Lab Animal Husbandry
1/52
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
53 Terms
Rabbit
Oryctolagus cuniculus
Rabbit - not rodent but a lagomorph
Size range: 3lbs to 20lbs
About 45 different breeds
Uses: Meat, fur, research & pets
Anatomy
Nictitating membrane
(Third eyelid)
Highly vascular ears
Fragile spine
Continuously growing teeth (Hypsodontic – continuously erupting like horse).
Two pairs of upper incisors
One way digestive tract- need high fiber, long stem fiber
Large cecum
Antibiotic sensitivity
Behavior
Can be housebroken – good pets
Chewers
Not heat tolerant
Not typically aggressive
Coprophagic = eat feces especially while young but throughout adulthood too
Nutrition
Need roughage: Timothy or oat hay
Ad lib
Commercial pellets
Veggies & fruits – no more than 20%
Young free feed pellets; adults measure intake
Salt addition not necessary
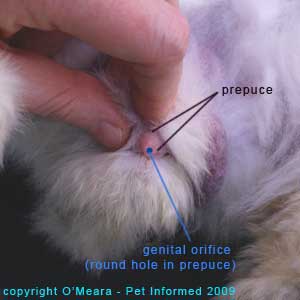
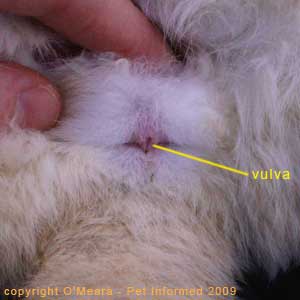
Determining Sex of a Rabbit
Breeding
Male – buck
Female – doe
young – kit
Process of giving birth – kindling
Life span- 5 to 6 years
Sexual maturity ~ 5.5 months
Induced ovulators – no estrous cycle unless in the presence of a male; they ovulate during breeding
Breeding Continued…
Gestation 29-35 days
Nesting box
Extremely rich milk
Do not disturb doe and kits first two weeks
Weaned at about 4 weeks
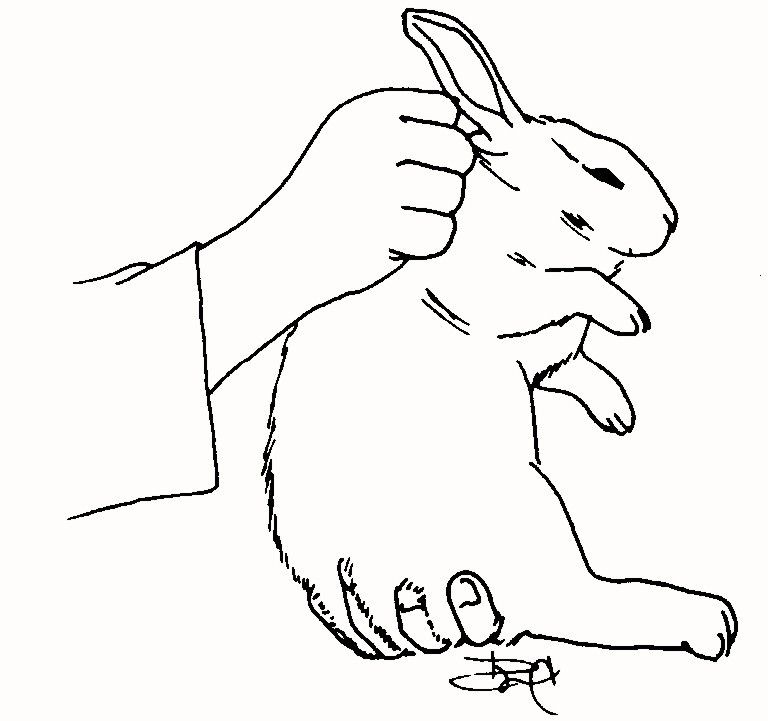
Restraint
Never pick up by the ears
Ok to scruff but always support the hindquarters
Return to cage hind end first

Pasteurella/Pasteurellosis
(Snuffles)
•Clinical Signs:
- Discharge from eyes and/or nose
- Squinting or redness of eyes
- Ears infection – resulting in head tilt
- Abscesses
•Treatment:
–Antibiotics - injections preferred over oral
–Eye and/or nose drops
–Easy to treat – hard to cure
–Many rabbits are chronically infected
Pasteurella
•Prevention:
–Quarantine new rabbits for 30 days
–Reduce stress
–Avoid overcrowding
–Avoid dietary changes
–Keep litter clean
Uterine pyometra
•Unspayed female rabbits
•Uterine bacterial infection
•Clinical signs: Older female, listless, not eating
•Diagnostics: radiographs, ultrasound exploratory surgery
•Treatment: surgery
•Prevention – spay early; If breeding the
rabbit, spay when breeding life is over.
