7-1st Lecture on Fossils
1/16
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
17 Terms
What is a fossil?
Remains of a once-living organism, includes skeletons, tracks, impressions, trails, borings, and casts.
Often found in consolidated rock, sometimes preserved in ice.
Have we always known about fossils?
Romans used it as jewellery. Snake heads carved into ammonites.
Human interactions with fossils is old.
When was the science geology born?
Enlightenment time, people valued evidence and equality. 1750s, when geology was born. Wealthy people or vicars.
What is palaeontology?
Study of fossil remains of plants and animals.
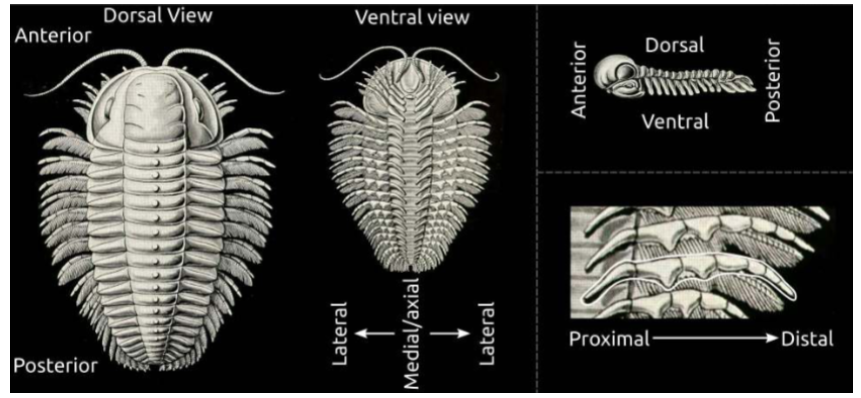
How do we describe directions on an animal?
Anterior - faces the front
Posterior - faces back
Dorsal - furthest from the ground
Ventral - nearest to the ground
Proximal - close e.g. bicep
Distal - further away e.g. hand


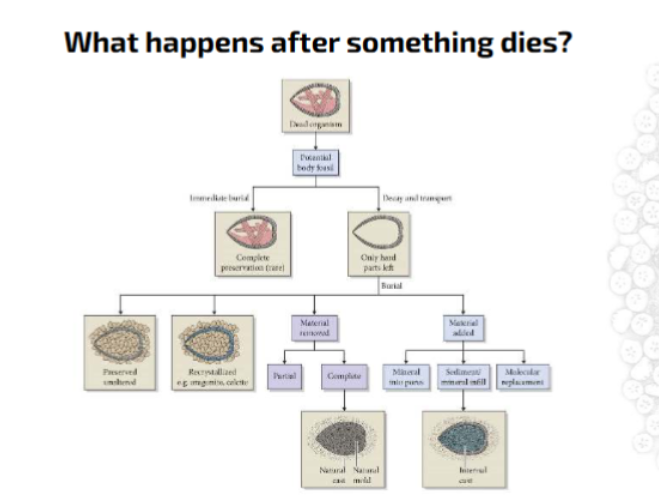
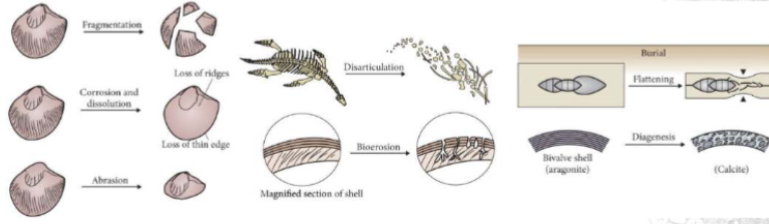
What is taphonomy?
Study of the transition of all or part of an organism and its traces from the biosphere into the lithosphere.
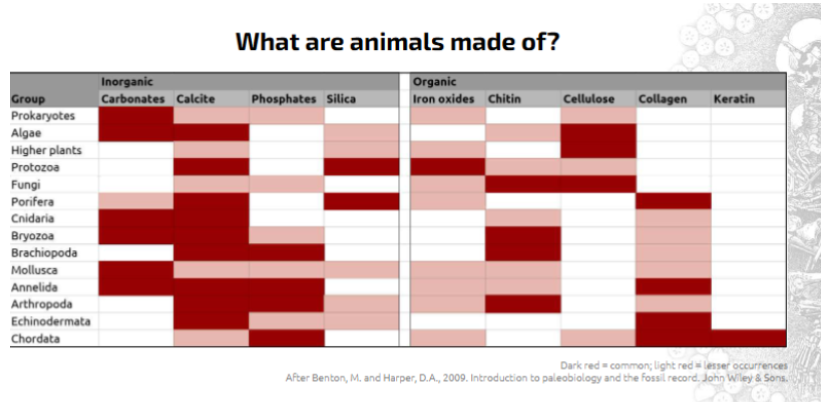
Inorganic vs organic?
Inorganic - without C-H bonds
Organic - with C-H bonds or with O or N
What is the classification scheme?
