Microbio - Exam 3
0.0(0)
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/178
Earn XP
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
179 Terms
1
New cards
phenotypic methods
the observation of the microscopic and macroscopic morphology, physiology, and biochemical properties of a microbe
2
New cards
immunologic methods
the analysis of a microbe using antibodies, or of a patient’s antibodies using prepackage antigens
3
New cards
genotypic methods
the analysis of a microbe’s DNA or RNA
4
New cards
point-of-care diagnosis
tests that can performed at the bedside so that patient care can continue without delay
5
New cards
viable nonculturable (VNC) microbes
microbes that cannot be grown in the lab and are currently being identified through studies such as the Human Microbiome Project
6
New cards
saliva and sputum
samples (2) taken from the mouth, nasopharynx, or throat (via swab)
7
New cards
aseptically via catheter or “clean catch” midstream
2 methods of urine collection from the bladder
8
New cards
swabbing or scraping
2 methods of collection from a skin lesion
9
New cards
swabbing or using a punch biopsy tool
2 methods of collection from a wound
10
New cards
sterile needle aspiration
method of collection for fluids such as blood, cerebrospinal fluid, and tissue fluid
11
New cards
1. nonnutritive maintenance media
2. buffering system
3. anaerobic environment
devices maintain collected samples in stable conditions through 3 methods
12
New cards
selective media
media type used in cases where the suspected pathogen is present in small numbers or is easily overgrown by normal biota
13
New cards
differential media
media type used to identify definitive characteristics such as reactions in blood and fermentation patterns
14
New cards
dichotomous key
a flowchart with two choices at each fork in the chart that is used for microbial identification
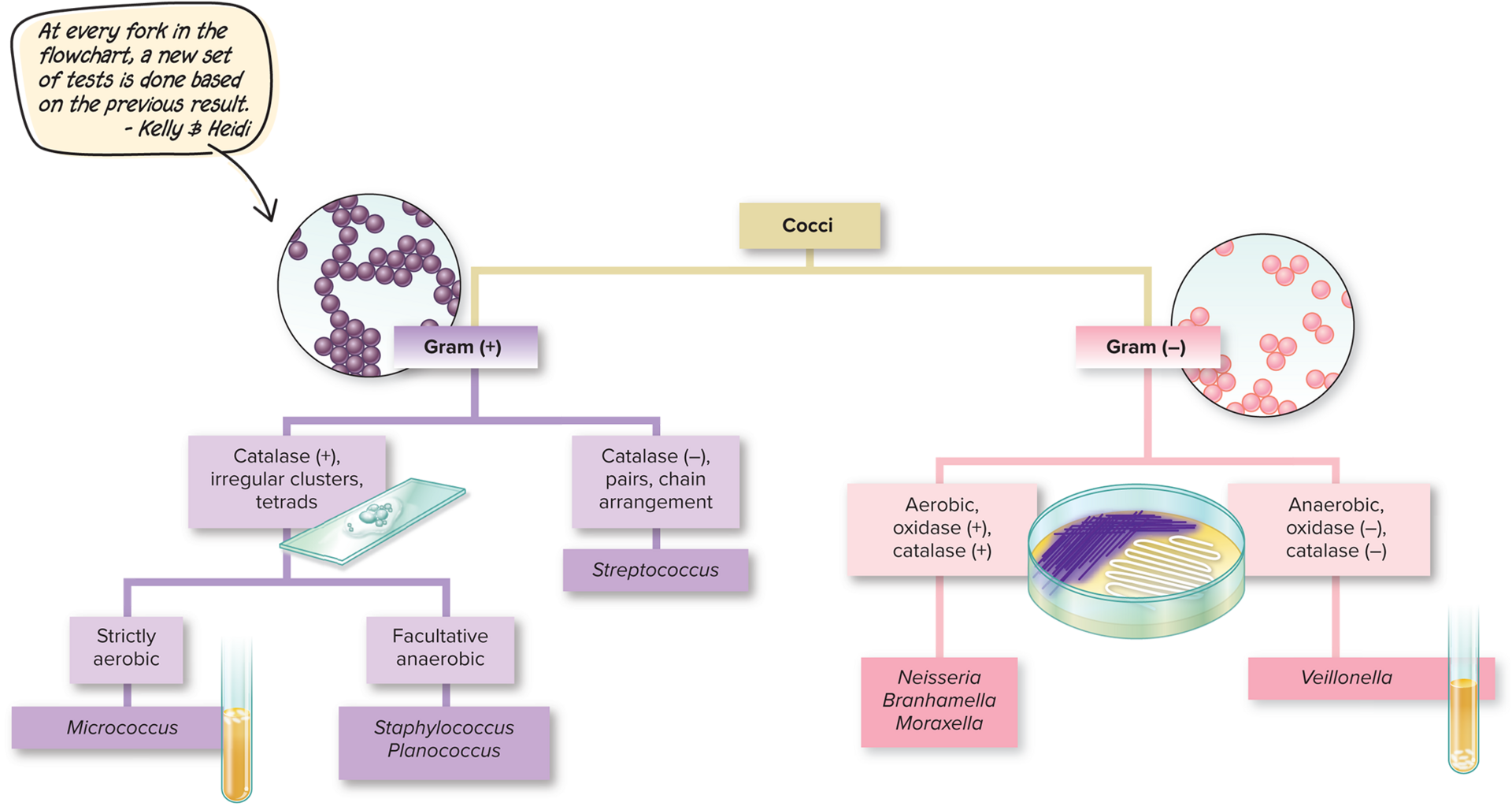
15
New cards
biochemical testing
a phenotypic testing method based on enzyme-mediated metabolic reactions that is visualized by a color change
16
New cards
antimicrobial susceptibility testing
a phenotypic testing method that incorporates a panel of commonly used antimicrobials and tests their susceptibility while identifying the pathogen
17
New cards
phage typing
a phenotypic testing method that relies on bacteriophages and is useful in identifying some bacteria (ex: *Salmonella*) and is used to trace strains in epidemics
18
New cards
1. culturing takes a minimum of 18-24 hours
2. many infectious conditions may be caused by nonculturable organisms (meaning the cultured organism is a bystander)
2 major drawbacks of phenotypic methods
19
New cards
serology
the branch of immunology that deals with *in vitro* diagnostic testing of serum
based on the principle that when a particular antigen is exposed to its specific antibody, it will fit perfectly
based on the principle that when a particular antigen is exposed to its specific antibody, it will fit perfectly
