Eukaryotes and Prokaryotes
1/40
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
41 Terms
Structure of the plasma membrane
Bilayer, mostly phospholipids
Boundary of the cell
Function of plasma membrane
Allow communication with the external environment
Selectively permeable
What is the fluid mosaic model?
Proteins embedded in the bilayer can move sideways within the layer, giving it mobility
What do receptor proteins in the plasma membrane allow?
The cell to receive signals from the environment and pass them on to the inside of the cell
What do transport proteins in the plasma membrane allow?
Small molecules, such as ions, to enter and exit the cell
The flexibility of the plasma membrane allows
Cell growth and cell movement
Structure of phospholipids
Glycerol
Phosphate
Two fatty acid chains
Hydrophobic head or tail?
Tail
Hydrophilic heads or tails?
Head
Amphipathic
Molecules that have both hydrophobic and hydrophilic properties
Is the lipid layer 2D or 3D?
2D
What are liposomes?
Closed spherical vesicles formed when phospholipids are added to pure water.
This is due to the amphipathic nature of phospholipids. The hydrophobic tails are not exposed to water and the hydrophilic heads are.
What are the hydrophilic heads exposed to?
Water on the outside of the membrane
Name four roles of membrane proteins
Transporters
Anchors
Receptors
Enzymes
Describe transporter proteins.
Transport tridents, metabolites and ions across the bilayer
Describe anchor proteins
Anchor the membrane to macromolecules
Describe receptor proteins
Detect chemical signals in the environment and transmit them to the interior of the cell
Describe enzymes.
Catalyses specific reactions
What are the two types of membrane proteins?
Integral
Peripheral
Name three integral membrane proteins.
Transmembrane proteins
Monolayer-associated proteins
Lipid-linked proteins
Transmembrane proteins
Stretch across the lipid bilayer as a single a-helix, as multiple a-helices or as a b-barrel.
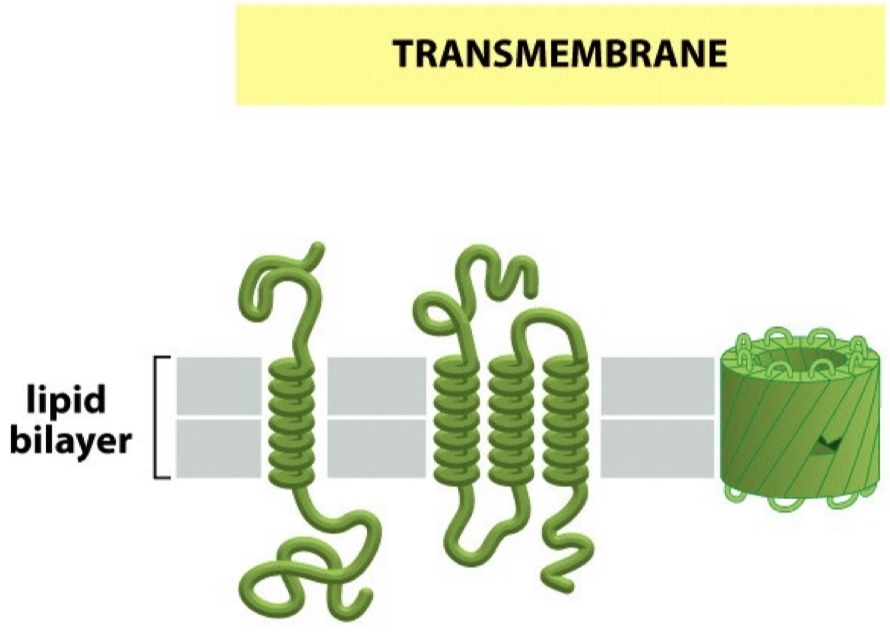
Monolayer-associated proteins
Anchored to the cytosolic surface (the side of the membrane that faces the inside of the cell) via an amphipathic a-helix.

