Spinal chord associated plexi and nerves - LCC
1/41
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
42 Terms
filum terminale
extension of the pia matter that connects the inferior end of the spinal cord to the coccyx

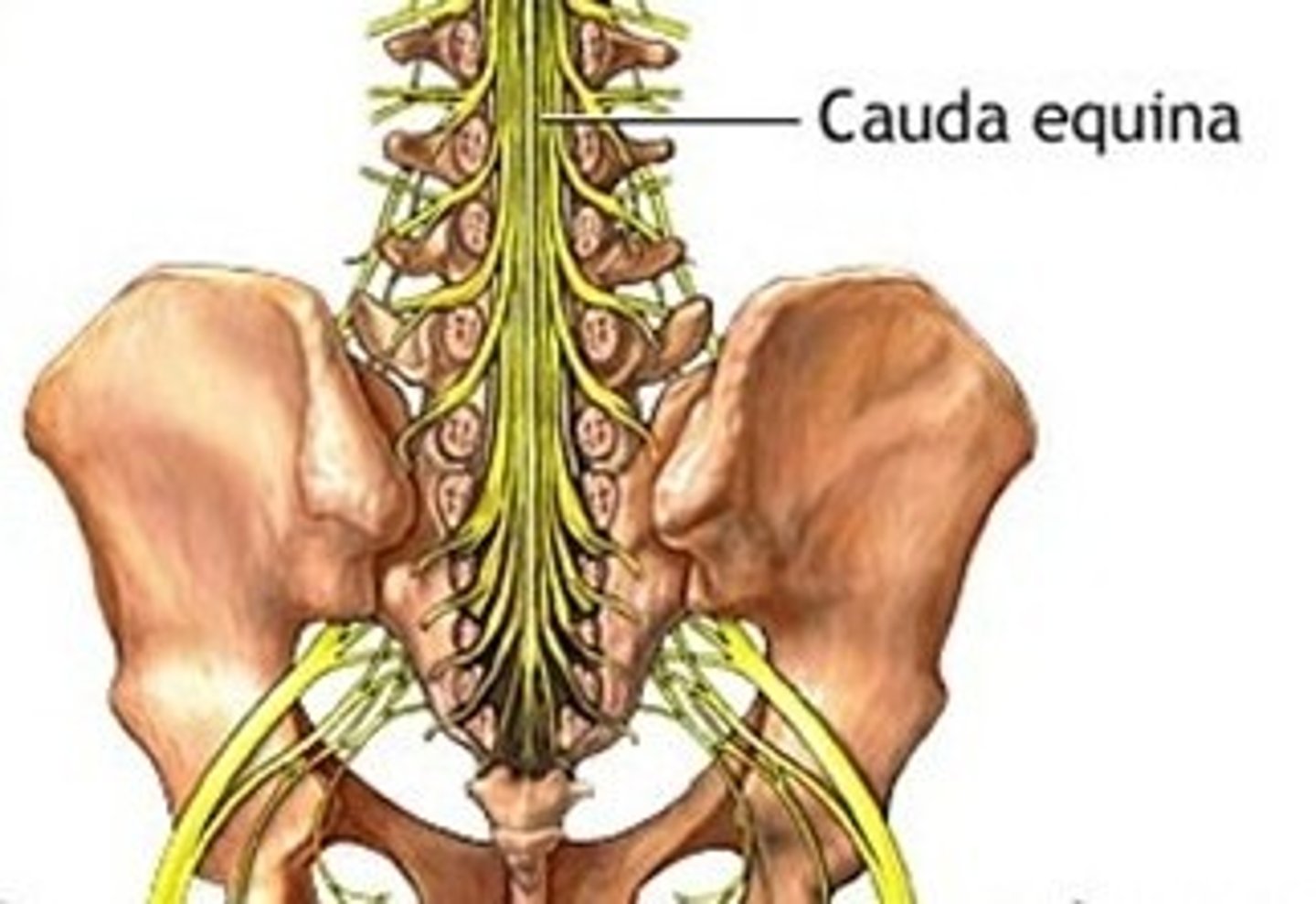
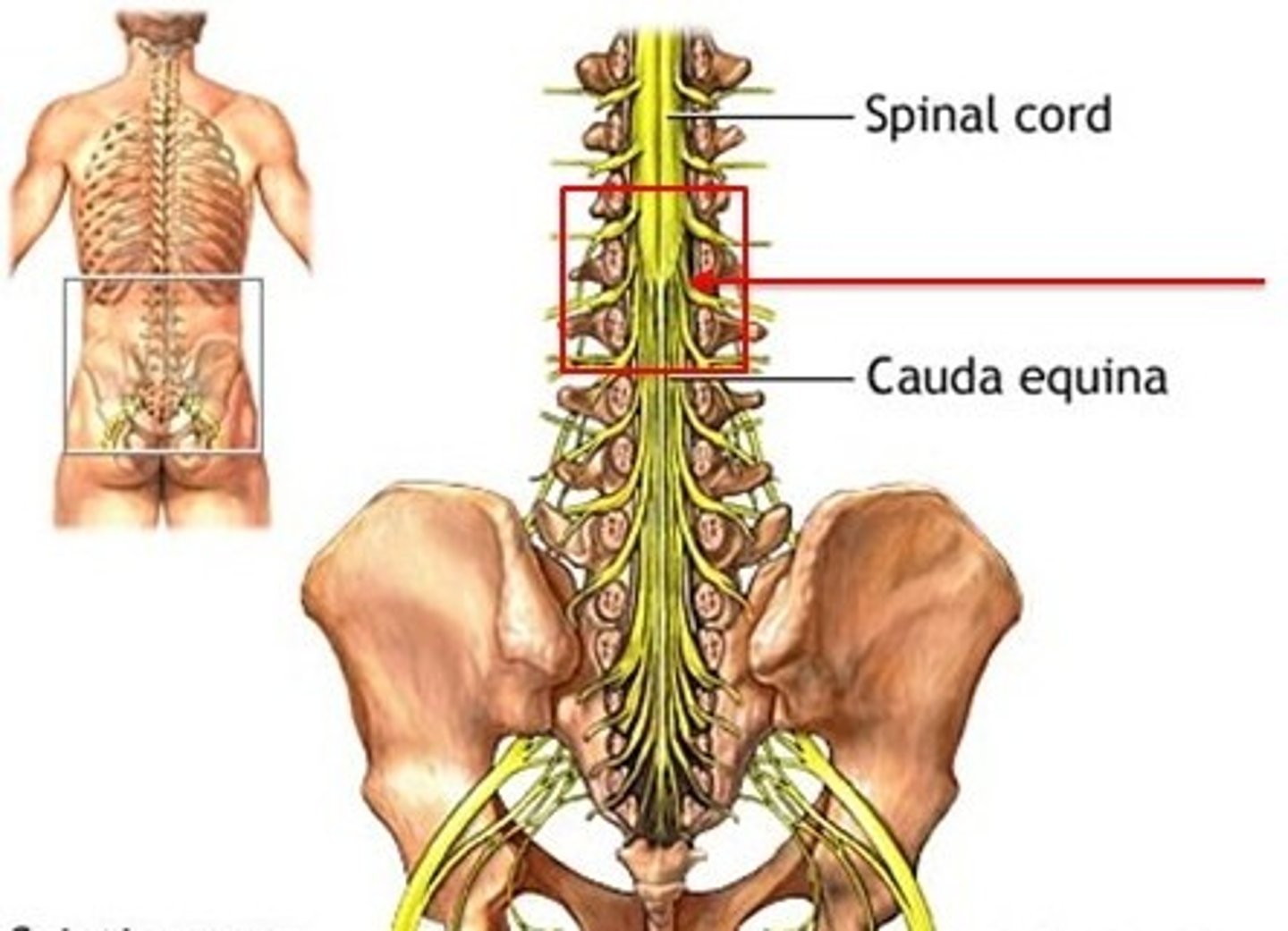
cauda equina
Sometimes called the horsetail
