describe the A&P of the immune system (TEAS 7)
1/57
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
58 Terms
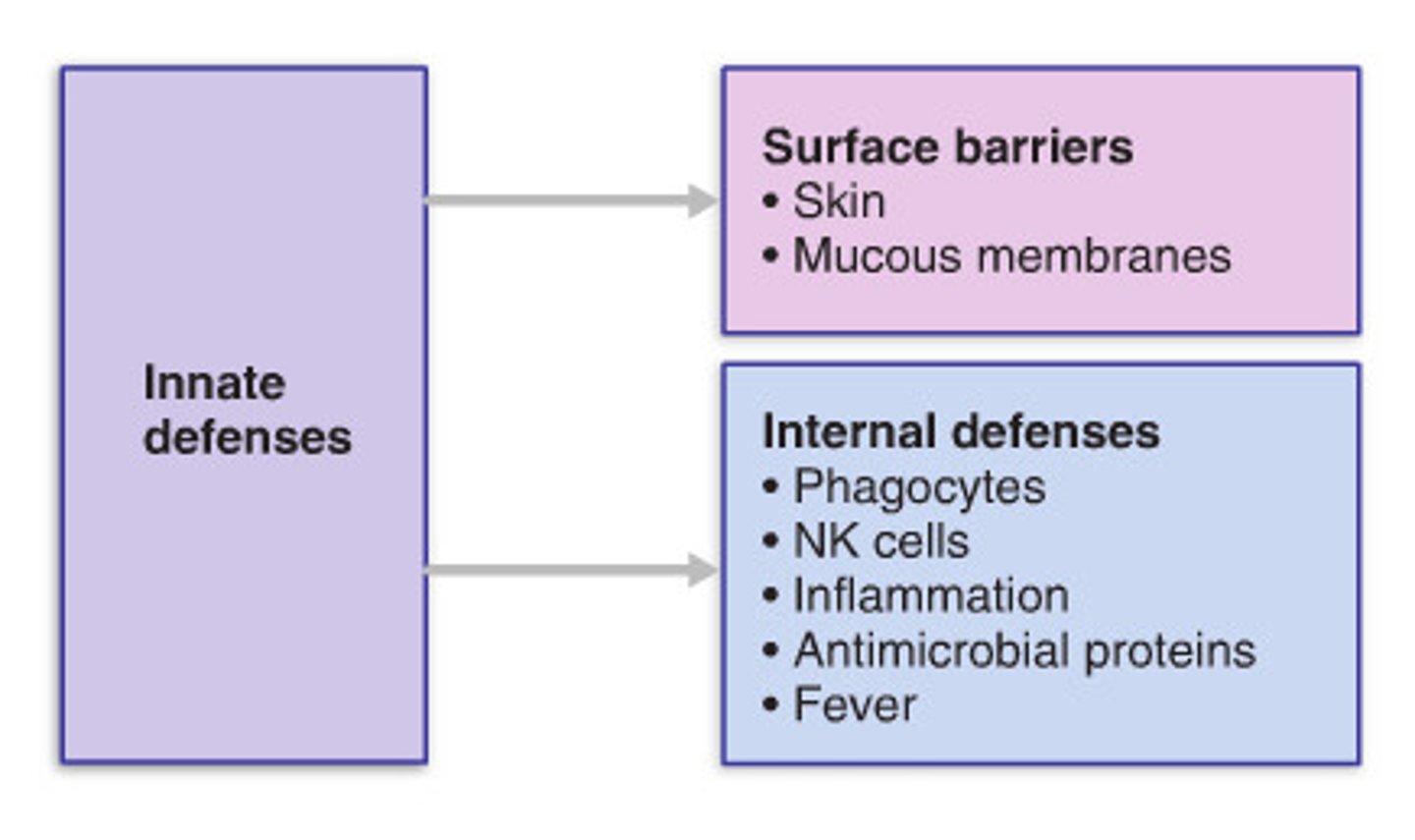
innate defenses
a nonspecific response to pathogens by the immune system
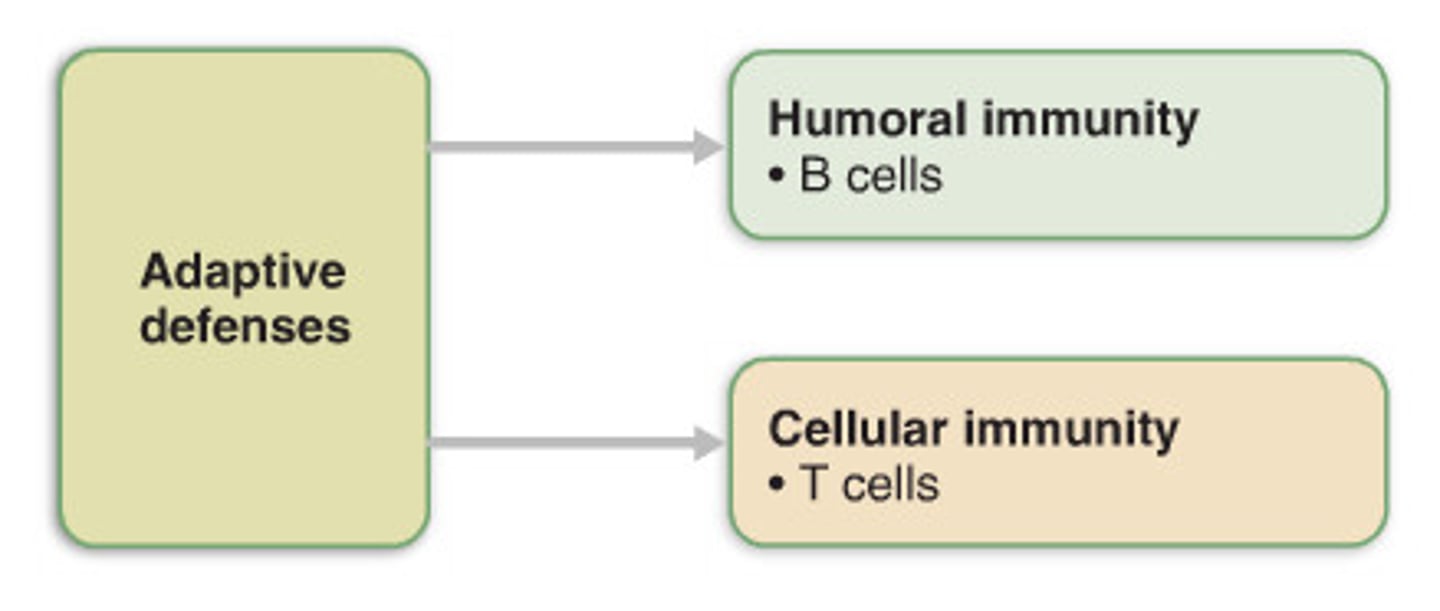
adaptive defenses
a specific response by the immune system to a given pathogen
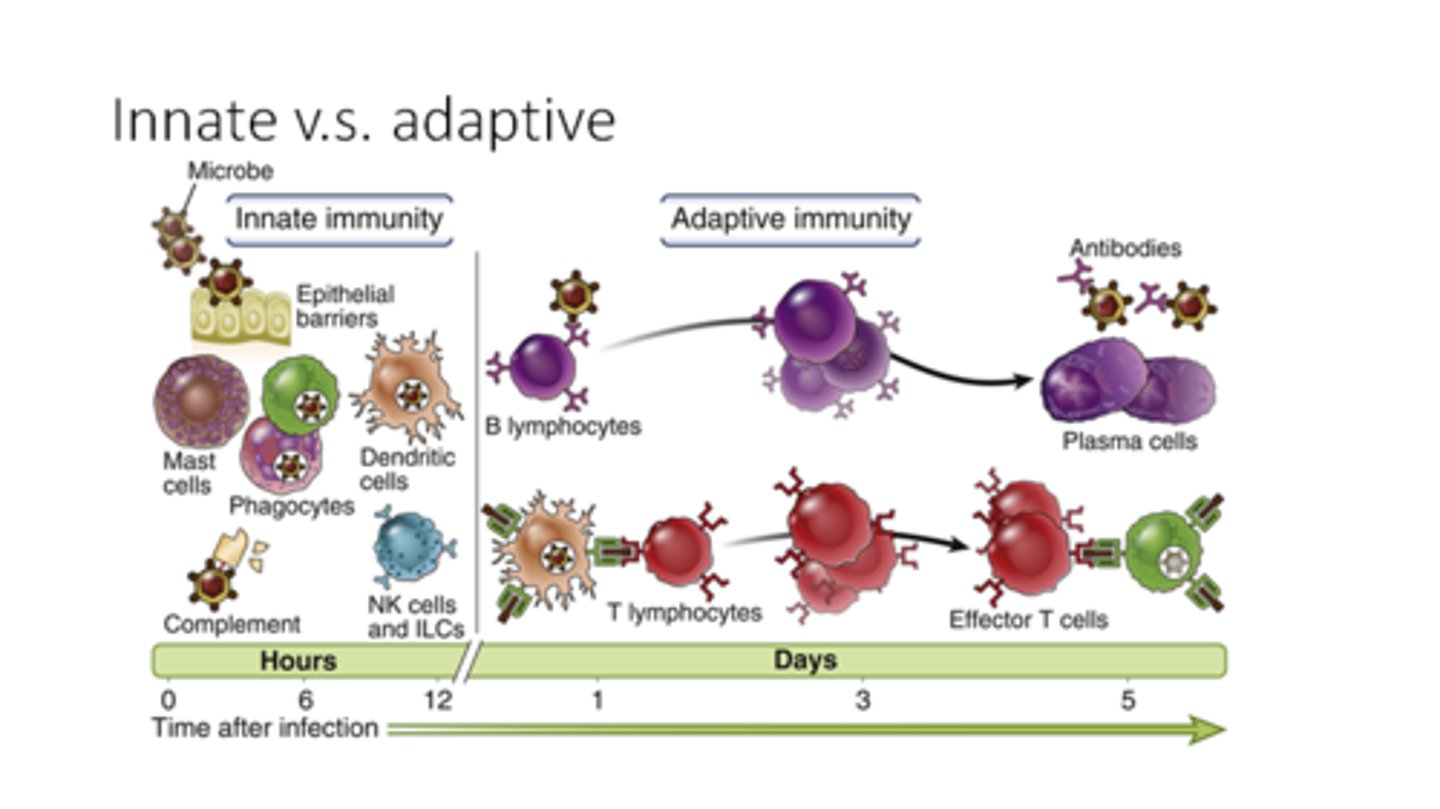
innate immune system
a collection of nonspecific barriers and cellular responses that serve as an inborn first and second line of defense against pathogens

adaptive immune system
a kind of passive or active immunity in which antibodies to a particular antigen are present in the body
B cells
lymphocytes that mature in bone marrow and make antibodies in response to antigens
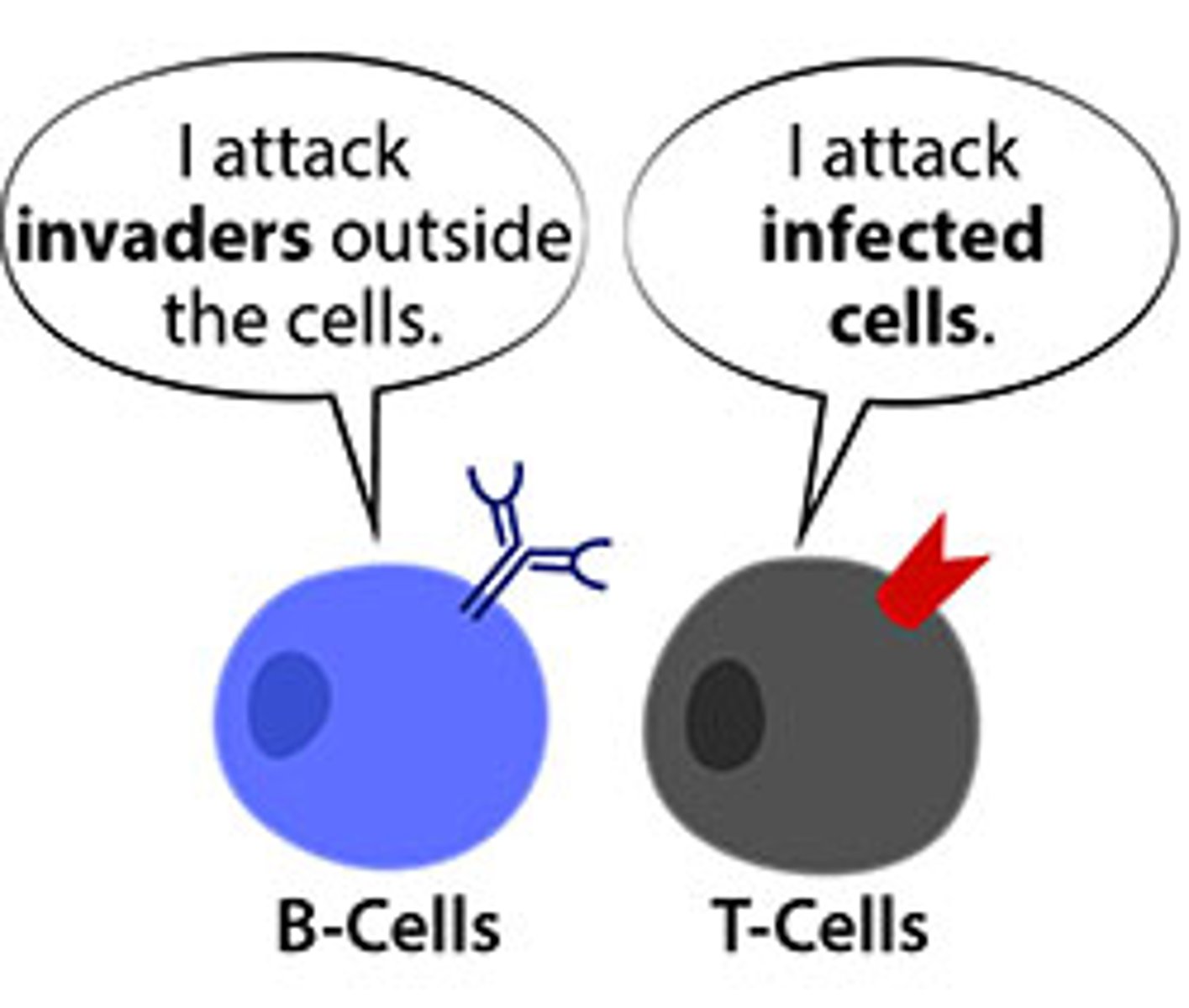
T cells
white blood cells that mature in the thymus and participate in an immune response
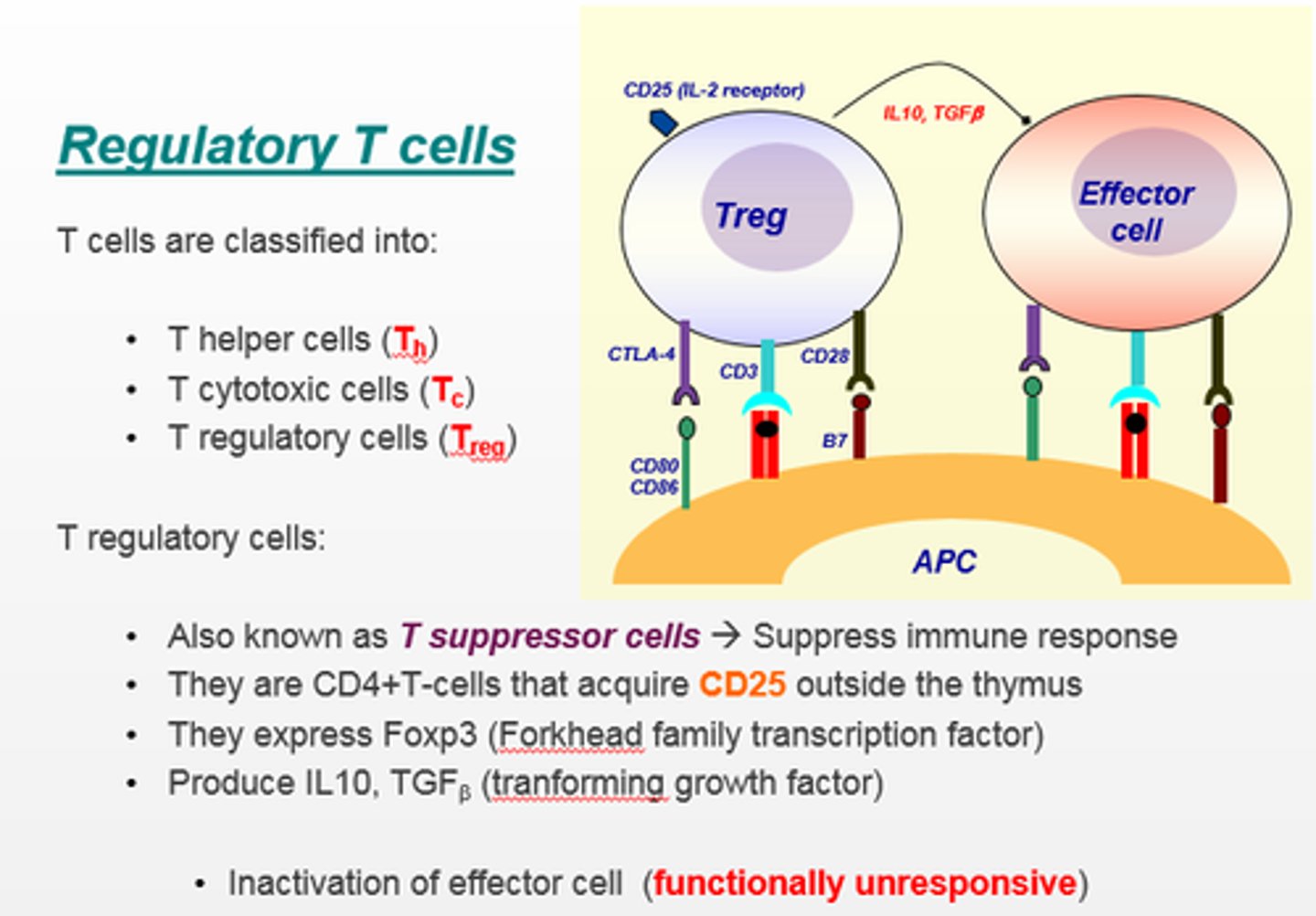
the immune system protects the body against:
disease-causing agents known as pathogens.
the immune system is composed of
both innate (nonspecific) and adaptive (specific) defenses that are designed to protect the body from PATHOGENS and other foreign invaders.
the innate immune system has three main lines of defense:
first; skin, mucus, and secretions keeps pathogens from entering the body,
second; phagocytes, specific proteins, inflammatory response to fight pathogens that have entered the body
third; is the adaptive immune system.
lymphocytes such as B cells and T cells not only fight the pathogen but also
retain the memory of the specific pathogen.
if the barrier fails, then the adaptive immune system specifically
identifies, targets, and remembers the pathogen.
pathogens enter through body openings of the
digestive, urinary, and reproductive systems; injury can also create ways for pathogens to enter
the lymph system is critical to the functioning of the immune system because
pathogens form the blood also circulates through the lymph
B cells and T cells resides in the
lymph nodes and are activated when a pathogen is encountered.
commensal micro-organisms
microscopic organisms that live in or on the human body without causing it harm.
histamine
a white blood cell secretion that triggers capillary permeability and vasodilation.
