Plants & Society Exam III
0.0(0)
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/186
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
187 Terms
1
New cards
What is genetics?
The study of inheritance
2
New cards
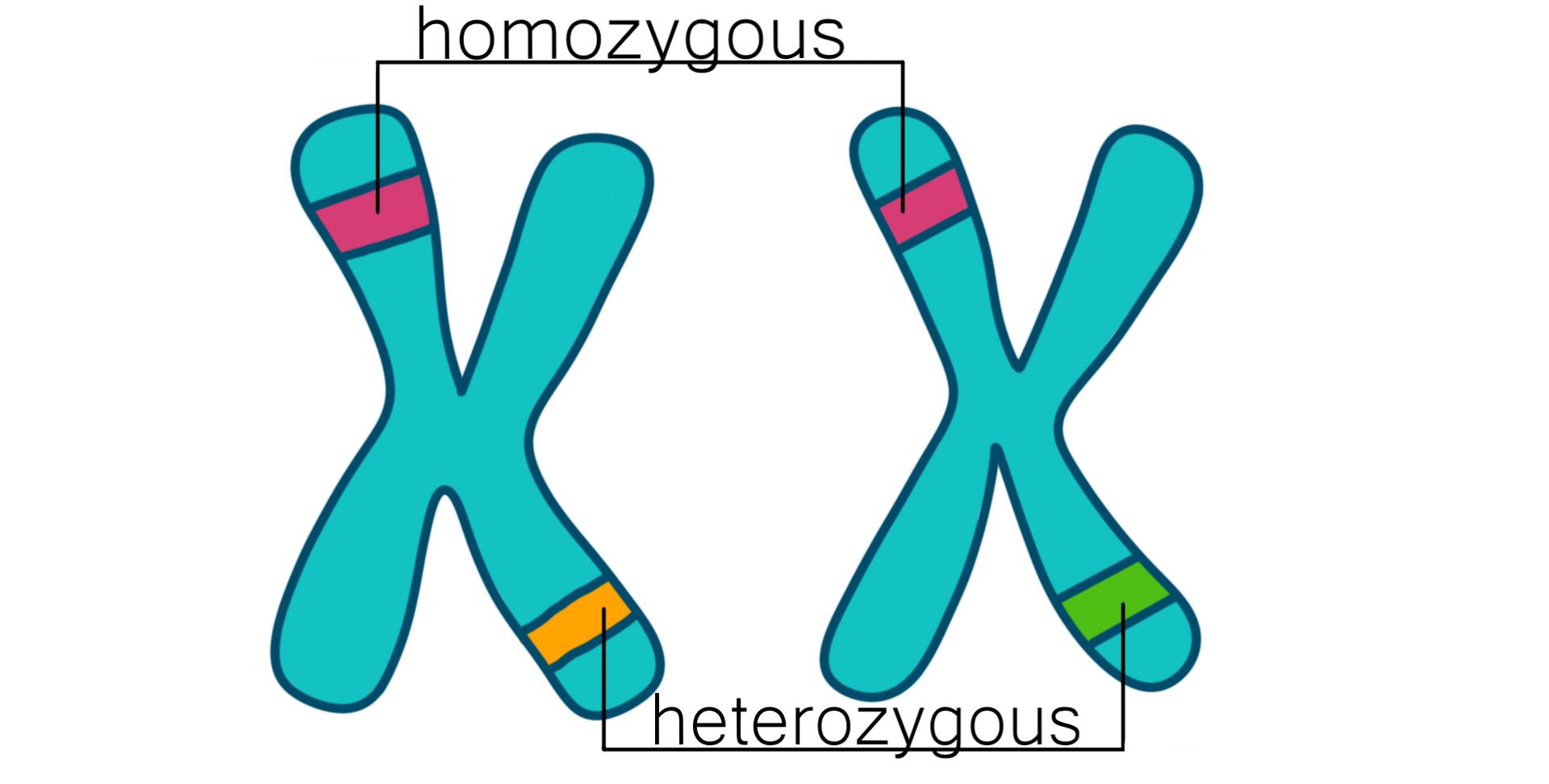
What is Homozygous?
