MD-3 Influenza Therapeutics
1/43
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
44 Terms
What are the 2x main types of seasonal influenza outbreaks?
- Seasonal Influenza.
- Pandemic/epidemic.
What happens in seasonal influenza outbreaks?
- Most common.
- Variant of previous strain.
- Mutation via antigenic drift.
- Most population will have partial immunity.
- Milder symptoms and fewer mortalities.
What happens in pandemic/epidemic influenza?
- Usually a new strain (eg non-human origin).
- Antigenic shift occurs.
What is antigenic shift?
Sudden and unpredictable mutation
2 or more different virus strains combine to form a new subtype of HA/NA
Accumulation of amino acid mutations that allow H to escape neutralising antibodies
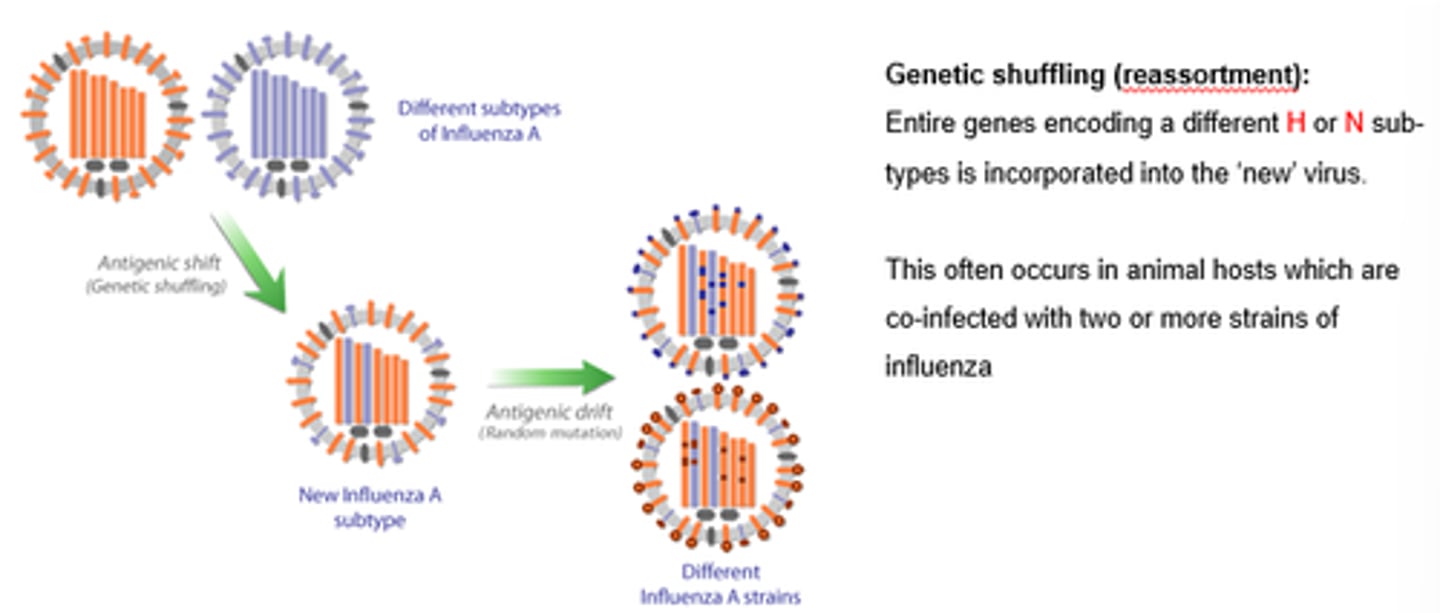
How does antigenic shift occur?
Dif flu strains exchange genetic material, creating a new virus strain.
Often from non-human species.
Accumulation of amino acid mutations that allow H to escape neutralising antibodies
What happens during antigenic shift at cellular level?
- Viral RNAs move to cell surface after replication.
- Entire proteins eg H/N from dif strains are swapped.
- Forms new virus.
What is the impact of antigenic shift on immunity?
- New virus strain completely different.
- No natural protection against it.
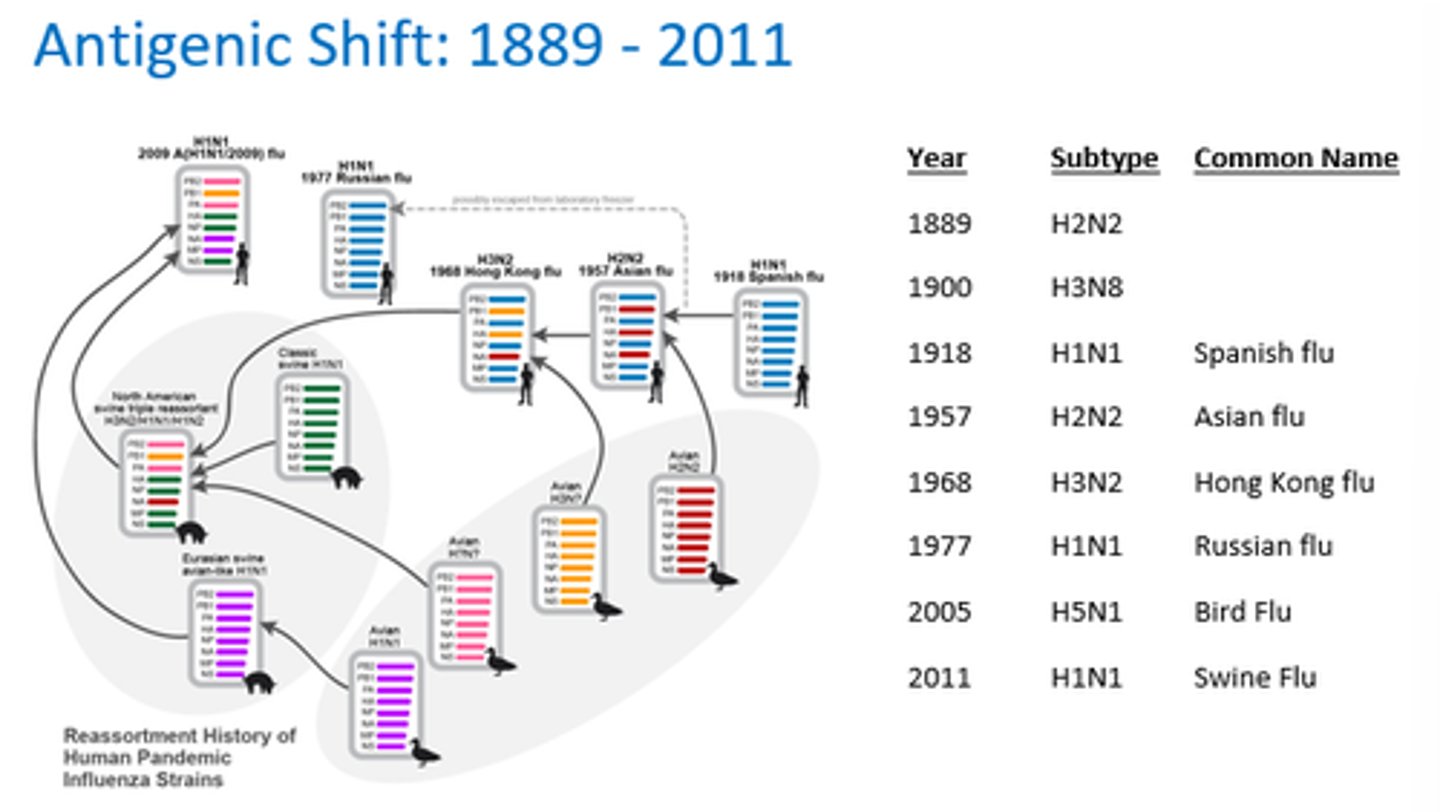
How does antigenic shift differ from antigenic drift?