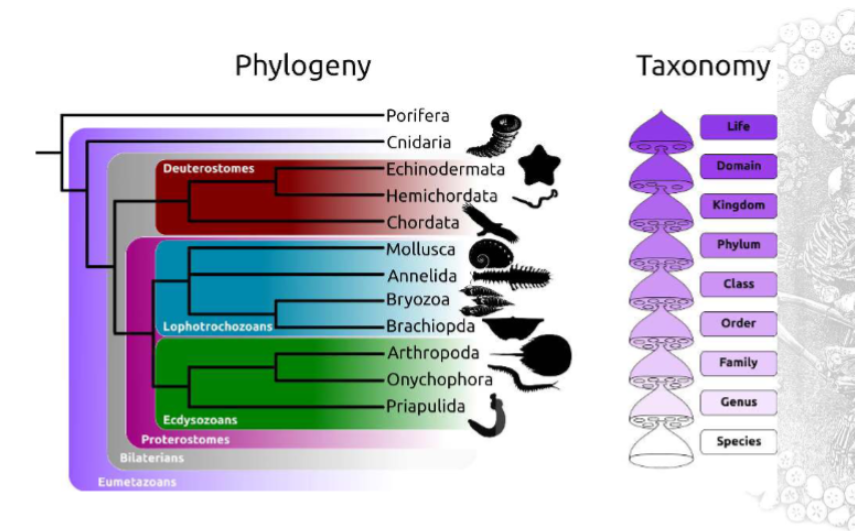
The corals are members of the phylum Cnidaria: they are animals with radial symmetry, and one opening through which they do everything. They excrete a hard skeleton.
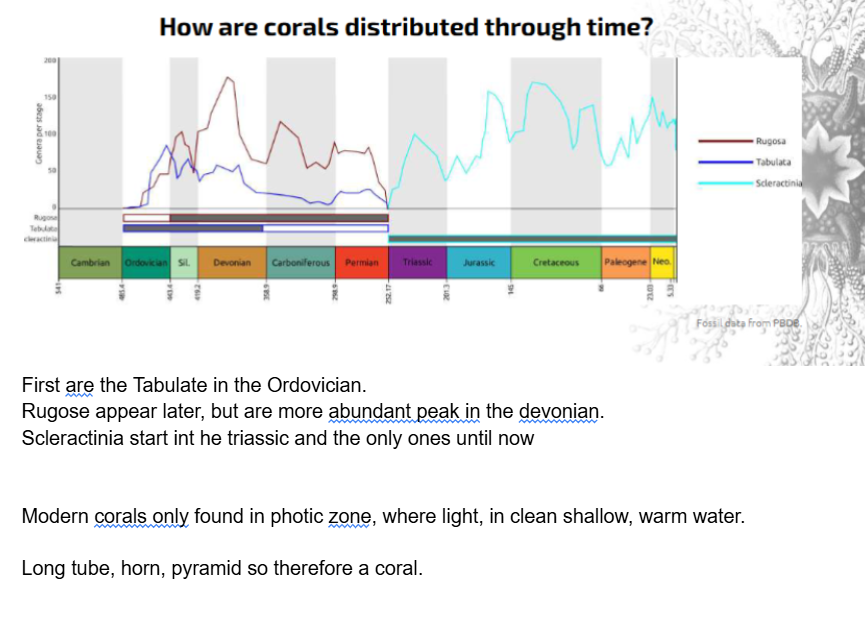
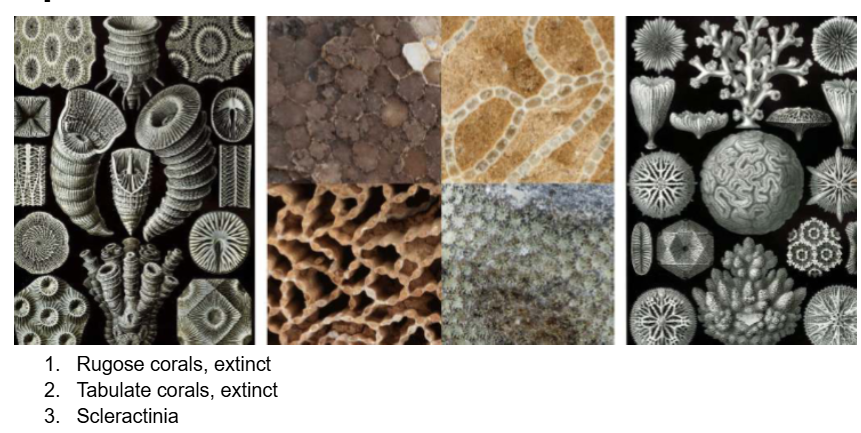
Corals are marine, and comprise three major groups – the Rugosa, Tabulata, and Scleractinia.
Rugose and tabulate corals appear in the Ordovician and die out at the end of the Permian period. Scleractinian corals evolved in the Triassic and are the corals we see today.
Reef ecosystems are really important – and have been throughout geological time.The groups that create reefs differs through time and with different environmental condition
Corals come in a range of forms, but all have septa (radial structures) and tabulae (transverse ones). These are developed to differing degrees depending on the group.
Rugose corals have strong septae, and are robust, calcitic corals (but have a wide range of forms).
Tabulate corals are colonial, calcitic and have well-developed tabulae. Septae are reduced.
Scleractinian corals are aragonite, and have a relatively light, porous skeleton
Corals are not too difficult to ID in a rock, especially if cracks in the rock split them at an angle.
Coral morphology, if in life position, or level of fragmentation if not, can tell you where you are on a reef.
As long as you're looking at a scleractinian coral with photosynthetic symbionts (called zooxanthellae, FYI), then you're looking at a depositional environment that is:
In the photic zone
Warm
Probably agitated
Relatively low on clastic sediment input
But you need to be more careful with this assumption the older rocks get.
We can tell using corals that Earth's rotation is slowing (!?).
Corals
NIDERIAN ?
A coral is a marine invertebrate
They lack bilateral symmetry
Animals that can be solitary (alone) or colonial (form colonies e.g. coral reefs)
Secrete calcium carbonate skeletons
Symbiosis - mutual association with algae
One opening
Asexually and sexually
What is a cnidarian?
Larger group that includes corals and jellyfish, and sea anemones) that has stinging cells called cnidocytes used for capturing prey and defence.
Non bilaterian, radial body plan.
Stinting cells