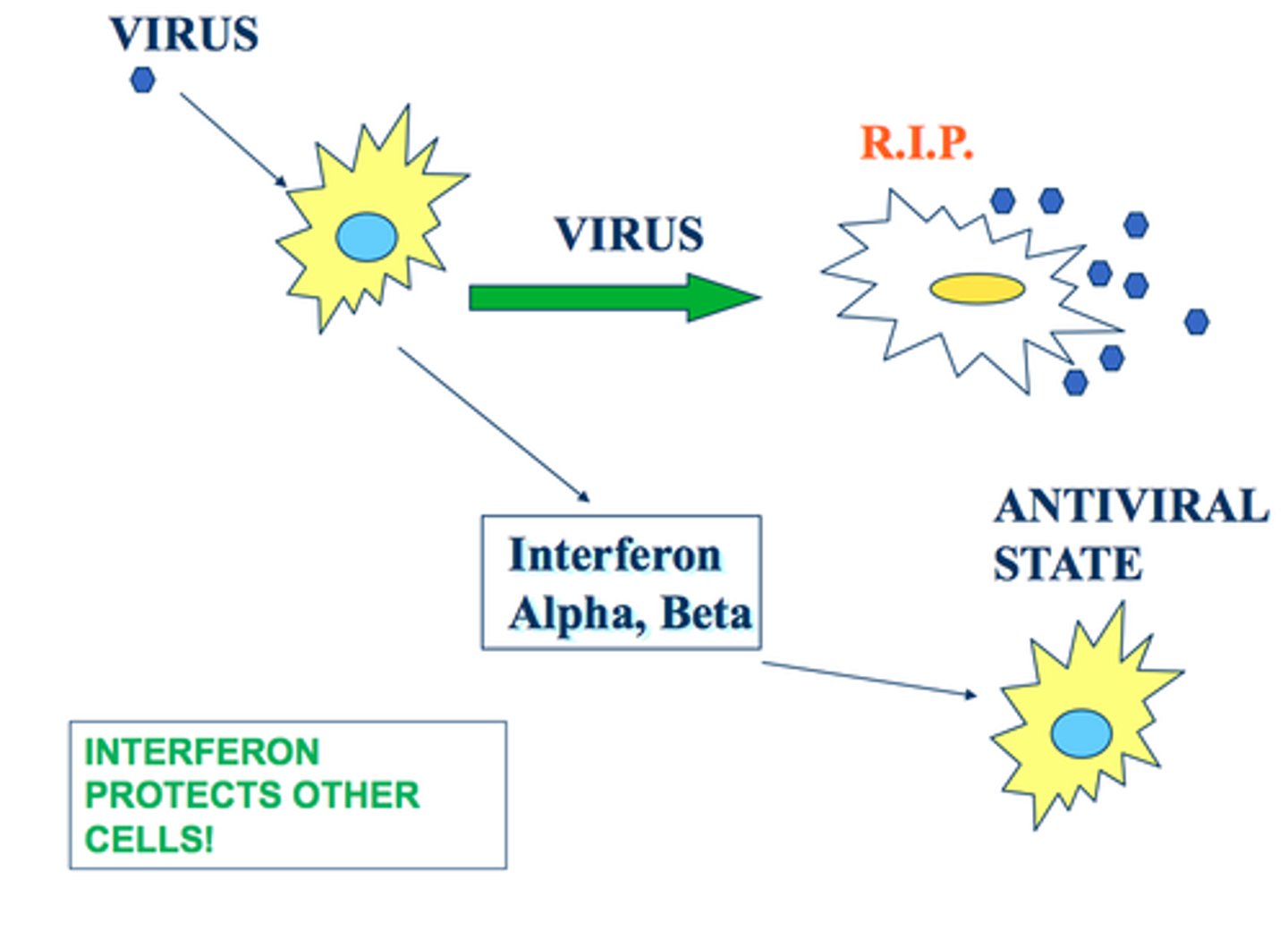
interferons
proteins secreted by leukocytes when they are infected with viruses
antimicrobial
a substance that kills or inhibits growth of micro-organisms with minimal damage to the host.
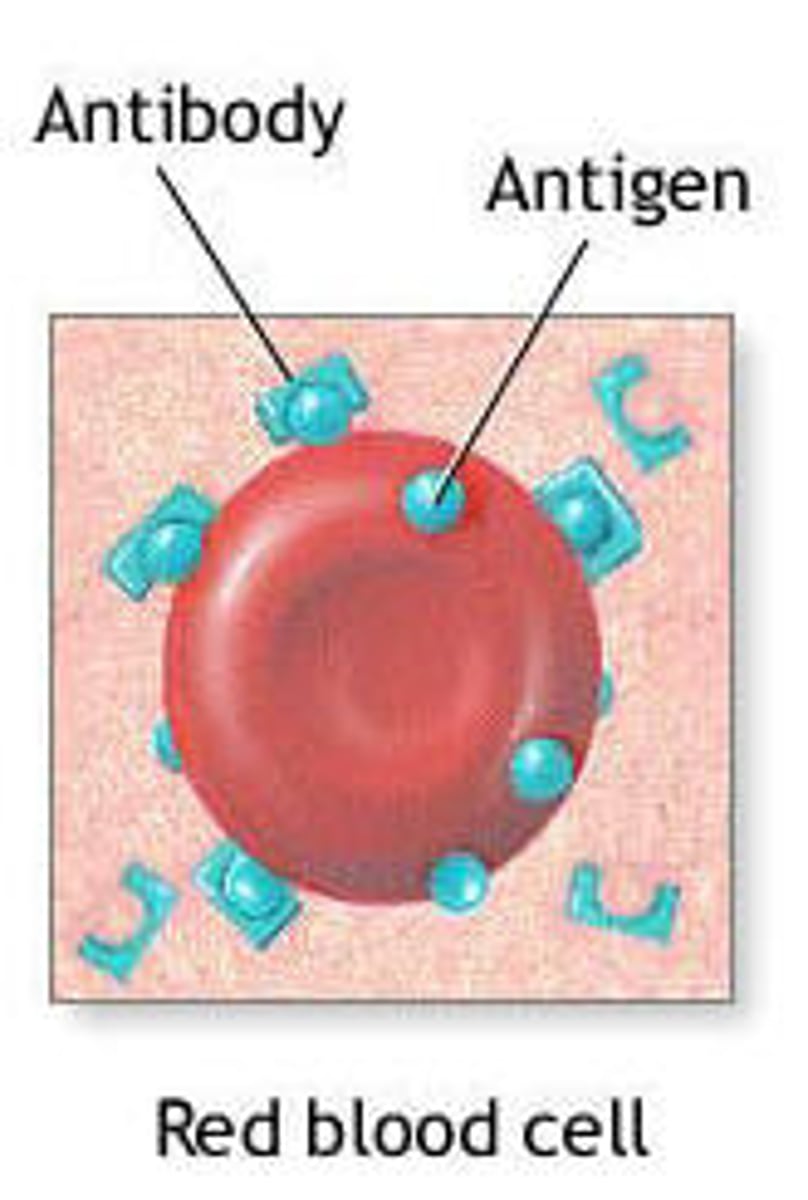
antigens
substances on the surface of agents that act to identify them, to the body, as being native or foreign