20
New cards
**false**, we test all kinds of body samples including urine, cerebrospinal fluid, whole tissues, and saliva
**T/F**: serology involves only the testing of sera
21
New cards
agglutination reactions
an immunologic testing method where the antigens are whole cells or organisms (ex: RBCs, bacteria, or viruses displaying surface antigens)
also used to determine blood compatibility and to diagnose rickettsial infections
also used to determine blood compatibility and to diagnose rickettsial infections
22
New cards
precipiation reactions
an immunologic testing method where the antigen examined is a soluble molecule
23
New cards
immunochromatography
the use of devices with antigens or antibodies embedded in matrices that detect the presence of antigens or antibodies in a sample
ex: drugstore pregnancy tests
aka “lateral flow test”
ex: drugstore pregnancy tests
aka “lateral flow test”
24
New cards
antibody titers
an antigen-antibody reaction in liquid that reveals the concentration of antibodies in a sample
determined by serially diluting serum into test tubes/wells of a microtiter plate
used to diagnose autoimmune disorders (ex: lupus) and determine past disease exposure (ex: rubella)
determined by serially diluting serum into test tubes/wells of a microtiter plate
used to diagnose autoimmune disorders (ex: lupus) and determine past disease exposure (ex: rubella)
25
New cards
titer
the highest dilution of serum that still produces agglutination
(the more a sample can be diluted and still react with antigen = greater antibody concentration = greater _____ )
(the more a sample can be diluted and still react with antigen = greater antibody concentration = greater _____ )
26
New cards
serotyping
an antigen-antibody technique to identify, classify, and subgroup certain bacteria into categories (serotypes)
uses antisera against cell antigens (ex: capsule, flagellum, cell wall)
used to identify *Salmonella* species and strains
uses antisera against cell antigens (ex: capsule, flagellum, cell wall)
used to identify *Salmonella* species and strains
27
New cards
Western blot test
an immunologic testing method for separating and identifying antigen or antibody mixtures by 2D electrophoresis in polyacrylamide gel, followed by immune labeling
28
New cards
direct testing (of FAbs)
an immunofluorescent testing method in which an unknown specimen or antigen is fixed to a slide and exposed to a FAb solution of known composition
^^+ if antibody-antigen complexes form and remain bound to the sample^^
used to identify/locate microbial antigens on cell surfaces/in tissues and identify causative agents of syphilis, gonorrhea, meningitis, etc.
^^+ if antibody-antigen complexes form and remain bound to the sample^^
used to identify/locate microbial antigens on cell surfaces/in tissues and identify causative agents of syphilis, gonorrhea, meningitis, etc.