Having the same genes in a pair; identical alleles
3
New cards
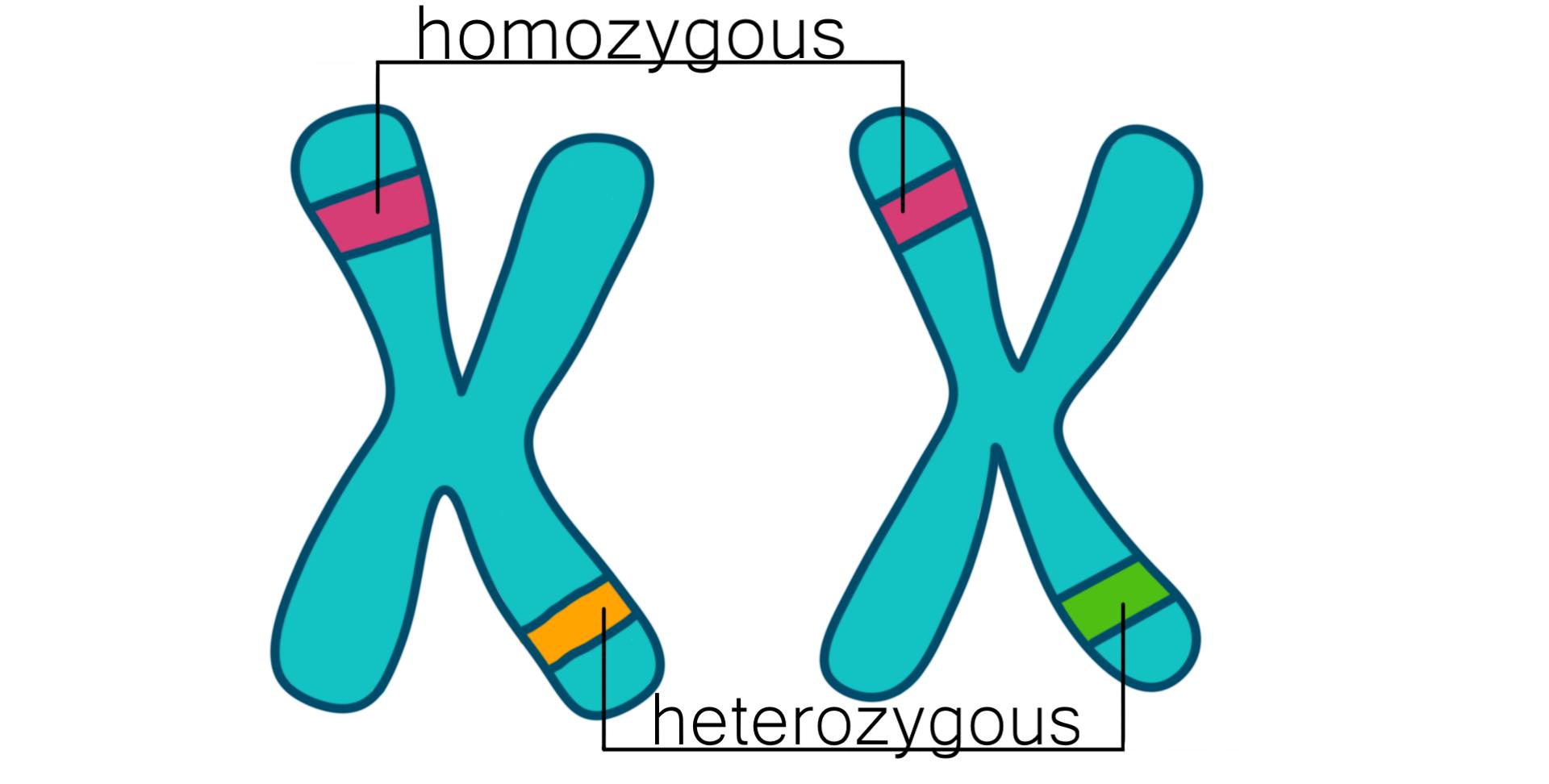
What is Heterozygous?
having unlike genes in a pair; two different alleles
4
New cards
What is a Phenotype?
