Speech Disorders Exam 3
1/69
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Assessment of speech sound disorders
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
70 Terms
Types of relational analysis
traditional analysis
phonological process analysis
other: intelligibility
PCC/Severity
stimulability
traditional analysis is most appropriate for
children with few articulation errors
relatively good intelligibility
problem is articulatory
traditional analysis considers what 2 variables
position the sounds are misarticulated
prevocalic
postvocalic
intervocalic
types of errors made
substitutions
omissions
distortions
additions
omission
sound is deleted all together
distortion
non english sound produced for an english sound
addition
adding an extra sound
relational analysis is best for
older children regardless of intelligibility
does relational analysis analysis compare child’s production to adult target?
yes
independent analysis is best for what age
very young children and/or children who are very unintelligible
independent analysis yields
an inventory of sounds and syllable structures produced
relational analysis yields
types of errors and operating phonological processes
How to determine phonological issue
errors with whole classes of sounds (all fricatives, all stops, etc)
idiosyncratic
“of unknown origin”
glottal replacement
consistently using glottal stop in replacement for a phoneme
strong sound preference/phoneme collapse
child using one phoneme to replace many phonemes
backing
substitution of later developing sounds for earlier ones
/t, d/ to /k, g/
metathesis
switching around sounds
“caterpillar” - “callapiter”
denasalization
taking a nasal sound away
frequency of occurence
number of times a particular process occurs in a sample
percentage of occurence
more specific, requires more analysis but provides more information
5/8 (63%) vs 5/30 (17%)
articulation issue
more sound errors
phonological issue
low intelligibility
consistent phoneme errors
assessment definition
process of arriving at a diagnosis
assessment can be synonymous with
evaluation / diagnostics
purpose of assessment
obtain good understanding or diagnosis of client’s issue
identify need for referral
identify need for treatment
determine focus, structure, length, & frequency of treatment
monitor client’s progress & describe changes in communication disturbance