The bundle of nerve roots that occupy the vertebral canal from L2 to S5 is called the
conus medullaris
tapered tip at the end of the spinal cord around L1 and L2
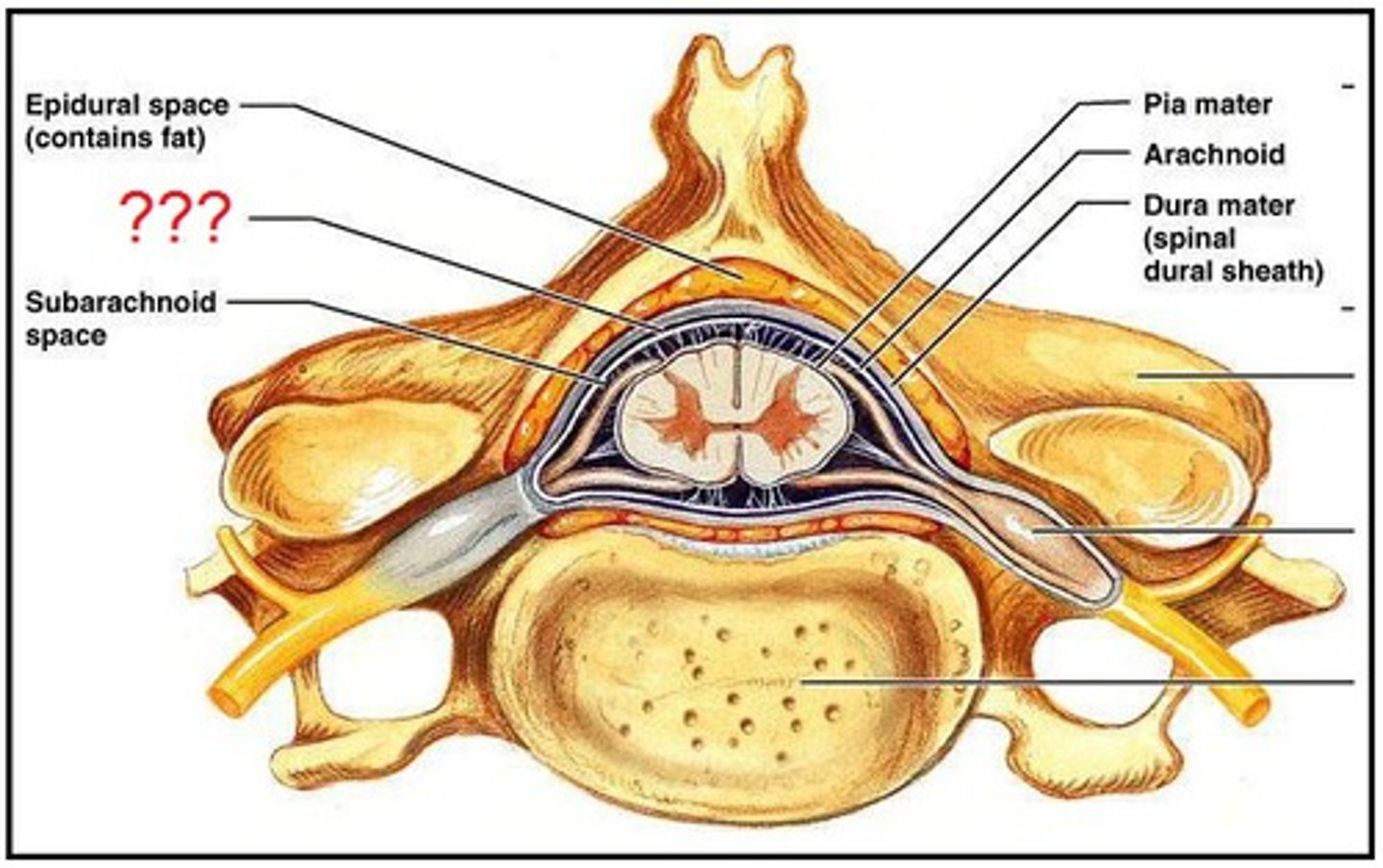
epidural space
Within the vertebral canal, lies between bone and dura mater
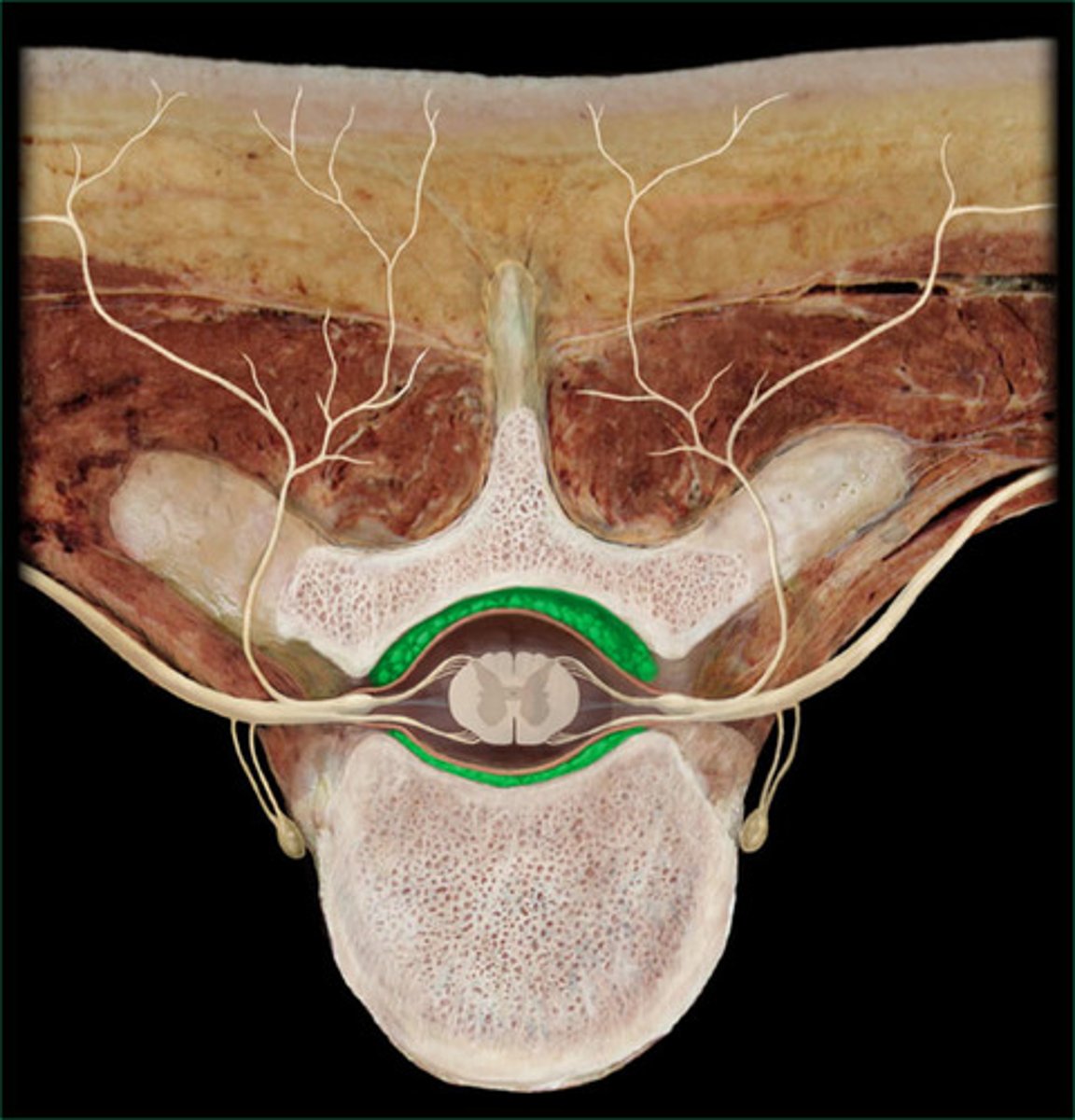
Subdural space
Found between dura mater and arachnoid.