An expression of genes present; physical traits
5
New cards
What is a Genotype?
the actual genes present
6
New cards
List 3 characteristics of early awareness of inheritance.
1. traits are passed from parents to offspring
2. Artificial selection was practiced by farmers
3. today we have clear understanding of the nature of genes and the scientific basis for selective breeding
2. Artificial selection was practiced by farmers
3. today we have clear understanding of the nature of genes and the scientific basis for selective breeding
7
New cards
List 4 characteristics of Genes.
1. hereditary material (DNA) found in chromosomes
2. organized in units (a segment of DNA molecule)
3. Each gene codes for the formation of one protein
4. Genes control all phases in the life of an organism
2. organized in units (a segment of DNA molecule)
3. Each gene codes for the formation of one protein
4. Genes control all phases in the life of an organism
8
New cards
Where do genes occur?
chromosomes (at a specific location); on the homologous chromosome, there is a second gene for the same trait at the same location
9
New cards
What are Homologous chromosomes?
look alike and carry genes for the same traits
10
New cards
What are Gametes?
haploid and contain 1 of each homologous chromosome
11
New cards
What happens to the zygote?
receives one haploid set of chromosomes from egg and one set from the sperm
12
New cards
For any genetic trait, organisms have 2 genes. It will receive...
one gene on a specific chromosome from one parent and another gene for that same trait on the homologous chromosome from the other parent
13
New cards
What are Alleles?
1. alternate forms of a genes
2. gene that controls flower color may have alleles that specify purple or white flowers
2. gene that controls flower color may have alleles that specify purple or white flowers
14
New cards
What are dominant traits?
Each trait one allele generally masks/is dominant over the other
15
New cards
What are recessive traits?
non dominant allele
16
New cards
Who is the father of genes?
Gregor Mendel (19th century); Augustinian monk who lived and worked in an Austrian monastery
17
New cards
Why was Mendel's work ignored?
it was no mainstream; too brilliant; hard to understand
18
New cards
Summarize Mendelian Genetic findings.
experiments with garden peas that demonstrated the principles of heredity; garden peas easy to work with (self pollinate but easy to cross)
19
New cards
List the 7 contrasting pairs of traits from Mendel and the Garden Pea.
Mendel selected seven contrasting pairs of traits:
Tall versus dwarf plants
Yellow versus green seeds
Round versus wrinkled seeds
Green versus yellow pods
Inflated versus constricted pods
Purple versus white flowers
Terminal versus lateral flowers
Tall versus dwarf plants
Yellow versus green seeds
Round versus wrinkled seeds
Green versus yellow pods
Inflated versus constricted pods
Purple versus white flowers
Terminal versus lateral flowers

20
New cards
What is monohybrid crossing?
Mating individuals that differ in only one trait
21
New cards
What was the offspring of the cross called, and what did they produce?
F1 generation, or first filial generation; produced yellow seed
22
New cards
F2 generation, or second filial generation
1. Approximately 3/4 yellow and 1/4 green
2. 3:1 ratio
23
New cards
What are the 3 Molecular basis of heredity?
1. how traits are passed from one generation to another
2. Understanding nucleic acids and what they do
3. explains how genes function
2. Understanding nucleic acids and what they do
3. explains how genes function
24
New cards
What are Nucleic Acids?
chemical compounds composed of repeating units called nucleotides
25
New cards
List 3 basic units of the DNA molecule.
1. one sugar (either ribose or deoxyribose)
2. one phosphate group (PO4)
3. one nitrogenous base
2. one phosphate group (PO4)
3. one nitrogenous base
26
New cards
List the 2 Nitrogen (Purine) bases
*adenine (A)
*guanine (G)
*guanine (G)
27
New cards
List the 3 Nitrogen (Pyrimidine) bases
*cytosine (C)
*thymine (T) only in DNA
*uracil (U) only in RNA
*thymine (T) only in DNA
*uracil (U) only in RNA
28
New cards
What is DNA?
