Lecture 13: WAT Expansion And Accumulation
1/40
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
41 Terms
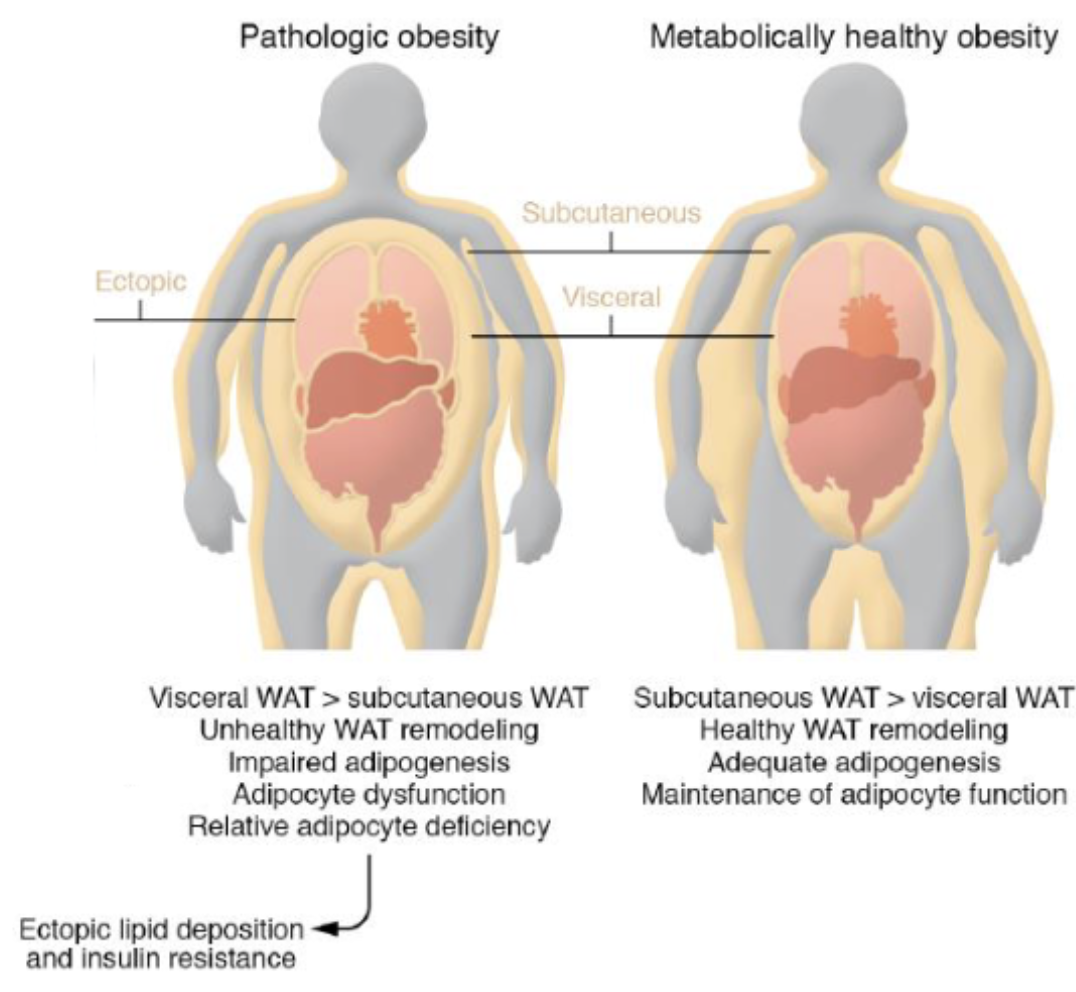
What is the difference between metabolically healthy and pathologic obesity patients?