29
New cards
indirect testing (of FAbs)
an immunofluorescent testing method that recognizes the Fc region of antibodies, known antigens are added to the test serum and the binding of fluorescent antibody is visualized through fluorescence microscopy
30
New cards
enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) test
an immunologic testing method that uses an enzyme-linked indicator antibody to visualize antigen-antibody reactions
used to detect antibodies in diseases such as AIDS
used to detect antibodies in diseases such as AIDS
31
New cards
indirect ELISA test
ELISA test that detects microbe-specific antibodies in patient sera
used for antibody screening of HIV, various rickettsial species, hepatitis A & C, and *Helicobacter*
used for antibody screening of HIV, various rickettsial species, hepatitis A & C, and *Helicobacter*
32
New cards
direct ELISA test
ELISA test that detects antigens and may be performed using the sandwich test or utilizing computer chips
33
New cards
*in vivo* testing
an immunologic testing method where an antigen is introduced into a patient to elicit some sort of visible reaction
34
New cards
tuberculin reaction
a type of *in vivo* test in which PPD is injected superficially under the skin and the area of reaction is measured
aka *Mantoux test*
aka *Mantoux test*
35
New cards
specificity and sensitivity
the most effective diagnostic tests have a high degree of these two characteristics
36
New cards
specificity
the property of a test to focus on only a certain antigen/antibody and not react with unrelated or distantly related ones
(low false-positive rate)
(low false-positive rate)
37
New cards
sensitivty
the property of a test which refers to the detection of even minute quantities of antigens/antibodies in a specimen
(low false-negative rate)
(low false-negative rate)
38
New cards
polymerase chain reaction (PCR)
a genotypic testing method that results in the production of numerous identical copies of DNA or RNA molecules within hours
can amplify the nucleic acid of bacteria, viruses, protozoa, and fungi
can amplify the nucleic acid of bacteria, viruses, protozoa, and fungi
39
New cards
real-time PCR (qPCR)
a PCR method that uses fluorescent labeling and the fluorescence is measured in real time as the reaction is running
40
New cards
multiplex PCR
a PCR method that contains primers for multiple organisms instead of just one
41
New cards
transcription-mediated amplification
a genotypic testing method that does not require temperature changes and instead uses 2 enzymes (reverse transcriptase and RNA polymerase)
42
New cards
hybridization
a genotypic testing method that matches complementary strands of nucleic acid and is used to locate a specific site or type of nucleic acid
43
New cards
probes
small fragments of single-stranded DNA or RNA that are known to be complementary to the specific sequences of DNA or RNA being studied
44
New cards
fluorescent *in situ* hybridization (FISH)
a genotypic testing method that involves the application of fluorescently labeled probes to intact cells within a patient specimen or an environmental sample
45
New cards
microarrays
a genotypic testing method that uses “chips” containing gene sequences from thousands of different possible infectious agents
46
New cards
whole-genome sequencing
a genotypic testing method that is particularly useful for rapid analysis of outbreaks and drug-resistant organisms
47
New cards
pulsed-field gel electrophoresis (PFGE)
a genotypic testing method that involves the separation of DNA fragments that are too large for conventional gel electrophoresis methods
often used in acute outbreaks of foodborne, etc. infections
often used in acute outbreaks of foodborne, etc. infections
48
New cards
mass spectrometry
an additional diagnostic technology that has been utilized to determine the structure and composition of various chemical compounds and biological molecules to provide highly accurate microbial identification within minutes
49
New cards
first line of defense
any barrier (physical, chemical, or microbiota) that blocks invasion at the portal of entry or limits access to internal tissues that is general in action
50
New cards
second line of defense
“innate immunity.” the internal system of cells, fluids, and processes (ex: inflammation and phagocytosis) that acts rapidly at the local and systemic level once the first line of defense is overcome
51
New cards
third line of defense
“adaptive immunity,” highly specific system that is only acquired as each foreign substance is encountered by lymphocytes; provides long-term immunity
52
New cards
1. body **surveillance**
2. **recognition** of foreign material
3. **destruction** of foreign-demmed entities
roles of the immune system (3)
53
New cards
markers
any trait or factor of a cell/virus/molecule that makes it distinct and recognizable
aka *antigens*
aka *antigens*
54
New cards
self
natural markers of the body that are recognized by the immune system (no threat)
55
New cards
nonself
molecules recognized by the immune system as containing foreign markers indicating a need for immune response
56
New cards
pathogen-associated molecular patterns (PAMPs)
molecules on the surface of microbes that are not present on host cells that mark the microbes as foreign
57
New cards
pattern recognition receptors (PRRs)
molecules on the surface of host defense cells that recognize PAMPs
58
New cards
mononuclear phagocyte system (MPS)
collection of monocytes and macrophages that are scattered through the extracellular spaces that function to engulf and degrade foreign molecules
59
New cards
lymphatic system
the compartmentalized network of cells/vessels/organs that serve as sites for the development of immune cells and reactions
includes: spleen, thymus, lymph nodes, etc.
includes: spleen, thymus, lymph nodes, etc.
