Image Acquisition Errors
1/47
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
48 Terms
What is an important step in analysis of the image data?
Recognizing exposure filed borders
If a PSP is unable to recognized an exposure field border, the image analysis data will also include all the information _________ that border
Outside
Inappropriate collimation margins and/or _________ may also result in both histogram and rescaling errors
Beam alignment

Is this single exposure field ideal, permitted, or inappropriate?
Ideal

Is this single exposure field ideal, permitted, or inappropriate?
Permitted

Is this single exposure field ideal, permitted, or inappropriate?
Inappropriate

Is this beam alignment correct or inappropriate?
Correct

Is this beam alignment correct or inappropriate?
Correct
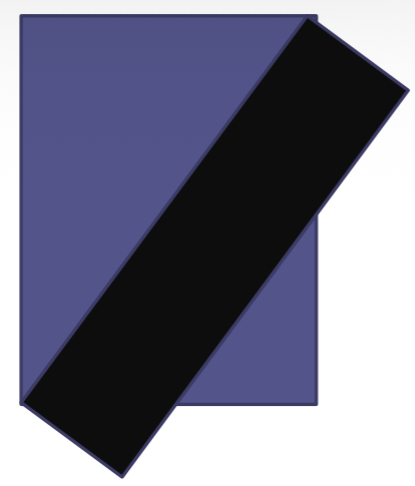

Is this beam alignment correct or inappropriate?
Inappropriate
For appropriate multiple field distribution, the field must be:
center to plate segment
collimation must be “clean” with margins between fields and between edge of field and plate’s edge
What do acceptable multiple fields look like?
symmetrical field distribution
clean collimation between fields
no overlap
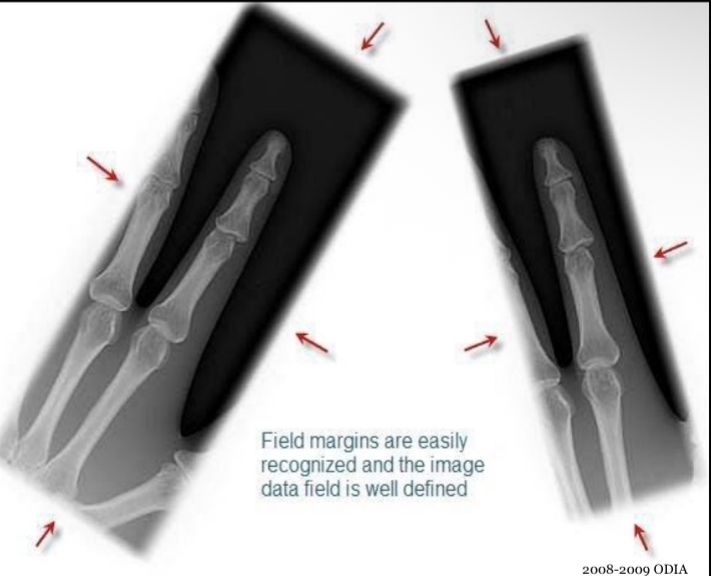
What is this image showing?
clearly demonstrates that exposure field borders, collimation borders, were recognized
everything outside the black area is clear, which shows that the borders were recognized

