AP Human Geo Unit 2 Study Guide
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/73
Earn XP
Last updated 3:24 AM on 1/31/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
74 Terms
1
New cards
Five major population agglomerations
* East Asia
* South Asia
* Europe
* Southeast Asia
* Eastern part of North America
* South Asia
* Europe
* Southeast Asia
* Eastern part of North America
2
New cards
Ecumene
The portions of Earth’s surface occupied by permanent human settlement
3
New cards
Arithmetic density
People/total land area
* aka population density
* EX: 84.5/ sq miles OR 85.4 mi^2
* Shares a little about population distribution, but doesn’t indicate where in the total area they live
* aka population density
* EX: 84.5/ sq miles OR 85.4 mi^2
* Shares a little about population distribution, but doesn’t indicate where in the total area they live
4
New cards
Physiological density
People/arable land
* measures the pressure on agriculture land in a country
* A small percentage of a region’s land is capable of growing crops
* More useful to determine a regions carrying capacity
* measures the pressure on agriculture land in a country
* A small percentage of a region’s land is capable of growing crops
* More useful to determine a regions carrying capacity
5
New cards
Agricultural density
Farmer/arable land
* measures of relationship between population and resources and the level of a country’s development
* Gives indication of the efficency of the regions farmers
* Developed countries have a low agricultural population density because the farmers have more tech to produce large amounts of food with low workers
* measures of relationship between population and resources and the level of a country’s development
* Gives indication of the efficency of the regions farmers
* Developed countries have a low agricultural population density because the farmers have more tech to produce large amounts of food with low workers
6
New cards
Carrying capacity
the population a region can support without signification environmental deterioration
* can change overtime
* EX: technological changes in agriculture can increase this
* can change overtime
* EX: technological changes in agriculture can increase this
7
New cards
Age structure
Percentage of the population (or number of people of each sex) at each age level in a population
* youthful, aging, maturing, and declining
* youthful, aging, maturing, and declining
8
New cards
Sex ratio
The number of males per 100 females in the population
* in more developed countries there’s more women because they’re expected to live longer
* in more developed countries there’s more women because they’re expected to live longer
9
New cards
Population pyramid
Age-sex composition graph based on only gender and age data that shows information on birthrates, death relates, how long people live on average, and economic development
* can show past events (war, baby booms, baby busts, etc)
* can show past events (war, baby booms, baby busts, etc)
10
New cards
Demographic momentum
the tendency for growing population to continue growing after a fertility decline because of their young age distribution
* important because this happens once a country moves to a different stage in the dtm
* important because this happens once a country moves to a different stage in the dtm
11
New cards
Crude birth rate
The number of live births per year for each 1000 people
* education and healthcare, and contraceptives can cause this to decline
* education and healthcare, and contraceptives can cause this to decline
12
New cards
Total fertility rate
the average number of children who would be born per woman of that group in a country, assuming every woman lived through her childbearing years
* reflects cultural norms
* Changes with social, economic, and political roles
\
* reflects cultural norms
* Changes with social, economic, and political roles
\
13
New cards
Infant mortality rate
The number of children who die before their 1st birthday
* one of the most important factors that affects increasing life to drop
* one of the most important factors that affects increasing life to drop
14
New cards
Crude death rate
Number of deaths of an area per 1000 population
15
New cards
life expectancy
The average number of years people live
* commonly expressed from the time of a person’s birth
* Can change with current social, economic and medical conditions
* commonly expressed from the time of a person’s birth
* Can change with current social, economic and medical conditions
16
New cards
Replacement fertility
the total fertility rate at which women would have only enough children to replace themselves and their partner
* rate is mostly 2.1 children
* rate is mostly 2.1 children
17
New cards
Zero population growth
A decline of the total fertility rate to the point where the natural increase rate equals zero