- Shift swaps entire proteins between strains, creating a new virus.
- Drift involves small mutations in viral genes over time.
What are the 2x types of influenza therapeutics?
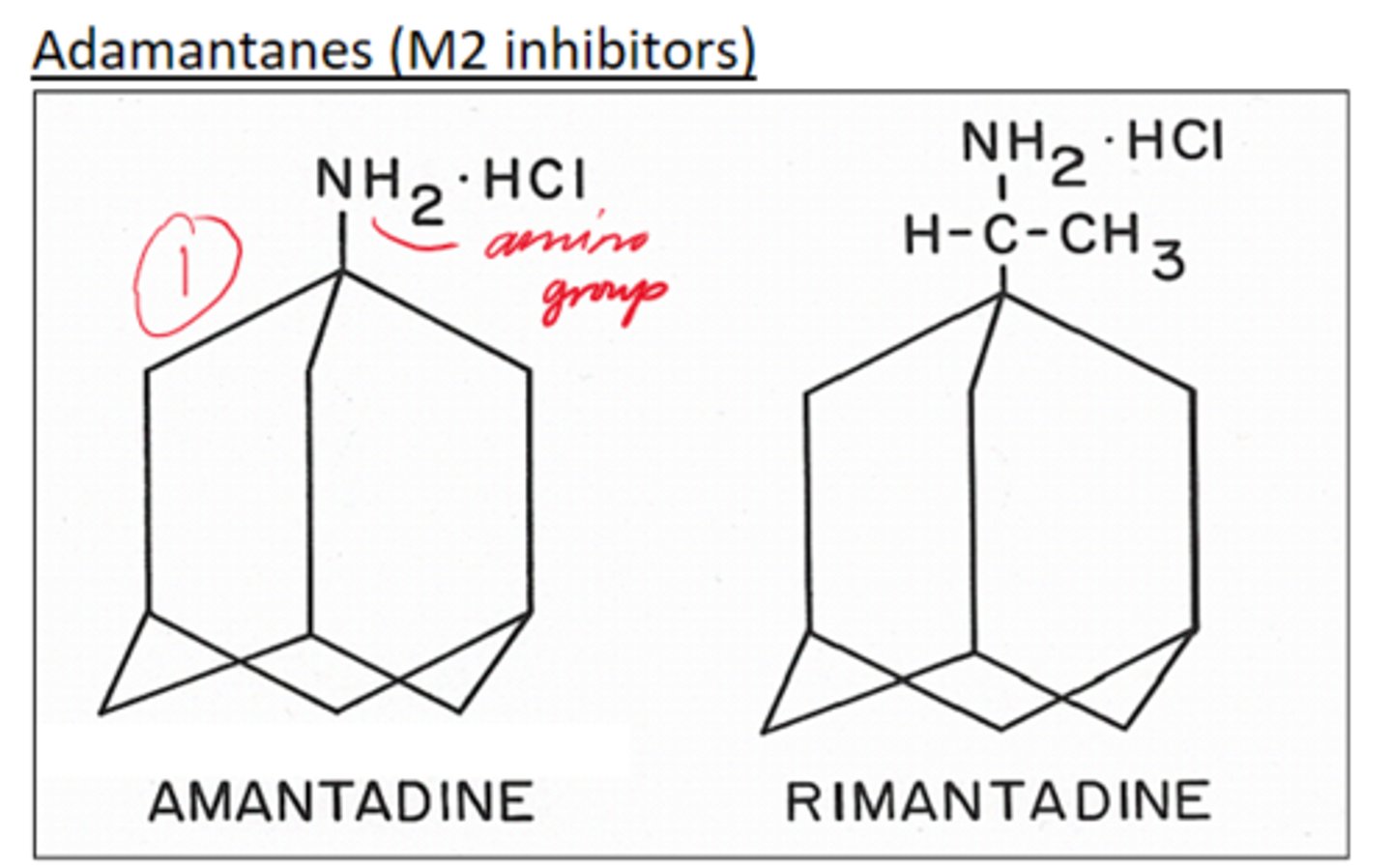
1 - Adamatanes (M2 inhibitors).
2 - Neuraminidase inhibitors.
Give 2x examples of Adamantanes (M2 inhibitors)
Amantadine and Rimantadine.
Give 2x examples of Neuraminidase inhibitors.
Oseltamivir and Zanamivir
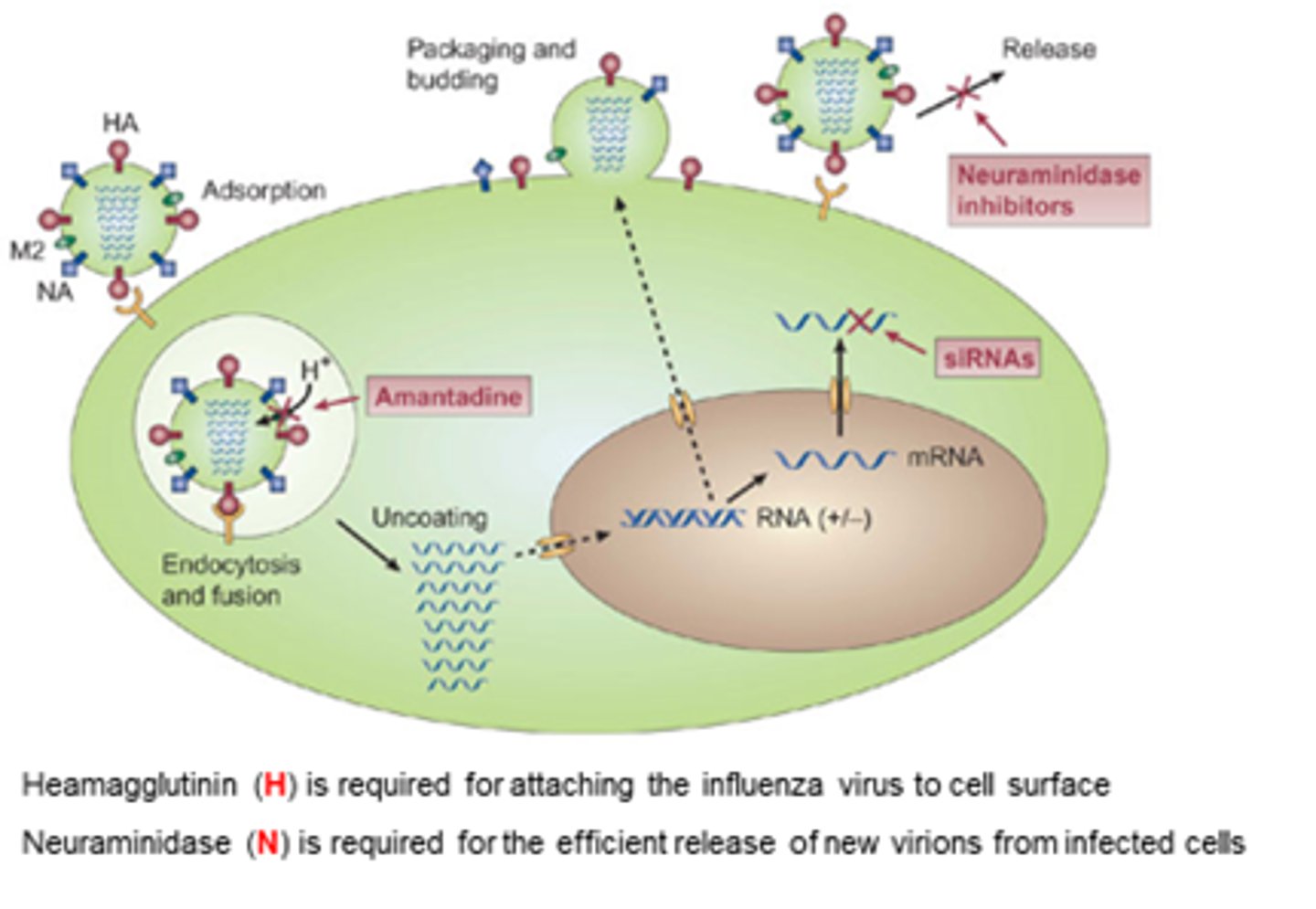
What is the M2 channel responsible for in influenza therapeutics?