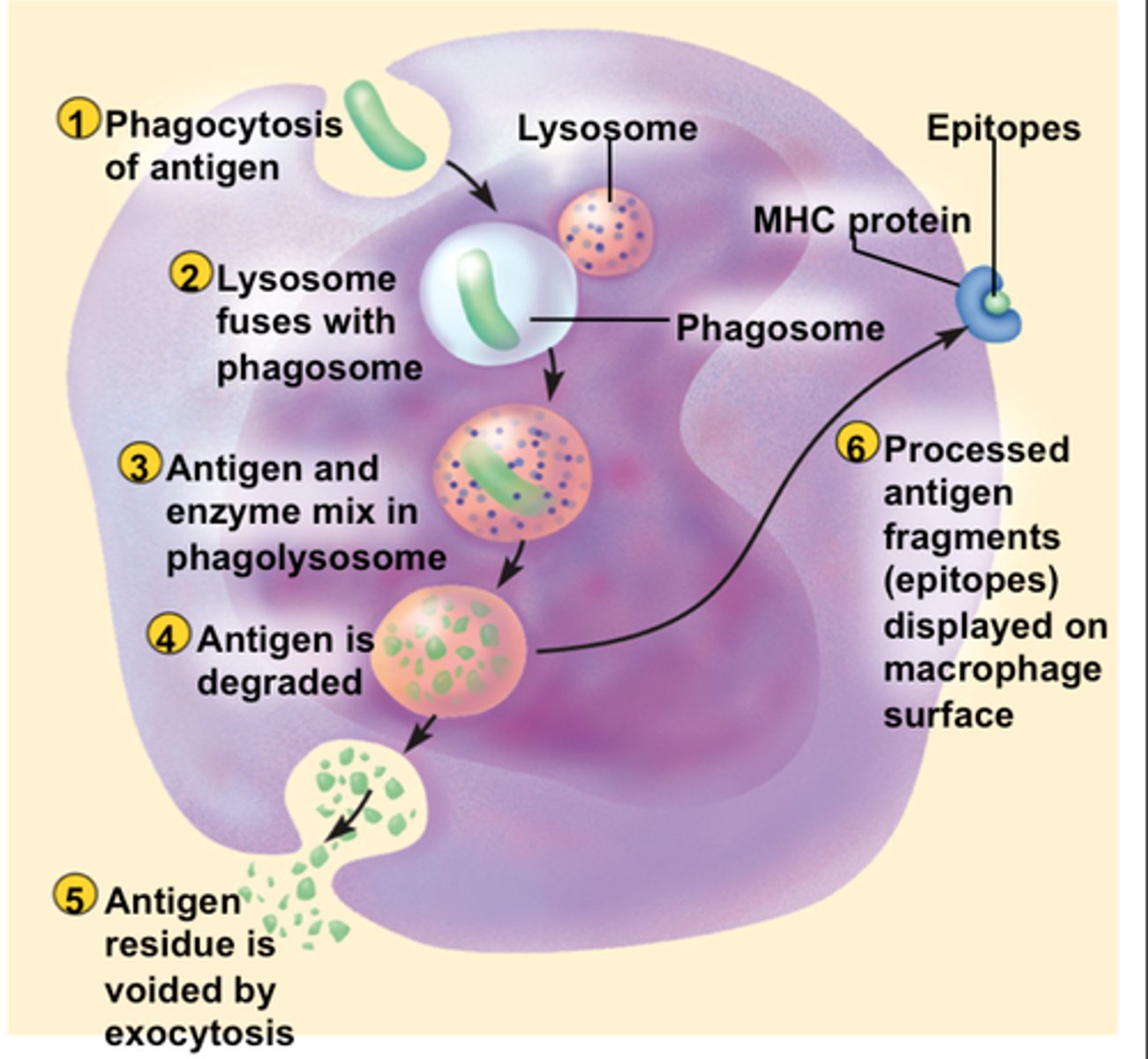
antigen presenting cells
a cell that displays foreign antigens with major histocompatibility complexes on their surfaces
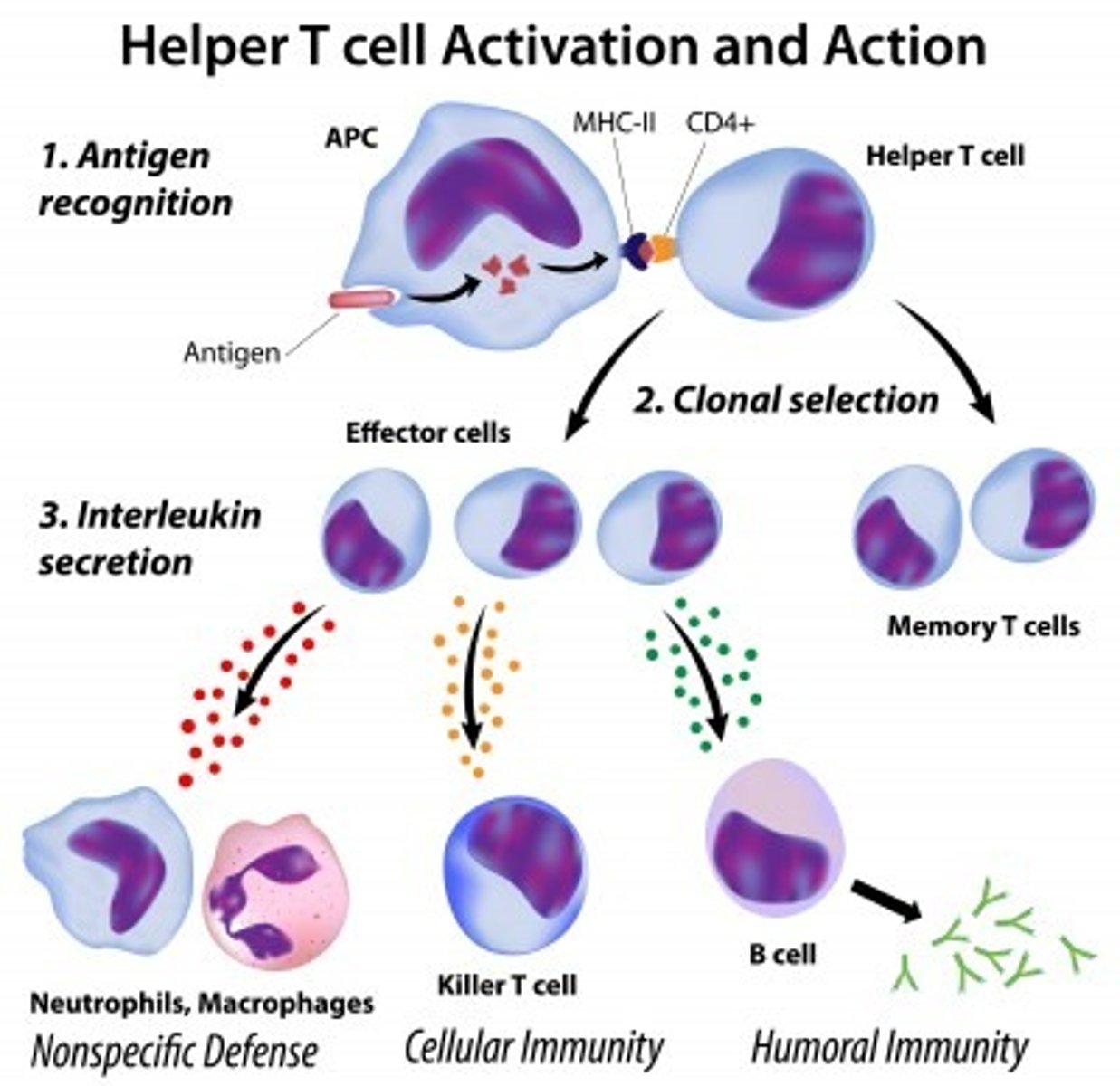
Helper T cells
a type of lymphocyte that secretes interleukins, a protein that triggers the action of other cells, including the attack of foreign cells by the cytotoxic cell.