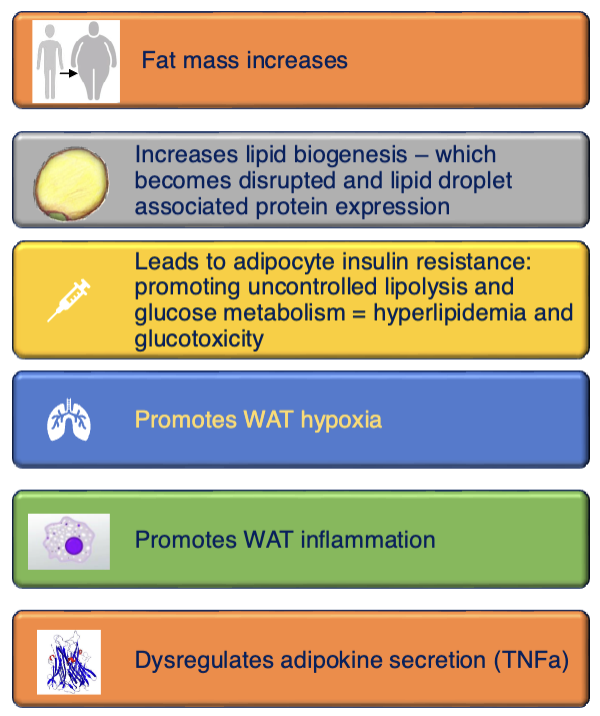
What can WAT mass change be a result from?
WAT mass changes may result from hypertrophy, hyperplasia, or of a combination of both
What is hypertrophy?
Swelling of existing adipocytes to accommodate excess nutrients as triglycerides
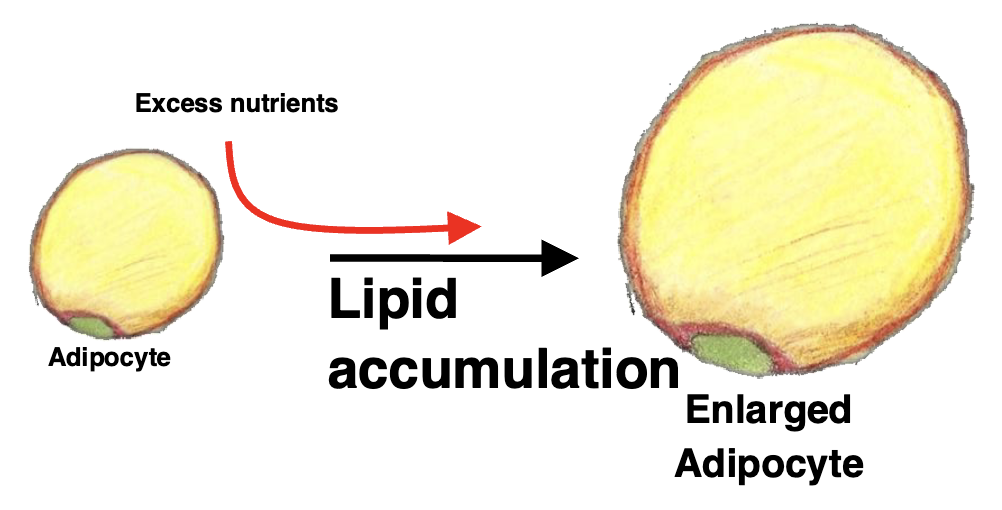
Is hypertrophy normal?
Yes
Acts as a buffer to manage to nutrient storage and mobilization
Can help normal tissue expansion
Chronic hypertrophy disrupts normal physiological
What happened to mice on a high fat diet for weeks?
Chronic hypertrophy
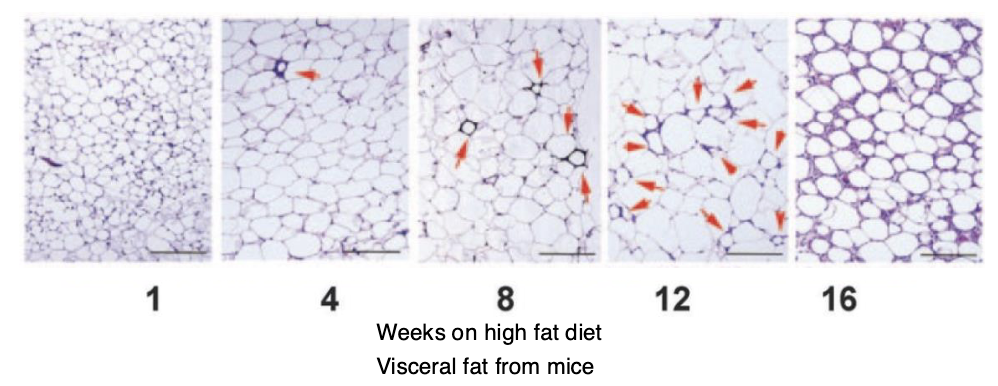
What does chronic hypertrophy promote?