- Uncoats particle after it's been endocytosed.
- Allows H+ ions to acidify viral capsid, for uncoating and viral RNA release.
When is the neuraminidase enzyme required?
At the end of replication to chop off the cell surface receptor.
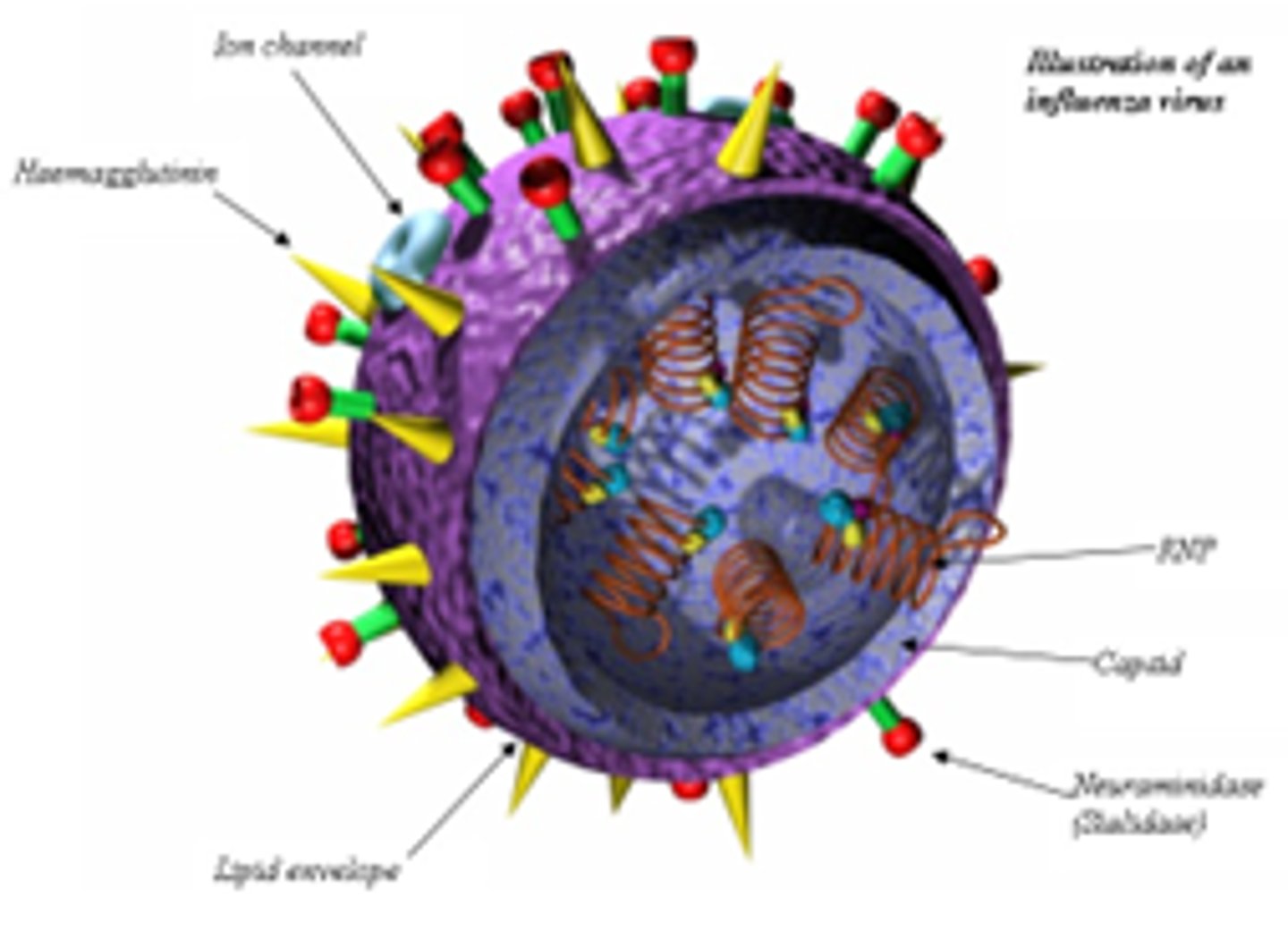
What is haemagglutinin required for?
Attaching the influenza virus to the cell surface.
What is neuraminidase required for?
Efficient release of new virions from infected cells.