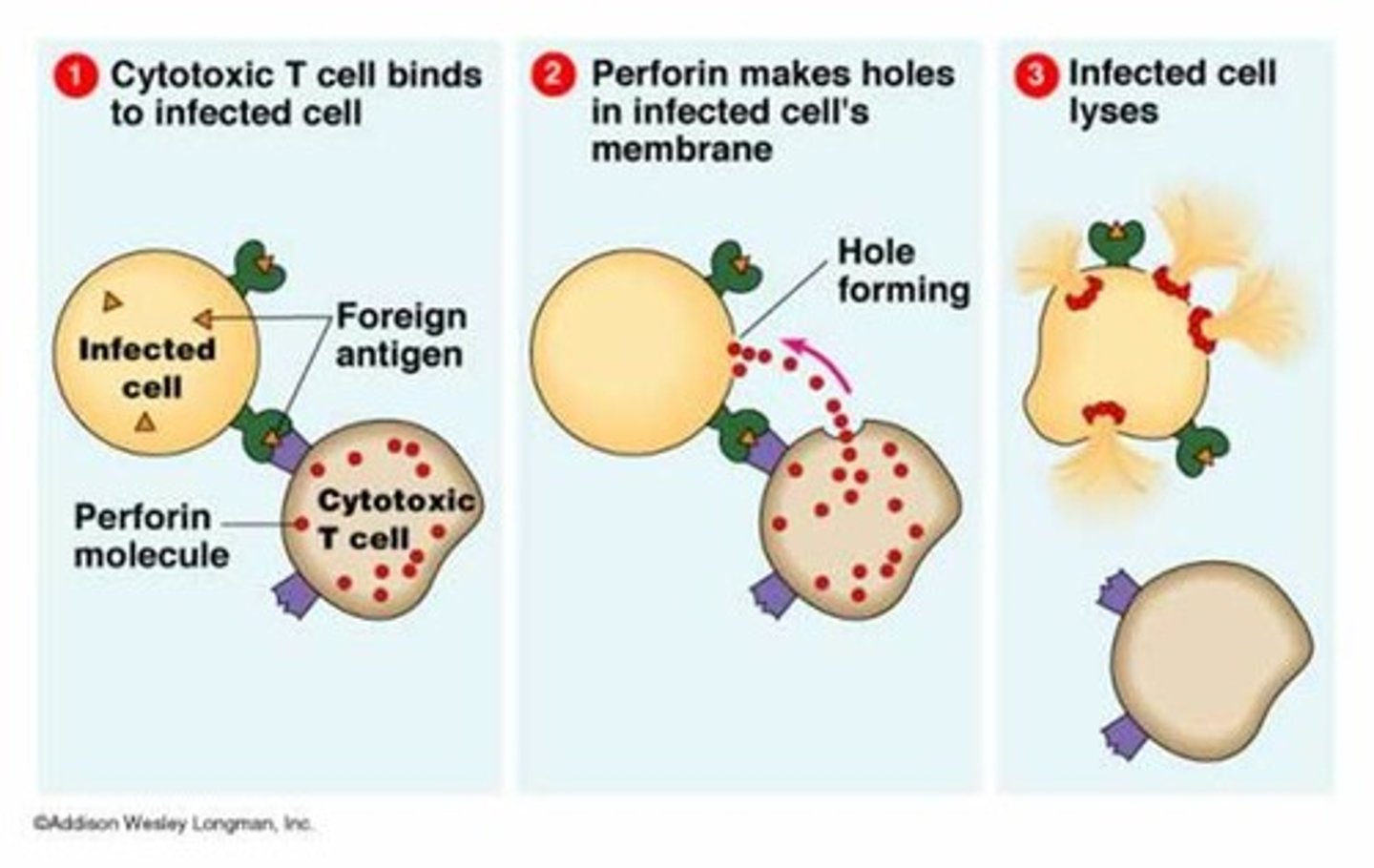
Cytotoxic T cells
the category of lymphocyte that attacks foreign cells
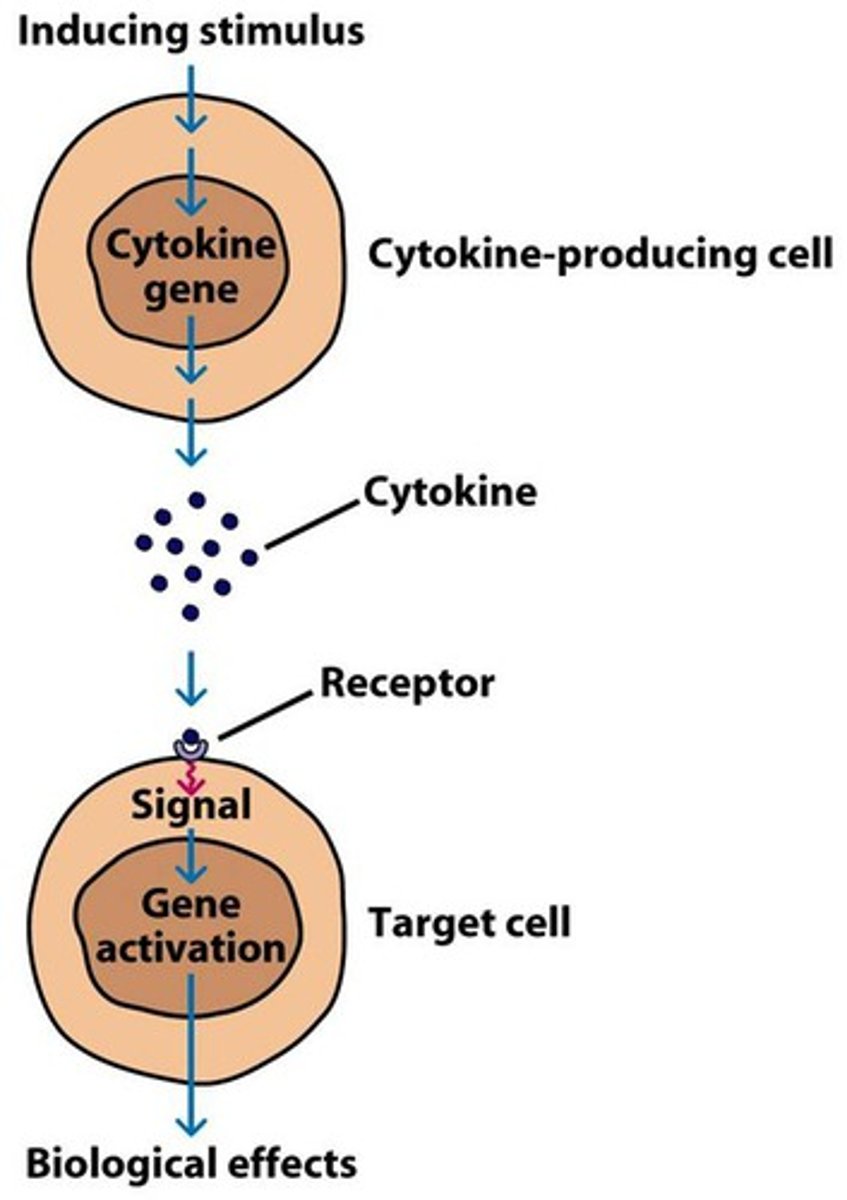
cytokines
Cell signaling molecules are released primarily by helper T cells and macrophages. Certain cytokines activate cytotoxic T-cells
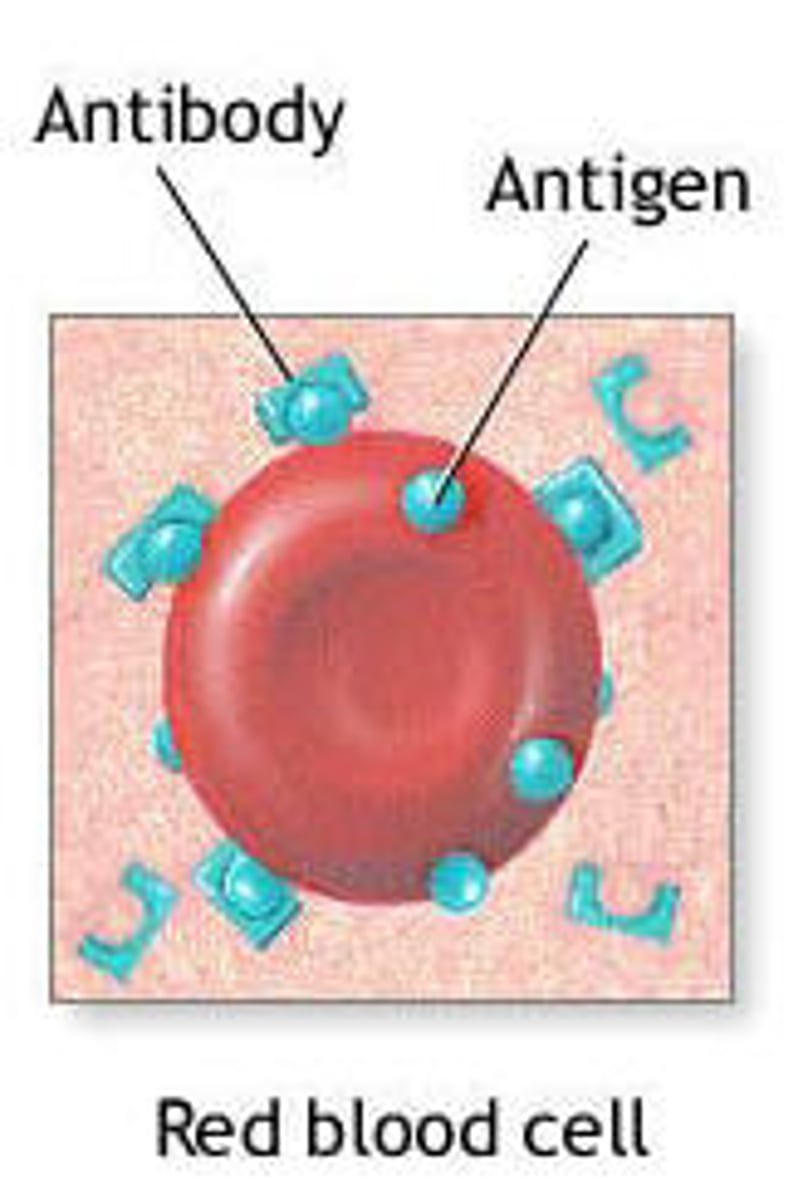
antibody
A blood protein that counteracts a specific antigen
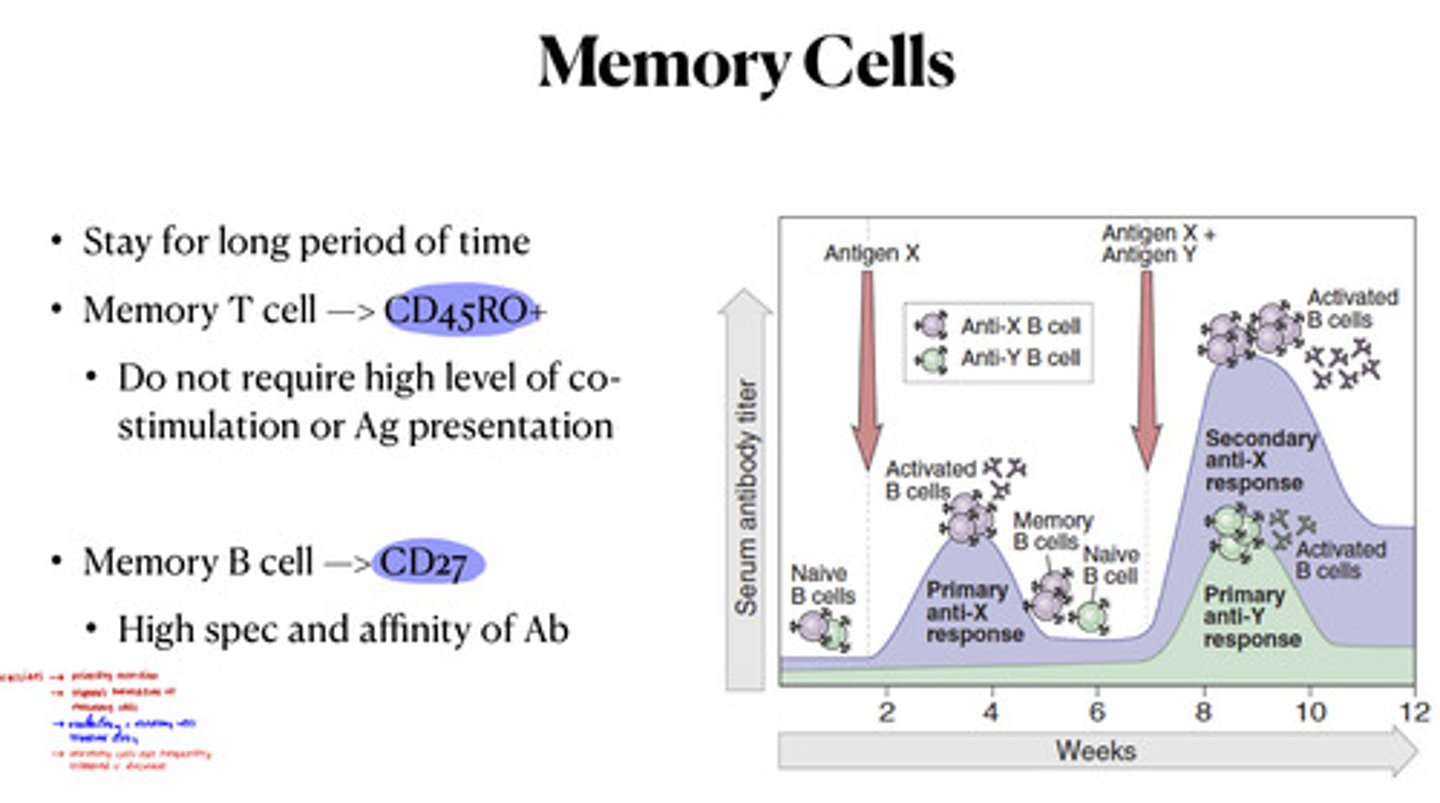
memory cell
A lymphocyte that responds to an antigen upon reintroduction
one of the first responses of innate immunity is called
"inflammatory response" where histamines are released, increasing not only blood flow to the area but also the number of white blood cells known as phagocytes to the area.
fever is also sometimes used by the body to
speed up the immune response.
other internal barriers within the innate immune system include
antimicrobial peptides and "natural killer (NK)" lymphocyte cells that attack host cells that harbor intracellular pathogens.
the innate immune system is a series of
nonspecific barriers such as physical, cellular, and soluble components.
the adaptive immune system has two general responses to
specific pathogens such as cellular or humoral.
the cellular response of the adaptive immune system
destroys the infected cell
the humoral response of the adaptive immune system
destroys pathogens found in body fluids using antibodies secreted by B cells
the adaptive system responds by remembering signature molecules called
antigens from pathogens to which the body has previously been exposed.
the adaptive immune system's functional cells are
lymphocytes called T cells and B cells
the antigen-presenting cells such as macrophages digest pathogens and
present the pathogen's antigen signature to "helper" T cells.
depending on the type of antigen presented to the helper T cells,
either a B cell or a cytotoxic T cell is activated.