Lipid-linked protein
Attached to either side of the bilayer via a covalent attachment to a lipid molecule
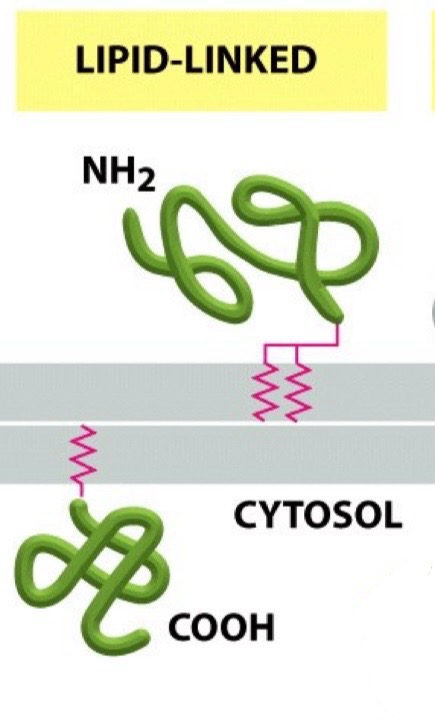
Name a peripheral membrane protein
Protein-attached protein
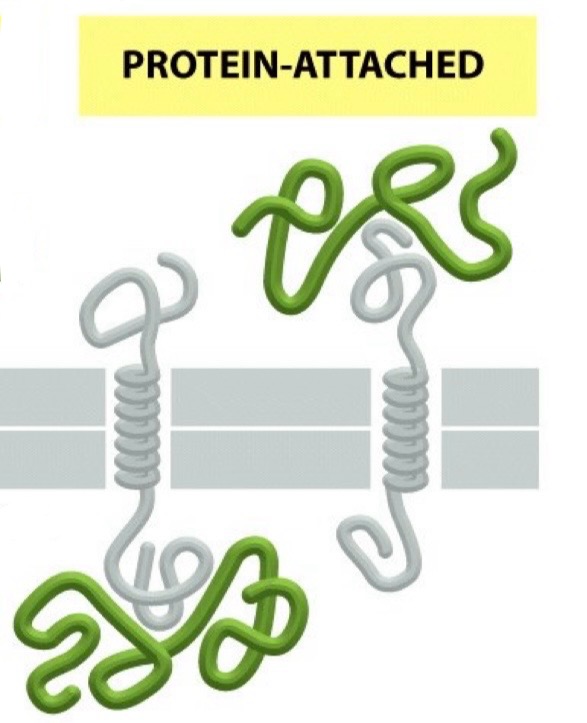
Protein-attached protein
Attached to membrane by relatively weak non-covalent interactions with other membrane proteins
Organelles within prokaryotes
Flagellum
Plasma membrane
Cell wall
Capsule
Cytosol
Ribsomes
DNA
+ Cilia on the outside
Features of the nucleus (4)
Contains DNA
Surrounded by double-membrane nuclear envelope, with nuclear pores which are gateways for molecules to move in and out, enabling communication
Storehouse for genetic information
Contains nucleolus and DNA associated with proteins that are packed together
Brief overview on gene expression
DNA synthesis (replication)
RNA synthesis (transcription)
Protein synthesis (translation)
Endoplasmic reticulum
Made up of interconnected tubes and flattened sacs
Rough ER and Smooth ER
Location where the majority of cell membrane components and materials for export are made
Continuous with the membrane of the nuclear envelope
RER
Rough ER
Contains ribosomes
Makes membrane and secreted proteins
Manufactures lipids and proteins (by ribosomes bound to the rough ER surface)
SER
Smooth ER
Makes membrane vesicles
What is the cytosol?
The fluid inside cells, where majority of the organelle’s proteins are manufactured
Differs from the cytoplasm as the cytosol is the fluid part and the cytoplasm is there cytosol and everything suspended within it such as organelles
Do cytosolic proteins have sorting signals?
No, they remain at their site of manufacture.
Protein signal sequence
Majority of organelle proteins are manufactured in the cytosol (on ribosomes)
Sorting signals within the amino acid sequence direct proteins to their requisite organelle
If a protein has a signal for the nucleus it gets sent there
If there is no signal, it stays in the cytosol (some proteins function in the cytosol)
Protein signal sequence- ER pathway
If the protein has an ER signal sequence, an SRP (signal recognition particle) binds to it
The ribosome and growing protein get directed to the rough ER membrane
Within the ER, proteins fold up, assemble with other proteins, form disulphide bonds and are enhanced with oligosaccharide chains
What are vesicles?
Membrane-enclosed sacs
What is the function of transport vesicles?
Move substances from one location to another
How do transport vesicles work?
Vesicles bud off “pinches off” from the ER
They capture free molecules in the lumen and molecules embedded in the membrane
The vesicle fuses with the membrane of another membrane-enclosed compartment, transferring the captured molecules to that organelle
What is the Golgi Apparatus?
Stacked, flattened membrane sacs
What is the function of the golgi apparatus?
To process and modify new proteins and lipids
Add specific chemical groups
Target them to their destinations