WAT dysfunction
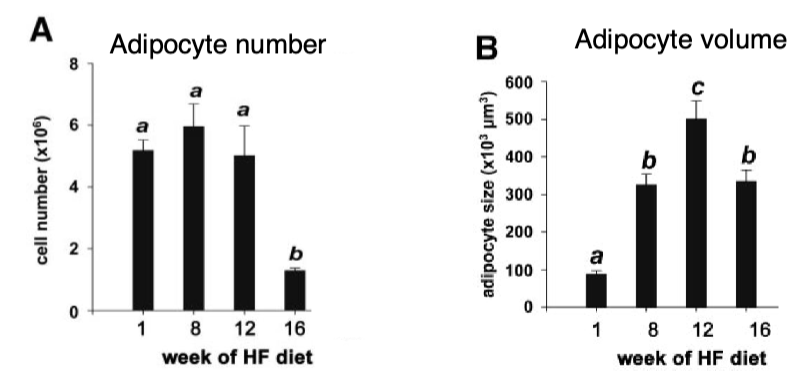
What does chronic adipocyte hypertrophy lead to?
Swelling of existing adipocytes to accommodate excess nutrients as triglycerides
Continued over nutrition leads to the dysregulation in lipid droplet biogenesis
Leads to max lipid droplet size = dysfunctional adipocyte
Leads to hypoxia, fibrosis, and inflammation
Leads uncontrolled lipolysis and lipid spillover
What does hypertrophy promote?
Hypoxia, fibrosis, and inflammation
What is hypoxia?
A reduction or lack of oxygen (cellular or organ level)
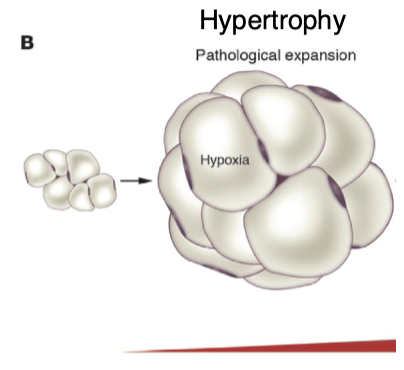
What does hypertrophy lead to?
Hypoxia
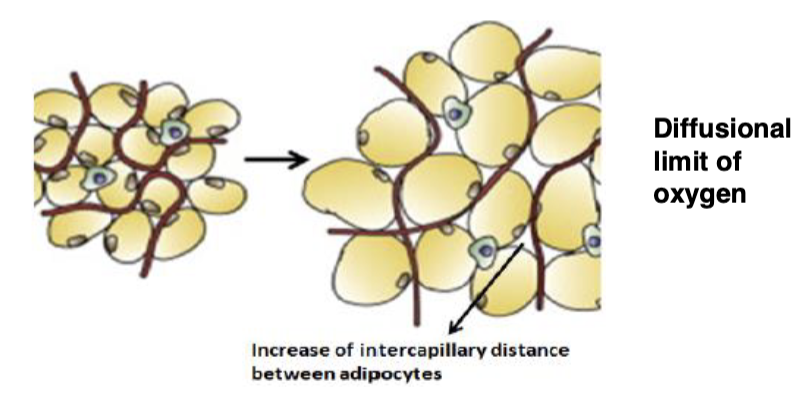
Is having less oxygen at the cellular level a problem?
Yes
Lack of oxygen for cellular process
ER-Stress
Mitochondria Dysfunction
Adipocyte death
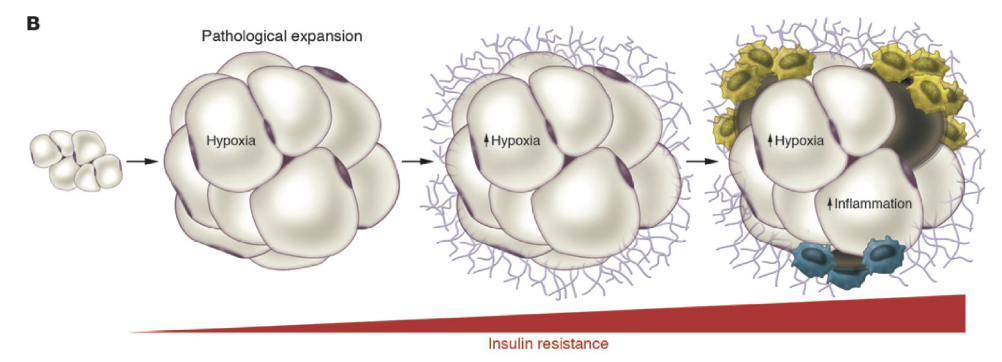
What is the acute hypertrophy hypoxic response?