formal assessment
standardized measures
compare child to standard norms
administration dictated by an examiner’s manual
result in statistical scores
Informal assessment
non standardized measures
compare child to themselves, informal norms, or a certain criteria
administration is determined by clinician
result in informal info or scores
independent analysis purpose
describe phonemes & syllable shapes that occur in a speech sample
independent analysis is most appropriate for
children in the “first 50 words” stage
less than 30 months old
children with VERY low intelligibility
norms: 15 months
/b, d, h/
norms: 18 months
/b, t, d, m, n, h, w/
norms: 21 months
/b, t, d, m, n, h, w/
norms: 24 months
/b, p, t, d, k, g, m, n, h, w, f, s, r/
syllable structure norms: 12 months
v
cv
cvc
cvcv
syllable structure norms: 24 months
v
cv
cvc
cvcv
cvcvcv
clusters emerging
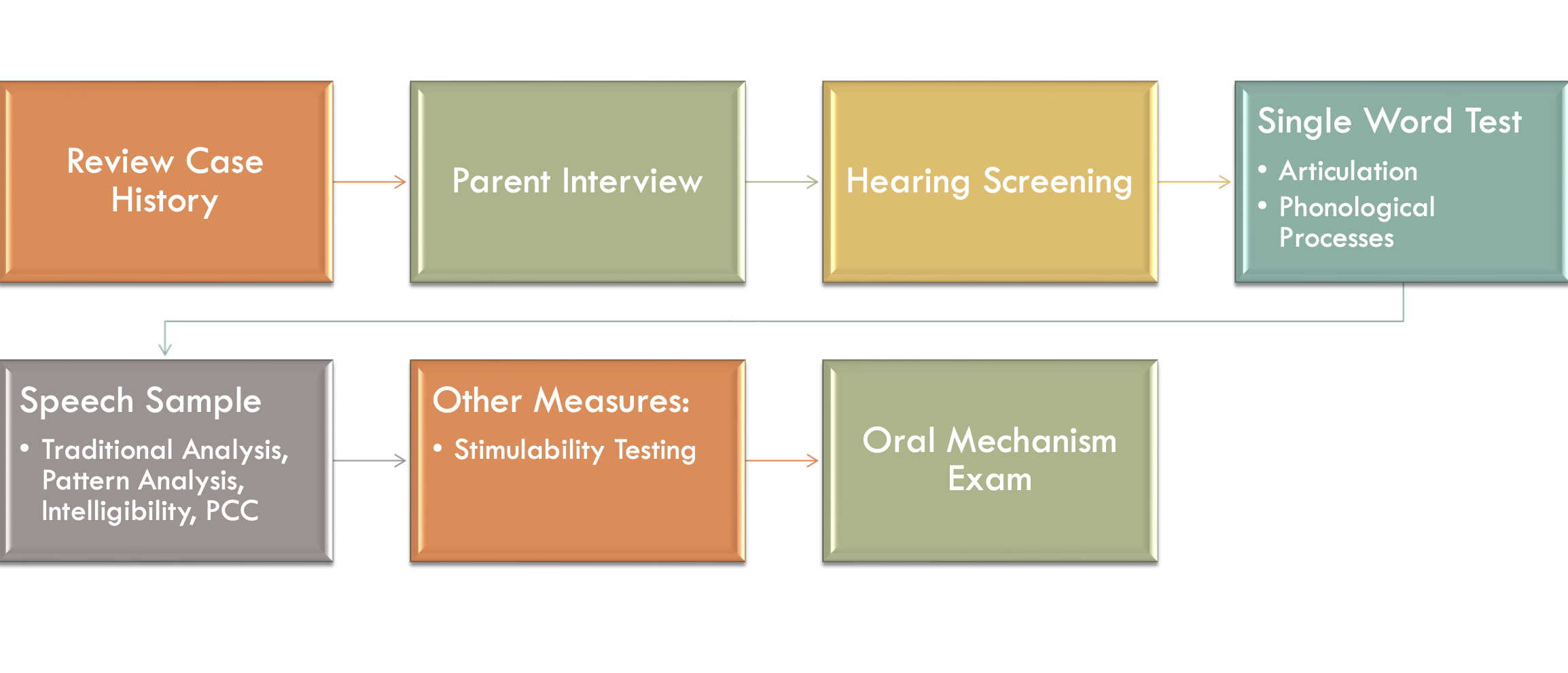
formal measures
articulation exams
phonological process exams
informal measures
sampling techniques
relational analysis
single word articulation tests AKA
citation tasks
single word articulation provide