Anterior median fissure
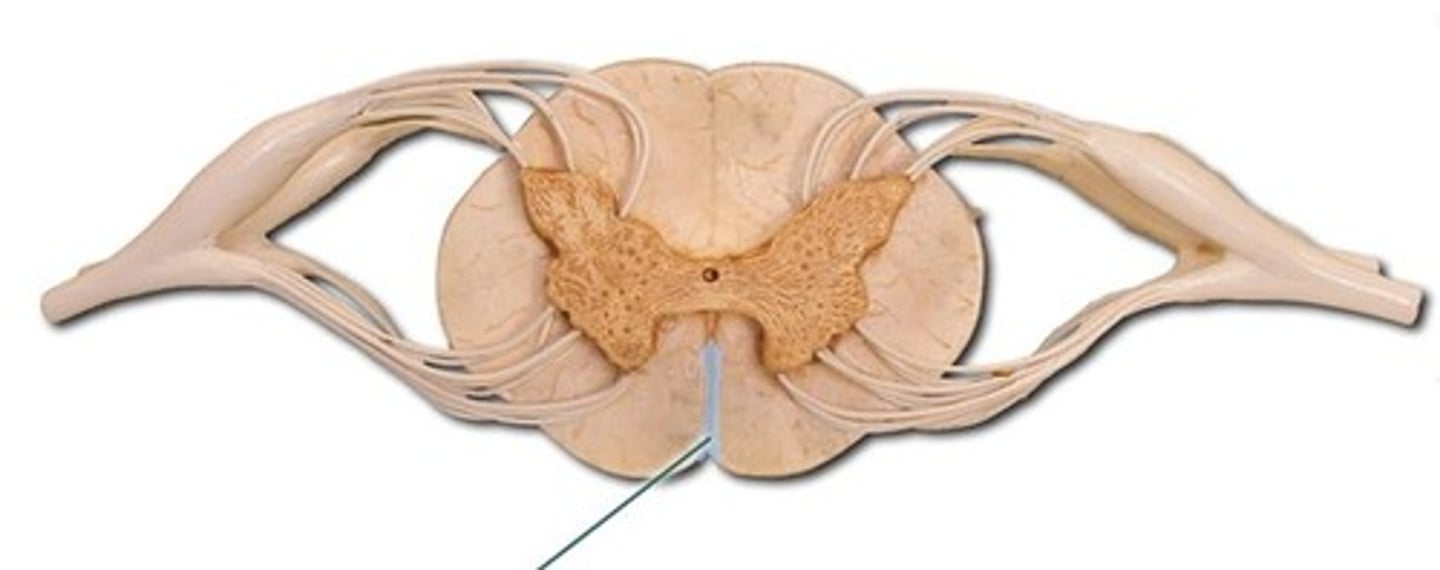
central canal
Contains blood vessels and nerves
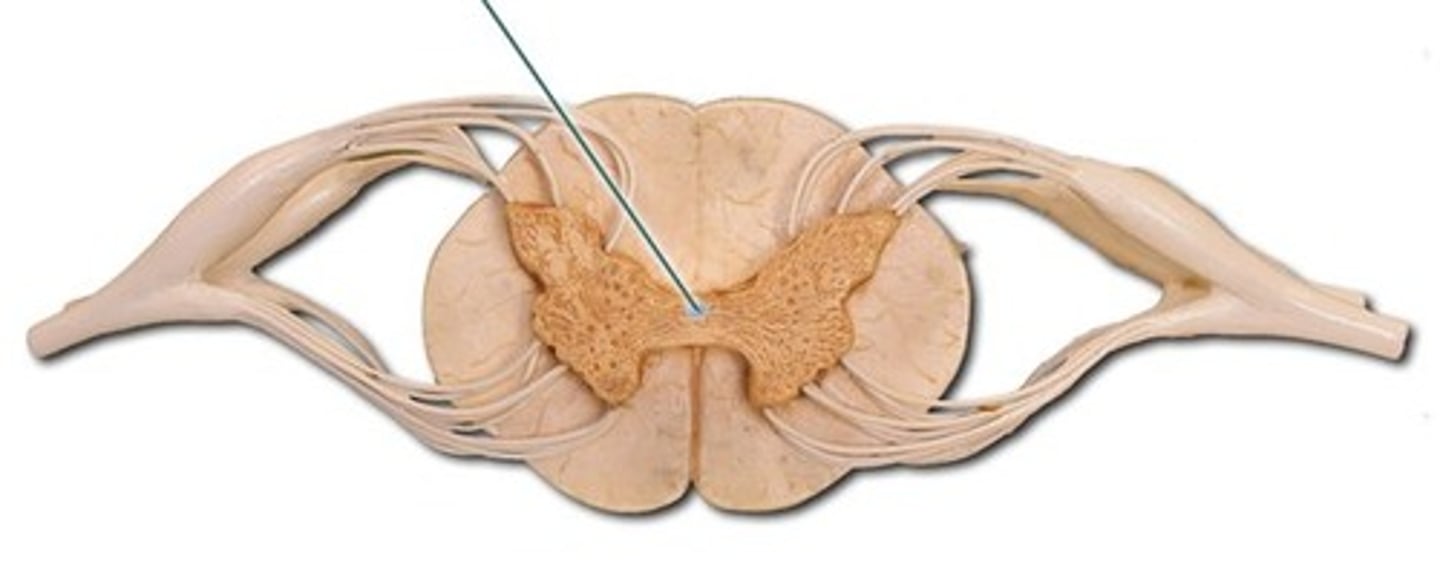
Posterior median sulcus
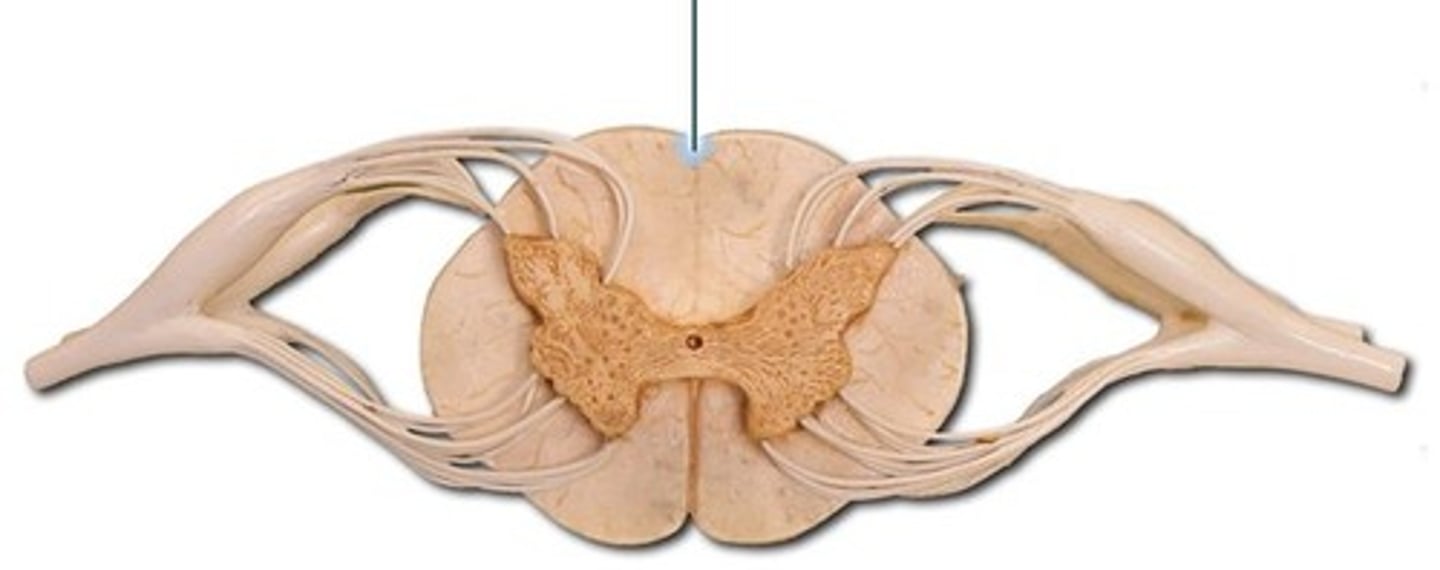
Gray matter commissure
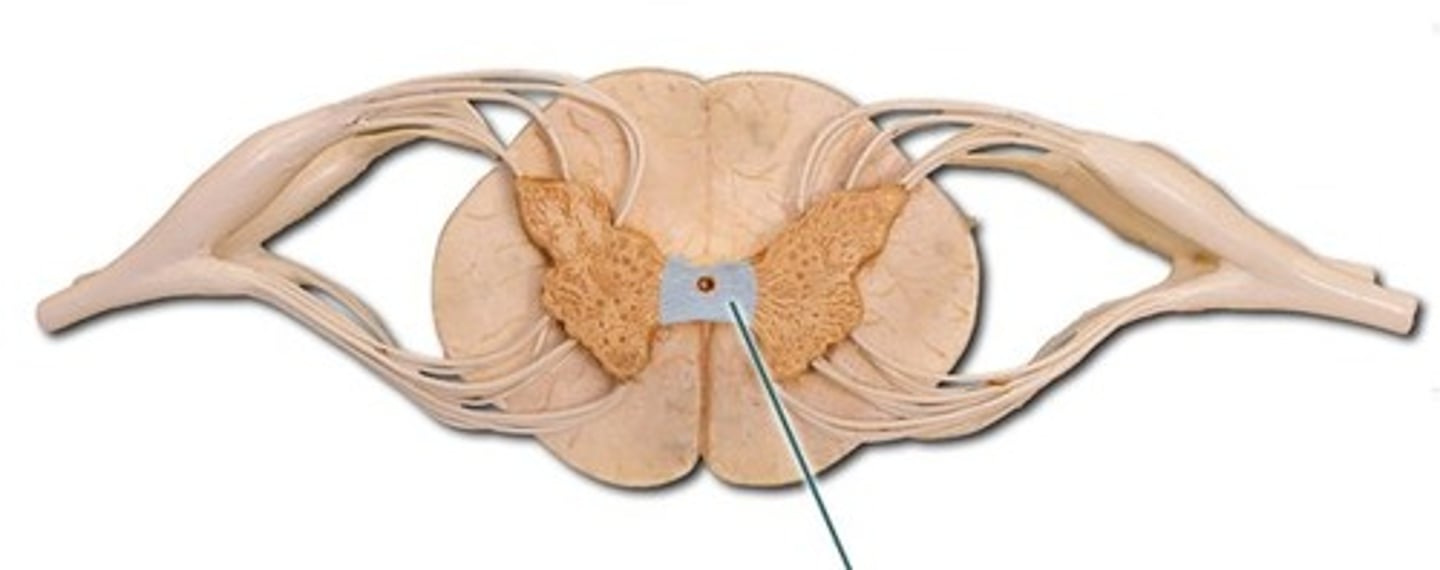
White matter commissure (dorsal or ventral)
dorsal horn
Gray matter
sensory nuclei that receive and process incoming somatosensory information.
