ANP Final Review
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/133
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
134 Terms
1
New cards
anatomy
study of the structure and shape of the body's and its parts and relationships to one another
2
New cards
physiology
how the body and its parts work and function
3
New cards
levels of structural organization
atoms -tiny building block
molecules- two or more atoms
cells- smallest units of all living things
tissues- groups of similar cells that have a common function
organs- structure composed of two or more tissue types that perform a specific function for the body
organ system- groups of organs that cooperate to accomplish a common purpose
organism- organ systems make up the living body or the organism
molecules- two or more atoms
cells- smallest units of all living things
tissues- groups of similar cells that have a common function
organs- structure composed of two or more tissue types that perform a specific function for the body
organ system- groups of organs that cooperate to accomplish a common purpose
organism- organ systems make up the living body or the organism
4
New cards
integumentary system
external covering of the body - skin, hair, nails
functions: waterproofs the body, cushions and protects deeper tissue, regulate body temp, perspiration, pressure, pain receptor, and alert body surface
functions: waterproofs the body, cushions and protects deeper tissue, regulate body temp, perspiration, pressure, pain receptor, and alert body surface
5
New cards
skeletal system
bones, cartilage, ligaments, and joints
functions: supports body, framework, protective function (skull)
functions: supports body, framework, protective function (skull)
6
New cards
muscular system
skeletal muscles
functions: movement, work hand and hand with the skeletal system
functions: movement, work hand and hand with the skeletal system
7
New cards
nervous system
brain, spinal cord, nerves, sensory receptors
functions: control system, responds to stimuli from the inside and outside
functions: control system, responds to stimuli from the inside and outside
8
New cards
endocrine system
endocrine glands, pituitary, thyroid, parathyroid, adrenals, thymus, pancreas, pineal, ovaries, testes
functions: control body activities acts slower, produce chemical molecules (hormones)
functions: control body activities acts slower, produce chemical molecules (hormones)
9
New cards
cardiovascular system
heart and blood vessel
functions: carries oxygen, nutrients, hormones, substances to and from the tissue cells; heart=blood pump; white blood cells protect invaders ex. bacteria
functions: carries oxygen, nutrients, hormones, substances to and from the tissue cells; heart=blood pump; white blood cells protect invaders ex. bacteria
10
New cards
lymphatic system
lymphatic vessels, lymph nodes, lymphoid organs, spleen, tonsils
Functions: lymphatic vessels- return fluid leaked from the blood to the blood vessels; lymph nodes and lymphoid organs- help to cleanse the blood and host the cells involved immunity and blood fluids
