prefrontal and anterior temporal lobes chapter 28
1/45
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
46 Terms
association cortex
cerebral cortex areas not directly involved with sensation or movement
prefrontal cortex divided into 3 areas
named for their anatomic location
-latereal prefrontal association cortex
-medial prefrontal association cortex
-ventral prefrontal association cortex
executive function
refers to a spectrum of abilities including working memory, judgment, planning, sequencing activity, inhibition, task switching, abstract thought, behavioral regulation, decision-making, and initiation
sustained attention
the ability to attend to an activity over time
selective/prioritization attention
the ability to attend to important information and ignore distractions
divided attention
the ability to attend to important information and disregard distractions
shifting/switching attention
the ability to change from one task to another
goal directed behavior (executive function): lateral prefrontal cortex
deciding on a goal
planning how to accomplish the goal
executing a plan
monitoring the execution of the plan
divergent thinking: lateral prefrontal cortex
the ability to conceive of a variety of possibilities
lateral prefrontal cortex lesion (impaired executive function)
-unable to set goals, plan, execute a plan, or monitor the execution of a plan
-have little effect on intelligence as measured by conventional intelligence tests
despite the ability to perform normally on conventional intelligence tests
people with prefrontal lesions function poorly in daily life because they lack goal direction and behavioral flexibility
medial prefrontal association cortex
-Involved in emotions, self-awareness, and motivation
-Identifies emotional stimuli and generates and perceives emotions
-Perceives others' emotions and makes assumptions about what other people believe and their intentions
emotion
is short-term subjective experience
medial prefrontal association cortex lesions
-cause apathy and lack of emotions and insight
-people report not feeling an emotions
-abnormal processing here (with BG and thalamus) impairs understanding of other's emotions, beliefs, and intentions
the emotion loop
-involves multiple brain areas
-links emotion, cognitive, and motor systems
-involved in reward-seeking behavior; concerned with finding pleasure
regulating emotions
-involves multiple brain areas
-loss of normal regulation of emotions causes emotional lability
emotional lability
abnormal, uncontrolled expression of emotions
3 aspects of emotional lability
-abrupt mood shifts
-involuntary, inappropriate emotional expression in the absence of subjective emotion
-emotion is triggered by nonspecific stimuli unrelated to the emotional expression
motivation
a reward seeking and an avoidance seeking pathway
-ventral striatum lesions cause behavioral disturbances
motivation: reward seeking pathway
reward pathway comprises dopamine neurons
dopamine
the motivation neurotransmitter all natural stimuli that reinforce behavior and all drugs of abuse increase dopamine in the ventral striatum
addiction
loss of behavioral control in response to a stimulus combined with the continued use of a substance, regardless of the negative consequences
motivation: avoidance seeking pathway
People can also be motivated to avoid undesired outcomes
ventral prefrontal association area
connects with areas regulating mood and affect
-part of our decision-making process involves imaging consequences and then attending to resultant emotional signals
for people with lesions in the social behavior loop