* more developed countries are either at or near zero population growth
* more developed countries are either at or near zero population growth
18
New cards
Doubling time
The time it takes a population to double in size can be estimated using the rule of 70/72
19
New cards
Demographic equation
* Future population = Current population + (number of births – number of deaths) + (number of immigrants – number of emigrants)
* Used to describe the future population of a region of any scale
* Used to describe the future population of a region of any scale
20
New cards
Net migration
The difference between the level of immigration and the level of emigration
* includes citizens and non citizens
* includes citizens and non citizens
21
New cards
DTM stage 1
High birth rate and death rate, low population growth
* EX: no countries today
* EX: no countries today
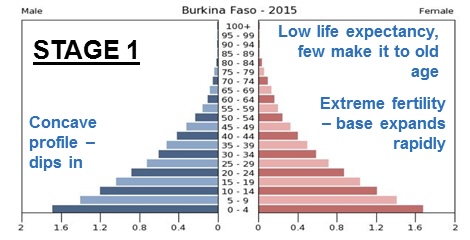
22
New cards
DTM stage 2
* high birth rate, falling death rates (medical revolution)
* high population growth
* high population growth
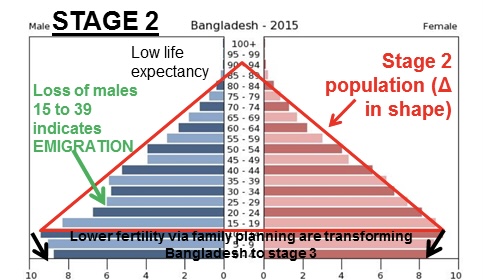
23
New cards
DTM stage 3
* moderate growth
* declining birth rate (education and healthcare) and a more slowly declining death rate
* urbanized and more industrialized families have less children
* EX: Mexico, Turkey, Indonesia
* declining birth rate (education and healthcare) and a more slowly declining death rate
* urbanized and more industrialized families have less children
* EX: Mexico, Turkey, Indonesia
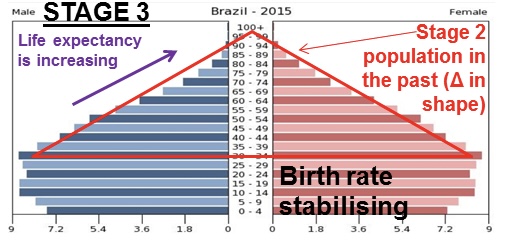
24
New cards
DTM STage 4
* typically the stationary population pyramid and indicates a population that is not significantly growing or shrinking
* steady/low birth rate
* low death rate -> high life expectancy
* EX: United States, China
* steady/low birth rate
* low death rate -> high life expectancy
* EX: United States, China
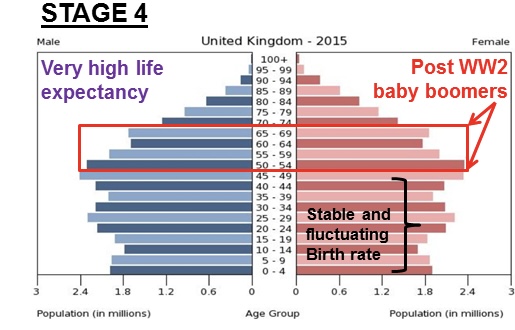
25
New cards
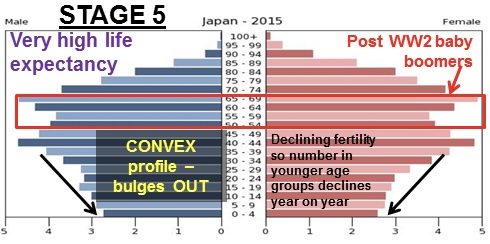
DTM Stage 5
* negative growth
* decreasing birth rate
* death rate exceeds birth rates
* EX: Japan, Germany
* decreasing birth rate
* death rate exceeds birth rates
* EX: Japan, Germany
26
New cards
Epidemiological transition model
* created by Abdel Omran to explain the changing death rates and more common causes of death within societies
* Stage 1 - FAmine and Disease
* Stage 2 - Receding Pandemics
* Stage 3 - Degenerative and Human-Created Diseases
* Stage 4 - Delayed Degenerative Diseases
* Stage 5 - Reemergence of Infectious and Parasitic Diseases
* Stage 1 - FAmine and Disease
* Stage 2 - Receding Pandemics
* Stage 3 - Degenerative and Human-Created Diseases
* Stage 4 - Delayed Degenerative Diseases
* Stage 5 - Reemergence of Infectious and Parasitic Diseases
27
New cards
Thomas Malthus’ theory
\n the world's population was growing faster than the rate of food production, and as a result, mass starvation would occur
* people need to exercise “moral restraint”
* The poor shouldn’t receive social services
* No more public school
* people need to exercise “moral restraint”
* The poor shouldn’t receive social services
* No more public school
28
New cards
Thomas Malthus theory carrying capacity
* more humans than available resources
* the human population will outgrow the carrying capacity therefore we need to stop population growth
* the human population will outgrow the carrying capacity therefore we need to stop population growth
29
New cards
Sustainability
The idea that socially responsible companies will outperform their peers by focusing on the world’s social problems
* the saving of resources for future generation to allow them to live at the same or higher standard of living than the population today
* the saving of resources for future generation to allow them to live at the same or higher standard of living than the population today
30
New cards
Overpopulation
\n the number of people in an area that exceeds the capacity of the environment to support life at a decent standard of living
31
New cards
Preventive checks
measures taken by humans to reduce shortages
* could be reducing the population through better financial planning and possibly anti-natalist policies
* could be reducing waste through better recycling
* could be reducing the population through better financial planning and possibly anti-natalist policies
* could be reducing waste through better recycling
32
New cards
Positive checks
Events that increase deaths
* the effects of war, disease and famine in controlling excess population growth
* the effects of war, disease and famine in controlling excess population growth
33
New cards
\n Esther Boserup’s theory of agricultural intensification (a.k.a. “Cornucopian Theory”)
* as population would increase, there would be more food production because there would be more pressure on the agricultural system