Functions: lymphatic vessels- return fluid leaked from the blood to the blood vessels; lymph nodes and lymphoid organs- help to cleanse the blood and host the cells involved immunity and blood fluids
11
New cards
respiratory system
nasal passages, pharynx, larynx, trachea, bronchi, lungs
functions: keep the body constantly supplied with oxygen and to remove carbon dioxide
functions: keep the body constantly supplied with oxygen and to remove carbon dioxide
12
New cards
digestive system
mouth, esophagus, stomach, small intestines, large intestines, rectum, liver, pancreas
functions: break down food and deliver products to the blood
functions: break down food and deliver products to the blood
13
New cards
urinary system
kidneys, ureters, bladder, urethra
functions: removes nitrogenous the from blood into the urine maintain body's water and salt balance, acid-base balance in the blood
functions: removes nitrogenous the from blood into the urine maintain body's water and salt balance, acid-base balance in the blood
14
New cards
reproductive system
testes, scrotum, penis, duct system, ovaries, female vagina
functions: produces offspring
functions: produces offspring
15
New cards
anatomical position
body is erect with the feet parallel and the arms hanging at the sides with the palms facing forward and thumbs pointing away from the body
16
New cards
superior/cranial/cephalad
towards the head end or upper part of a structure or the body; above
17
New cards
inferior/caudal
away from the head end/ toward the lower part of the structure; below
18
New cards
anterior/ ventral
toward or at the front of the body; in the front of
19
New cards
posterior/ dorsal
toward or the back side of the body; behind
20
New cards
medial
toward or the mid-line of the body; the inner side of
21
New cards
lateral
away from the mid-line of the body; outer side of
22
New cards
intermediate
between a more medial and more lateral
structure
structure
23
New cards
proximal
close to the origin of the body part of the point of attachment of a limb to the body trunk
24
New cards
distal
farther from the origin of a body of part or the point of attachment of a limb to the body trunk
25
New cards
superficial
toward a body surface
26
New cards
deep
away from the body surface; more internal
27
New cards
sagittal section
cut made along a lengthwise, longitudinal plane; dividing the body into right and left parts
28
New cards
frontal section
cut made along a lengthwise plane, dividing the body or an organ into anterior/posterior parts
29
New cards
transverse section
cut made along a horizontal plane, dividing the body or organ into superior / inferior parts (cross section)
30
New cards
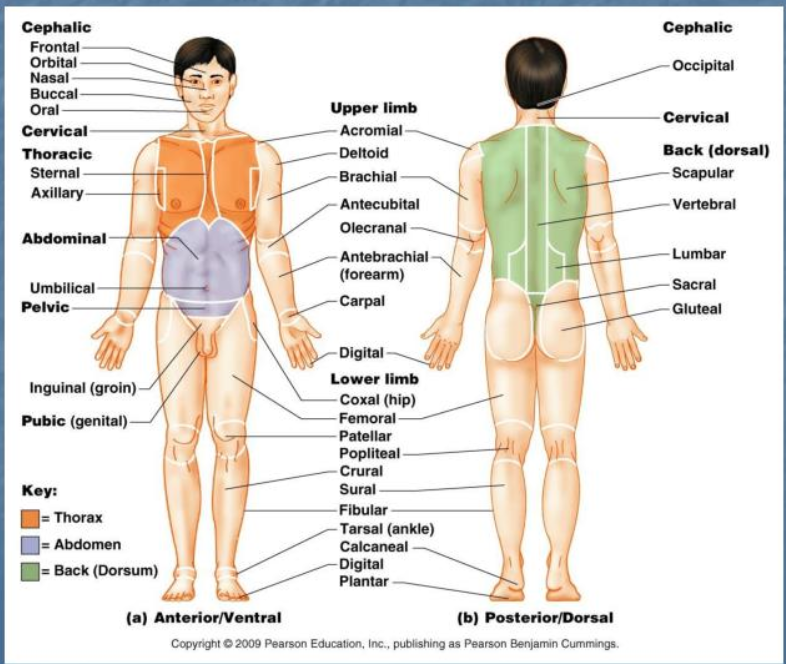
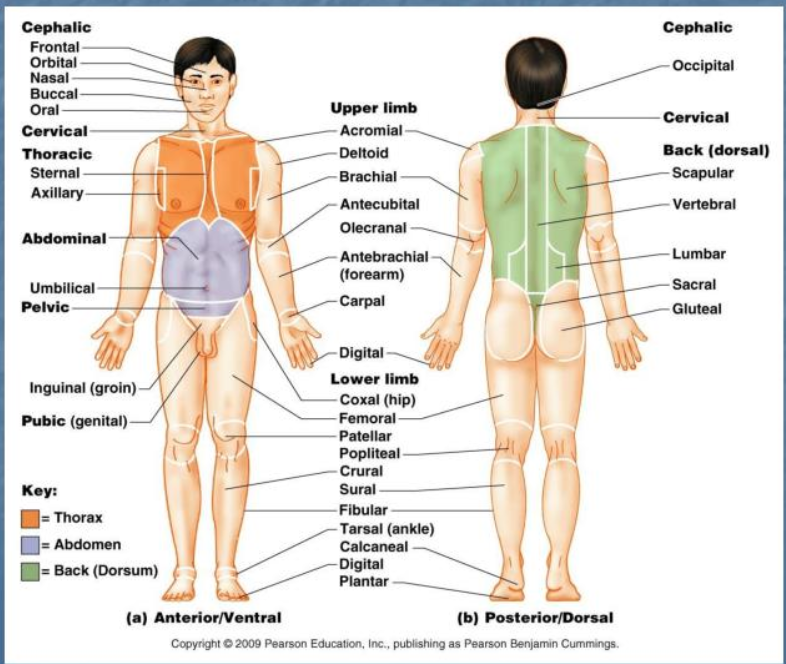
anterior body landmarks
nasal, orbital, oral, buccal, cervical, sternal, acromial, axillary, thoraric, brachial, antecubital, abdominal, umbilical, pelvic, carpal, digital, coxal, inguinal, pubic, patellar, fernoral, fibular, crural (leg), tarsal
31
New cards
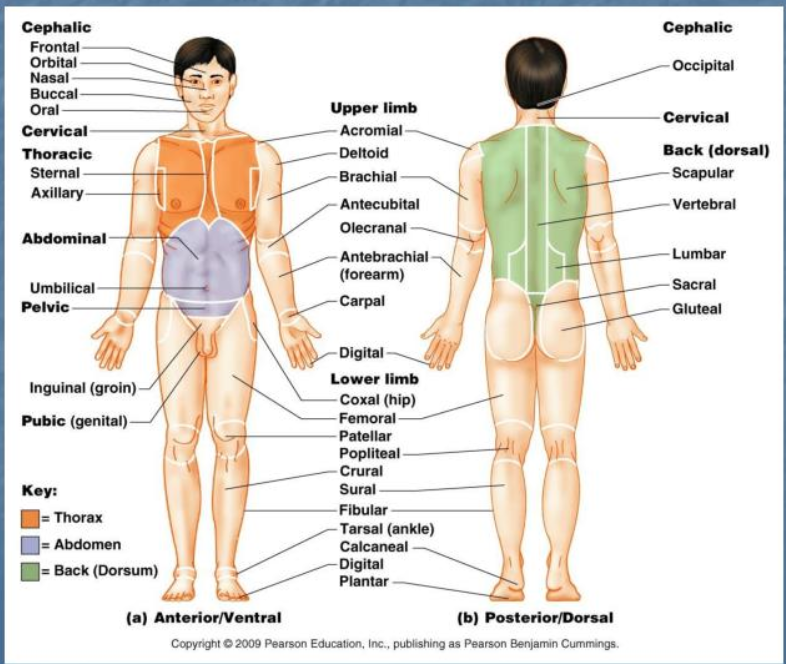
posterior body landmark
cephalic, occipital, deltoid, scapular, vertebral, lumbar, sacral, gluteal, popiteal, sureal
32
New cards
what are the four types of tissue
connective, epithelial, muscle, and nervous
33
