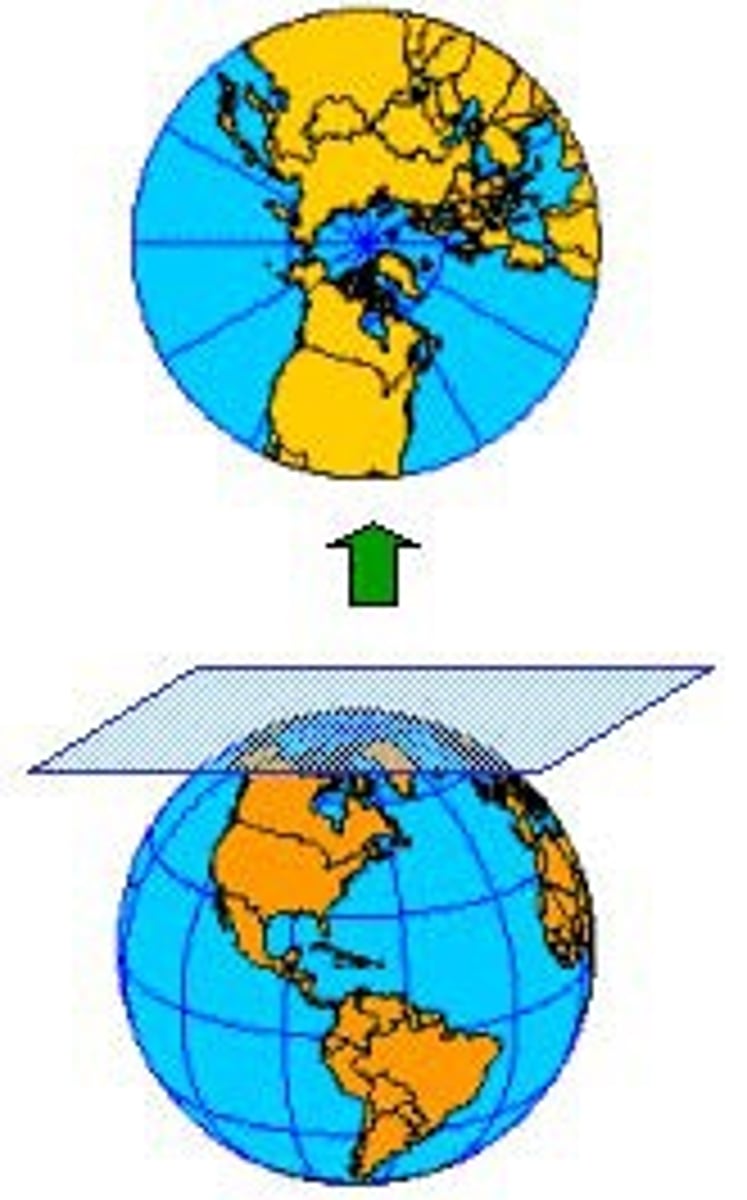
Planar
A type of map in which the details of the globe are projected onto a plane (a flat surface) yielding a rectangular-shaped map. Cylindrical maps have a lot of distortion towards the edges.
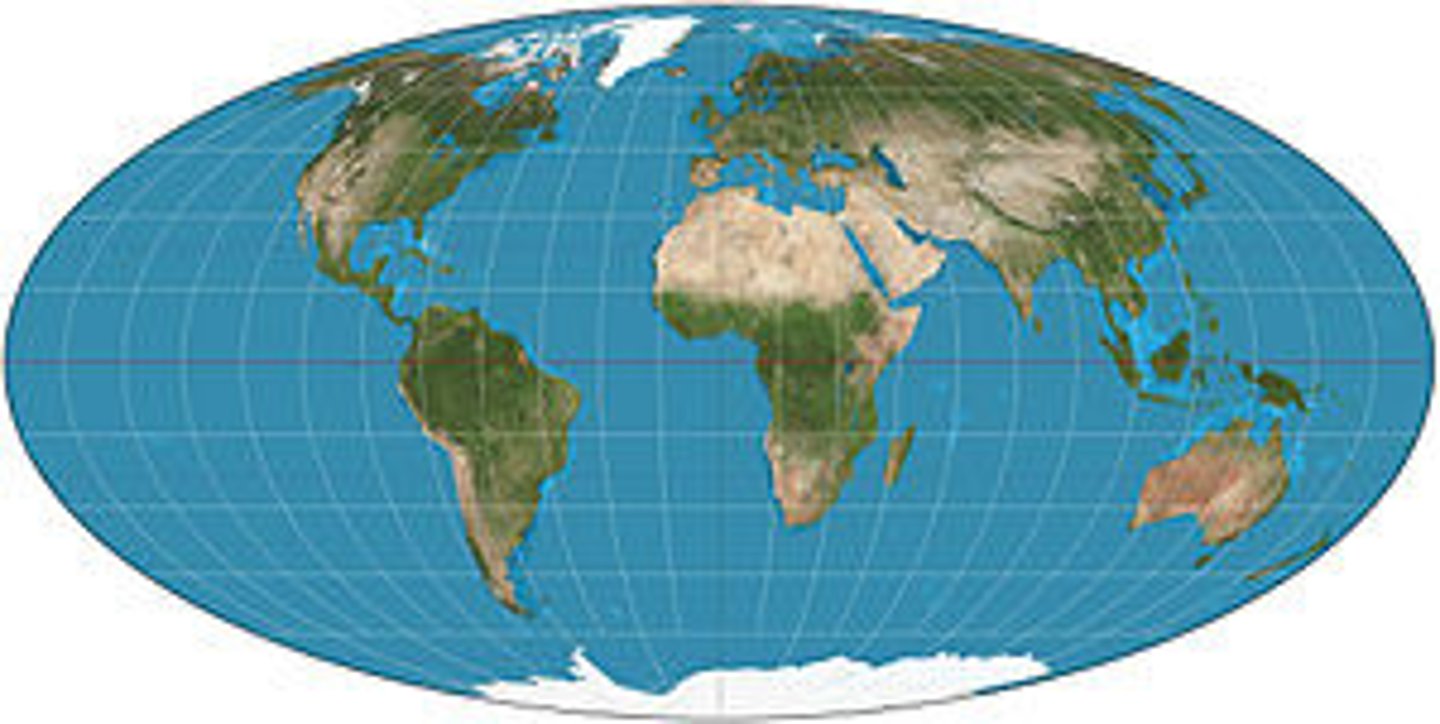
Molleweide
A projection of a map of the world onto an ellipse, with lines of latitude represented by straight lines (spaced more closely toward the poles) and meridians represented by equally spaced elliptical curves. This projection distorts shape but preserves relative area.
absolute location
the precise point where a place is located on the Earth's surface. It is determined using latitude and longitude coordinates.
absolute distance
total length between two points, regardless of the path taken. It is a fixed measurement and does not consider direction.
relative location
describes a place in relation to another place. It is not fixed and can change based on the reference point used for comparison.
relative direction
position of one object in relation to another, without using specific measurements like north or east. It is based on landmarks or other objects for orientation.
relative distance
The measurement of the distance between two points based on surrounding landmarks or objects, rather than using specific units of measurement.