*hereditary material
*sequence of the bases in DNA makes up the genetic code
*often called the double helix (double stranded molecule twisted into a helix)
*Pairs of bases extend across
A=T, G=C
*sequence of the bases in DNA makes up the genetic code
*often called the double helix (double stranded molecule twisted into a helix)
*Pairs of bases extend across
A=T, G=C
29
New cards
What are the sides of a DNA helix composed of?
sugars and phosphates
30
New cards
What is RNA?
*Single stranded
*manufacture of proteins by carrying out the instructions coded on the DNA molecule
*manufacture of proteins by carrying out the instructions coded on the DNA molecule
31
New cards
What are the differences between RNA and DNA?
1. DNA is Double stranded while RNA is Single Stranded
2. DNA is a double helix while RNA is a single helix
3. DNA has Deoxyribose sugar while RNA has ribose sugar
4. DNA stores and transmits genetic information while RNA acts as a template for making proteins.
5. DNA is found in the nucleus only. RNA is found everywhere in the cell
6. There is only one kind of DNA. There are three kinds of RNA--tRNA, mRNA, rRNA
2. DNA is a double helix while RNA is a single helix
3. DNA has Deoxyribose sugar while RNA has ribose sugar
4. DNA stores and transmits genetic information while RNA acts as a template for making proteins.
5. DNA is found in the nucleus only. RNA is found everywhere in the cell
6. There is only one kind of DNA. There are three kinds of RNA--tRNA, mRNA, rRNA
32
New cards
List the 3 Types of RNA
1. mRNA=messenger RNA
2. rRNA = ribosomal RNA
3. tRNA = transfer RNA
2. rRNA = ribosomal RNA
3. tRNA = transfer RNA
33
New cards
What is a Transcription?
synthesis of an RNA molecule from a DNA template:
1. mRNA carries information for a protein out to the cytoplasm
2. mRNA attaches to a ribosome
1. mRNA carries information for a protein out to the cytoplasm
2. mRNA attaches to a ribosome
34
New cards
What does the DNA do during transcription?
1. part of DNA molecule unwinds
2. One strand serves as template for synthesis of mRNA
3. molecule of DNA rewinds and mRNA leaves the nucleus
2. One strand serves as template for synthesis of mRNA
3. molecule of DNA rewinds and mRNA leaves the nucleus
35
New cards
What are 4 characteristics of Genetic Code?
*Every 3 bases on the RNA is called a codon
*Each codon specifies an amino acid
*universal
*In the cytoplasm, the mRNA attaches to a ribosome
*Each codon specifies an amino acid
*universal
*In the cytoplasm, the mRNA attaches to a ribosome
36
New cards
What is a Translation?
1. mRNA molecule is translated into a protein
2. mRNA molecule is read codon by codon to form a chain of amino acids
3. Amino acids are carried to the ribosome by tRNA
2. mRNA molecule is read codon by codon to form a chain of amino acids
3. Amino acids are carried to the ribosome by tRNA
37
New cards
What happens to the amino acid as the mRNA is translated?
the amino acid chain elongates
38
New cards
What are 3 characteristics of the Universal Code?
*Genetic code and protein synthesis is the same in all living organism
*One organism can understand the genetic instructions of another organism Universal code
*Using tools of genetic engineering scientists can transfer genes from one organism to another
*One organism can understand the genetic instructions of another organism Universal code
*Using tools of genetic engineering scientists can transfer genes from one organism to another
39
New cards
What classifies as a macronutrient? (3)
carbohydrates, proteins, and fats (required in large amounts)
40
New cards
What is a Calorie?