What is this rescaling error occurred by?
The image incorporate the extra exposure in the form of scatter and off-focus radiation
Prior to image creation, the exposure values extracted from the PSP are subject to a process known as?
Quantization
Quantization is a unique ______ assigned to each sample or pixel
Value
What can quantization also be referred to as?
Sampling frequency
Both sampling (time between samples) and quantization are the processes of?
Analog-to- digital conversion (ADC)
Histograms graphically represent a collection of exposure values extracted from the _______
Receptor
An image is created after a histogram of the extracted image data is analyzed using one of two formats:
priori histogram analysis
neural histogram analysis
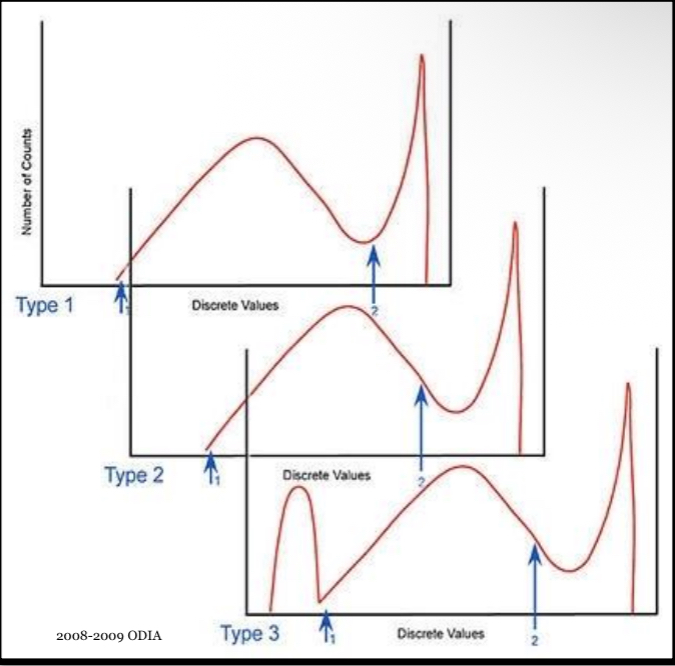
Priori histogram analysis
three types
involves comparing the exposure data set to a single standardized exposure data set fir a matching examination
Where does the standardized data set come from for priori histogram analysis?
Derived during experiments that used like subjects under ideal conditions
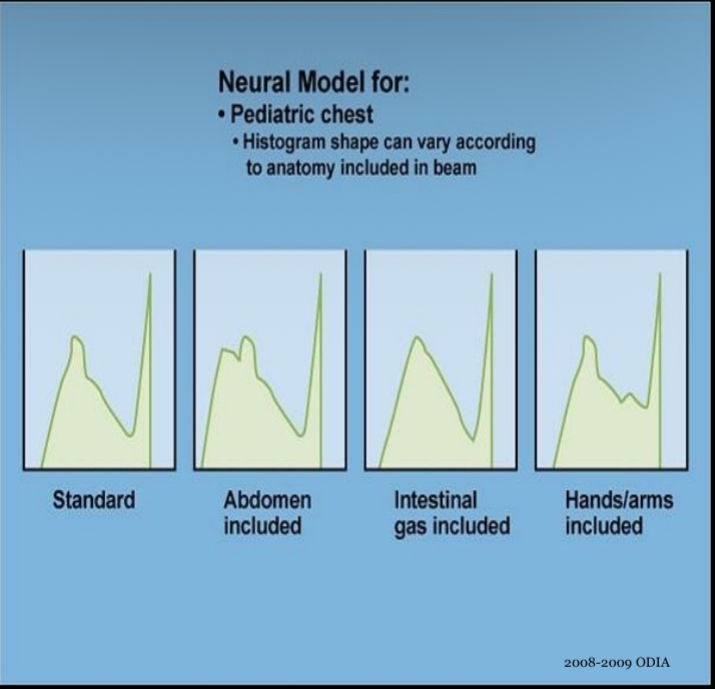
Neural histogram analysis
data extracted from the PSP are compared to two or more pre-defined histograms
an image is created after extracted image data is matched to one of the pre-defined histograms
What are some examples of histogram analysis errors?
incorrect anatomic menu selection (by user)
exposure field not detected
unexpected material in data set
large exposure error (plate saturation)
inappropriate rescaling (light or dark image)
The predetermined values used to create the image are known as?
Values of interest
The process of matching the captured image values to a standardized set of values is called?
Automatic rescaling
What does automatic rescaling permit for?
The consistent output of image data and image display appearance even when errors in exposure technique are present
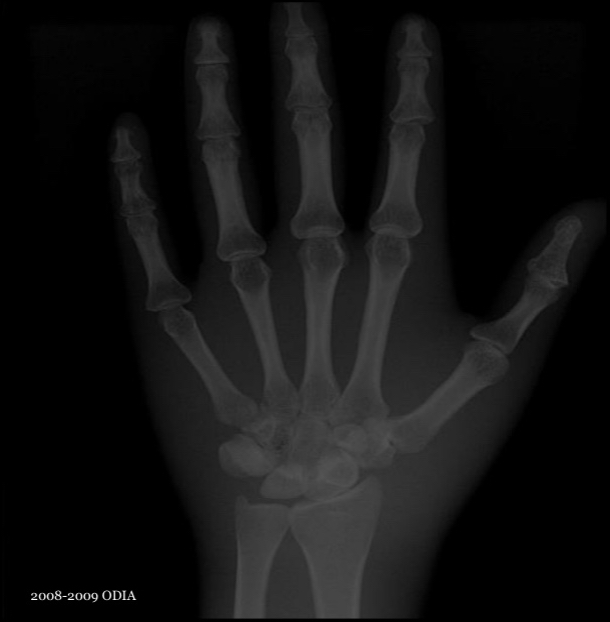
What is this image showing?
Excessive exposure without rescaling
What is this image showing?
Excessive exposure with rescaling
Low intensity radiation response: background radiation:
cassette-based system is constantly refreshed
cassette-less system plate is storage phosphor
stores background exposure
PSP responds to an exposure as low as _____ uR
60
Background radiation is between ____-_____ uR/day
40-80
Imaging plates unused for more than ____ hours should be erased
48
Scatter radiation is much _______ intense than background radiation
More
When is scatter radiation produced?
During Compton interaction
Compton reaction
a primary photon interacts with an outer shell electron and changes direction
not part of useful beam
Ways at reducing scatter include:
beam limiting
optimal exposure
grid use
Beam limiting
As beam is restricted, fewer primary photons are emitted from the tube and collimator, thus creating fewer scattered photons
What are some examples of beam limiting?
Aperture diaphragms, cones/cylinders, and collimators
Overexposure produces _____ scatter radiation
More
What is one of the principal factors affecting the amount of scatter radiation produced?
kVp
As kVp _____ , the % of primary photons that will undergo scattering also increases
Increases
With digital radiography, _____ should be manipulated in order to compensate for grid use rather than mAs
kVp
Changes in ____ will not greatly affect radiographic contrast as it did with film/screen combinations
kVp
With digital imaging, a ___________ that occurs when the grid frequency is approximately equal to the Nyquist frequency
Grid error
Moire effect
the grid line is running in the sam direction as the movement of the laser beam that is scanning the imaging plate
occurs with digital image receptor systems when the grid lines are captured and scanned parallel to the scan lines in the imaging plate readers
To avoid the Moire effect, use a high-frequency grid of ____-____ lines per inch when using a stationary grid when a stationary grid is needed
103-178
The maximum spatial resolution in digital imaging is equal to the ________, which is ½ x the pixel pitch (mm)
Nyquist frequency
When does aliasing occur?
when the nyquist criterion is violated
when the spatial frequency exceeds the nyquist frequency
the incoming data would be sampled less than twice per cycle
aliased = misrepresentation of signal frequency