Trichobezoars
(Hairballs)
•Rabbits are clean and groom frequently
•Clinical signs: Not eaten in 24 hrs,
•Diagnostics: radiographs may be helpful
•Treatment: Drugs early on to change gut motility, or surgery (50% mortality rate)
•Prevention: High fiber diet; hair ball medication; frequent brushing, enzymes
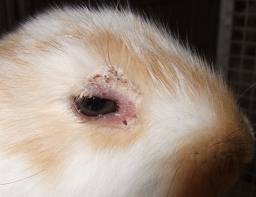
Skin Diseases
•Bacterial Infections: Treat with Antibiotics
–Live active culture yogurt
•Ringworm: Treat with topical medication, oral medication or medicated shampoos
•Fleas: Can use products safe for cats
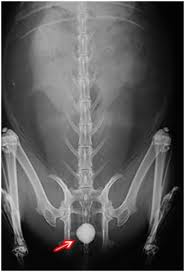
Cystic Calculi
(Bladder Stones)
•Clinical Signs:
Frequent urination, straining to urinate
Blood in the urine.
•Treatment: Surgical Removal
•Prevention: Less pellets, more fiber in the diet.
Parasites
•Mange (walking dandruff) – seen as hair loss and dandruff Diagnosis by skin scraping Treatment- medicated shampoo
•Ear mites: Dark crusty material in ears, scratching and shaking head – injectable or topical medication
•Coccidia (intestinal): Fecal testing to find - medication
Guinea Pig
Cavia porcellus
•Rodent - More closely related to porcupines and chinchillas
•Average weight 750 grams
Anatomy Guinea Pig
•No tail
•One pair of mammary glands
•Only pocket pet with premolar teeth
•Herbivore
•Open rooted continuously growing teeth (hypsodont)
•Born precocious:
–Born with teeth
–Born with eyes open
–Born with fur
•Heavy body weight for size
•Susceptible to Bordetella -respiratory disease
Behavior
•Seldom bite or scratch
•Respond well to attention
•Can be messy!
•Can’t climb – burrowing animals
•Can cause allergies in people
•Can be housed together
Nutrition
•Quality guinea pig pellets with Vit C
•Ad lib Timothy Hay
•Supplement with kale, cabbage, cilantro, etc and citrus daily
•Vitamin C required
–Scurvy otherwise
•Prone to obesity
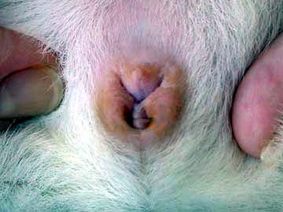
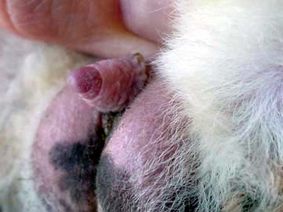
Determining the Sex of Guinea Pig
Breeding
•Average life span 5+ years
•Males are boars; Females are sows
•Puberty: very early in life
•Females need to be bred early in life, before 6-8 months of age – pelvic symphysis fuses
•Gestation ~ 59-73 days
Young are “precocious”
Restraint
•Do not scruff
•Support entire body
•Use towel if needed
Diseases: Scurvy
•Vitamin C deficiency
•Clinical Signs:
–anorexia; swollen, painful joints; bleeding from gums
•Treatment:
–Supplement with Vitamin C injections
–Improve diet
–Add Vitamin C to water
G.Pig Diseases: Dystocia and Pregnancy Toxemia
•Dystocia (difficulty birthing)
–Must be bred before 6-9 months of age
•Pregnancy Toxemia
–Toxemia seen in obese guinea pigs during late pregnancy.