Adipocytes quickly expand in size and, in the process, reach the diffusional limit of oxygen
The ensuing hypoxia is mild but induces a stress signal that drives new blood vessel formation to facilitate further expansion of WAT and reduce hypoxia. This acute effect can be thought of as “healthy” AT expansion
Is acute hypoxia normal?
Yes
Hypoxia causes the release of blood vessel forming (angiogenesis) factors from cells (adipocytes)
This promotes new capillary formation within the tissue to support its growth and function
What is the chronic hypertrophy response?
Adipocytes keep expanding in size and, in the process, exhaust the ability of WAT to produce new blood vessels. The ensuing hypoxia is greater and induces stress signals resulting in adipocyte cell death
Unhealthy
How does hypoxia alter WAT?
Tissue stress: nutrient deprivation
Stimulate inflammatory signals
Force adipocyte cell death and necrosis: stimulating lipid release
What are the drawbacks of stimulating vascular growth with hypoxia?
Increase vascularity in all tissues
Increase the risk of cancer
Would not solve the WAT expansion problem...only promote healthier WAT expansion in the short-term
What can hypertrophy induce?
WAT fibrosis
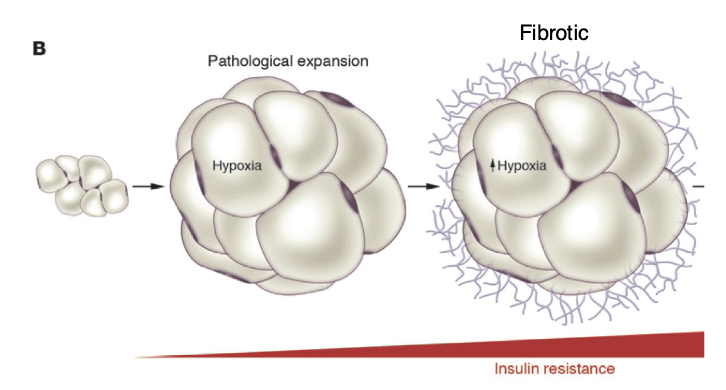
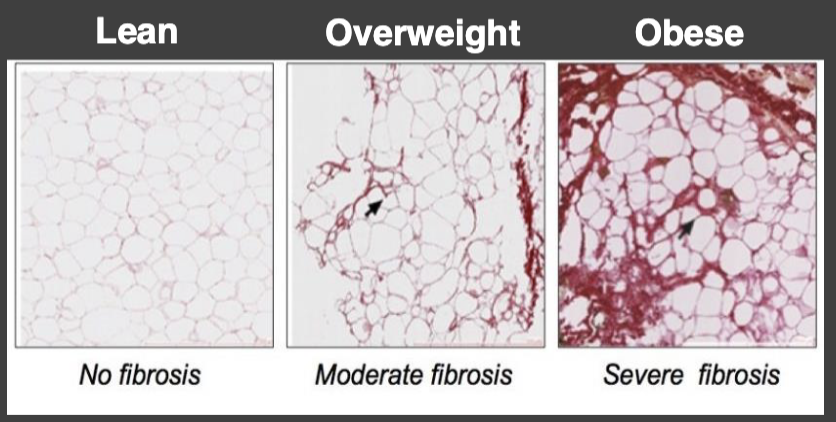
What is fibrosis?
The formation of excess connective tissue in an organ or tissue in a reparative or reactive process
How is fibrotic tissue made?
Fibroblast within the tissue/organ control the amount of collagen fiber and other extracellular matrix deposition
Is the fibrogenic process normal?