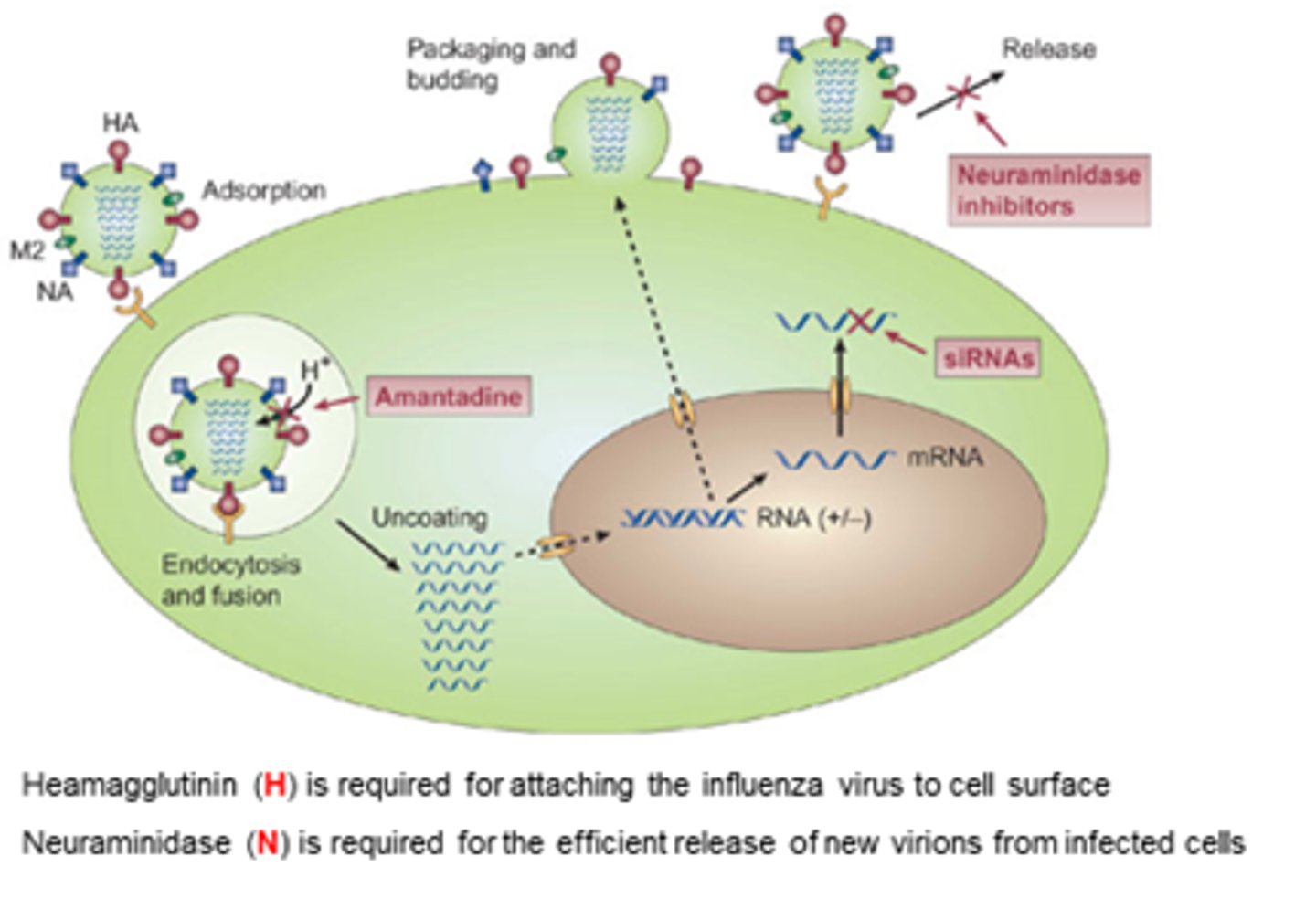
What is the MoA of Adamantanes (M2 inhibitors)?
- Interfere with function of transmembrane domain of the M2 protein of influenza A viruses.
- Blocks ability of H+ ions to get into capsid, decreasing release of viral RNA into infected cell, slowing replication.
- Decreases release of influenza A viral particles into the host cell.
Who is Amantadine used in?
How is it administered?
Adults and children aged >1.
Orally administered.
What is the effect of amatadine in incomplicated influenza?
Reduces duration of illness by 1 day when administered within 2 days of the onset.
What is Amantadine active against?
Influenza A only, not B!
What are some problems with amantadine?
- Rapid resistance development.
- Wide range of side fx and toxicity.
- No benefit against influenza B.
- Can interfere with and block other ion channels on cells.
Which M2 inhibitor (adamantane) is a less toxic alternative to amantadine?
Rimantidine - structurally similar and similar MoA

Adamantanes were no longer recommended as of 2000s.
How did we try and overcome this?
- Tried to make the structure more targeted towards influenza ion channel to reduce off-target fx.
- Reduced toxicity and sfx.
- Rapid resistance problem still!
What are Zanamivir and Oseltamivir?
Competitive neuraminidase inhibitors - target N protein required at end of replication.
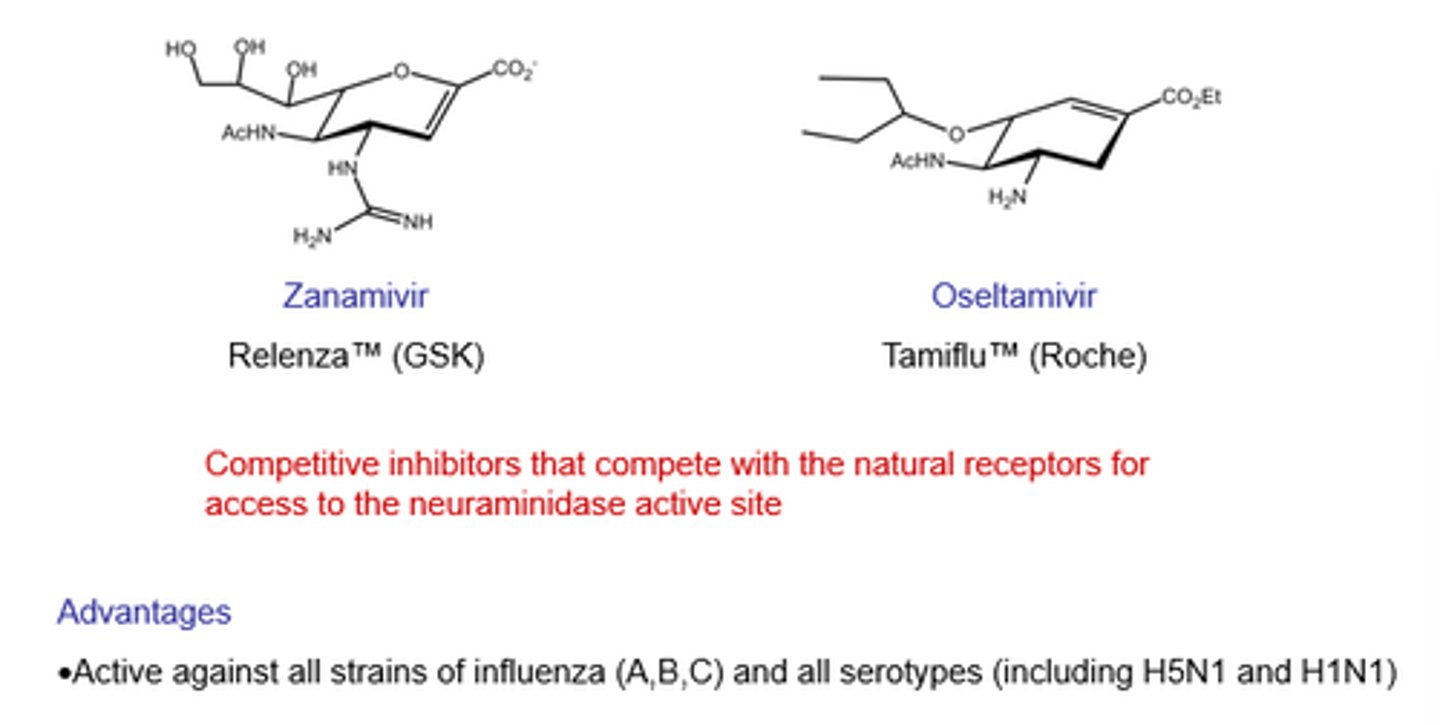
What's the main advantage of using neuraminidase inhibitors?
- Active against all serotypes/all types of neuraminidase!
- Strains don't matter.
What happened in the development of neuraminidase inhibitors?