60
New cards
lymphatic, circulatory
body systems that participate in immunity (2)
61
New cards
lymphatic fluid
plasma-like liquid formed when certain blood components move out of the blood vessels into extracellular spaces and diffuse & migrate into the lymphatic capillaries
transports WBCs, fats, cellular debris, etc.
transports WBCs, fats, cellular debris, etc.
62
New cards
lymphatic vessels
structures similar in appearance to thin-walled veins of the circulatory system through which lymph flows from the extremities to the heart and moves by the contraction of skeletal muscles
63
New cards
primary lymphatic organs
organs that are the sites of immune cell birth & maturation
includes: red bone marrow, thymus
includes: red bone marrow, thymus
64
New cards
secondary lymphatic organs
organs that are where immune cells are activated, reside, or carry out their functions
includes: SALT, MALT, GALT, lymph nodes, spleen, tonsils, Peyer’s patches
includes: SALT, MALT, GALT, lymph nodes, spleen, tonsils, Peyer’s patches
65
New cards
red bone marrow
the site of blood cell production, located in flat bones and the ends of long bones
66
New cards
thymus
butterfly-shaped organ near the tip of the sternum that is the site of T cell maturation
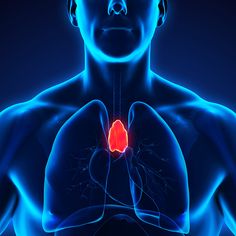
67
New cards
lymph nodes
bean-shaped organs that are clustered along lymphatic channels and large blood vessels of the thoracic & abdominal cavities that filter out materials in the lymph and provide cells for immune reactions
68
New cards
cortex
the outer rim of lymph nodes
69
New cards
paracortical area
the inner area of lymph nodes that contains T lymphocytes
70
New cards
medullary sinus
the inner area of lymph nodes that contains B lymphocytes and macrophages
71
New cards
spleen
the lymphoid organ in the upper left quadrant of the abdominal cavity that filters pathogens from the blood
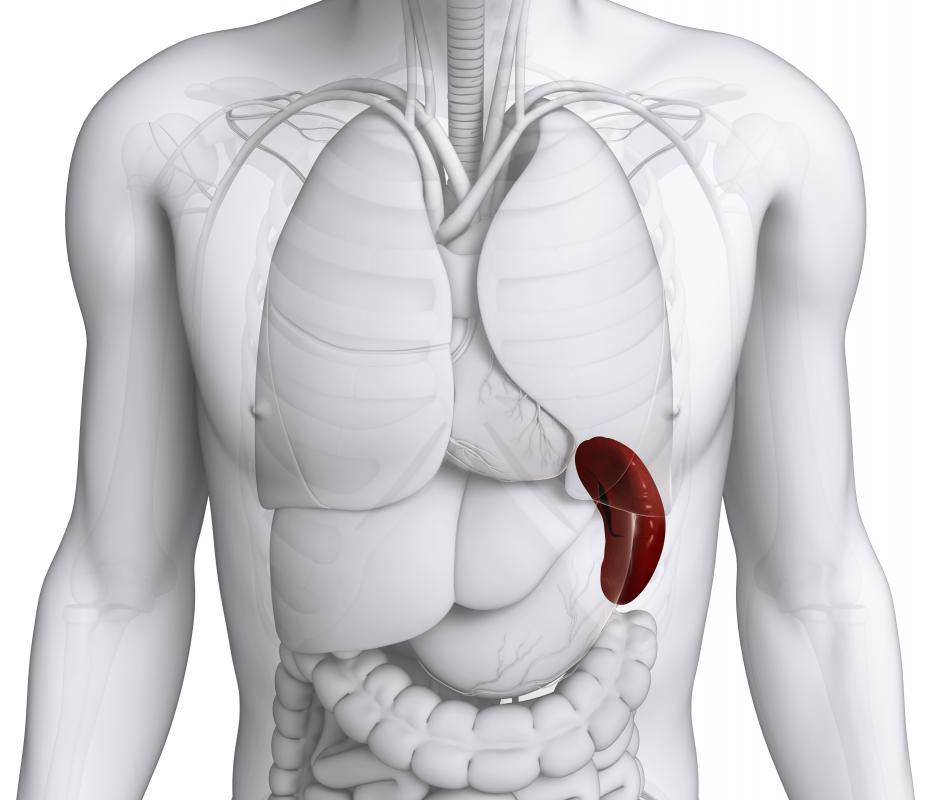
72
New cards
skin-associated lymphoid tissue (SALT)
contains B & T cells and underlies some skin surfaces
73
New cards
mucosa-associated lymphoid tissue (MALT)
contains B & T cells and underlies most mucosal surfaces
74
New cards
gut-associated lymphoid tissue (GALT)
a collection of lymphoid tissue in the GI tract
includes: appendix, lacteals, Peyer’s patches
includes: appendix, lacteals, Peyer’s patches
75
New cards
tonsils
a ring of lymphoid tissue in the pharynx that provides an active source of lymphocytes
76
New cards
Peyer’s patches
compact aggregations of lymphocytes in the ileum of the small intestine
77
New cards
whole blood
liquid connective tissue consisting of RBCs and WBCs suspended in plasma
78
New cards
hematopoiesis
the production of blood cells
79
New cards
differentiation
the process by which stem cells change by being subjected to a variety of growth factors and hormones
80
New cards
leukocytes
WBCs, primarily infection-fighting
81
New cards
granulocytes
leukocytes that have dark staining granules
includes: neutrophils, eosinophils, basophils, mast cells
includes: neutrophils, eosinophils, basophils, mast cells
82
New cards
agranulocytes
leukocytes that do __not__ have granules but have large nuclei
includes: B & T cells, macrophages, monocytes
includes: B & T cells, macrophages, monocytes
83
New cards
cytokine
a regulatory chemical, released by the immune system cells, that serves as a signal between different cells