an identifiable unit of production that examiners can more easily transcribe
single word articulation tests yield
a standardized score
prevocalic
consonants that precede a vowel and initiate a syllable (soap, cat)
intervocalic
consonant that is embedded (VCV) between tow vowels (camel, eager)
postvocalic
consonants that follow a vowel (VC) & terminate the syllable (soap, cat)
Goldman Fristoe Test of Articulation - 3 tests what age
2:0 to 21;11
gender based norms
Goldman Fristoe Test of Articulation - 3 examines what
artic in words
intelligibility
khan lewis phonological analysis - 3 tests what age
2:0 to 21;11
khan lewis phonological analysis - 3 examines what
phonology
Arizona Articulation and Phonology Scale - 4 tests what age
18-months to 21;11
gender based norms
Arizona Articulation and Phonology Scale - 4 examines
word artic
sentence artic
phonology
intelligibility tells us
what % of the time we understand someone
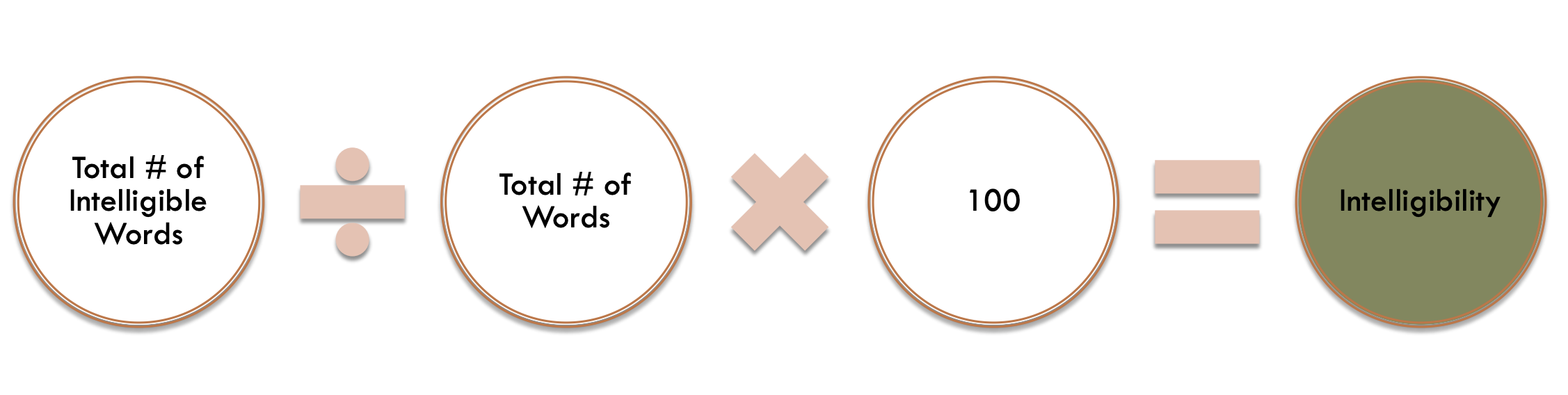
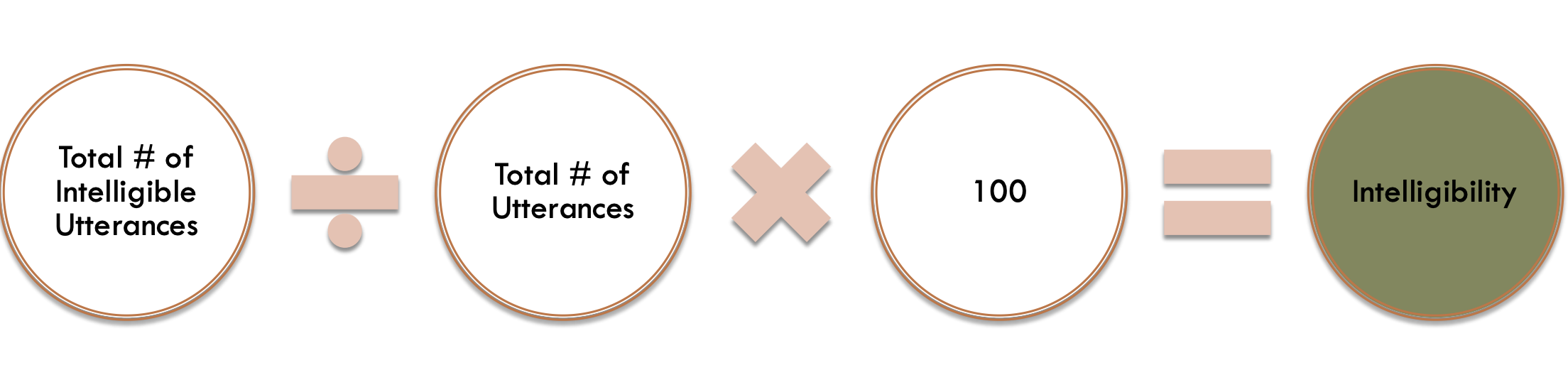
intelligibility analysis
transcribe sample
use a symbol to mark unintelligible words
intelligibility analysis for words
intelligibility analysis for utterances
intelligibility norms: 19-24 months