- We knew MoA of neuraminidase (same for all subtypes).
- Inhibitors tried to mimic the transition state structure of sialic acid.
- Non-specific inhibitors.
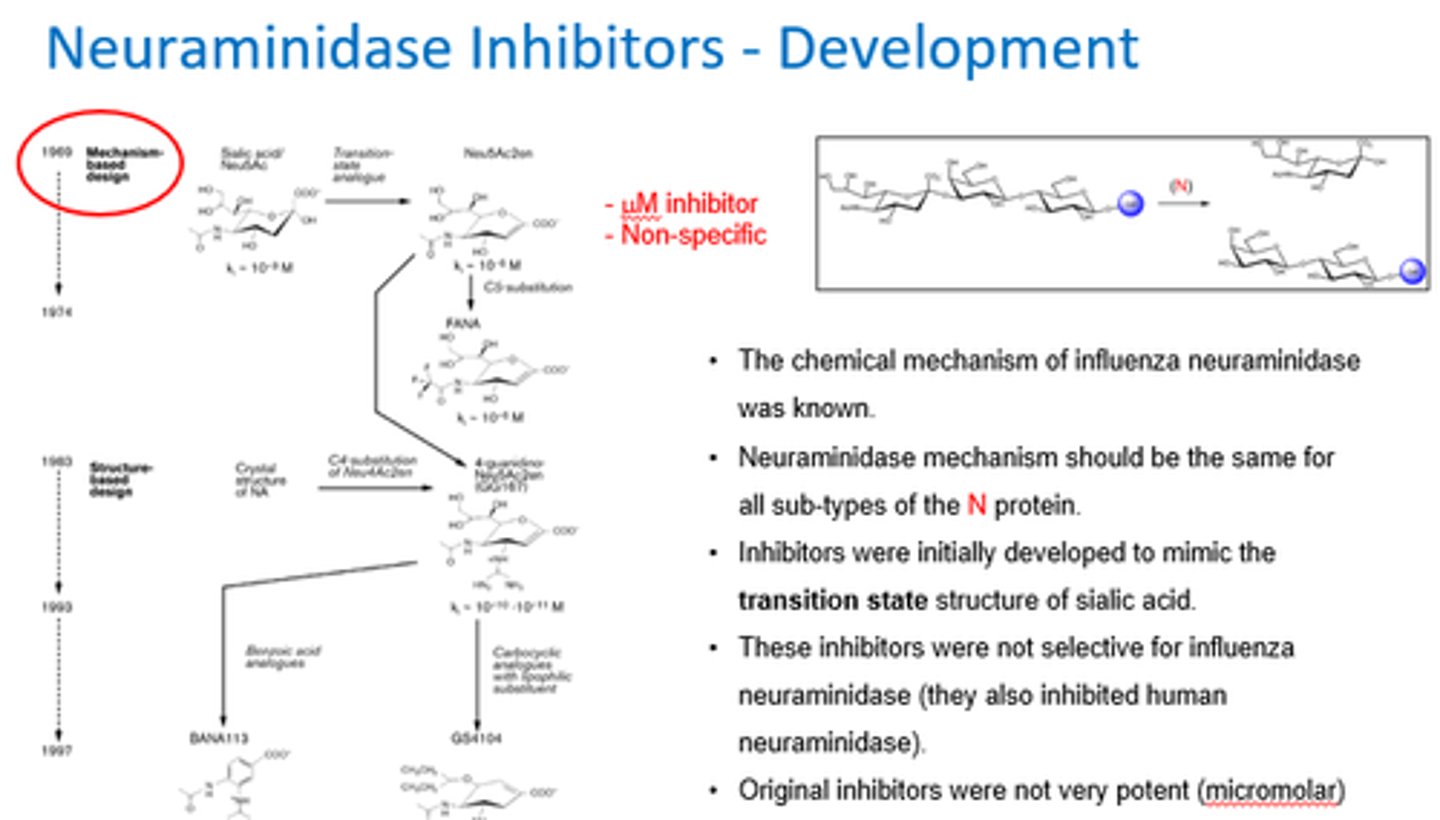
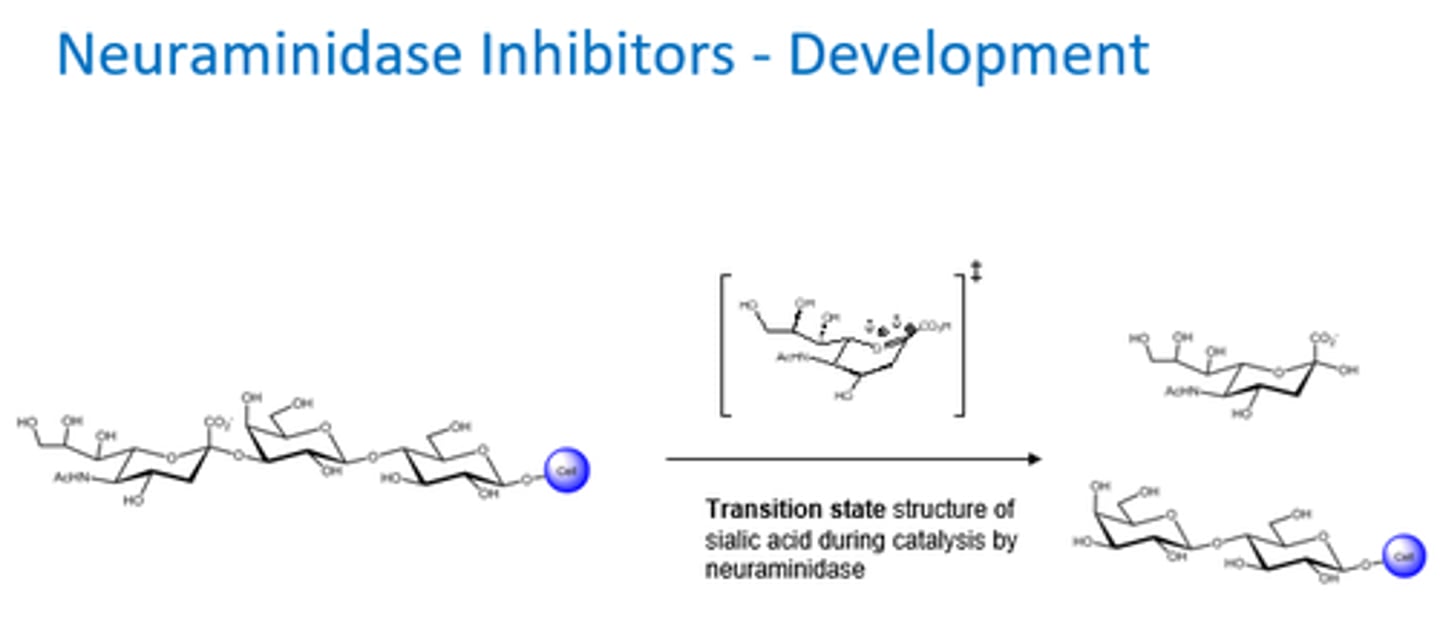
Why is the transition state so important in the development of neuraminidase inhibitors?
What were the key discoveries from the X-ray crystal structure of neuraminidase?
- Large empty pocket of space near OH-4 group of sialic acid unique to influenza nueraminidase.