* rejects the idea that population growth is problematic because Earth has finite resources and carrying capacity
* rejects the idea that population growth is problematic because Earth has finite resources and carrying capacity
34
New cards
Neo- Malthusian theories
* argue that population growth is a serious problem and is a greater threat for the future
* believe that continued population growth will lead to the depletion of nonrenewable resources such as petroleum and metals, pollution
* believe that continued population growth will lead to the depletion of nonrenewable resources such as petroleum and metals, pollution
35
New cards
Anti-natalist policy
\n policies that attempt to decrease the number of births in a country and are often used by developing countries
* Ex: China’s one child policy
* Ex: China’s one child policy
36
New cards
Pro-natalist policy
Programs designed to increase the fertility rate
* used to keep the economy vibrant
* EX: provided pto for mothers, free childcare, and family discounts on governmental services
* used to keep the economy vibrant
* EX: provided pto for mothers, free childcare, and family discounts on governmental services
37
New cards
\n International Conference on Population and Development (ICPD) (example to know and cite)
\
\
a conference aimed at looking for a beyond solution for slowing population growth that was not family planning
* The goals of the ICPD were to advance human rights and individual dignity by improving the quality of life for everyone. They wanted to improve sexual and reproductive health, women’s empowerment, and an end to gender violence and traditional practices. They said that if we invest in women and you, the sustainability and population dynamics will be impacted
* The goals of the ICPD were to advance human rights and individual dignity by improving the quality of life for everyone. They wanted to improve sexual and reproductive health, women’s empowerment, and an end to gender violence and traditional practices. They said that if we invest in women and you, the sustainability and population dynamics will be impacted
38
New cards
Dependency ratio
* dependent population/ potential workforce (15-65)
39
New cards
Migration
\n the Permanent or semiPermanent relocation of people from one place to another
40
New cards
Voluntary migration
* a movement made by choice
* combines a decision to move away from someplace with a decision to move toward someplace else
* combines a decision to move away from someplace with a decision to move toward someplace else
41
New cards
Immigrant
A person who migrates across an international border with the intention of staying permanently
42
New cards
Emigrant
* from the perspective of the country the person leaving, they are considered this
43
New cards
Net migration
* immigration - emigration
44
New cards
Push factor
\n negative circumstances, events, or conditions present where they live that compels a person to leave
EX: political instability, wars, poverty, natural diasaters
EX: political instability, wars, poverty, natural diasaters
45
New cards
46
New cards
Pull factor
\n a destination based on its positive conditions and circumstances that migrants are drawn to after they leave their old location
Ex: job opportunities, closer to relatives, better climate, inclusive culture
Ex: job opportunities, closer to relatives, better climate, inclusive culture
47
New cards
Source region
Location where an air mass forms
* must be a relatively large and uniform area
* 4 source regions : polar, arctic, equatorial, and tropical
* must be a relatively large and uniform area
* 4 source regions : polar, arctic, equatorial, and tropical
48
New cards
Destination region
\n the area of destination a migrant is trying to reach
49
New cards
Intervening opportunity
* a nearer opportunity that greatly diminishes the attractiveness of sites farther away
* EX: a migrant might find a job along the way
* EX: a migrant might find a job along the way
50
New cards
Intervening obstacle
\n barriers that make reaching their desired destination more difficult
51
New cards
\n Ravenstein’s “Laws of Migration”
* short Distances: most migrants only travel a short distance (distance decay)
* Urban Areas: migrants traveling long distances usually settle in large urban areas
* Multiple Steps: most migration occurs through step migration (a process in which migrants reach their eventual destination through a series of smaller moves
* Rural to Urban: Most migration in history has been from rural agricultural areas to urban city areas
* Counter Migration: each migration flow produces a movement in the opposite direction
* EX: while migrants from Mexico came to USA, some retired US citizens migrated to Mexico for weather
* Youth: most migrants are younger adults between 20-45
