2.4.1 Production, Productivity, and Efficiency
1/39
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
40 Terms
Job production
involves the manufacture or delivery of one-off or a small number of items
↳ labour-extensive and expensive
benefits of job production
Can charge higher prices
Products tailored to customer needs
Motivated workers
disadvantages of job production
High costs
Slow production
Inconsistent work load
Batch production
involves the production of small quantities of identical products
↳ production is sped up making it less expensive
benefits of batch production
unit costs are lower because output is higher
production is flexible as each batch can vary
more use of machinery
disadvantages of batch production
more complex machinery needed = expensive
workers may be less motivated as they tend to be specialised in one process
Cell production
involves dividing the production into multi-skilled teams (cells) each responsible for a particular part
↳ combined elements of job and flow production
benefits of cell production
closeness of cell members should improve communication
workers become multi-skilled and more adaptable for future needs
greater work motivation
quality improves
disadvantages of cell production
workers may feel they are too pushed
may not allow a firm to use machinery as intensely as traditional flow production
the allocation of work : cells has to be efficient so they can cope
Flow production
involves the production of a large volume of identical products
benefits of flow production
economies of scale
quality stays consistent
high output efficiency
disadvantages of flow production
high initial machinery costs
machines can break
repetitive tasks may lower worker motivation
production
the level of output achieved by a business i.e. the total number of products produced in a given time
productivity
Productivity, on the other hand , is a measure of the rate of production
It is the amount of output that can be produced with a given input of resources
Factors influencing productivity of machinery
Age of machinery and maintenance
Training of operatives
Quality of inputs e.g. a high quality printer can jam if cheap paper is used
Hours used versus downtime
efficiency of programming
Unforeseen events e.g. power cuts
labour productivity

Labour productivity will be influenced by a number of factors including
Training and skills of the workforce
Motivation
Complexity of the product
Operational efficienc
involves maximising the output achieved from given inputs including machinery, materials and people
Efficiency can be improved using a number of methods, these include
Increasing capacity utilisation
Increasing labour productivity
Lean production techniques
Choosing the optimal resource mix, labour v capital intensive
Using technology
capital productivity
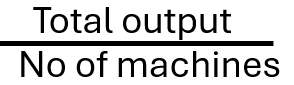
target productivity
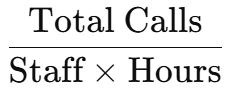
percentage difference for target productivity
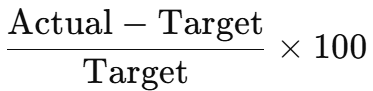
Increasing labour productivity
lowers labour cost per unit (assuming employee costs stay the same) and hence unit cost
therefore it is important to use workers efficiently
labour productivity can be increased in a number of ways
Training
Increasing motivation e.g. financial or non - financial rewards, job design
Implement new technology
Better working practises
Improved recruitment and selection
why do firms want to increase productivity
to lower cost and increase profits
this makes them more competitive in the market
ways to improve productivity
specialisation and the division of Labour
Workers focus on specific tasks, increasing efficiency and output quality
Recruitment, selection and training
Hiring the right people and developing their skills boosts productivity
Motivation of workers
Motivated employees work harder and more efficiently
Working practises
efficient systems e.g. flexible hours or teamwork improve workflow and output
labour flexibility
Flexible workers can adapt to different roles, reducing downtime and increasing efficiency
technology
Automation and digital tools speed up production and reduce human error
If businesses can raise their productivity they will be able to produce more output with the same input resources. This will mean that cost will be lower. This enable businesses to be more competitive?
Lower costs mean the firm can reduce prices or increase profit margins. This allows the farm to compete better on price or reinvestment in quality or innovation
difficulties in increasing labour productivity
May impact negatively on quality and customer satisfaction
Damage to long term reputation
Increase waste affecting unit cost
Employees may feel exploited
Working harder for the same pay, may work with unions to negotiate higher wages
Business benefiting but not the employees
Increased workload leading to stress and demotivation
efficiency
this is about making the best use of a company’s resources
Operations management
involves combining the four factors of production or resource inputs:
Land
Labour
Capital
Enterprise
the optimal resource mix
the best way of combining the factors of production in order to meet these requirements within financial constraints
costs
often used to measure efficiencya
average unit costs
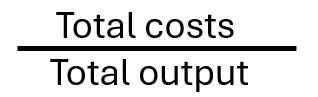
factors influencing efficiency
outsourcing
Hiring external firms can reduce costs and improve focus on core activities
relocating
Moving operations can lower labour or rent costs and improve access to resources
downsizing
reducing staff cuts costs and removes inefficiencies but may risk lower morale
delayering
Removing management layers speeds up communication and decision making
investing in new technology
Modern equipment boost speed, accuracy, and lower long term costs
lean production
minimising waste and maximising value improves efficiency and reduces costs
labour intensive
uses a relatively high proportion of labour i.e. workers in the production of a good or service
Production relies on human workers than machines
common in service industries or tasks needing personal input
tends to occur in the tertiary sector
capital intensive
uses a relatively high proportion of capital such as machinery in the production of a good or service
Production relies more in machinery and technology than Labour
Often used in mass production or automated industries
tends to occur in the secondary sector of economy i.e. manufacturing
advantages of capital intensive
Increased productivity
Improved quality and speed
Reduced labour costs
Greater opportunities for economies of scale (the benefits to a business of producing on a large scale that lead to a fall in unit costs)
disadvantages of capital intensive
High investment outlay
Lack of human initiative
Greater resistance to change by workforce e.g. retraining to use new equipment
advantages of labour intensive
Often cheaper, especially when produced in low wage locations
Workforce can easily adapt to change, especially if multi-skilled
Continuous improvement through workforce can benefit the firm e.g. new ideas
Government funding often available to protect jobs in the economy
disadvantages of labour intensive
Industrial relations can be a problem e.g. strikes
Lack of skilled workers in some industries
HRM costs can be very high e.g. recruitment, selection and training