- Glutamate (acidic AA) formed a H bond with OH-4 group

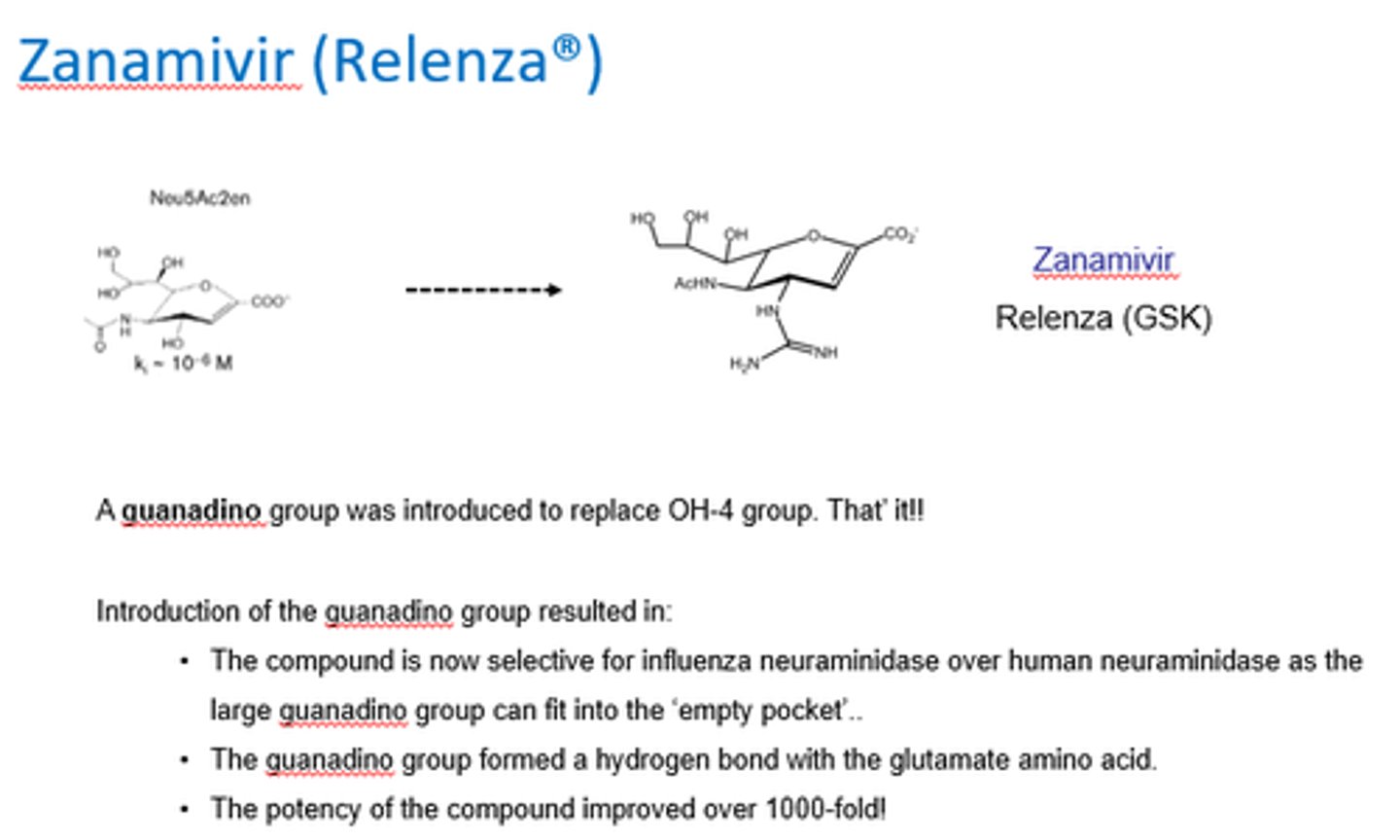
How was Zanamivir (Relenza) created?
A guanadino group was introduced to replace OH-4 group.
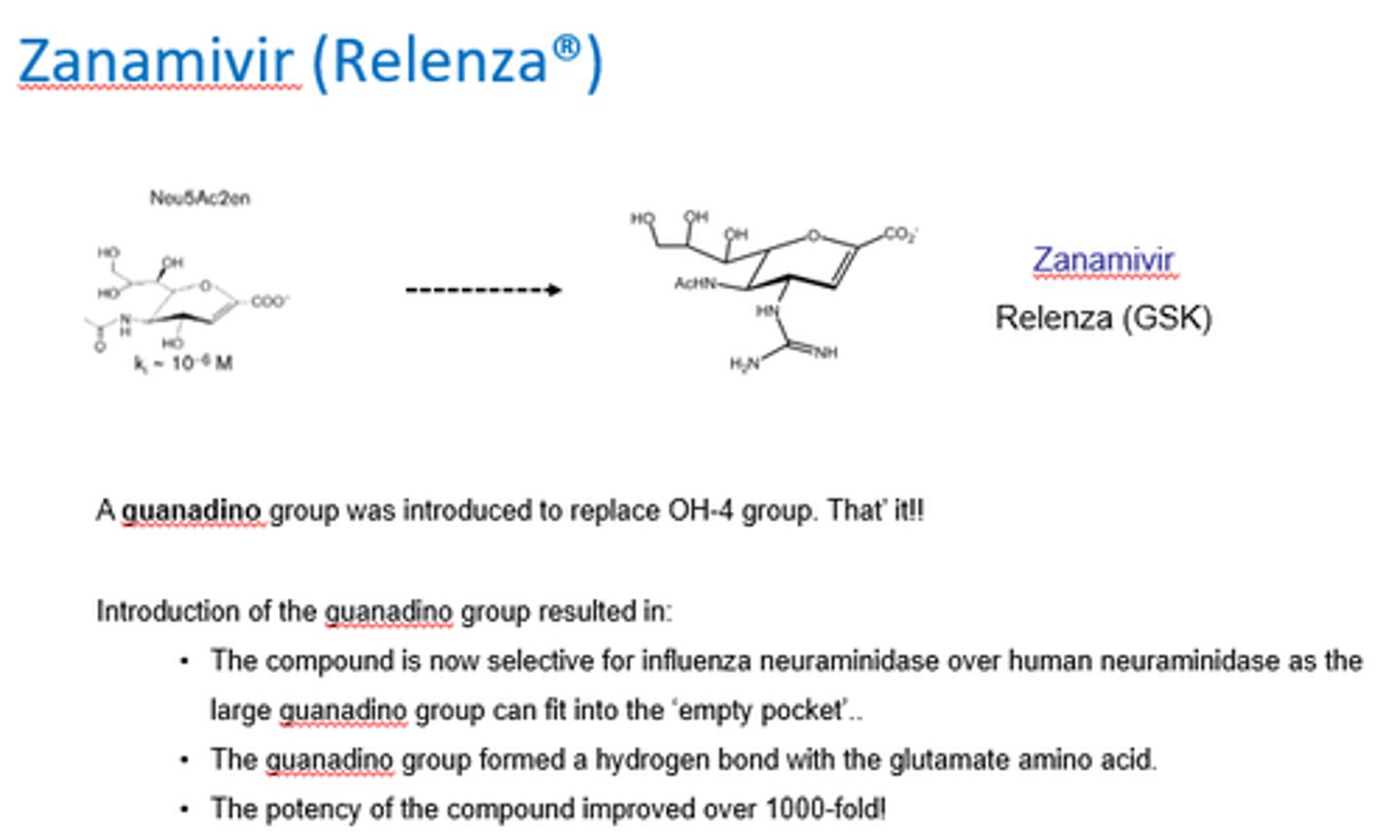
What did the introduction of a guanadino group to replace the OH-4 group do in the creation of Zanamivir?