*A measure of energy
*The amount of energy to raise the temperature of one gram of water one degree Celsius
*The amount of energy to raise the temperature of one gram of water one degree Celsius
41
New cards
List the three types of Carbohydrates
1. Monosaccharides
2. Disaccharides
3. Polysaccharides
2. Disaccharides
3. Polysaccharides
42
New cards
Define Monosaccharides and list the 3 parts
*Simple sugars
*Building block of more complex carbohydrates
1. Glucose (abundant)
2. Fructose
3. Galactose
*Building block of more complex carbohydrates
1. Glucose (abundant)
2. Fructose
3. Galactose
43
New cards
Define Disaccharides and list the 3 parts
Two monosaccharides chemically joined
1. Sucrose
2. Lactose
3. Maltose
1. Sucrose
2. Lactose
3. Maltose
44
New cards
What is sucrose and the formula?
glucose + fructose
45
New cards
What is lactose and the formula?
1. Milk Sugar
2. glucose + galactose
2. glucose + galactose
46
New cards
What is maltose and the formula?
*glucose + glucose
*germinating grains
*germinating grains
47
New cards
Define Polysaccharides and give 3 examples.
*complex carbohydrates
*hundreds to thousands of sugar units
*Glucose is the only monosaccharide
*Distinguished by the way in which the glucose units are joined together, their arrangement, and their number
1. Starch
2. Glycogen
3. Fiber (cellulose)
*hundreds to thousands of sugar units
*Glucose is the only monosaccharide
*Distinguished by the way in which the glucose units are joined together, their arrangement, and their number
1. Starch
2. Glycogen
3. Fiber (cellulose)
48
New cards
How is Glucose made and how is it transported?
*During digestion, other carbohydrates are broken down or converted to glucose
*Transported by the blood to all the cells in the body *Within cells, respiration breaks down glucose to produce energy necessary to sustain life
*Transported by the blood to all the cells in the body *Within cells, respiration breaks down glucose to produce energy necessary to sustain life
49
New cards
What is Fructose and Galactose?
*both monosaccharides
*same chemical make up as glucose, C6H12O6, differing only in the arrangement of the atoms
*Converted into glucose and metabolized
*High fructose corn syrup (sweeter than sucrose)
*same chemical make up as glucose, C6H12O6, differing only in the arrangement of the atoms
*Converted into glucose and metabolized
*High fructose corn syrup (sweeter than sucrose)
50
New cards
What is Starch?
*Storage form of glucose found in plants
*Seeds, some fruits, tubers, and tap roots
*Starch in foods can be traced directly to plant origin: starch in bread or pasta from wheat
*Seeds, some fruits, tubers, and tap roots
*Starch in foods can be traced directly to plant origin: starch in bread or pasta from wheat
51
New cards
Examples of Starches in Human Diet
*Grains (wheat, rice, and corn)
*Underground crops (potato, sweet potato, & cassava) *Legumes (beans and peas)
*Underground crops (potato, sweet potato, & cassava) *Legumes (beans and peas)
52
New cards
How and what are starches broken down to?
*broken down to glucose by enzymes in saliva/small intestine
*transported by blood to body cells
*transported by blood to body cells
53
New cards
Where is Glycogen found and not found?
*liver and skeletal muscles
*excess glucose--stored as glycogen
*only 1 day's worth of glycogen stored
*not in plants
*excess glucose--stored as glycogen
*only 1 day's worth of glycogen stored
*not in plants
54
New cards
What is carbohydrate loading?
*eat lots of starchy foods to build glycogen reserves
(excess glucose stored as fat)
(excess glucose stored as fat)
55
New cards
List 3 characteristics of Fiber (polysaccharide)
*from plants
*not digestible
*provides bulk
*not digestible
*provides bulk
56
New cards
What are sources of fiber?
1. fruits
2. veggies
3. seeds
4. whole grain
2. veggies
3. seeds
4. whole grain
57
New cards
List the types of dietary fibers (7)
1. cellulose
2. lignin
3. hemicellulose
4. pectin
5. gums
6. mucilages
7. other
2. lignin
3. hemicellulose
4. pectin
5. gums
6. mucilages
7. other
58
New cards
What is Cellulose (fiber)?
*principal component of plant cell walls
*made of glucose
*humans can't break it down--passes through digestive system as roughage
*made of glucose
*humans can't break it down--passes through digestive system as roughage
59
New cards
What are Pectins (fiber)?