New cards
connective tissue
- form ligaments, tendons, fat and bones
- all connective tissues share: well vascularized, extracellular matrix
-connect body parts together by ligaments, tendons, etc
-made of nonliving substances found outside of the cell
-other substances they have are collagen, elastin, mast cells, and macrophages
- all connective tissues share: well vascularized, extracellular matrix
-connect body parts together by ligaments, tendons, etc
-made of nonliving substances found outside of the cell
-other substances they have are collagen, elastin, mast cells, and macrophages
34
New cards
epithelial
-found in the epidermis and form the lining of internal organs such as the intestines
-line and cover the surfaces of internal organs
- simple (one cell layer)
-stratified (more than one cell layer)
-cells are avascular
-endocrine: makes and releases hormones that travel in the bloodstream and control the actions of other cells or organs; pituitary, thyroid,
adrenal
-exocrine: have ducts, secrete onto a surface; sebaceous/sweat glands, salivary glands
-line and cover the surfaces of internal organs
- simple (one cell layer)
-stratified (more than one cell layer)
-cells are avascular
-endocrine: makes and releases hormones that travel in the bloodstream and control the actions of other cells or organs; pituitary, thyroid,
adrenal
-exocrine: have ducts, secrete onto a surface; sebaceous/sweat glands, salivary glands
35
New cards
muscle
- make up the majority of the heart
-contract and shorten to produce movement
-muscle cells: microfibers
- types: smooth, cardiac, skeletal
-contract and shorten to produce movement
-muscle cells: microfibers
- types: smooth, cardiac, skeletal
36
New cards
nervous
-make up the majority of the brain and spinal cord
- neurons: transmit signal to muscle and glands
-neuroglia: supports neuronal function
- neurons: transmit signal to muscle and glands
-neuroglia: supports neuronal function
37
New cards
basement membranes
bottom layer that's connected to connective tissues
38
New cards
stratified squamous
Shape/Layers: several layers; at free edge
Location(s): esophagus, mouth, outer portion of skin.
Functions: protects underlying tissues in areas subject to abrasion.
Location(s): esophagus, mouth, outer portion of skin.
Functions: protects underlying tissues in areas subject to abrasion.
39
New cards
stratified cuboidal/columnar
Shape/Layers: two cell layers; vary in size/shape.
Location(s): ducts of large glands; are rare
Functions: protection; secretion
Location(s): ducts of large glands; are rare
Functions: protection; secretion
40
New cards
transitional epithelium
Shape/Layers: somewhat cuboidal; many layers
Location(s): urinary system (bladder, uterus, urethra).
Functions: lines very few organs; allows urine to be stored in bladder; stretches.
Location(s): urinary system (bladder, uterus, urethra).
Functions: lines very few organs; allows urine to be stored in bladder; stretches.
41
New cards
glandular epithelium
Shape/Layers: single cell layer; disc shape
Location(s): thyroid, adrenals, pituitary, liver, pancreas.
Functions: secretion (hormones to blood vessels/sweat and oils to skin's surface).