- Increased selectivity for flu neuraminidase over human.
- Bc large guanadino can fit into empty pocket.
- Guanadino group formed H bond w/glutamate amino acid.
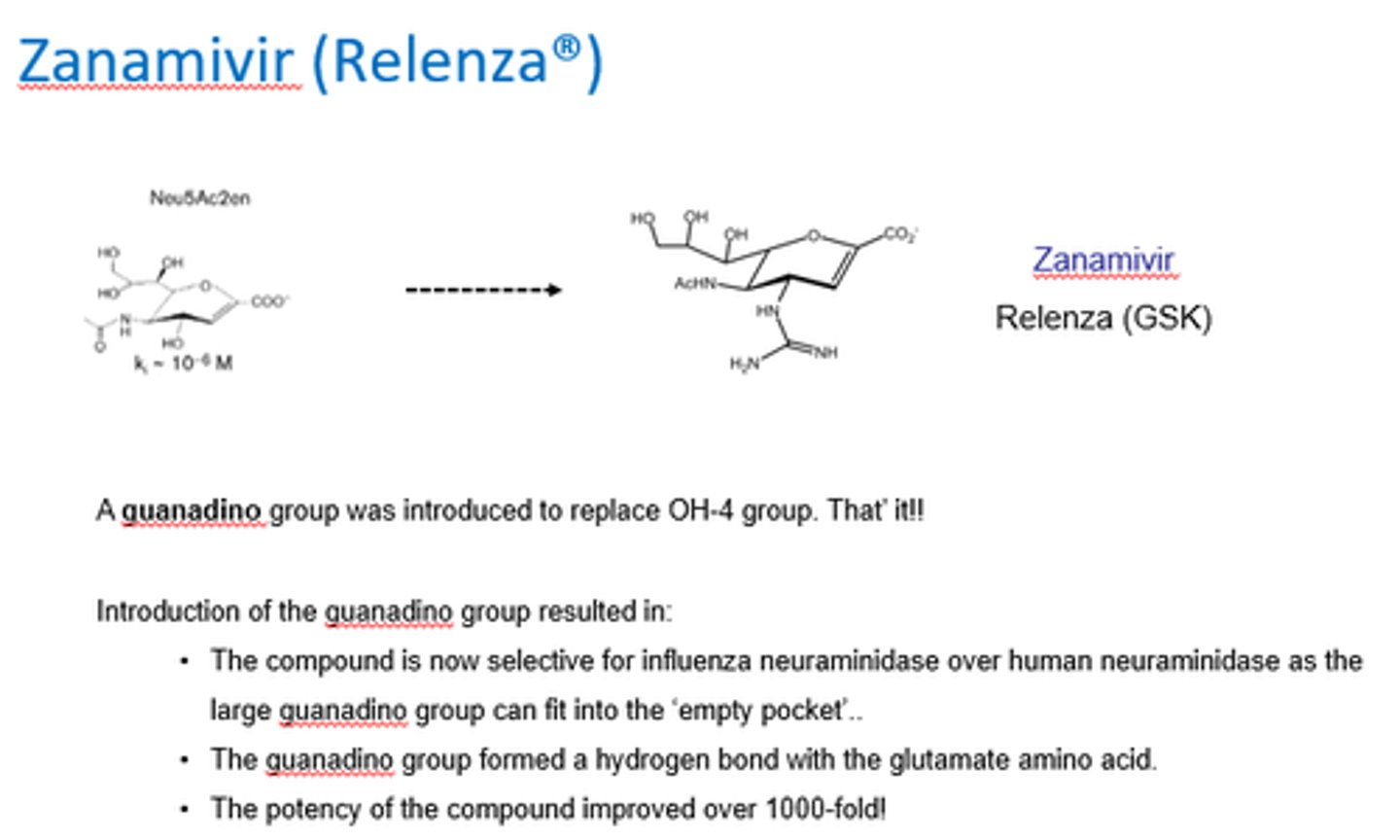
What acid-base property is required in Zanamivir?
Needs to be basic to interact tightly w/acid.
How is Zanamivir delivered?
- Via inhalation of a dry powder.

Why do we deliver Zanamivir as an inhaled formulation?
- Direct to site of infection.
- Excreted unchanged by kidneys - not much metabolism.
- Can't be delivered orally.

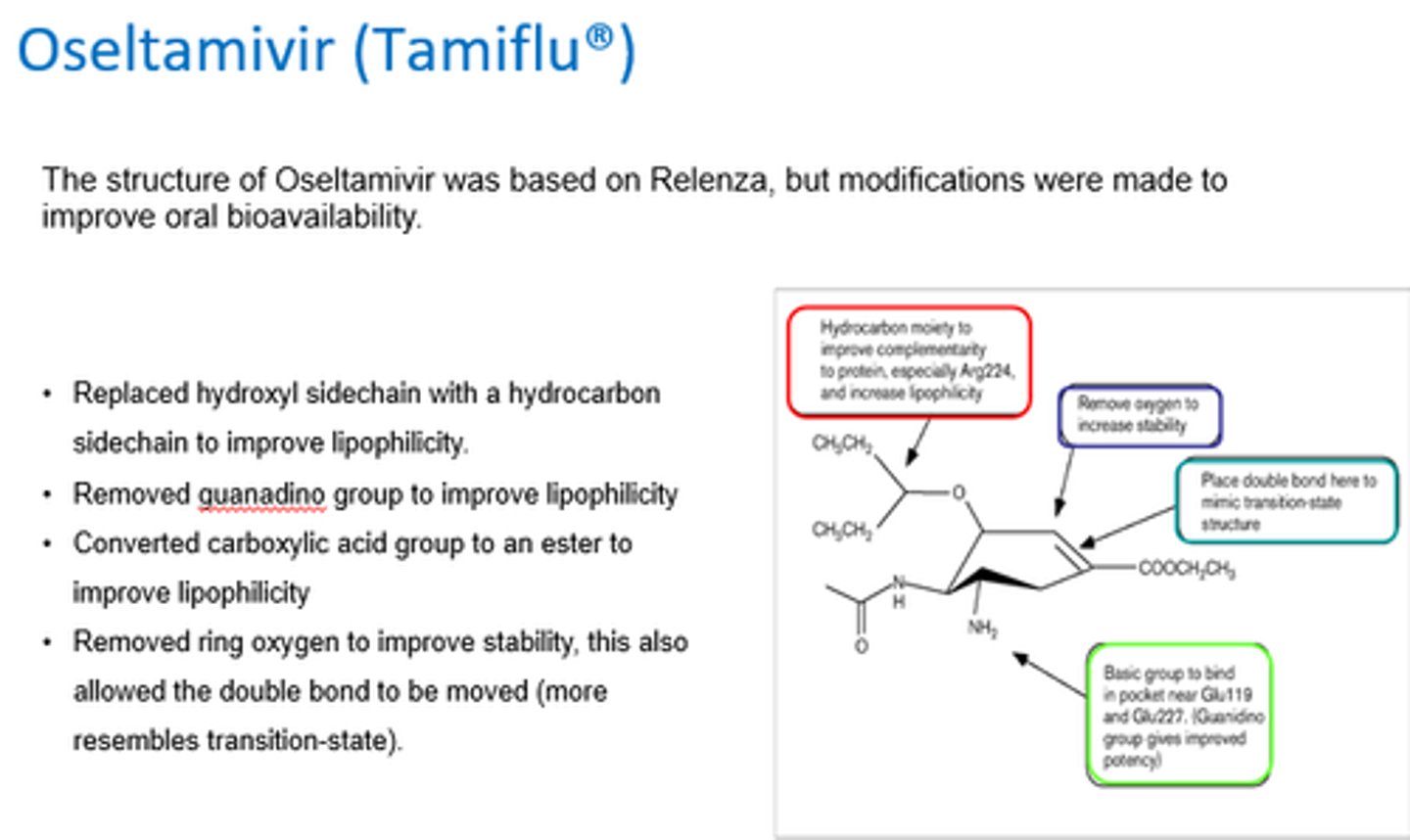
What modifications were made to the structure of zanamivir to create Oseltamivir, to improve lipophilicity?