*cell wall polysaccharides
*middle lamella
*middle lamella
60
New cards
What are Hemicelluloses (fiber)?
*cell wall polysaccharides
61
New cards
Where do you find Gums and mucilages?
*exudates from plants
*also thickening agents
*also thickening agents
62
New cards
What are another dietary fiber from polysaccharides?
red and brown algae
63
New cards
Give examples of Insoluble fibers and list the benefits.
1. Cellulose (wheat bran)
2. Lignin
3. Some hemicelluloses
*speeds up passage of food through large intestine
*reduces risk of colon cancer
64
New cards
Give examples of Soluble fibers and list the benefits.
1. algal polysaccharides
2. gums (oat bran)
3. mucilages
4. pectins (apples)
5. other hemicelluloses
*lowers cholesterol
2. gums (oat bran)
3. mucilages
4. pectins (apples)
5. other hemicelluloses
*lowers cholesterol
65
New cards
List 4 characteristics of Protein.
*large complex molecules
*composed of amino acids
*structural components
*regulate bodily functions
*composed of amino acids
*structural components
*regulate bodily functions
66
New cards
How many naturally occurring amino acids are there?
20
67
New cards
How are the proteins in our food digested?
broken down into amino acids by enzymes in the digestive tract and transported in the blood stream
68
New cards
What is the role of dietary protein?
*to supply amino acids for the body to make human proteins
*All 20 amino acids are necessary for protein synthesis
*All 20 amino acids are necessary for protein synthesis
69
New cards
How many amino acids can the human body synthesize?
11
70
New cards
What are the 3 Essential Amino Acid Characteristics
*Cannot be stored by the body
*must be present simultaneously in the diet
*need all in each meal
*must be present simultaneously in the diet
*need all in each meal
71
New cards
What are the essential amino acids? (9)
1. Histidine
2. Isoleucine
3. Leucine
4. Lysine
5. Methionine
6. Phenylalanine
7. Threonine
8. Tryptophan
9. Valine
2. Isoleucine
3. Leucine
4. Lysine
5. Methionine
6. Phenylalanine
7. Threonine
8. Tryptophan
9. Valine
72
New cards
What are the nonessential amino acids? (11)
1. Alanine
2. Arginine
3. Asparagine
4. Aspartic acid
5. Cysteine
6. Glutamic acid
7. Glutamine
8. Glycine
9. Proline
10. Perine
11. Tyrosine
2. Arginine
3. Asparagine
4. Aspartic acid
5. Cysteine
6. Glutamic acid
7. Glutamine
8. Glycine
9. Proline
10. Perine
11. Tyrosine
73
New cards
What are Complete Proteins?
*contain all 9 essential amino acids
*most proteins derived from animals
*most proteins derived from animals
74
New cards
What are Incomplete Proteins?
*plant proteins
*lack 1 ore more essential amino acid
*lack 1 ore more essential amino acid
75
New cards
What are Complementary Plant Proteins? Give some examples
*combining complementary plant proteins that can supply all E.A.A.
*beans and corn
*beans and corn
76
New cards
What essential amino acids are beans low/high in?
*low in methionine
*high in tryptophan and lysine
*contains complementary proteins
*high in tryptophan and lysine
*contains complementary proteins
77
New cards
What essential amino acids is corn low/high in?
*low in lysine and tryptophan
*high in methionine
*complementary plant proteins
*high in methionine
*complementary plant proteins
78
New cards
What is Malnutrition?
quality deficiency in which 1 or more essential nutrients is lacking even though there's enough calories
79
New cards
What is Undernutrition?
insufficient calories to maintain energy requirements
80
New cards
What are Fats (lipids)?
*organic molecules
*diverse group of compounds
*insoluble in water
*diverse group of compounds
*insoluble in water
81
New cards
List 3 types of fats.
1. Triglyceride
2. Steroid
3. Phospholipid
2. Steroid
3. Phospholipid
82
New cards
What are Tryglycerides and how are they formed?