Location(s): thyroid, adrenals, pituitary, liver, pancreas.
Functions: secretion (hormones to blood vessels/sweat and oils to skin's surface).
42
New cards
pseudostraified columnar
Shape/Layers: some cells are shorter than others
Location(s): respiratory tract
Functions: absorption, secretion, lines most of the respiratory tract.
Location(s): respiratory tract
Functions: absorption, secretion, lines most of the respiratory tract.
43
New cards
apical surface
free/unattached surface
44
New cards
diffusion
epithelial tissues have no blood flow, they are able to receive needed nutrients and expel wastes
45
New cards
areola
type of loose connective tissue that separates the cells of the body from the blood stream; "go-between" for nutrients and wastes to leave and enter the blood stream on their way to and from the body cells
46
New cards
adipose
type of connective tissue also known as a fat. Its purpose is to store excess nutrients and fats as energy. It also serves as a type of insulation for the body.
47
New cards
cartilage
connective tissue that is used as both a protective and supportive structure within the body. This particular type of connective tissue can be found in the nose, ear, ribs, and vertebral disks.
48
New cards
irregular
dense connective tissue with irregularly arranged fibers that provides strength where tension is exerted in various directions such as in the dermis
49
New cards
regeneration
replacement of destroyed tissue by the same kind of cells.
50
New cards
fibrosis
thickening and scarring of connective tissue, usually as a result of injury
51
New cards
effects of scar tissue
Scar not only affects the beauty of body surface, but also can hinder the physiological function of related tissues or organs, and even lead to deformities.
52
New cards
Tissue regeneration
Tissue regeneration includes regeneration of epithelial tissue, regeneration of fibrous tissue, regeneration of cartilage tissue and bone tissue, regeneration of blood vessels, regeneration of muscle tissue, and regeneration of nerve tissue.
53
New cards
serous
doesn't open to the exterior
-parietal (outer layer)
-visceral (inner layer)
-line cavities close to the exterior
-parietal (outer layer)
-visceral (inner layer)
-line cavities close to the exterior
54
New cards
mucous
-opens to the exterior
-always wet or moist
-always wet or moist
55
New cards
peritoneum
lines the abdominal cavity and covers its organ
56
New cards
pleura
surrounds the lungs
57
New cards
pericardium
surrounds the heart
58
New cards
synovial membranes
- type of connective tissue membrane
59
New cards
epidermis
-capable of keratinizing
- layers: stratum corneum, stratum lucidum, stratum glandular, stratum basale
- layers: stratum corneum, stratum lucidum, stratum glandular, stratum basale
60
New cards
dermis
- made up of dense connective tissue
-"hide"
cutaneous glands reside-contain collagen and elastic fibers
- contain pain and touch receptors
-"hide"
cutaneous glands reside-contain collagen and elastic fibers
- contain pain and touch receptors
61
New cards
hypo-dermis
- made up of adipose tissue
62
New cards
melanin
freckles and moles: melanin concentrated in one spot
tan: more melanin is produced when you are exposed to the sun
-protects by absorbing harmful rays
tan: more melanin is produced when you are exposed to the sun
-protects by absorbing harmful rays
63
New cards
blackheads and whiteheads
whiteheads are when a sebaceous gland duct gets blocked by sebum; blackheads are when it's blocked but the accumulated material oxidizes, dries, and darkens
64
New cards
sebaceous gland
oil glands
-secrete their secretions into a hair follicle
-sebum is the product
-secrete their secretions into a hair follicle
-sebum is the product
65
New cards
sudoriferous gland
sweat glands
66
New cards
stratum basale
hair is formed by division
67
New cards
acne
active infection of sebaceous gland
68
New cards
arrector pili
tiny muscle attached to the hair follicle
69
New cards
hair root
the skin and extends down to the deeper layers of the skin
70
New cards
hair shaft
the visible part of the hair that sticks out of the skin
71
New cards
ABCD Rule of Melanoma
A- asymmetry-pigmented spot
B- border irregular; not smooth, but exhibit indents
C- color; different colors (black,brown,blue/red)
D- diameter: bigger than 6mm
B- border irregular; not smooth, but exhibit indents
C- color; different colors (black,brown,blue/red)
D- diameter: bigger than 6mm
72
New cards
ossification
the process of bone formation
73
New cards
epiphyseal plate
It provides for longitudinal growth of the long bones during childhood.