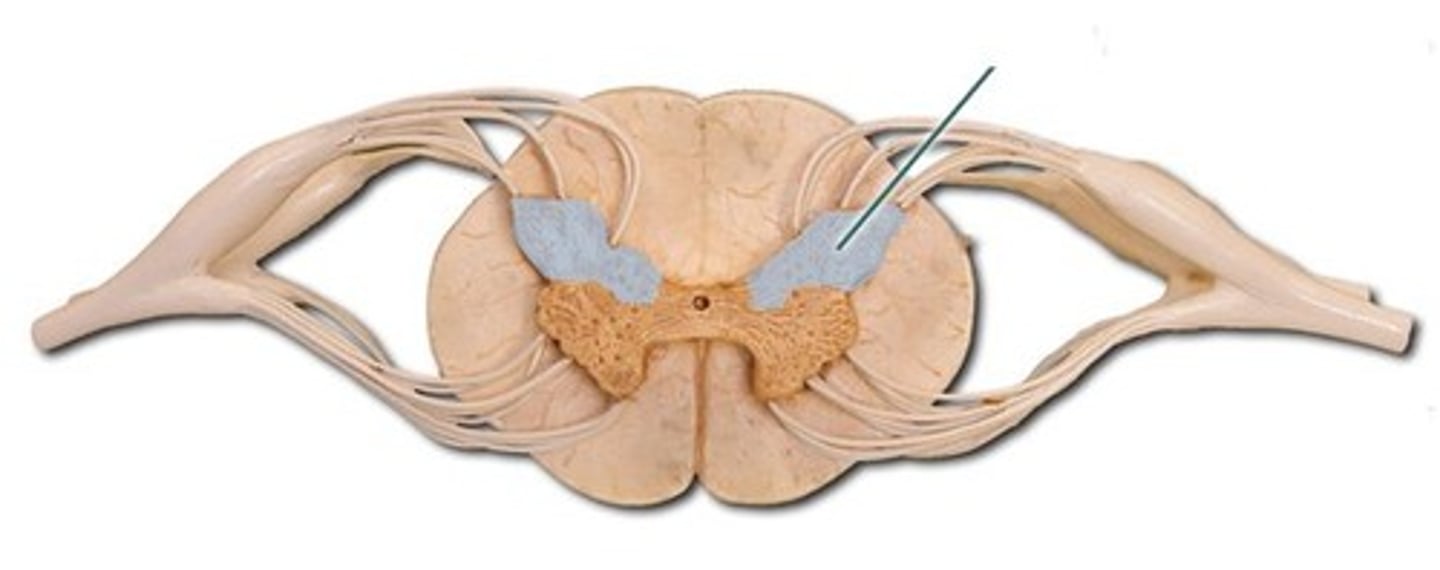
lateral horn
Gray matter
autonomic neurons that innervate visceral and pelvic organs.
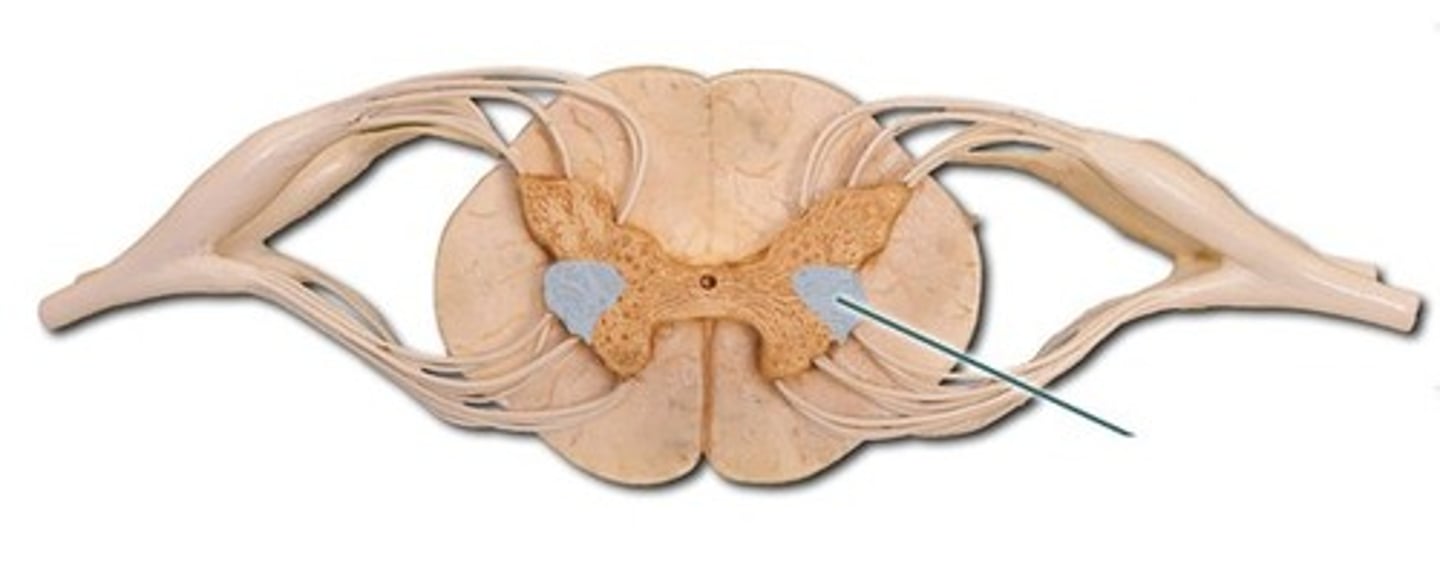
ventral horn
Gray matter
motor neurons that innervate skeletal muscle.
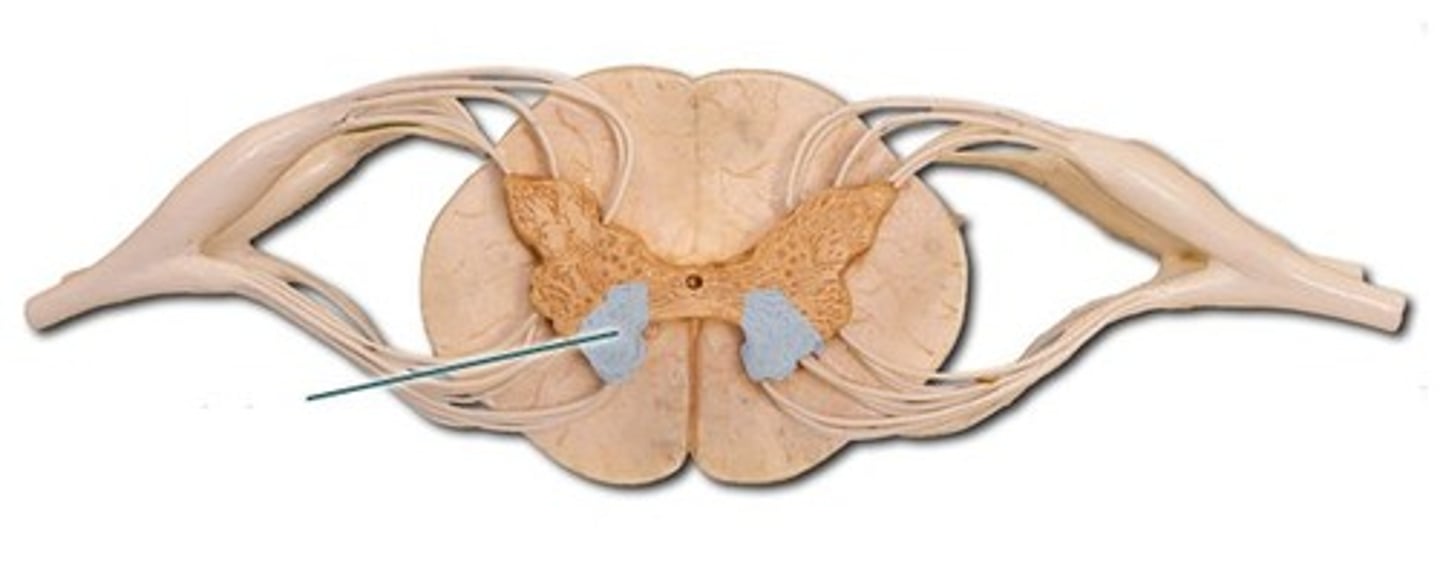
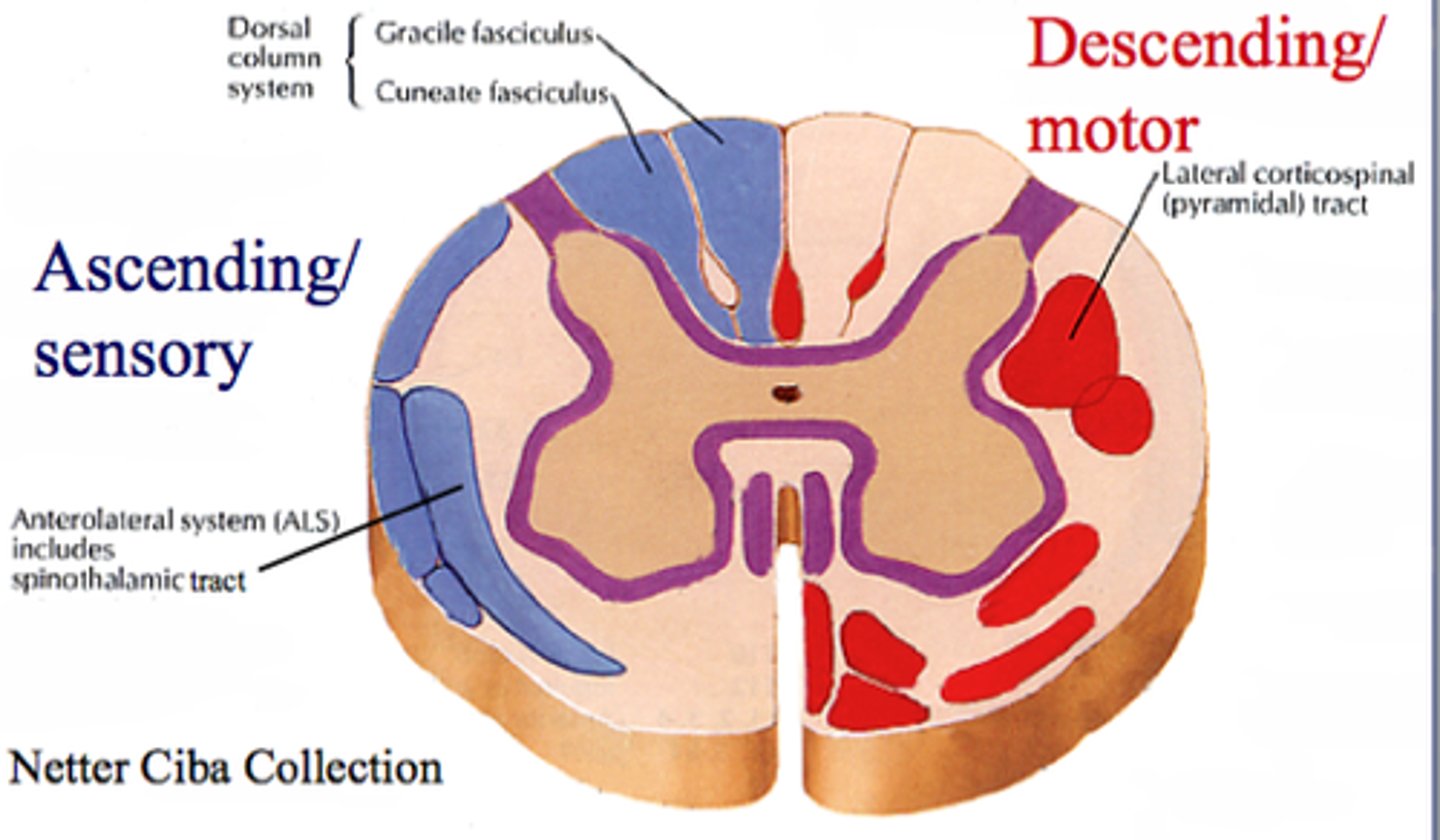
Dorsal column
White matter
sensory to the brain
