IB DT: Topic 8.4: Sustainable innovation
1/14
Earn XP
Description and Tags
For prectice questions/ppt go to https://docs.google.com/presentation/d/17rEg9HqnJCSkZSOUNK2WukmTYqTz3ocmfqTjpS0077g/present?slide=id.g18732d80aa1_0_0
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
15 Terms
What is sustainable innovation?
Innovation that facilitates the diffusion of sustainable products and solutions into the marketplace. Yields both top and bottom line returns as developing systems that are environmentally friendly lowers costs through reducing the resources required.
Sustainable innovation relies on cooperation between stakeholders such as government and manufacturers- why does this make it complex?
Both parties have different views
Sustainable innovation requires a radical change which is time-consuming and expensive
It is the broadest approach going beyond technical solutions - based ob a socio-technical system (interaction between people and technology) rather than just considering product improvement.
The huge timescale means sustainability is difficult to maintain- it requires up to 40 years to implement.
What is a top down strategy? What are its advantages and disadvantages?
Breaking a system into smaller, component parts
Advantage: decisions are made relatively quickly
Disadvantage: management believes it has monopoly on good ideas- people cannot volunteer
What is a bottom up strategy? What are its advantages and disadvantages?
Piecing together components or systems to give rise to a more complex system
Advantages: more motivational for those involved
Disadvantages: Time consuming as it is sometimes difficult for individuals to make a decision
How can government intervention be involved in terms of regulation?
Setting and policing rules to avoid or limit environmental issues caused by undesireable technologies
How can government intervantion be involved in terms of education?
Providing consumers with information and guidance in the choice of products and services that are more sustainable
How can government intervention be involved in terms of taxes and subsidies?
Taxes to penalise environmentally damaging technologies and influence consumer choice of sustainable products and services.
What is macro energy sustainability?
The influence of international treaties and policy, government change and role of government.
How a nation, region or whole world would establish large scale behaviours for sustainability.
Influenced through: international treaties and energy policies, instruments for change and disincentives, national systems changing policy when government leadership changes
What is micro energy sustainability?
The area of sustainability that focuses on hoe individuals, organisations and businesses decide what activities they should engage in and how to allocate their resources.
Influenced by the government changing attitudes by raising awareness, and the promotion of individual and business action towards energy sustainability
What is energy security?
The association between national security and the availability of natural resources for energy consumption. The uneven distribution of energy supplies among countries has led to significant vulnerabilities.
What is energy demand?
The flow of energy over the course of a day/year - rarely constant, putting a responsibility on those that generate and manage the flow of energy to understand when the peaks and troughs of energy use occur
What is a smart grid?
A modernised electrical grid that uses analogue or digital information and communications technology to gather and act on information in an automated fashion to improve the efficiency, reliability and sustainability of the production and distribution of electricity.
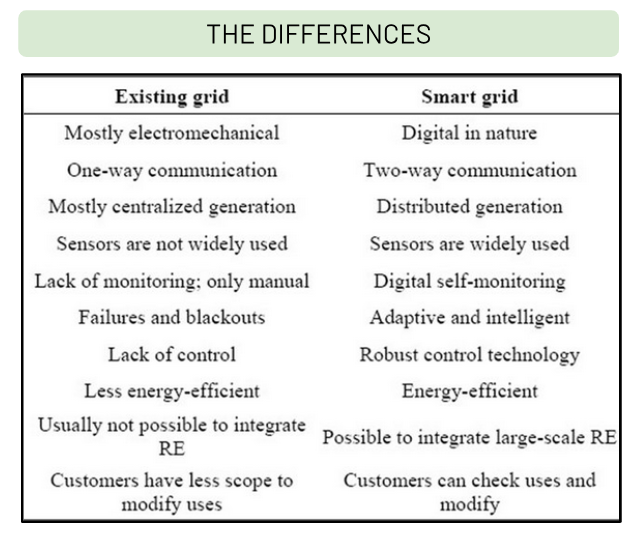
What are the differences between the existing grid and a smart grid?
What are the advantages of smart grids?
New jobs (to manufacture and install)
Innovation (enables business growth)
Lower costs (more efficient)
Improves reliability (reducing outages)
Higher customer satisfaction (lower costs and improved reliability)
What are the disadvantages of smart grids?
Can be hacked (privacy and security concern)
Complex (not a single component)
Expensive installation