1404- Biochem- catabolism 1
1/36
Earn XP
Description and Tags
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=0OMNyVzLnVc
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
37 Terms
What is catabolism?
The sequence of enzyme catalyzed reactions by which relatively large molecules in living cells are broken down , or degraded.
General pathway for Protein breakdown
Protein → Amino acid → ammonia (excreted as urea ) + carbon skeleton used ( recycled in varyinging biosynthetic pathways
Overview of processes in the breakdown of protein
Transamination → deamination → urea cycle
How are amino acid building blocks generated
By the digestion of proteins in the intestine
Degradation of proteins in the cell
Primary uses of amino acids
Building blocks for protein and peptide synthesis
As a source of nitrogen for the synthesis of other amino acids and other nitrogenous compounds.
What happens to excess nitrogen
Cannot be stored.
Used as metabolic fuel.
converted into urea while the carbon skeleton transforms into a metabolic intermediate via the citrate acid cycle.
Types of metabolic intermediates
Glucogenic
ketogenic
Glucogenic metabolic intermediates
Degraded to alpha ketoglutarate, succinyl- CoA, fumerate or oxaloacetate.
Glucose precursors
Ketogenic Intermediates
Degraded into acetyl- CoA or acetoacetate
Can be converted into fatty acids or ketone bodies.
Glucogenic non- essential amino acids
Alanine
Argine
Asparagine
Glucogenic essential amino acids
Histidine, Methione, Threonine, Valine
Glucogenic and ketogenic non essential amino acid
Tyrosine
Glucogenic and ketogenic essential amino acid
Isoleucine, Phenylalanine, Tryptophan
Ketogenic essential amino acids
Lysine and Leucine
Transamination
Combines reversible amination and deamination
Mediates redistribution of amino acid groups
Does not occur at the alpha position of an amino group
Which amino acids undergo transamination?
All except lysine, threonine, proline and hydroxyproline
Role of alpha keto-glutarate/L- glutarate in transaminase reactions
Acts as an amino group donor/ acceptor pair
Transamination and essential amino acids
Usually unidirectional b/c the body can’t synthesize the equivalent alpha keto acid
Enzymes and substrate involved in transamination
Pyroxidal phosphate
Another amino acid/alpha-keto acid pair
What is the function of glutamate and Glutamine for most amino acids?
They act as donors
Why does glutamate acts like a donor for most amino groups?
This is because the alpha amino group of most amino acids originate from glutamate.
What is the importance of glutamine in amino acids?
They contribute to side chain N in the biosynthesis of tryptophan and histidine.
Carries NH3 from peripheral tissues to the kidneys, where amide N is hydrolysed by the enzyme glutaminase; this process regenerates glutamate and free ammonium ion, which is excreted in the urine.
What are aminotransferases
enzymes that catalyze the transfer of amino groups from amino acids to alpha-keto acids derived from pyroxidoxal phosphate.
Location of pyroxidoxal phosphate
Found at the active site of the ‘resting’ aminotransferase, covalently attached to alpha amino acid group of a lysine residue of the enzyme.
How is pyroxidal phosphate linked to the enzyme?
By formation of a schiff base between its aldehyde group and the e amino group of a specific lysyl residue at the active site and held covalently through its positive charged nitrogen atom and the negatively charged phosphate group.
Mechanism of transamination
'Ping pong’ double displacement
Enzymes involved in the conversion of inorganic ammonium into alpha amino nitrogen of amino acids
include glutamate dehydrogenase, glutamine synthases and aminotransferases.
Nitrogen atom conversion to free ammonium ion
The nitrogen atom that is transfered to alpha keto- glutamate in the transamination reaction via oxidative deamination.
What is the oxidative deamination process catalysed by?
glutamate dehydrogenase, which converts glutamate to alpha-ketoglutarate and ammonia.
How does the oxidative deamination reaction proceed?
by the removal of an amino group from glutamate via dehydrogenation of the C-N bond, followed by hydrolysis, resulting of the Schiff base producing alpha-ketoglutarate and releasing ammonia.

Which product does the oxidative deamination equilibrium favors and why?
It favors the formation of alpha-ketoglutarate→ glutamate due to the release of ammonia, which drives the reaction forward.
Where is glutamate dehydrogenase located?
in the mitochondrial matrix of cells.
Why is glutamate dehydrogenase located in the mitochondria of cells?
It sequesters free amonnia, which is toxic
What is glutamate dehydrogenase activity regulated by in most vertebrates?
availability of substrates like alpha-ketoglutarate and ammonia
allosteric inhibitors - GTP and ATP
Allosteric activators GDP and ADP
What are the two principle forms in which nitrogen can be transported?