fine touch and joint position (proprioception_
Lateral column
White matter
Motor information from the brain
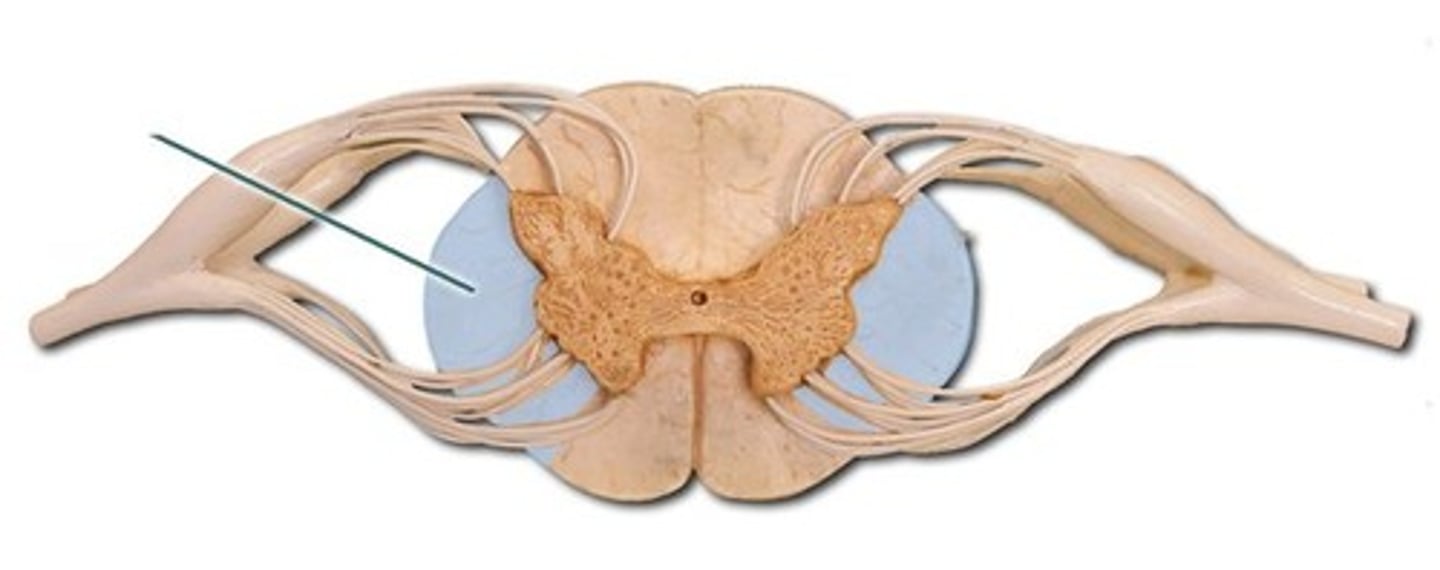
Sensory tract
Areas of white matter in the columns
Carry ascending sensory signals to the brain
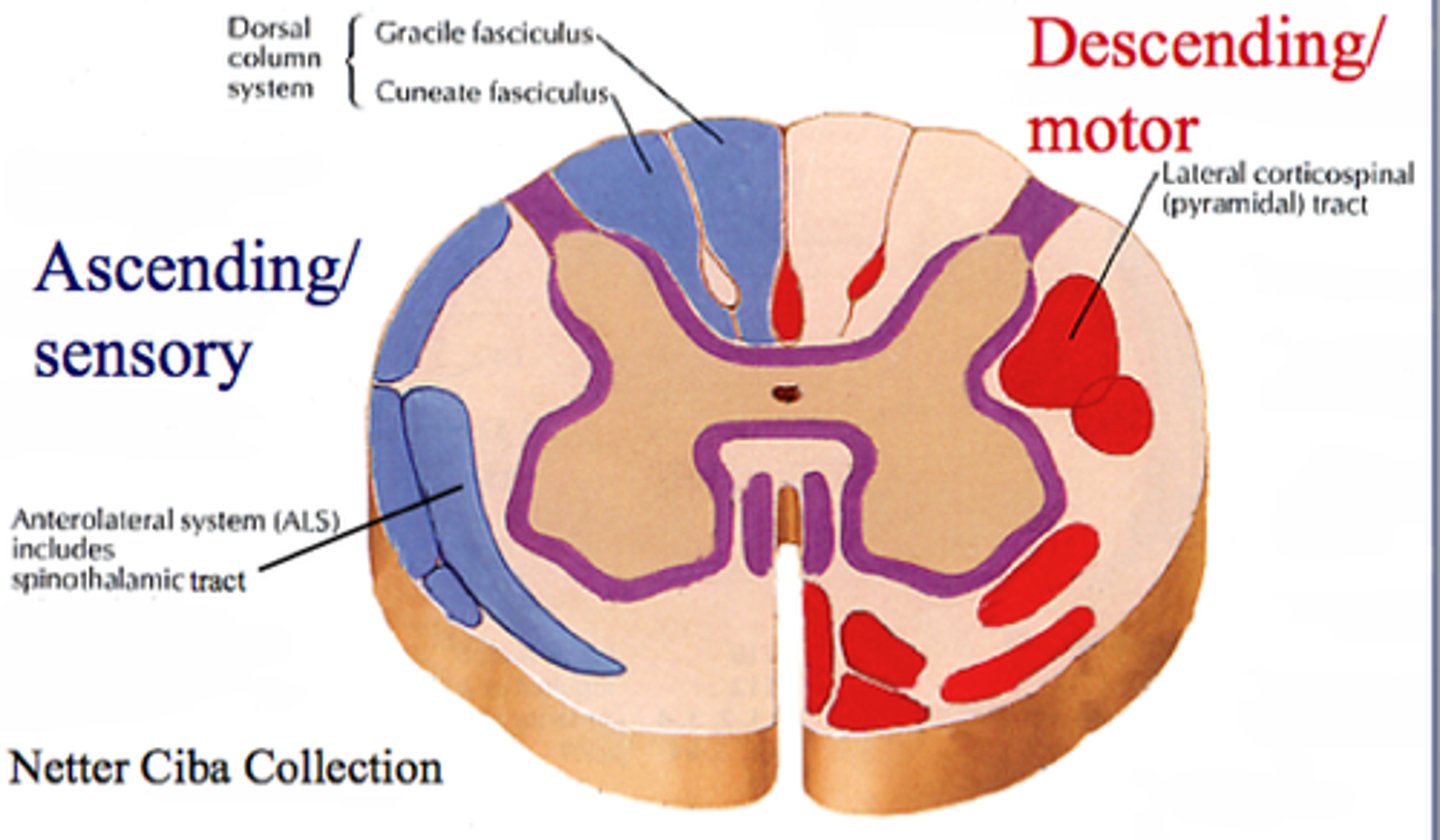
Motor tract
Areas of white matter in the columns
Carry descending motor signals to the body