*95% of lipids in foods - fats and oil
*Formed from glycerol and 3 fatty acids
*Formed from glycerol and 3 fatty acids
83
New cards
List 5 characteritics of Fatty Acids
*simplest form of lipids
*building blocks for triglycerides and phospholipids
*carbon chain w/ hydrogen attached
*body can synthesize most fatty acids
*number of carbon and hydrogen atoms varies
*building blocks for triglycerides and phospholipids
*carbon chain w/ hydrogen attached
*body can synthesize most fatty acids
*number of carbon and hydrogen atoms varies
84
New cards
What are the 3 fatty acids that must be supplied by the diet?
1. Linoleic acid
2. Linolenic acid
3. Arachidonic acid
2. Linolenic acid
3. Arachidonic acid
85
New cards
What are the types of fatty acids?
1. Saturated: all single bonds between carbon atoms
2. Unsaturated: have one or more double bonds
2. Unsaturated: have one or more double bonds
86
New cards
List 3 characteristics of Saturated Fats.
1. mostly saturated fatty acids
2. solid at room temperature
3. animal fats such as lard, butter, and beef fat
2. solid at room temperature
3. animal fats such as lard, butter, and beef fat
87
New cards
What are some characteristics of Vegetable Oils.
1. mostly unsaturated fatty acids
2. liquid at room temperature
2. liquid at room temperature
88
New cards
What are some vegetable oils with monounsaturated fatty acids
1. olive oil
2. peanut oil
3. canola oil
2. peanut oil
3. canola oil
89
New cards
What are some vegetable oils with polyunsaturated fatty acids
1. corn oil
2. soybean oil
3. safflower oil
2. soybean oil
3. safflower oil
90
New cards
Give 3 examples of saturated fats in plants
1. coconut oil
2. palm oil
3. cocoa butter
2. palm oil
3. cocoa butter
91
New cards
What is Hydrogenation?
*addition of hydrogen to make an unsaturated oil, a saturated fat
*converts a liquid oil into a solid fat - margarine
*unsaturated oil has been chemically modified by hydrogenation
*converts a liquid oil into a solid fat - margarine
*unsaturated oil has been chemically modified by hydrogenation
92
New cards
What are the bad effects that diets high in saturated fats lead to?
*colon, breast, and prostate cancers
*blood cholesterol levels-linked to cardiovascular disease
*blood cholesterol levels-linked to cardiovascular disease
93
New cards
What are the good effects that diets high in unsaturated fats have lead to?
*lower blood cholesterol levels
*lower the risk of cardiovascular disease
*lower the risk of cardiovascular disease
94
New cards
What is cholesterol? What is it used for?
*steroid
*4 carbon rings
*part of lipid component of cell membranes
*used in the synthesis of sex hormones and more
*Insoluble in the watery medium of blood
*4 carbon rings
*part of lipid component of cell membranes
*used in the synthesis of sex hormones and more
*Insoluble in the watery medium of blood
95
New cards
What are trans fats?
*unsaturated fat with transisomer
*raise cholesterol levels/cardiovascular disease
*raise cholesterol levels/cardiovascular disease
96
New cards
Where is cholesterol made?
synthesized in liver from saturated fatty acids and absorbed by intestinal cells from animal foods
97
New cards
List examples of food sources that contain cholesterol.
*eggs, butter, cheese, meat
*high saturated fats=increased cholesterol synthesis
*high saturated fats=increased cholesterol synthesis
98
New cards
What are the 2 types of Lipoproteins (lipids and proteins)?
*transported molecule
*Low-density lipoproteins (LDLs)
*High-density lipoproteins (HDLs)
*Low-density lipoproteins (LDLs)
*High-density lipoproteins (HDLs)
99
New cards
What are the bad effects of Low-density lipoproteins (LDLs)?
*bad cholesterol, causing deposits in arteries and leading to heart attacks and strokes
*transport cholesterol - all body cells
*transport cholesterol - all body cells
100
New cards
What are the good effects of High-density lipoproteins (HDLs)?
*remove excess cholesterol- body tissue
*carry to liver for degradation and elimination
*good cholesterol
*carry to liver for degradation and elimination
*good cholesterol