poor judgement and defective social intelligence cause severe problems in social function, employment, interpersonal relationships, and social status
thoughts and emotions
influence the functions of all organs
3 systems create stress response
-somatic nervous system
-autonomic nervous system
-neuroendocrine system
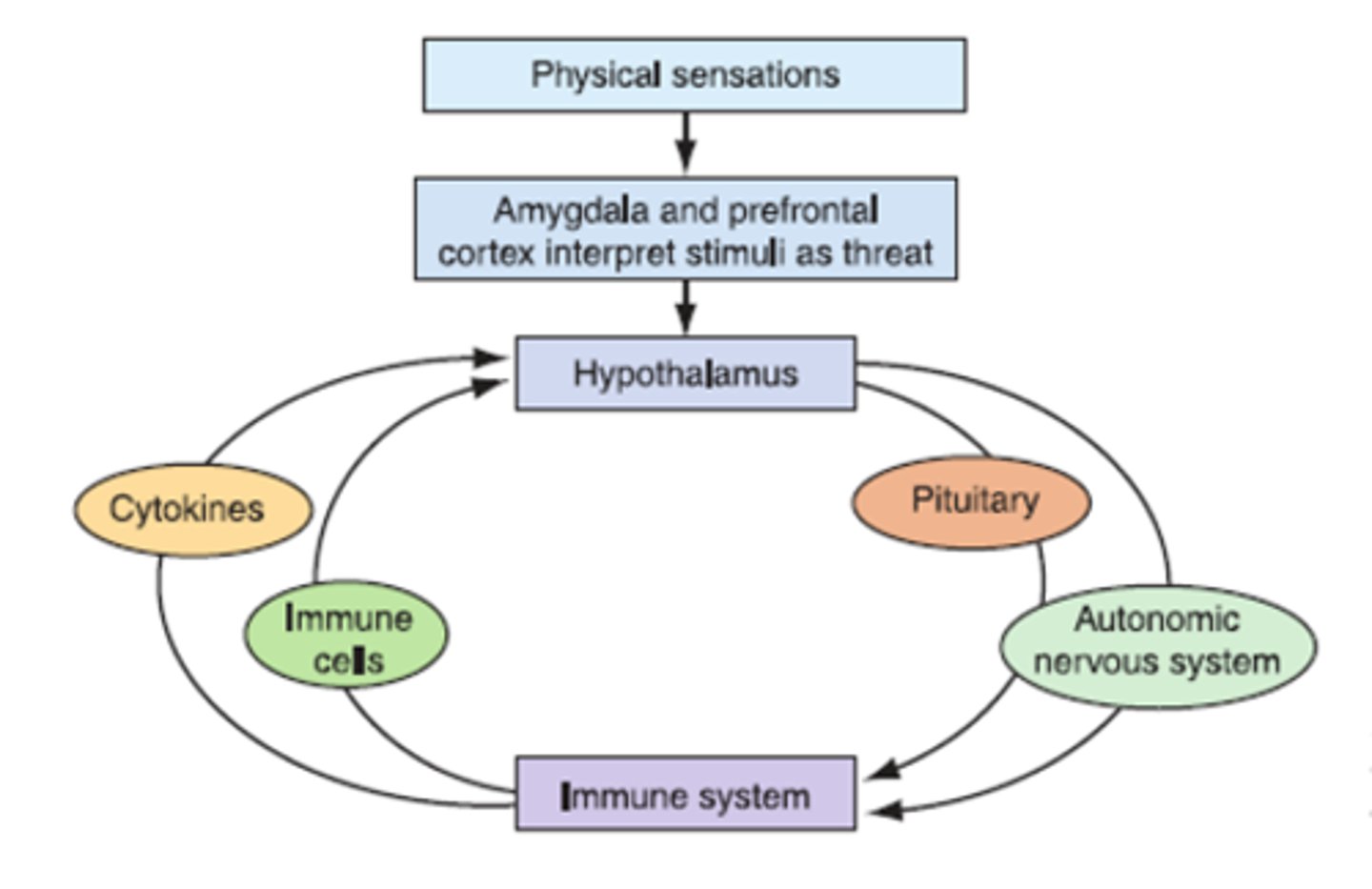
neurologic/psychiatric signs and symptoms
-delirium
-delusions
-hallucinations
-mania
-depression
-anxiety
-obsessive compulsive though and behaviors
-post traumatic stress disorder (PTSD)
-somatic symptom disorder
-autism spectrum disorders
-bipolar disorder
-schizophrenia
delirium
a transient mental disorder with a relatively rapid onset, a course that typically fluctuates, and is of brief duration (hours to weeks, typically days)
delirium symptoms
-reduced ability to maintain attention to external stimuli and to appropriately shift attention to new external stimuli, and disorganized thinking as manifested by rambling, irrelevant, or incoherent speech
-acute onset
-level of consciousness affected
delusions
are false beliefs, despite evidence to the contrary
hallucinations
sensory perceptions experienced without corresponding sensory stimuli
mania
is excessive excitement, euphoria, delusions, and overactivity
-racing thoughts, a disregard for consequences, and energetic behaviors typify mania
depression
a syndrome of hopelessness and a sense of worthlessness, with aberrant thoughts and behavior
-frequently occurs in dementia, parkinsons disease, multiple sclerosis, epilepsy
depression is linked to
neurotransmitter and neural activity abnormalities rather than to structural abnormalities
-people with depression have reduced levels of serotonin metabolites in their cerebrospinal fluid
anxiety
-the feeling of tension or uneasiness that accompanies anticipating danger
-autonomic system is overactive, skeletal muscles are tense, and the person is excessively alert
panic disorder
an episode of intense fear that begins abruptly and lasts 10-15 minutes
symptoms of panic disorder
-pounding heart
-rapid heart rate
-sweating
- feeling of choking
- difficulty breathing
-nausea
-feeling faint or light headed
-fear of fainting, going crazy, or dying
obsessive-compulsive disorder
characterized by persistent upsetting thoughts and the use of compulsive behavior in response to the obsessive thoughts
post traumatic stress disorder
-can develop in survivors of war, physical and sexual assault, abuse, accidents, disasters, and other serious trauma
people with PTSD
re-experience the original event in flashbacks or nightmares, avoid stimuli linked to the trauma and are hyperaroused
somatic symptom disorder
the disorder is psychologic with the patient subconsciously generating the problem to avoid responsibilities or conflict, or to demand care and emotion support from others
autism spectrum disorders
characteristics of autism spectrum disorder include a range of impaired social skills, restricted interests, and repetitive behaviors
bipolar disorder
-formerly called manic depression
-causes extreme mood swings that include emotional highs and lows
-mood swings alter activity levels, judgement, behavior, thinking and sleep
schizophrenia
-is a group of disorders consisting of disordered thinking, delusions, hallucinations, lack of motivation, apathy, and social withdrawal
-executive function, including planning, goal-orientation, and behavioral inhibition are impaired
-poor working memory interferes with considering possible alternatives
traumatic brain injury
people show poor judgment, decreased goal directed behavior, memory deficits, slow information processing, attentional disorders, and poor divergent thinking