Yes, as a tissue repairs, connective tissue deposition is normal and precedes inflammatory signals and prepare the tissue for the regenerative or healing process. If not fully removed after regeneration or healing this effect can lead to scarring
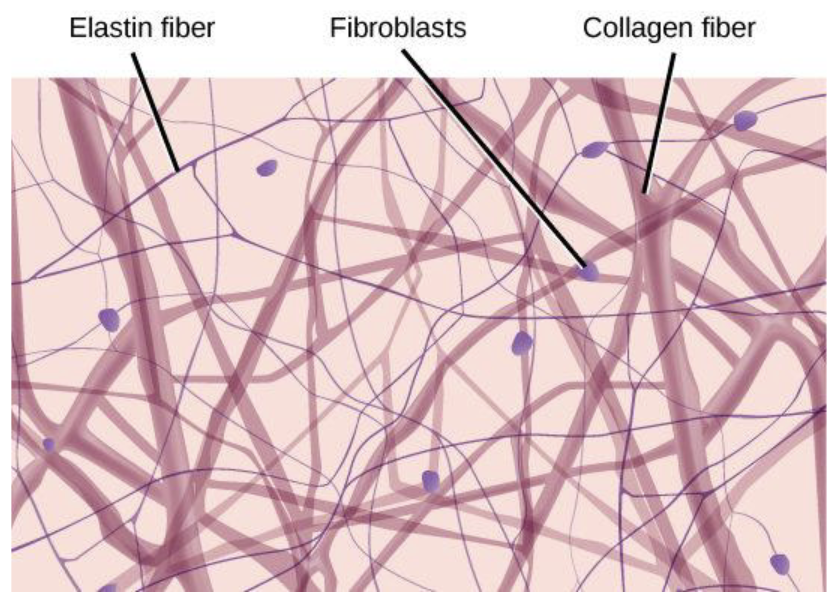
What are the 4 phases of fibrogenesis?
Initiation of the response (Poor diet, adipocyte hypertrophy, hypoxia)
Activation of effector cells (fibroblast)
Elaboration of extracellular matrix (production of collagen and fibers in between adipocytes)
Full progression of fibrosis and organ failure
What initiates WAT fibrosis?
Hypoxic conditions and adipocyte hypertrophy stimulate the secretion of pro-fibrotic signals that stimulate fibroblast cells within WAT to expand themselves and to produce collagen and other matrix materials
What does fibrosis mean for adipose tissue?
Increased tissue stiffness
Disruption of tissue organization and architecture
interfere with cell-cell communication
adipocyte-blood vessel communication
Activated fibroblast will secret hormones and factors that disrupt WAT biology
What can hypertrophy induce?
Adipose tissue inflammation
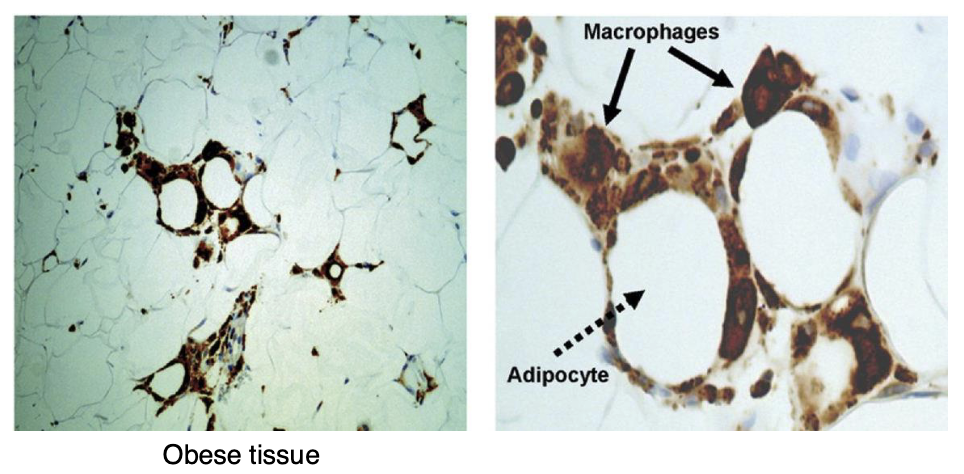
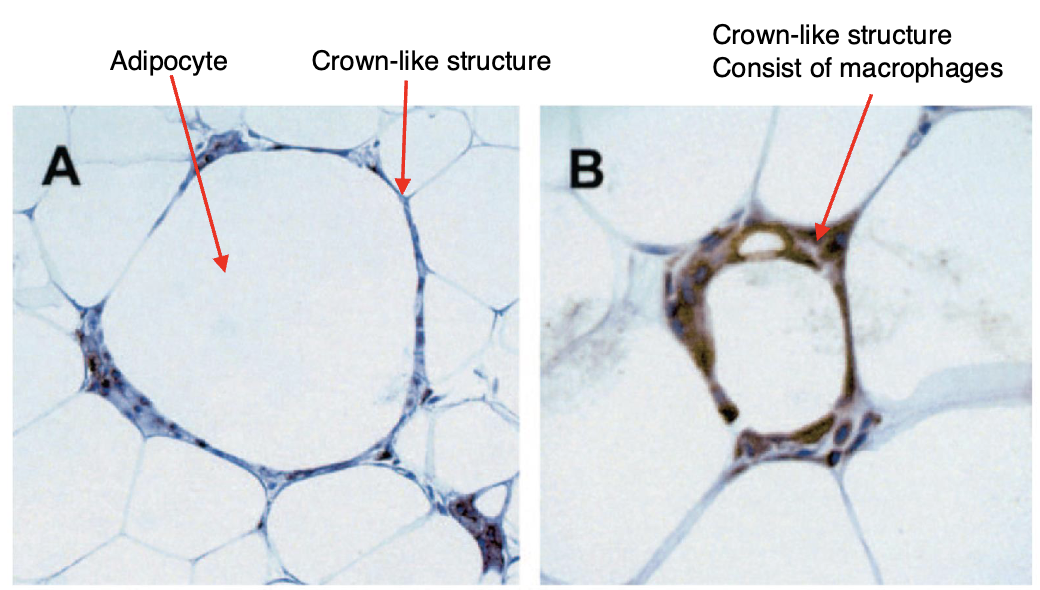
What are macrophages?