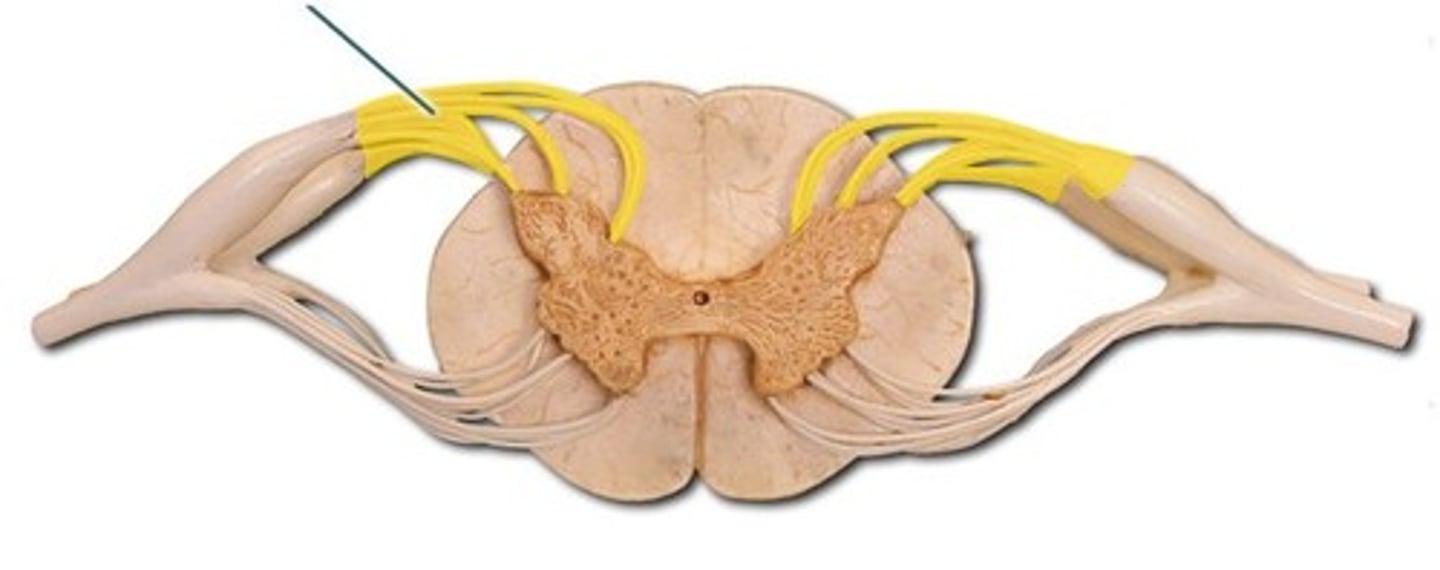
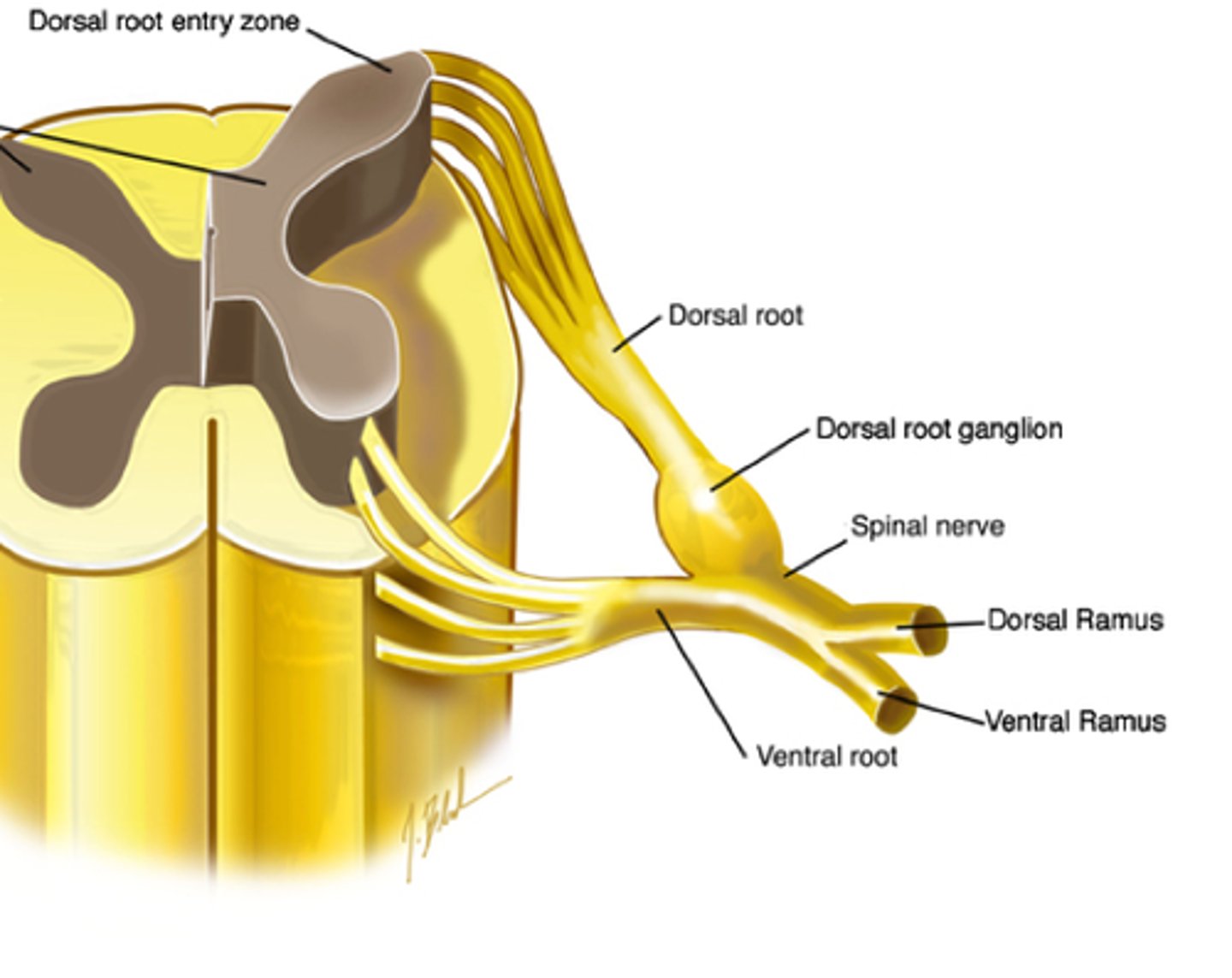
dorsal root
Contains afferent (incoming) sensory information within the spinal cord
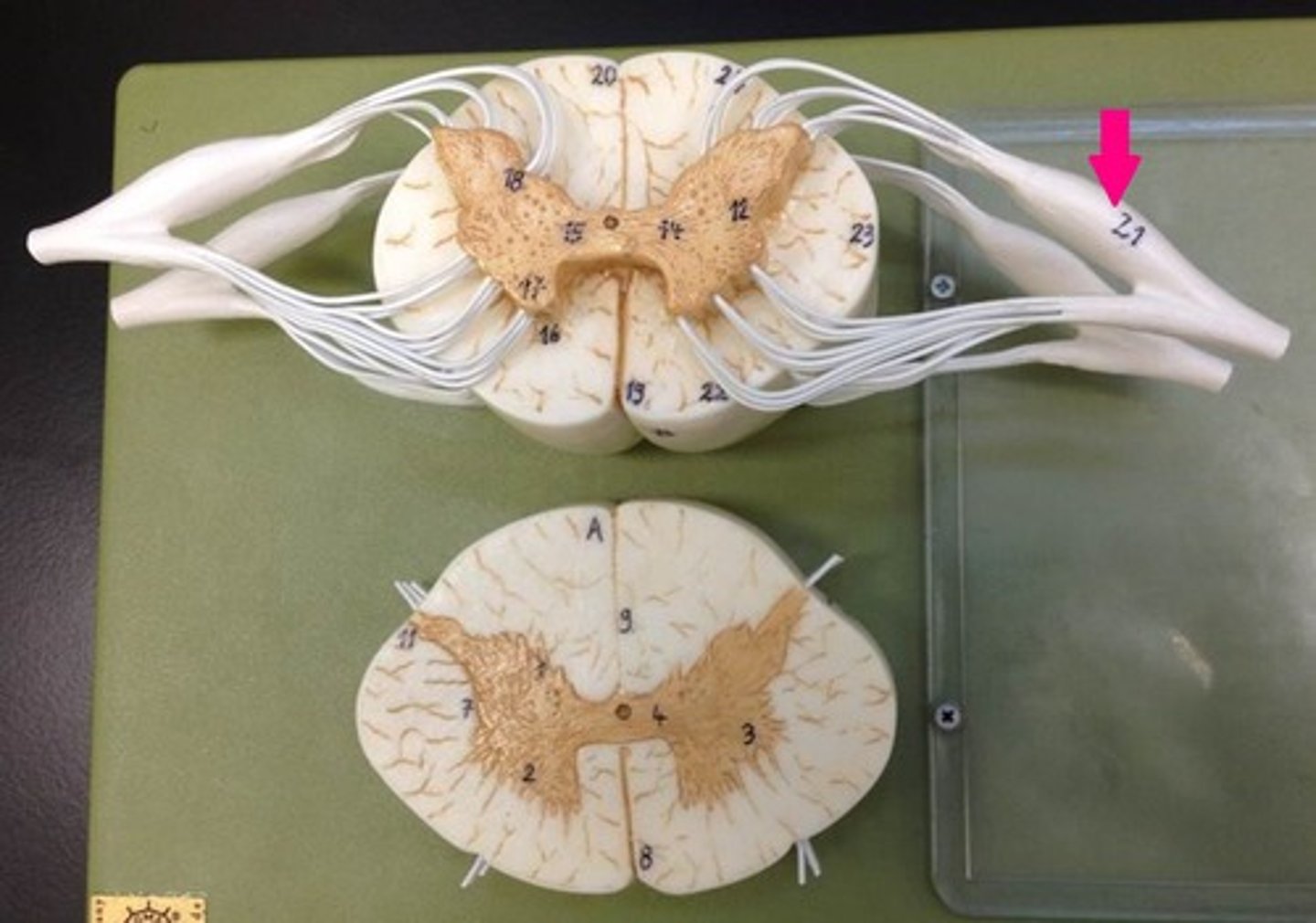
dorsal root ganglion
Thick spot before the dorsal root, filled with cell bodies of sensory neurons
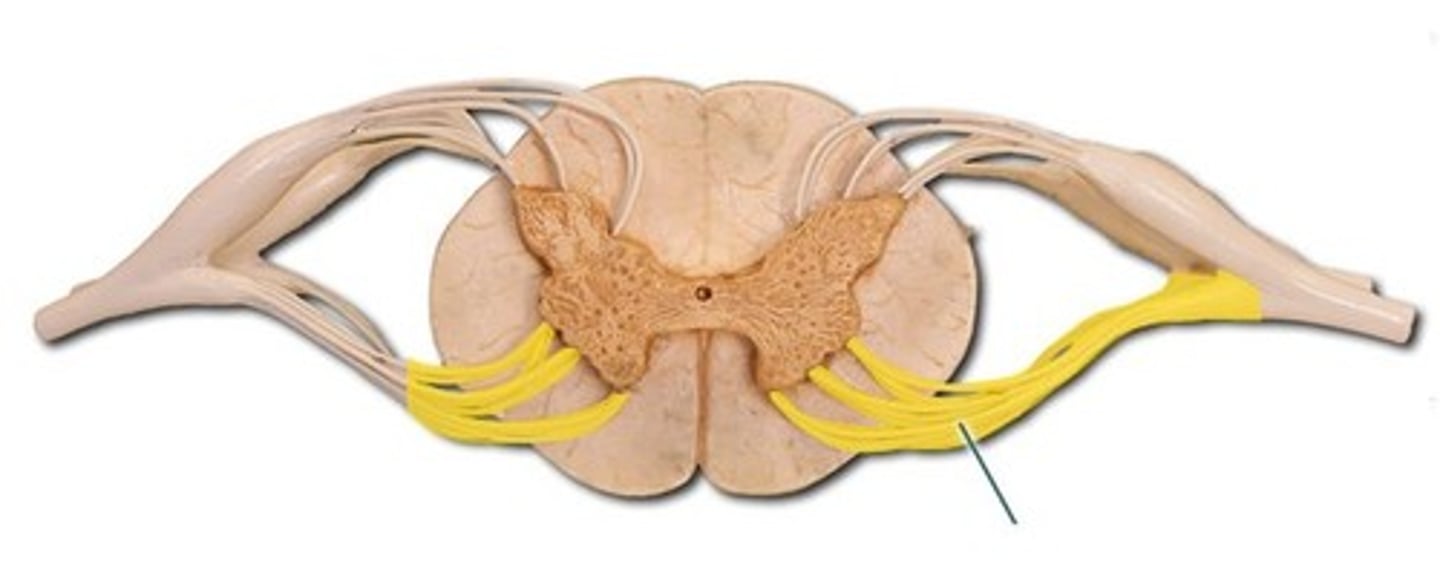
ventral root