- Replaced hydroxyl sidechain w/hydrocarbon to improve lipohilicity.
- Removed guanadino group.
- Converted COOH to ester.
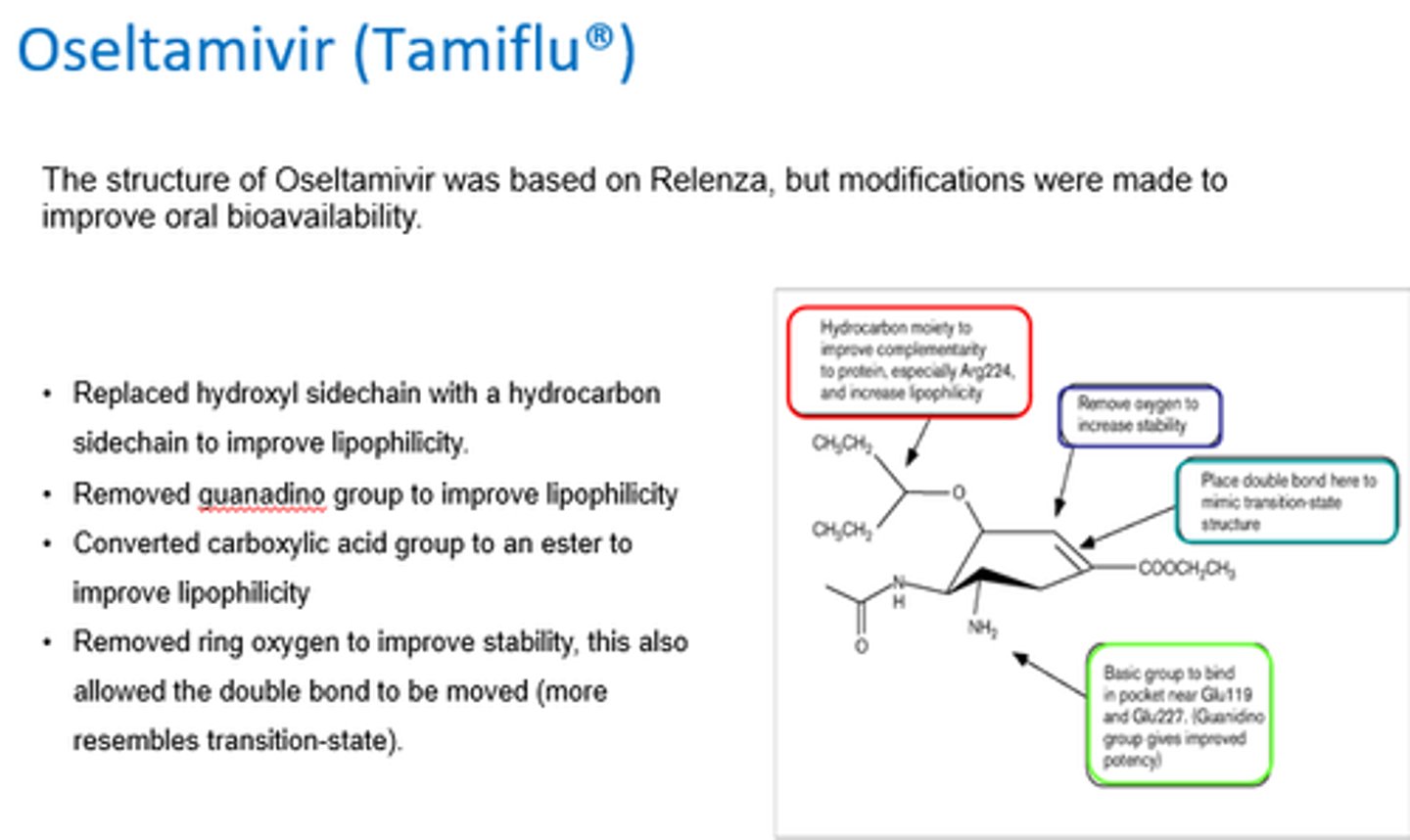
What modifications were made to the structure of zanamivir to create Oseltamivir, to improve stability?
- Removed ring oxygen, allowing double bond to be moved (so it resembles ttransition state).
Why is Zanamivir hard to absorb?
Bc hydrohilic groups give a low oral BA.
What were the key modifications in developing oseltamivir to improve oral BA?
- Increased lipophilicity by replacing hydroxyl and guanadino groups.
- Converted COOH to ester (prodrug) for better absorption.
- Removed oxygen ring for stability and TS resemblance.
How is oseltamivir administered?
Orally as 75mg tablets or syrup for children.
What is the t1/2 of active oseltamivir?
How is it excreted?
8-10 hours.
Excreted unchanged via kidneys
What key structural modifications improved oseltamivir's properties?
- Hydroxy replaced with hydrocarbon → improved lipophilicity.
- Guanidino replaced with amine → better solubility.
- Carboxylic acid converted to an ester → prodrug formation.
- Ring oxygen removed → increased stability
How is best to manage influenza - drugs or vaccines?
Vaccines - protection, but need to be produced in advance.
- Specific vaccine required for each serotype of influenza.
Drugs - no lasting protection.
- Active against all strains + serotypes bc act against neuraminidase active site.
- Can be stored/stockpiled.
- Resistance becoming more of a problem.
How is influenza managed seasonally?
- Vaccines!
- New strain normally derived from previous strain.
- So most population will have partial immunity.
- But can't stop antigenic shift in animals!

How is influenza managed in a pandemic?
- Not possible to have vaccine prepared against strain.
- Neuraminidase inhibitors 1st line.
- Administered more widely for prophylaxis to reduce spread.

What were the key discoveries
Why is the transition state so important in the development of neuraminidase inhibitors?
- Transition state is highest energy species in this reaction.
- Enzymes bind to TS and lower its energy.
- So Neuraminidase inhibitors needed to target TS structure!