–Prevention includes reducing stress during pregnancy and correct diet.
Guinea Pig Medical Issue - Hyperthermia
•Hyperthermia
–Temperatures over 80 degrees and humidity over 70%.
–Signs: panting, slobbering, lethargy, convulsions
–Treatment: cool water spray or bath
Hamster
• Mesocricetus auratus
–desert animal originally from the middle east
•In general, can be the most aggressive of all pocket pets
Anatomy
•Well developed cheek pouches
•Flank glands
•Lots of loose skin
•Hibernate
•Fatal reaction to some antibiotics
•Blunt noses
•Concentrated urine
Behavior
•Pugnacious (quick to quarrel)
•Nocturnal
•Escape artists
•Females cannot be housed with others (solitary animals)
•Nest builders
Hoard food
Nutrition
•Prone to obesity
•Hamster blocks
•Blunt nose, must put food in cage not in feeder troughs
•Need fresh water
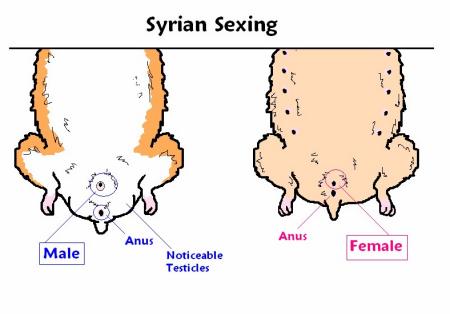
Determining Sex of Hamsters
Breeding
•Lifespan 18 - 24 months
•Puberty at 6 - 8 weeks
•Gestation ~ 16-18 days
•Litter size 6 - 8
•Weaned at 3 weeks
•Don’t disturb first 2 weeks – may cannibalize young
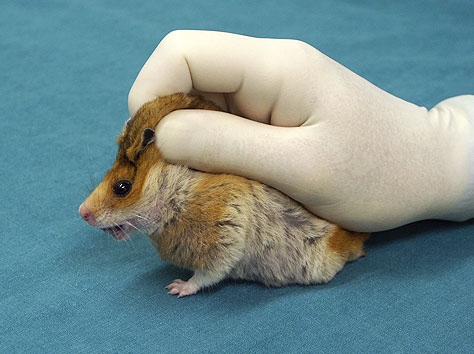
Restraint
•Scruff !
Hamster Common Diseases
•Pneumonia:
–Caused by Streptococcus or Pasteurella
–Open mouth breathing, discharge from eyes and nose, wheezing. Often die, even when treated.
•Proliferative Ileitis (wet tail)
–Often seen between 3 and 6 weeks of age
–Clinical Signs: lethargy, anorexia, diarrhea, wet anal area
–Usually fatal
Common Diseases
•Mange:
–More susceptible to demodectic (demodex = mite)mange than any other pocket pet.
–Clinical signs: alopecia, scaly skin and pruritic
–Treated with medicated shampoo
•Fractures:
–Leg fractures are common from injuries on exercise wheels.