Contains efferent (outgoing) motor fibres within the spinal cord
spinal nerve trunk
Structure D
Where the dorsal and ventral roots merge
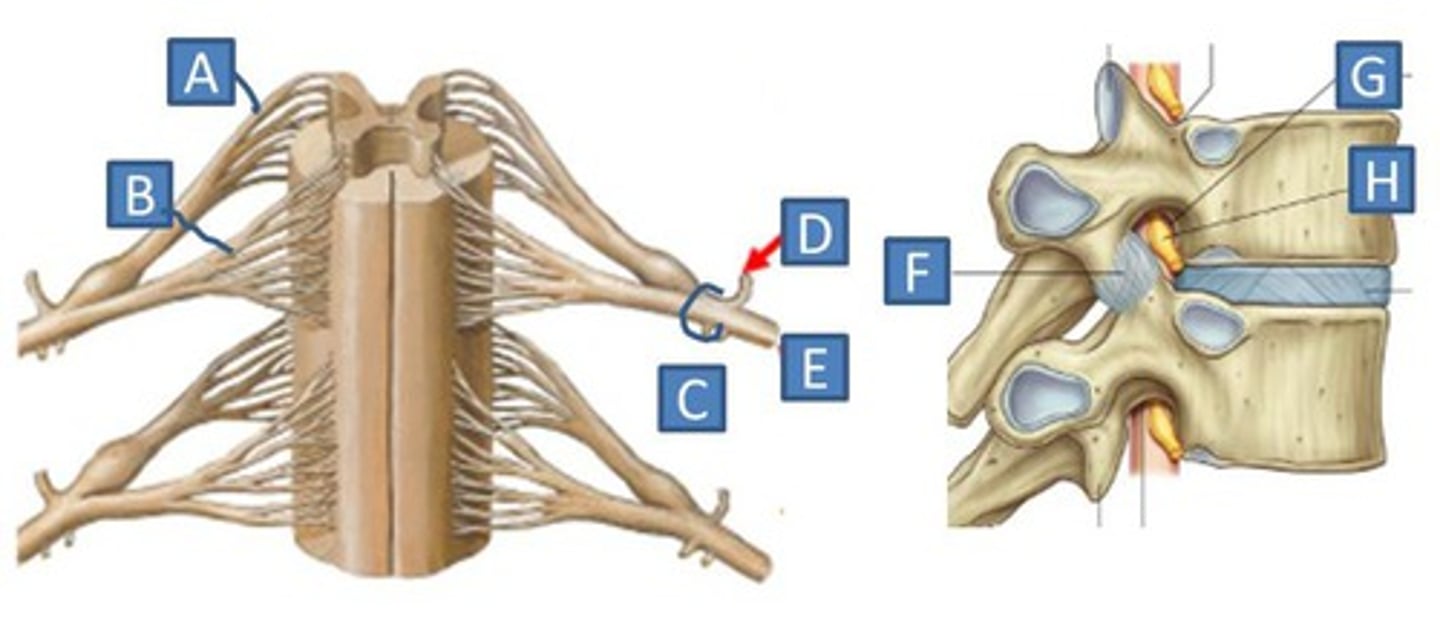
spinal nerve
31 pairs of nerves arising from spinal cord, all contain sensory and motor neurons which function in sensory input and motor output.
dorsal rami
Dorsal branch of a spinal nerve.