Phagocytic cells
Sentinels of the innate immune system to fight off infections
Macrophages are part of the innate immune response functions as the first line of defense against infection
Macrophages comprise the largest population of resident immune cells in visceral AT, constituting up to 10%
Macrophages are responsible for many housekeeping processes, such as removal of apoptotic and necrotic cells, modulation of angiogenesis, ECM remodeling, and differentiation of adipocyte precursors
What are crown-like structures?
Signals cell death and macrophage engulfment
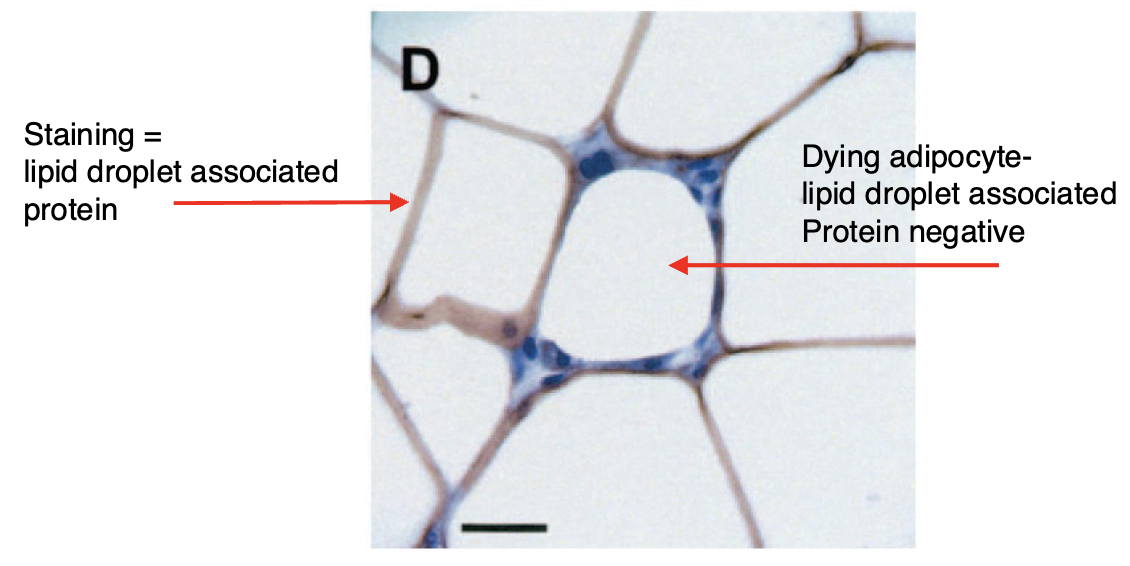
What does brown staining represent?
Brown staining represents a lipid droplet associated protein (note the loss of staining demonstrating dead adipocytes)
How do adipocytes signal to immune system?
Hypertrophy adipocytes secrete cytokines that attract immune cells to the WAT
Immune cells and macrophages elicit/mount a pro-inflammatory response
Encircle and engulf adipocyte
What is WAT inflammation?