84
New cards
pro-inflammatory cytokine
cytokine category that encourages adaptive and innate immune responses
85
New cards
anti-inflammatory cytokine
cytokine category that discourages adaptive and innate immune responses
86
New cards
vasodilators/vasoconstrictors
cytokine categories (2) that change the diameter of blood vessels or their permeability
87
New cards
growth factor
cytokine category that regulates lymphocyte growth or activation
88
New cards
T cell
lymphocyte with cell-mediated immunity that assist B cells
89
New cards
B cell
antigen-presenting lymphocyte that differentiates into plasma cells and releases antibody
90
New cards
respiratory, urinary, digestive, integumentary
body systems (4) that participate in the first line of defense
91
New cards
phagocytosis, fever, inflammation, antimicrobial products
the major categories (4) of the second line of defense
92
New cards
neutrophils
general purpose phagocytes that are found in high numbers in bacterial infections
93
New cards
macrophages
WBC derived from monocytes that leaves circulation and goes to the tissues; important in nonspecific phagocytosis, the regulation/stimulation/cleanup after immune responses
94
New cards
chemotaxis
1st step of phagocytosis
phagocytes migrate to the region of inflammation due to attraction by a gradient of stimulant products from parasite and host tissue at the site of injury
phagocytes migrate to the region of inflammation due to attraction by a gradient of stimulant products from parasite and host tissue at the site of injury
95
New cards
adhesion
2nd step of phagocytosis
phagocytes use their PRRs to recognize PAMPs, causing the 2 to stick together
phagocytes use their PRRs to recognize PAMPs, causing the 2 to stick together
96
New cards
engulfment
3rd step of phagocytosis
phagocytes make contact with their “prey” and extend pseudopods that enclose the cells/particles in a pocket
phagocytes make contact with their “prey” and extend pseudopods that enclose the cells/particles in a pocket
97
New cards
phagosome formation
4th step of phagocytosis
a vacuole (phagosome) internalizes the cells/particles and secretes more cytokines to further amplify the innate response
a vacuole (phagosome) internalizes the cells/particles and secretes more cytokines to further amplify the innate response
98
New cards
phagolysosome formation and killing
5th step of phagocytosis
lysosomes migrate to the phagosome and fuse with it to create a phagolysosome
granules with antimicrobial chemicals are released into the phagolysosome to poison & dismantle the material inside
lysosomes migrate to the phagosome and fuse with it to create a phagolysosome
granules with antimicrobial chemicals are released into the phagolysosome to poison & dismantle the material inside
99
New cards
destruction
6th step of phagocytosis
involves 2 systems of chemicals that act on the microbes in the phagolysosome
* oxygen-dependent system (reactive oxygen products)
* enzymes
involves 2 systems of chemicals that act on the microbes in the phagolysosome
* oxygen-dependent system (reactive oxygen products)
* enzymes
100
New cards
elimination
7th step of phagocytosis
small bits of undigestible debris are released via exocytosis
small bits of undigestible debris are released via exocytosis