74
New cards
Closed (simple) fracture
a fracture in which the bone breaks cleanly and does not penetrate the skin
75
New cards
Open (compound) fracture
a fracture in which the bone ends penetrate through the skin
76
New cards
first event of the repair of bone fractures
a hematoma is formed as a result of a blood-filled swelling and bone cells deprived of nutrition die
77
New cards
second event of the repair of bone fractures
the break is splinted by a fibrocartilage callus formed by CT cells of various types and it contains some cartilage matrix, some bony matrix, and collagen fibers. these act to splint the broken bone, closing the gap
78
New cards
3rd event of the repair of bone fractures
he bony callus is formed, more osteoblasts and osteoclasts migrate into the area and multiply, Fibrocartilage is gradually replaced by a callus made of spongy bone, called the bony callus.
79
New cards
4th event of the repair of bone fractures
the bony calllus is remodeled in response to the mechanical stresses placed on it, so that it forms a strong permanent "patch" at the fracture site.
80
New cards
axial skeleton
forms the longitudinal axis of the body
81
New cards
fontanels
Fibrous membranes that connect the cranial bones in infants. The rhythm of the baby's pulse can be felt in these "soft spots."
1. Allow the fetal skull to be compressed slightly at birth.
2. Because they are flexible, they allow the infant's brain to
grow during the later part of pregnancy and early infancy.
1. Allow the fetal skull to be compressed slightly at birth.
2. Because they are flexible, they allow the infant's brain to
grow during the later part of pregnancy and early infancy.
82
New cards
functions of the bones
support, protection, movement, storage, and blood cell formation
83
New cards
compact bone
dense and looks smooth and homogeneous
84
New cards
spongy bone
composed of small needlelike pieces of bone and lots of open space
85
New cards
long bones
Bones that are
typically longer than they are wide
- made mostly of compact bone. As a rule they have a shaft with heads at both ends.
- Examples: All of the bones of the limbs
(except the wrist and ankle bones)
typically longer than they are wide
- made mostly of compact bone. As a rule they have a shaft with heads at both ends.
- Examples: All of the bones of the limbs
(except the wrist and ankle bones)
86
New cards
short bones
Generally cube-shaped
Contain mostly spongy bone.
Examples: ankle and wrist bones, patella
(kneecap), sesamoid bones (form within
tendons)
Contain mostly spongy bone.
Examples: ankle and wrist bones, patella
(kneecap), sesamoid bones (form within
tendons)
87
New cards
flat bones
Bones that are thin, flattened, and usually curved, Contain two thin layers of compact bone sandwiched between a layer of spongy bone.
Examples: Skull, ribs, sternum (breastbone)
Examples: Skull, ribs, sternum (breastbone)
88
New cards
irregular bones
Bones that do not fit one of the preceding
categories.
Examples: Vertebrae and the hip bones.
categories.
Examples: Vertebrae and the hip bones.
89
New cards
diaphysis
Shaft, makes up most of the bone's length and is composed of compact bone.
90
New cards
periosteum
a fibrous CT membrane that covers and protects the diaphysis
91
New cards
epiphyses
Ends of the long bones.
Each end is composed of a thin layer of compact bone
enclosing an area filled with spongy bone.
Each end is composed of a thin layer of compact bone
enclosing an area filled with spongy bone.
92
New cards
epiphyseal plate
- A flat plate of hyaline
cartilage seen in young, growing bone.
- Cause the lengthwise growth of a long bone.
- By the end of puberty, when hormones stop long bone
growth, epiphyseal plates have been completely replaced by
bone, leaving only the epipyseal lines to mark their
previous location.
cartilage seen in young, growing bone.
- Cause the lengthwise growth of a long bone.
- By the end of puberty, when hormones stop long bone
growth, epiphyseal plates have been completely replaced by
bone, leaving only the epipyseal lines to mark their
previous location.
93
New cards
Yellow Marrow Cavity (Medullary Cavity)
- Cavity of a shaft
- Primarily a storage area for adipose (fat) tissue.
- Primarily a storage area for adipose (fat) tissue.
94
New cards
red bone marrow
Confined to the cavities of spongy bone of flat bones and the epiphyses of some long bones, which are where red blood cells are produced.
95
New cards
osteocytes
mature bone cells
96
New cards
osteoblasts
bone building cells
97
New cards
osteoclasts
bone destroying cells
98
New cards
lacunae
tiny cavities in bones or cartilage where osteocytes are found
99
New cards
lamellae
concentric circles in which the lacunae are arranged
100
New cards
Central (Haversian) Canals
Canals in bones that are surrounded by lamellae.
- Run lengthwise through the bony matrix, carrying blood
vessels and nerves to all areas of the bone.
- Run lengthwise through the bony matrix, carrying blood
vessels and nerves to all areas of the bone.