helper T cells produce
cytokines to activate a cytotoxic T cell
the helper T cells can also activate
B cells in response to a specific antigen. it induces the B cell to multiply rapidly into secretory cells called "plasma cells"
plasmas produces by the B cells will then
produce large amounts of antibodies that can bind the antigens
B cells also clone
memory cells at the same time; this allows the body to remember a specific antigen.
when the antigen appears again in the body,
this triggers the memory cells to form plasma cells, which quickly produces specific antibody to the antigen
active immunity
protection against a specific pathogen resulting from the production of antibodies in response to the presence of specific antigens [body produces its own antibodies; protection takes time, usually several weeks to develop]
![<p>protection against a specific pathogen resulting from the production of antibodies in response to the presence of specific antigens [body produces its own antibodies; protection takes time, usually several weeks to develop]</p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/4362157f-1347-4c55-a583-eed0434d89bf.png)
passive immunity
temporary immunity gained by a body that has acquired antibodies from an outside source [a person receives pre-made antibodies; protection is immediate]
![<p>temporary immunity gained by a body that has acquired antibodies from an outside source [a person receives pre-made antibodies; protection is immediate]</p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/f081757d-e0b9-48f8-aec8-2af02db7140c.jpg)
autoimmune disease
a pathology that results from the immune system mistaking part of the body as a pathogen
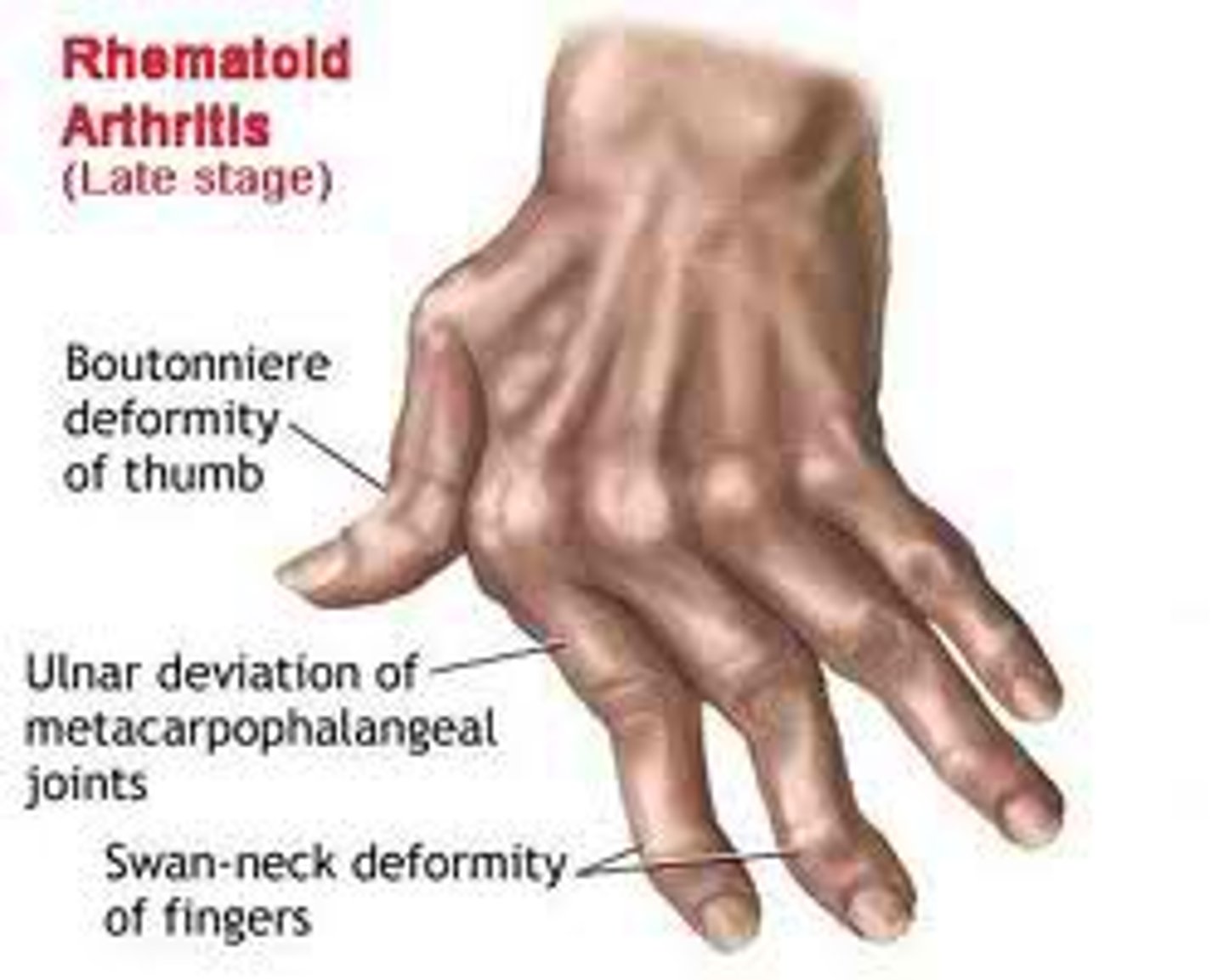
rheumatoid arthritis
A progressive disease that causes joint inflammation and pain
bone marrow
a soft material within the spongey bone and medullary cavity of long bones.