* they’re more likely to leave because they don’t have as much to hold onto
* Gender Patterns: most international migrants are young males, while more internal migrants are female
* women who live in traditional societies move in with their husbands
* Urban Areas: migrants traveling long distances usually settle in large urban areas
* Multiple Steps: most migration occurs through step migration (a process in which migrants reach their eventual destination through a series of smaller moves
* Rural to Urban: Most migration in history has been from rural agricultural areas to urban city areas
* Counter Migration: each migration flow produces a movement in the opposite direction
* EX: while migrants from Mexico came to USA, some retired US citizens migrated to Mexico for weather
* Youth: most migrants are younger adults between 20-45
* they’re more likely to leave because they don’t have as much to hold onto
* Gender Patterns: most international migrants are young males, while more internal migrants are female
* women who live in traditional societies move in with their husbands
52
New cards
Migration selectivity
* Age - younger people 18-30 are most likely to move
* education - people with a higher education are most likely to make long distance moves
* kinship & friends- people will follow family members that have moved to another area for a better life - chain migration helped create cultural neighborhoods
* education - people with a higher education are most likely to make long distance moves
* kinship & friends- people will follow family members that have moved to another area for a better life - chain migration helped create cultural neighborhoods
53
New cards
African slave trade
\n largest **forced migration** in history where 12.5 million Africans were captured, enslaved and forcibly moved from their homes in African to North America, the Caribbean, the Middle East, and South America
54
New cards
Forced migration
Slavery and events that produce idp, refugees, and asylum seekers
55
New cards
Voluntary migration
* transnational, transhumance, internal, chain, step, guest worker, and rural-to-urban
56
New cards
Refugee
when migrants flee quickly in order to stay alive and cross international border
57
New cards
Asylum seeker
\n political refugees who apply for asylum (protection) when they arrive in their country of destination
58
New cards
Internally displaced person
\n when migrants flee quickly to stay alive and can’t bring many items with them but they only move to another part of the same country
59
New cards
Chain migration
\n When people migrate to and settle in a new country, they often decide to locate in a city or community where others from their home country, family members, friends, or those from their culture group have previously settled
60
New cards
Step migration
Where people make a series of intermediate moves
61
New cards
Transhumance
* process of herders moving with their animals to different pastures during different season
* mountainous regions, herders move their animals to higher areas in the summer and lower elevations during the winter
* still takes place in Italy, Greece, and Turkey
* mountainous regions, herders move their animals to higher areas in the summer and lower elevations during the winter
* still takes place in Italy, Greece, and Turkey
62
New cards
Nomadism
\n a way of life, forced by a scarcity of resources in which groups of people continually migrate to find pastures and water
63
New cards
Guest worker
\n workers who migrate to the more developed countries of Northern and Western Europe, usually from Southern or Eastern Europe or from North America in search of higher-paying jobs
64
New cards
International migration
people move between countries, even close surrounding ones
65
New cards
Internal migration
people move to a different area of the same country
66
New cards
Inter-regional migration
Movement from one region to a different one
67
New cards
Intra-regional migration
Movement within one region
68
New cards
Rural-to-urban migration
\n when people leave villages and small towns every year for opportunities in the cities and more densely settled areas
69
New cards
Remittances
\n money sent to immigrants families and friends in the country they left
70
New cards
Diaspora
A dispersion of people from their homeland
71
New cards
Brain drain
\n brain drain- when migration out of a country is made up of many highly skilled people
72
New cards
Undocumented immigrant
People who enter a country without proper documents
73
New cards
Naturalization
The legal process by which citizens of one country become citizens of another
74
New cards
Visa program
\n an endorsement on a passport indicating that the holder is allowed to enter, leave, or stay for a specified period of time in a country