Module 1
1/29
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Basics of biochem
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
30 Terms
What are the four major classes of biomolecules?
Proteins
Nucleic Acids
Polysaccharides (carbohydrates)
Lipids
Through what different perspectives can we analyze the living state?
Chemical
Energy
Genetic
Evolutionary
What are the most abundant atoms within organisms?
Carbon, Hydrogen and Oxygen
What makes life on Earth possible?
Water, made up of two hydrogen and one oxygen
All known life forms are ______-based.
All known life forms are carbon based
Why is carbon-based life forms more favorable?
Very versatile in boding (stronger)
Its combustion releases more energy (and CO2 and H2O)
Soluble in water/ recyclable
What dictates the function for a biomolecule?
Its structure dictates its function
How do different functional groups affect biomolecules?
They determine their structure, functions and properties in biomolecules
Conformation
Moveable spatial arrangement of atoms within a molecule
The structure can be changed w/o breaking covalent bonds (usually single bonds)
Configuration
Fixed spatial arrangement of atoms within a molecule
The structure cannot be changed w/ o breaking covalent bonds
What are the different ways to affect configuration?
Double bonds (geometric isomers)
Chiral carbons
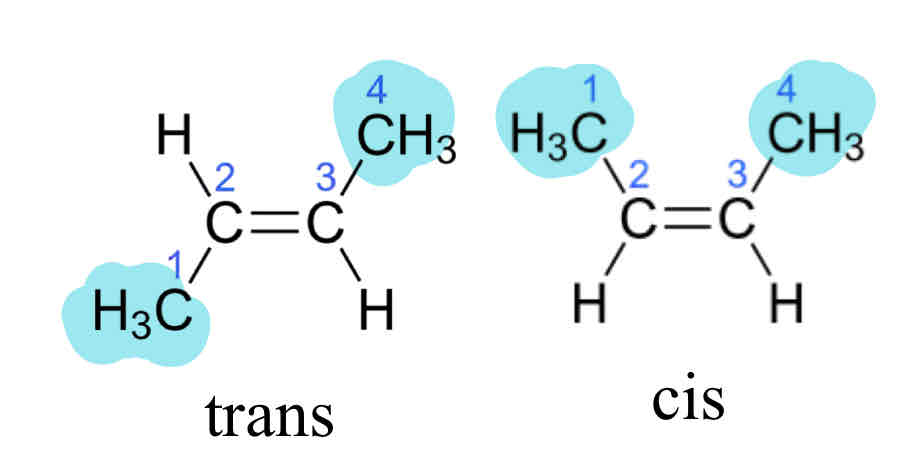
What re the two types of geometric isomers?
CIs isomers: groups on the same side of a double bond
Trans isomers: groups acroos from each other
Describe the structure and functions of proteins
Structure:
long unbranched polymers of amino acids.
folded amino acids into complex patterns
Function:
receptors
signal molecules
enzymes/ catalysts
Describe the structure and functions of amino acids
Structure:
linear polymers of nucleotides
bases are linked by phosphodiester bonds
Function:
store and transfer genetic information for cellular functions and interactions
Describe the structure and functions of lipids
Structure:
hydrophilic head
hydrophobic tails ( hydrocarbon chains )
Function:
formation of membranes/ barriers
energy storage (tails)
signaling
Describe the structure and functions of carbohydrates
Structure:
highly branched monosaccharide ( 6C) polymers
animals-branched glycogen, plants-starch
Function:
cell-cell recognition
energy storage
structural
Reasons why we need prokaryotic cells
Critical for our health:
help digest food
maintain a functional immune system
impact on mental health, obesity and intelligence
In Vitro
Studying the behaviour of molecules in an isolated environment
In Vivo
Studying the behaviour of molecules within a living organism
Definition of free energy
G=H-TS
Where:
g free energy (able to do work)
h is the number and kind of bonds (enthalpy)
s is the degree of randomness (entropy)
t is temperature in Kelvin
What are the characteristics of a spontaneous reaction?
Delta G is negative (final E is less than initial E)
Release free energy
Reaction is exergonic
What are the characteristics of a non-spontaneous reaction?
Delta G is positive (final E is more than initial E)
Needs input of free energy
Reaction is endergonic
What is it mean when a system is at equilibrium?
Delta G=0. There is no change in free energy
How do cells drive thermodynamically unfavourable reactions?
Doing coupling reactions where the sum of all free energy is negative (spontaneous)
Where is the energy taken to form ATP?
Taken from sunlight or fuels
How does the energy extracted from ATM serve in biochemical processes?
The energy released from its breaking down and synthesis is the link between catabolic and anabolic reactions
Where is the information about cells stored?
In DNA which is a linear sequence of nucleic acids
What does DNA provide for different organisms?
infos for the formation of other cellular processes
template production of identical DNA molecules
Explain the central dogma of biochemistry
DNA replication: making DNA from DNA
Transcription: mRNA chain of a gene
RNA (language)
Translation: how mRNA goes to protein (language)
Protein: made from amino acids/polypeptides
What influences the protein’s biological activity?
The structure of the protein which is moreover dictated by the amino acid s