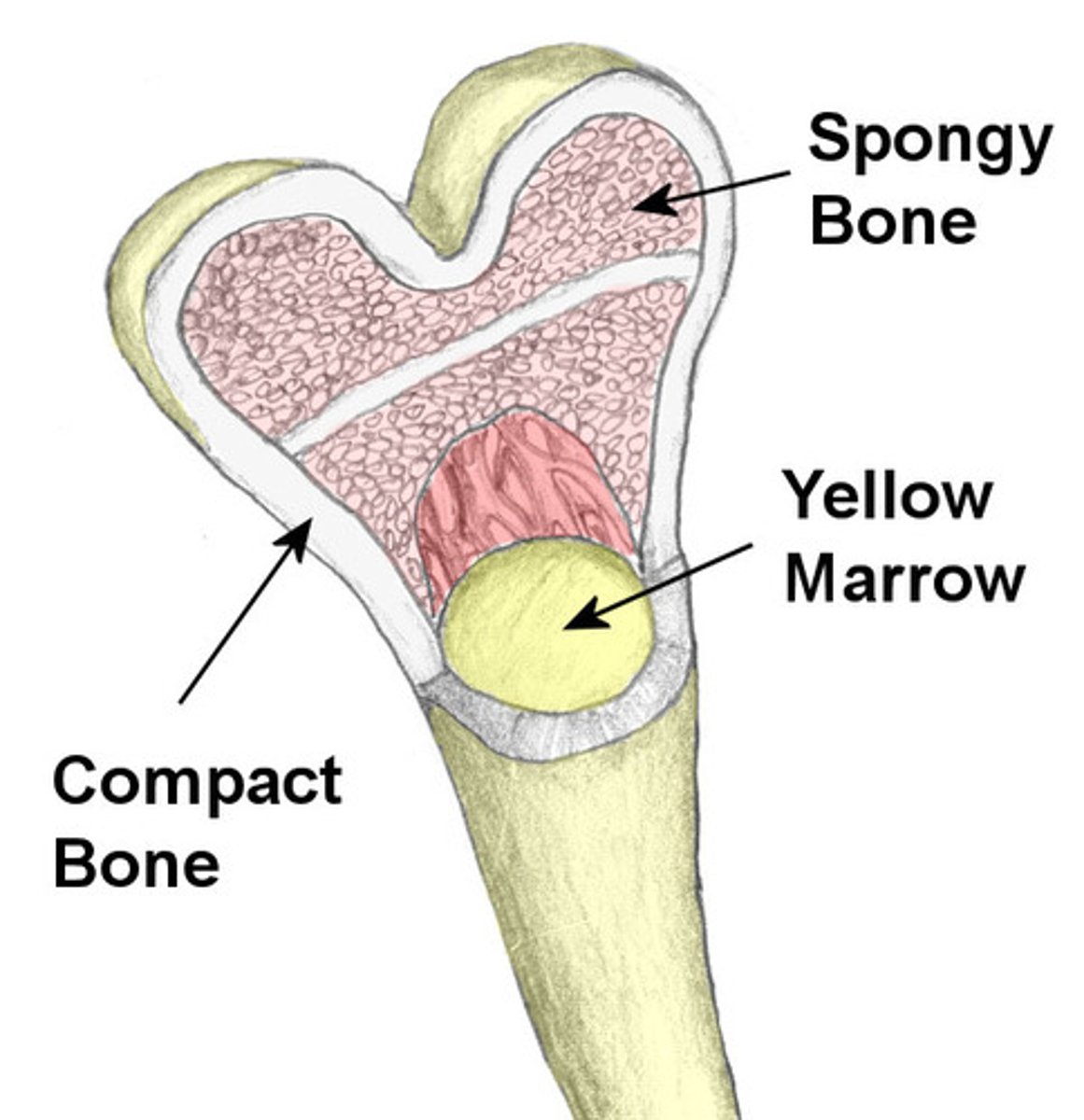
skeletal system
the system of bones in the body that provides protection for delicate organs and serves as the scaffold against which muscles pull for movement. it has three main functions: movement, protection, and storage of minerals and fats.
Both passive and active immunity can be
induced artificially
vaccinations introduce antigens, which are
weakened or killed to elicit an immune response.
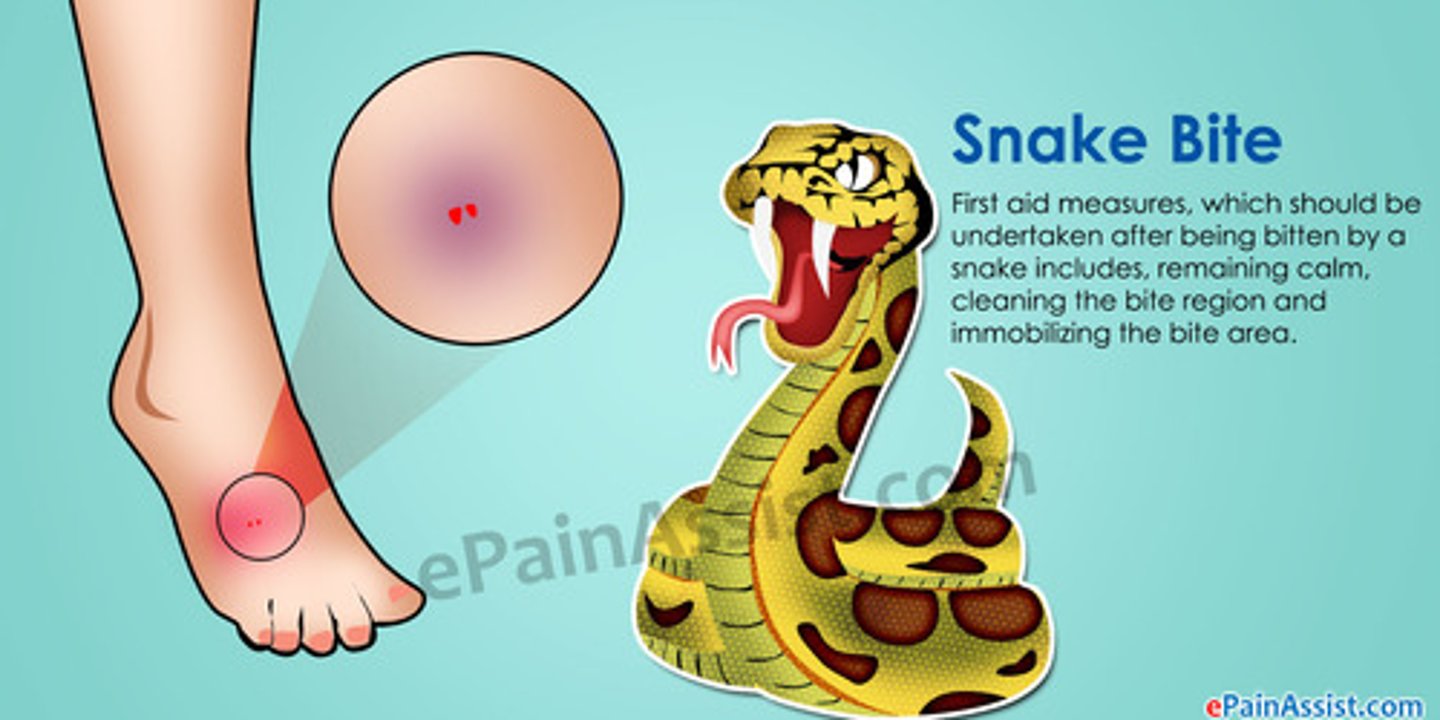
rapid treatment for a snake bite is an example of
passive immunity
acquired immunodeficiency syndrome (AIDS) is caused by
human immunodeficiency virus (HIV), which infects helper T cells and prevents them from activating cytotoxic T cells and B cells and prevents the adaptive immune system form operating.

conversely, an overactive immune system can target harmless foreign particles like pollen,
causing the body to overproduce huge amounts of antibodies that trigger a histamine release from mast cell, which results in allergy symptoms such as sneezing and mucus secretion.

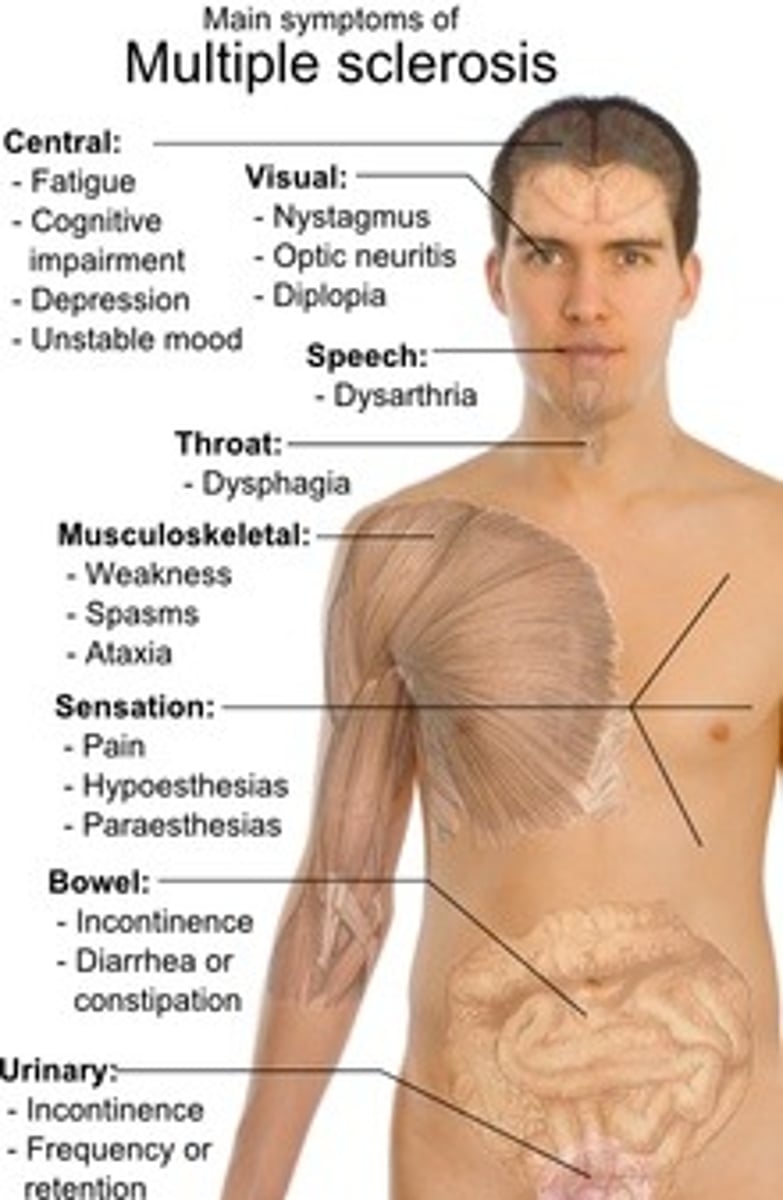
alternately, the immune system can mistakenly target a host molecule as a
foreign antigen, leading to autoimmune diseases such as diabetes, rheumatoid arthritis, and multiple sclerosis.