Obesity is characterized by low-grade inflammation
Impaired adipokine secretion
Recruitment of harmful macrophages instead of health macrophages
Enhances adipocyte cell death and lipid release into the blood
Impairs insulin signaling pathways
TNFalpha(α) is a major driver of WAT inflammation
How does hypertrophy induce adipocyte death?
By secreting TNFα (Tumor necrosis factor alpha)
Proinflammatory adipokine
Lowly expressed in adipose tissue but increases in response to obesity
Changes the immune cell composition in adipose tissue
Serves as a macrophage attractant-–bringing the macrophage to the dysfunctional adipocyte
Impairs insulin signaling in adipose tissue and muscle
Impairs pancreatic insulin secretion
What does TNFα correlate with?
Fat mass and adipocyte hypertrophy
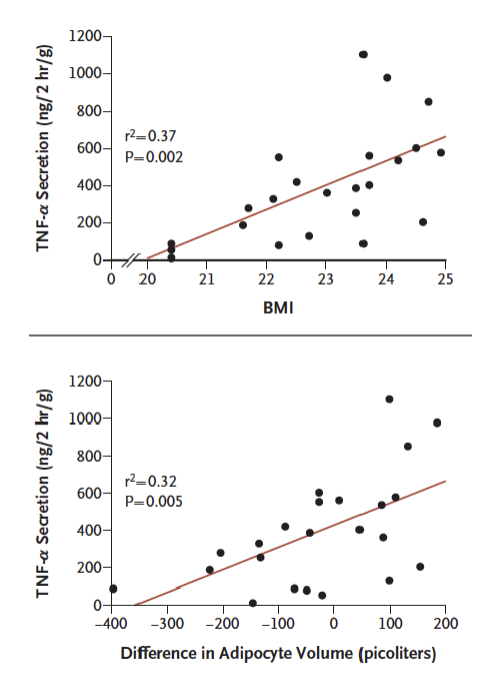
What do TNF-α secreting adipocytes recruit?
TNF-α secreting adipocytes recruit macrophages that secret TNF-α – vicious cycle
Can we target TNFa to stop WAT inflammation?
This has failed in mice: While anti-TNF therapy has reduced other symptoms of obesity such as fatty liver disease there has been NO impact on adipose tissue inflammation! Must be more to the story.....
What does adipocyte hypertrophy alter?
Adipocyte hypertrophy alters the immune cell composition of our adipose tissue
How is adipose tissue inflammatory attack sustained?
Elevated fatty acids, adipocyte hypertrophy, and hypoxia initiate the inflammatory response
Adipose tissue inflammation recruits' macrophages to sustain the inflammatory response
Macrophages account for 10% of lean adipose tissue mass but increases to 50% in obesity
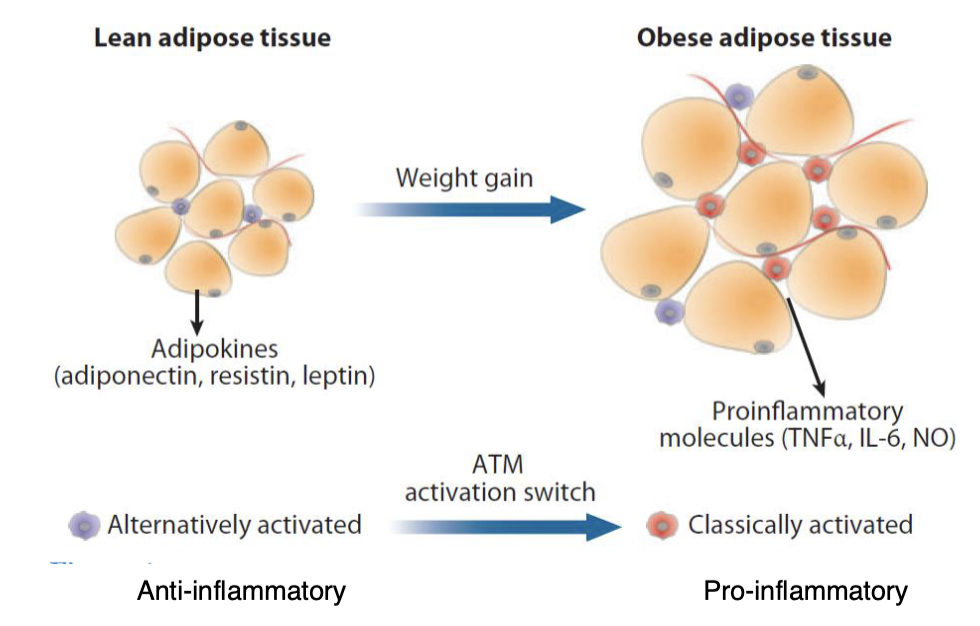
What is the difference between classical and alternatively macrophages?