Alanine via the alanine cycle
Glutamine
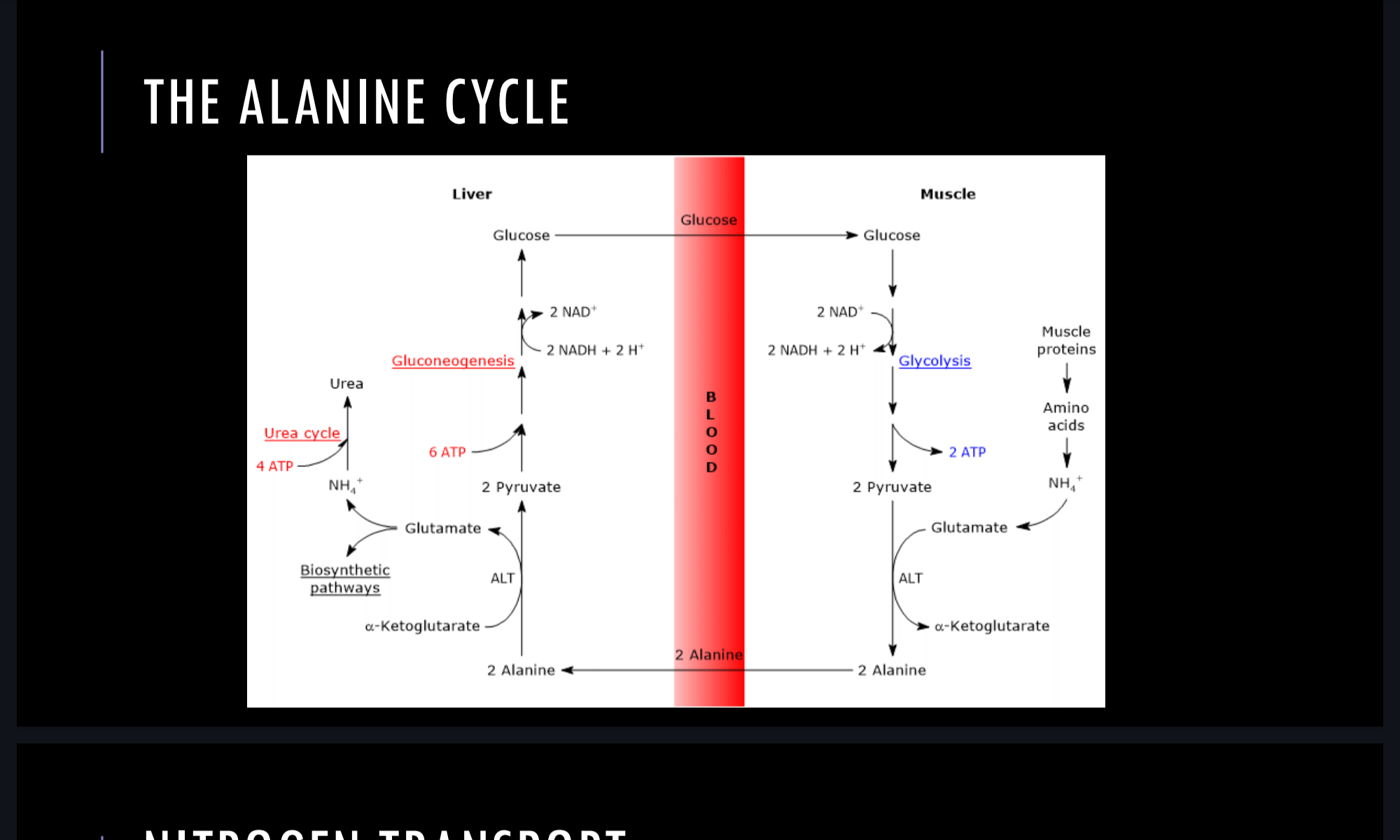
The alanine cycle
Glutamate formed by transamination reactions→the nitrogen is transferred to pyruvate to form alanine→ alanine is transported by blood to the liver for urea cycle.
Liver takes up the alanine→ converts back to pyruvate via transamination.
The pyruvate can be used for gluconeogenesis and the amino acid group appear as urea.
How is nitrogen transported as glutamine
through the action of glutamine synthetase. This synthesizes glutamine from NH4+ and glutamate in an ATP-dependent reaction.This allows for safe transport of ammonia in the bloodstream to the liver, where it can enter the urea cycle.
The Ns of the glutamine can be converted into urea via urea cycle