25-50%
intelligibility norms: 2-3 years
50-75%
intelligibility norms: 4-5 years
75-90%
intelligibility norms: 5+ years
90-100% (a few errors may persist)
severity analysis provides
info that determines if therapy is needed
support for your findings
factors that influence severity
child’s age
intelligibility
# of phonological processes
consistency of errors
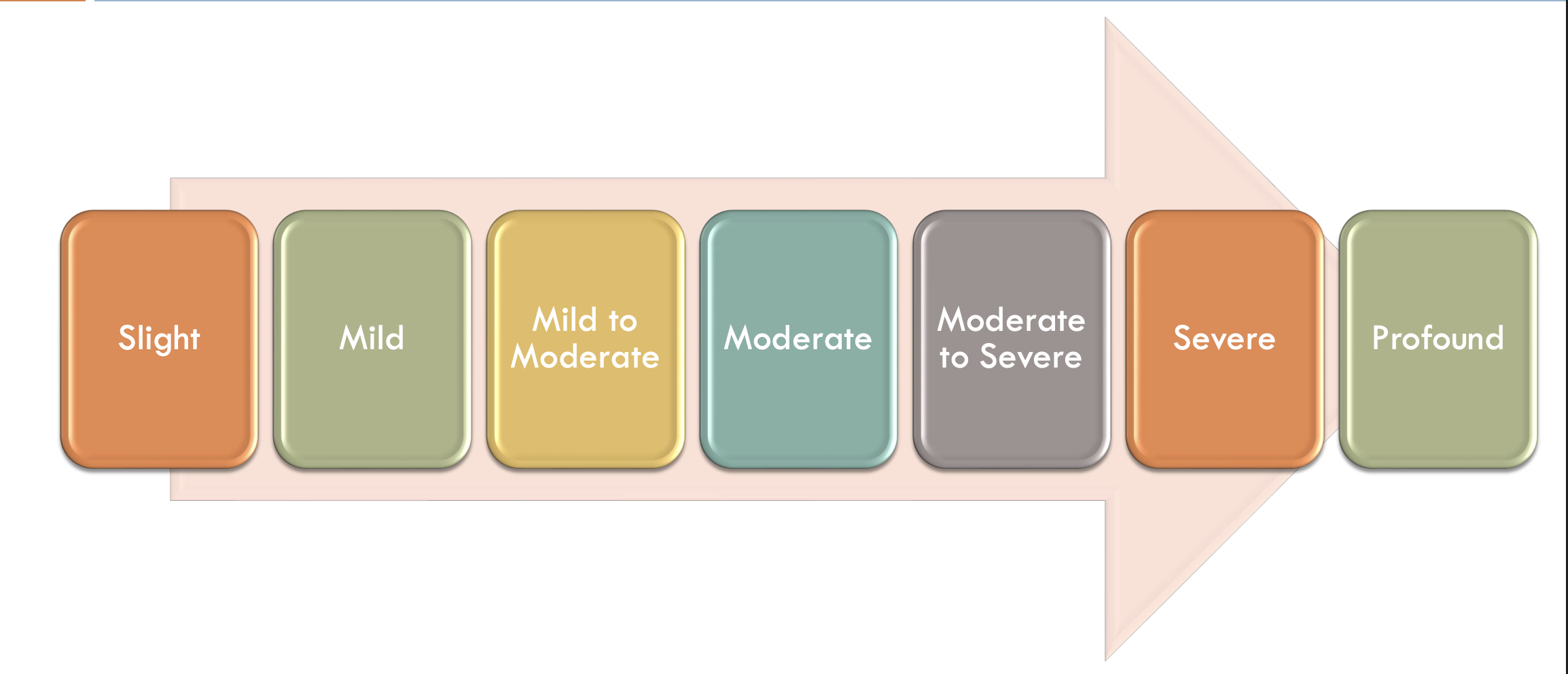
severity analysis scale
mild + = need for therapy
PCC Formula
#of correct consonants / total consonants x 100 = PCC
severity level
85-100%
mild
severity level
65-85%
mild-moderate
severity level
50-65%
moderate-severe
severity level
<50%
severe
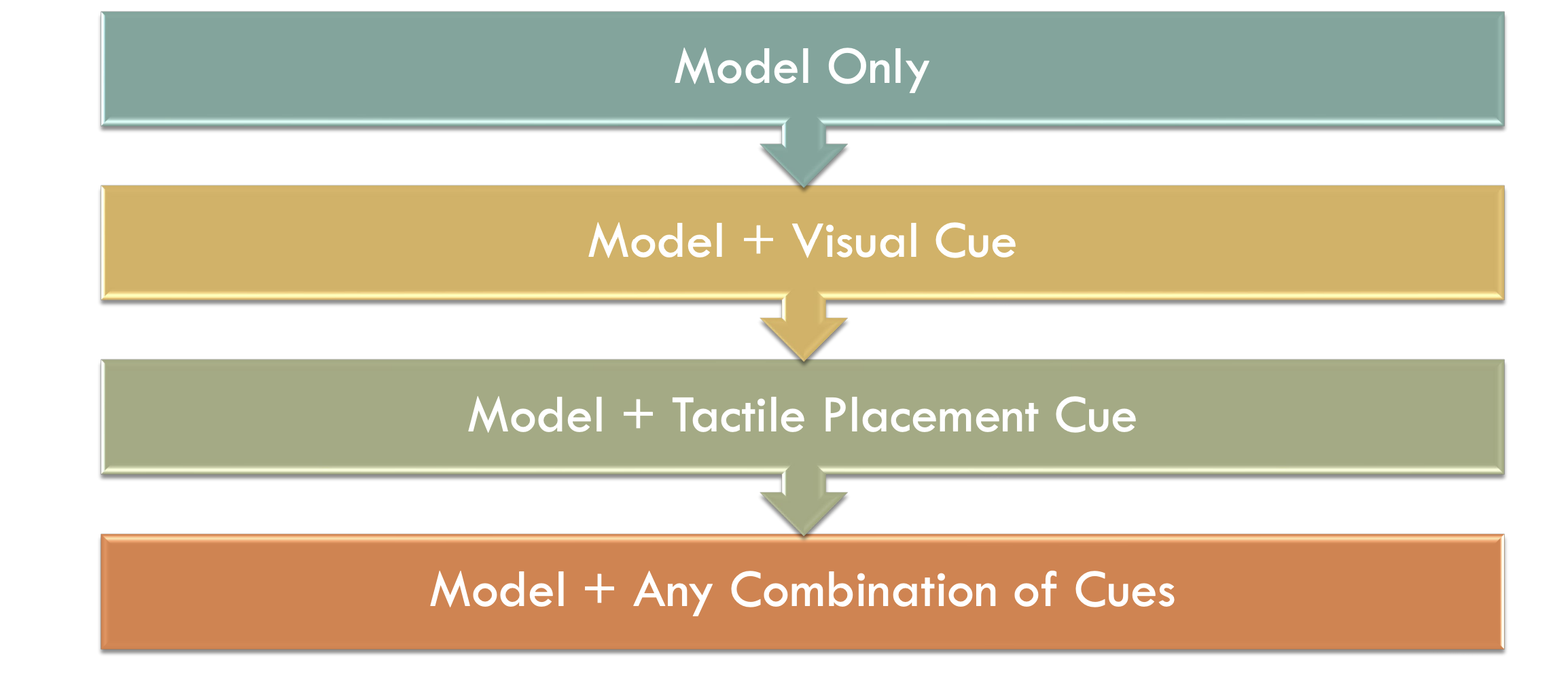
stimulability testing example
stimulability testing
client’s ability to make a correct/improved production of a misarticulated sound when given a model or additional stimulation
stimulability testing helps with
selection of therapy targets
identity cues/prompts that may be helpful in therapy
Normal speech production
errors due to bilingualism / dialect/ 2nd language
errors within normal developmental range
errors are slight & would not draw attention
speech production assessment example