the immune system works hand and hand with
other body systems to transport immune cells, signaling molecules, and antibodies throughout the body.
For example, the circulatory system, lymphatic system, integumentary system, and skeletal system; bone marrow.
the immune system works with circulatory system by
transporting white blood cells throughout the body.
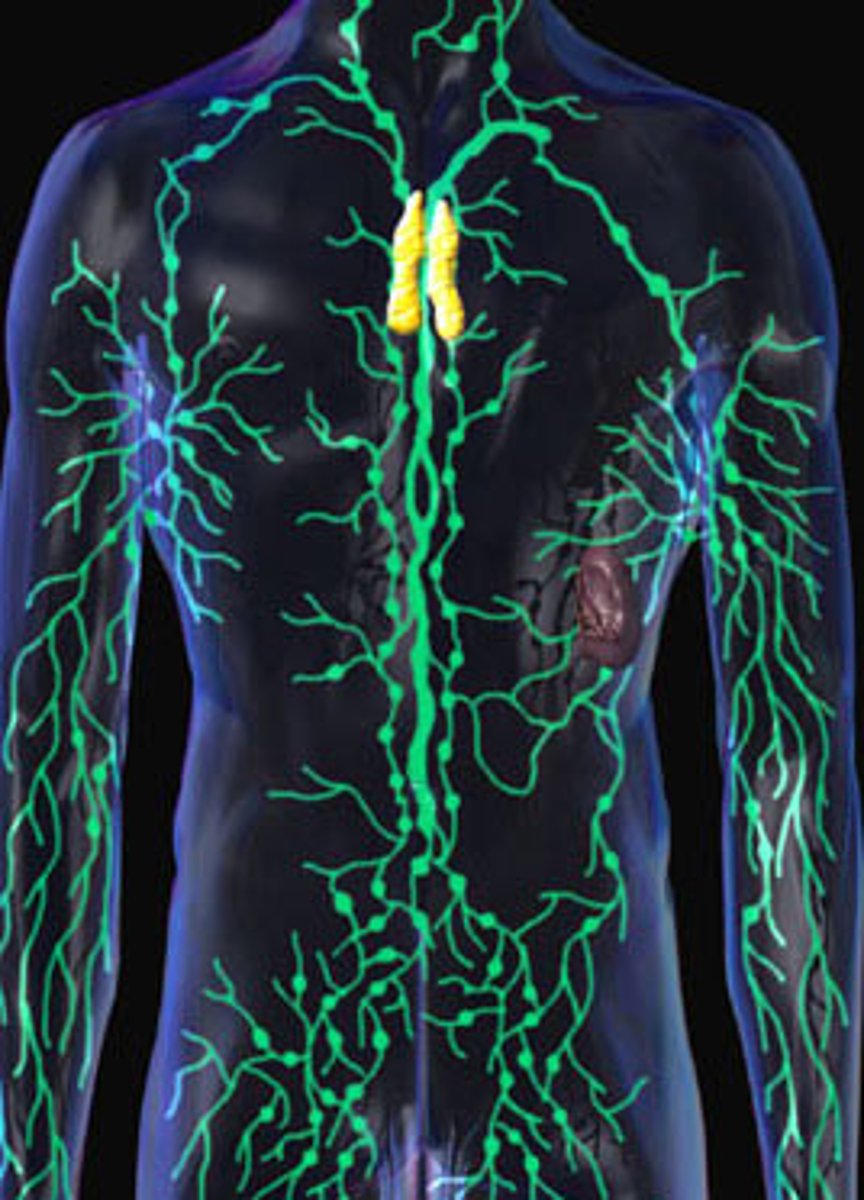
the immune system works with the lymphatic system by
draining fluid from the body tissues and delivering foreign material to the lymph nodes to be processed by the lymphocytes.
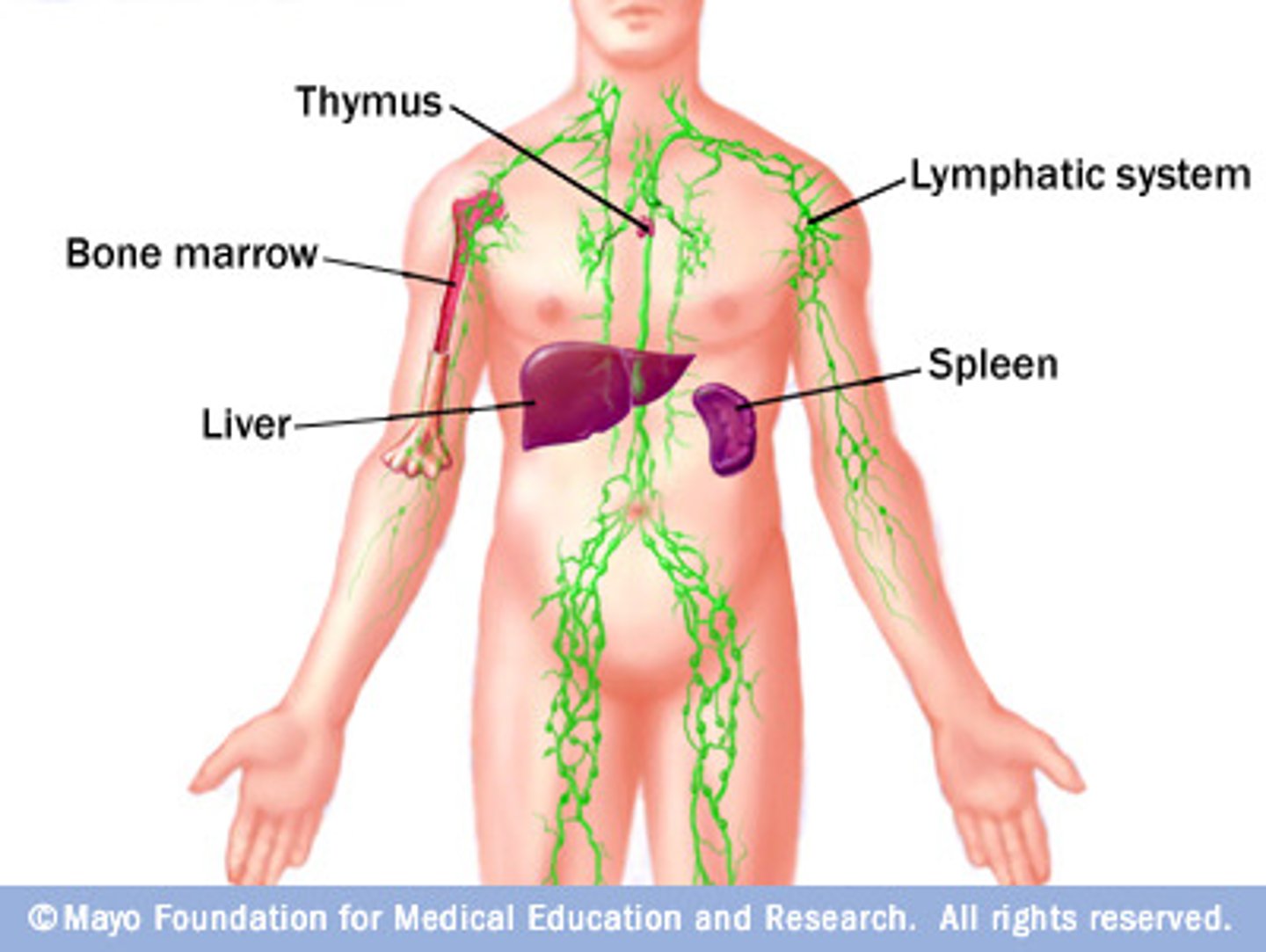
the immune system works with the skeletal system; red bone marrow by
producing white blood cells
the immune system works with the integumentary system by
being the first line of defense for most of the body.