Classically activated macrophages: M1 OBESE STATE!
Stimulates the deconstruction of extracellular matrixes
Promotes apoptosis and necrosis
Visceral fat tends to have more M1 macrophages
Alternatively activated macrophages: M2 LEAN STATE
Stimulates extracellular matrixes
Cellular proliferation
Angiogenesis
Subcutaneous fat tends to have more M2 macrophages
Why do M1 macrophage have negative health consequences?
M1 macrophages will:
Breakdown tissue integrity
Promote adipocyte cell death
Kills other cell types
Prevents angiogenesis
Alters WAT environment leading to overall changes in adipokine secretion
Recruits more M1 macrophages
What is lipolysis?
Normal function of adipocytes to control energy levels
Lipolysis is turned on in the fasted state
Increase cyclic AMP
cAMP levels phosphorylate hormone sensitive lipase (HSL, an enzyme)
HSL hydrolyzes triglycerides into free fatty acids
Free fatty acids released into the blood
Utilized for energy
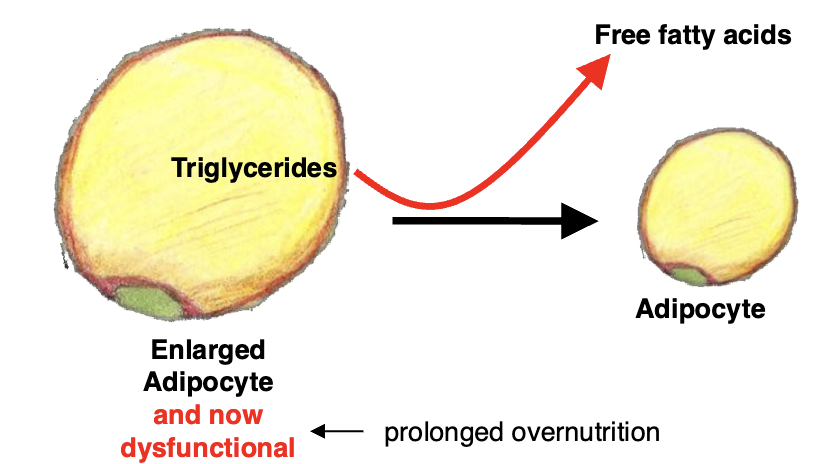
Why is lipolysis turned off in the fed state?
Glucose is available, do not need free fatty acids
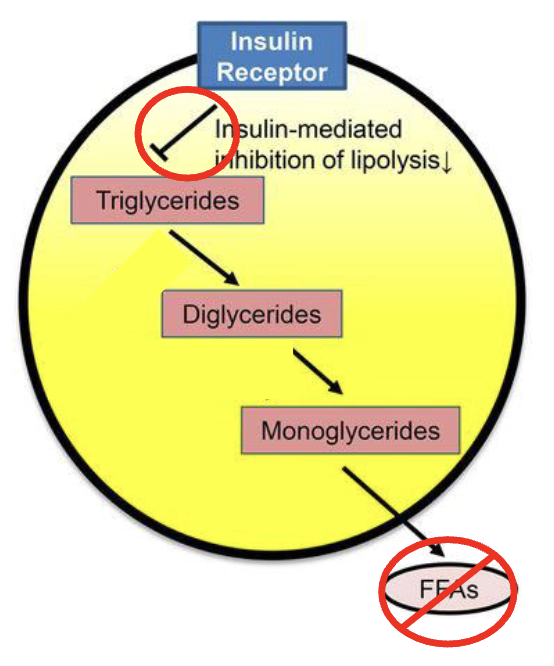
Why does insulin block lipolysis?
Insulin is telling the fat cell to stop converting triglycerides to free fatty acids (blocking lipolysis) and use glucose for energy and store excess as triglycerides
This does not happen in the obese state because fat cells are becoming enlarged and desensitized to insulin mediated signaling
Less insulin signaling means that insulin cannot turn off lipolysis in the fed state
What consequence does adipocyte hypertrophy have on WAT biology?
Adipocyte hypertrophy has a negative consequences on WAT biology