–May heal on their own, or may need amputation
Rat
Rattus norvegicus
–Rodent
–Quiet, intelligent, easily trained
–Nocturnal
–Burrow

Anatomy
•No gallbladder
•Open rooted incisors (hypsodont)
•Extensive mammary tissue
•Males have an os penis
•Harderian gland behind eyeball secretes porphyrin tears
•Average weight 350g
•Altricial
Nutrition
•Commercial diets
–Rodent blocks
•Omnivores – will eat anything
•No supplements
•Water in sipper bottles
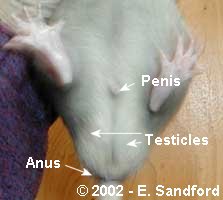
Determining Sex of Rats
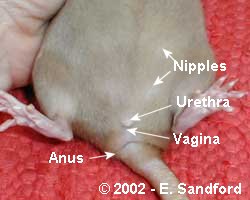
Sexing Young Rats

Breeding
•Life span 2 to 3 years
•Puberty at 50 to 60 days
•Gestation 21 days
•Litter size 7 to 11
•Wean at 21 days
•Pinkies/pups

Restraint
•Do not scruff
•Hold around neck and thorax, but do not squeeze too hard
•Can pick up by base of tail for short period
•Support the body

Common diseases
Mycoplasmosis (respiratory disease)
•Highly contagious
•Clinical Signs: Sneezing, nasal discharge, eye discharge, labored breathing
•Treatment: Long term antibiotics
•Prevention: Purchase from reputable breeder; Clean environment, good ventilation
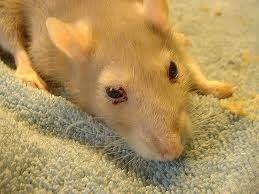
Sialodacryoadenitis
•Clinical Signs: red tear staining around eyes and nose, facial swelling, exophthalmos (bulging eyes)
•Causes: coronavirus
•Treatment: supportive care, antibiotics
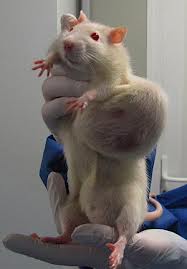
•Mammary Neoplasia:
–Frequently develop tumors. Mammary tissue covers most of the body, so lumps can appear anywhere.
–Grow quite large , are uncomfortable and may ulcerate and become infected.
–Surgical removal is necessary
Mouse
Mus musculus
•Mouse
•Rodent – world wide, many varieties
Anatomy
•Harderian gland
•Small size 25-40 grams
•Open rooted incisors - hypsodontic
•Extensive mammary tissue
•Fecundity – one pair plus one year equals one million
•Altricial
Behavior
•Timid
•Territorial
•Escape prone
•Social order poorly understood
•Will bite when handled roughly
•Nocturnal
Nutrition/Housing
•Metal or plastic cages with wire mesh
•Water bottles
•Bedding & nesting materials
•Enrichment
•Commercial diets
•No supplements
Anogenital Distance
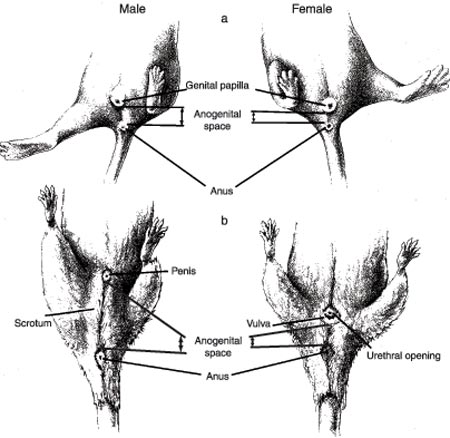
Detrmining Sex of Mice
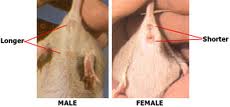
Breeding
•Life span 2 – 3 years
•Puberty at 28 to 40 days
•Gestation period 19-21 days
•Litter size 6 – 12
•Weaned at 21 days

Restraint
•Scruff and stretch
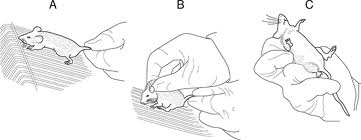
Common Diseases
•Mammary Neoplasia – same as rats
•Mycoplasmosis – same as rats
•Viral Diseases: more a problem is laboratory colonies than in pet mice
•Antibiotic toxicities: Procaine and streptomycin are fatal to mice