Carry motor information to muscles
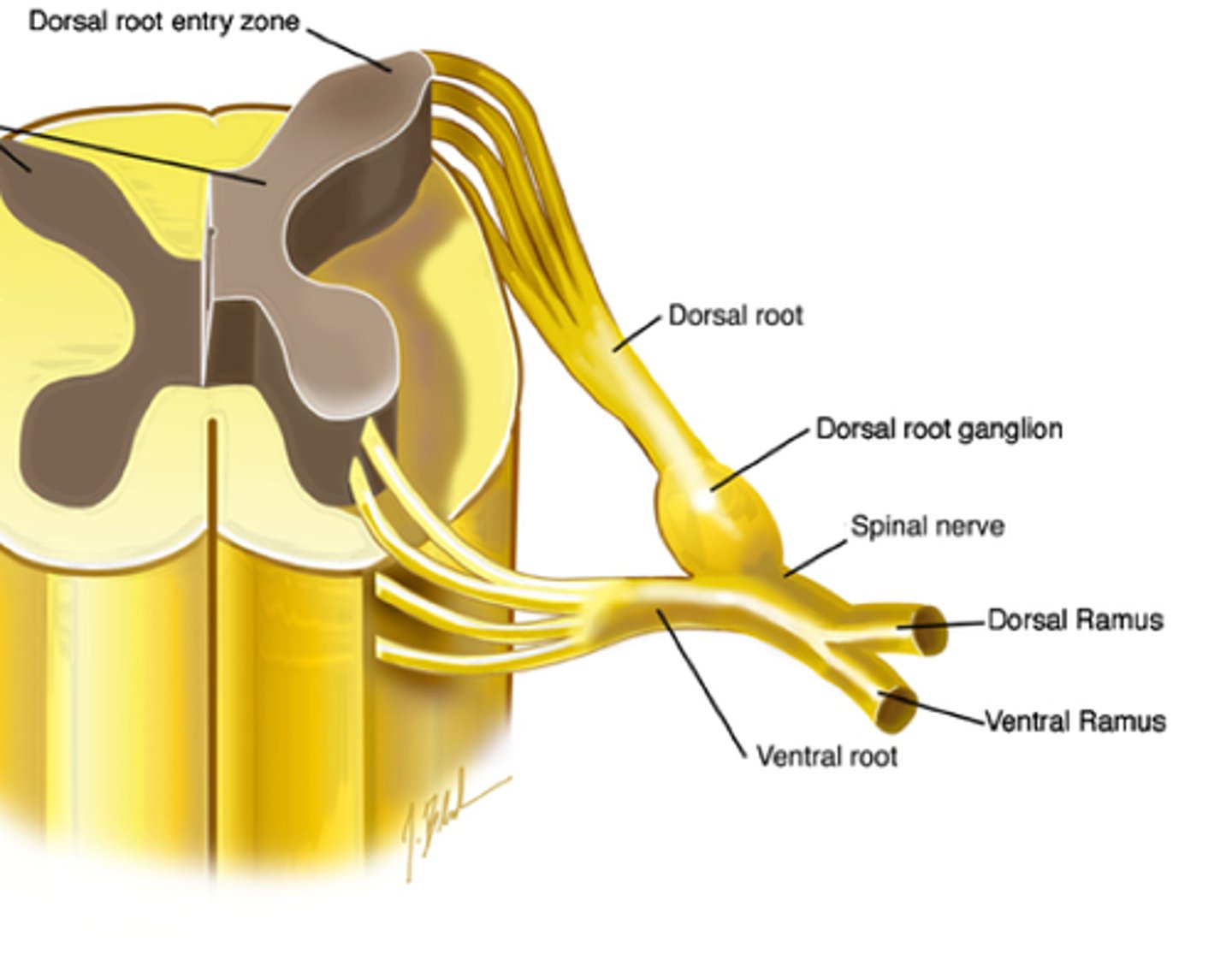
ventral rami
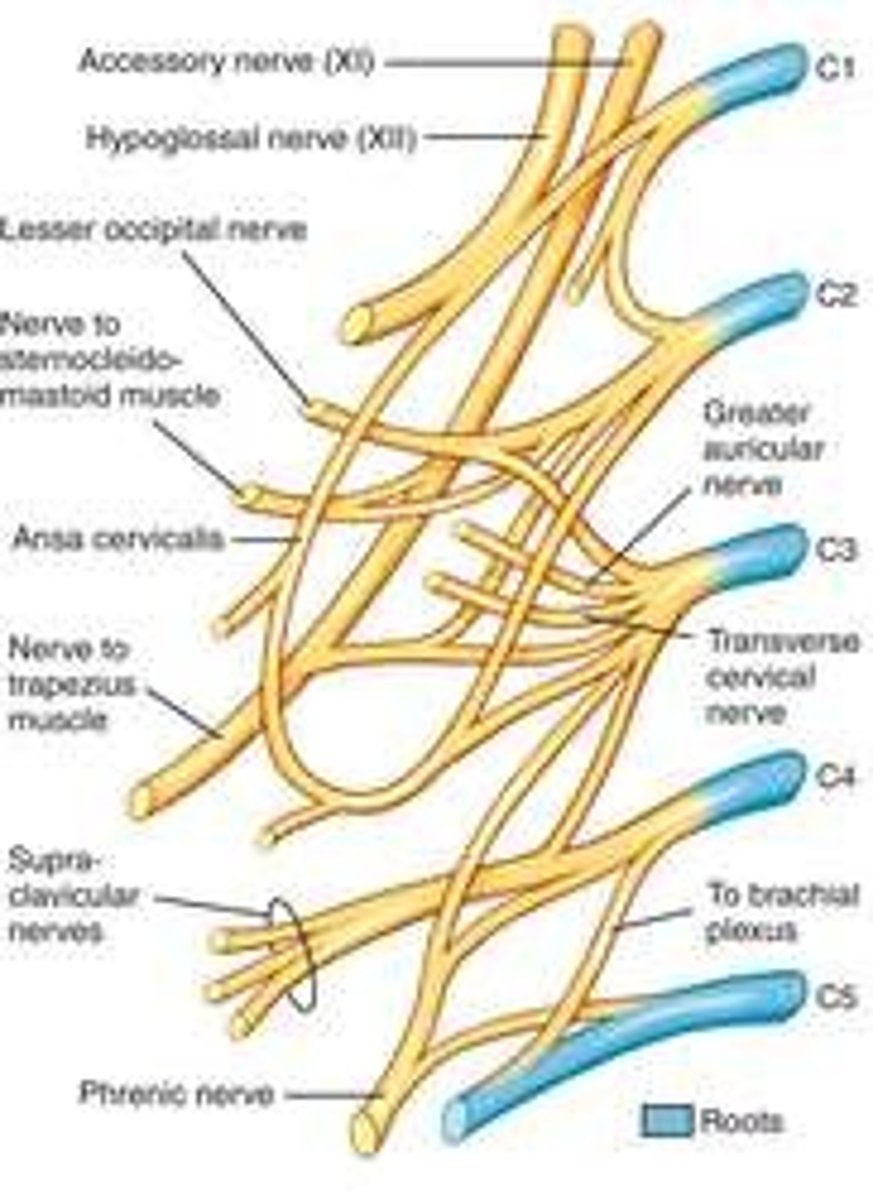
cervical plexus
Made up of nerves from C1-C4. Nerves formed from the cervical plexus innervate the back of the head, as well as some neck muscles.
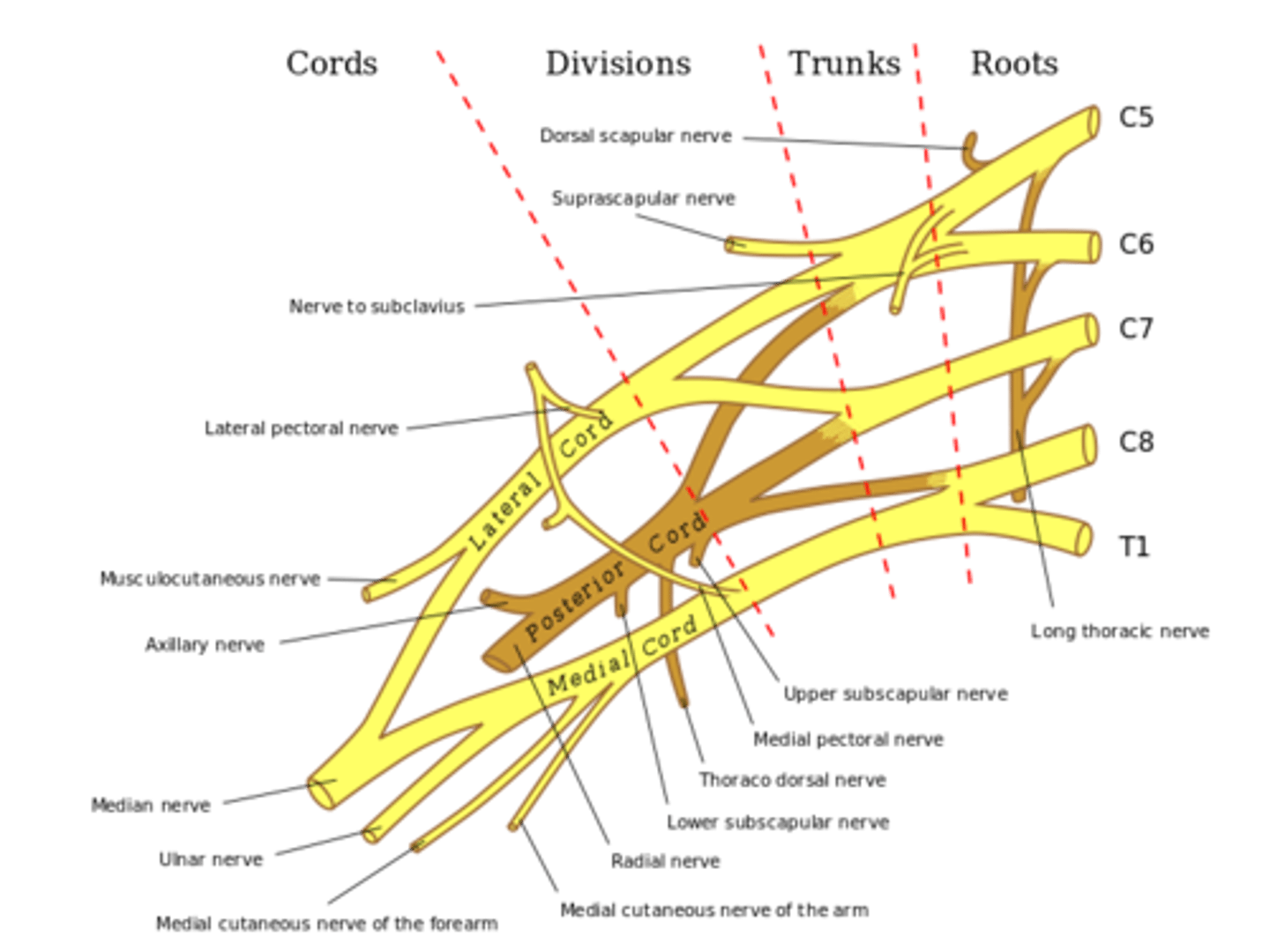
brachial plexus
Made up of nerves from C5-T1. Takes care of all muscles in upper extremity
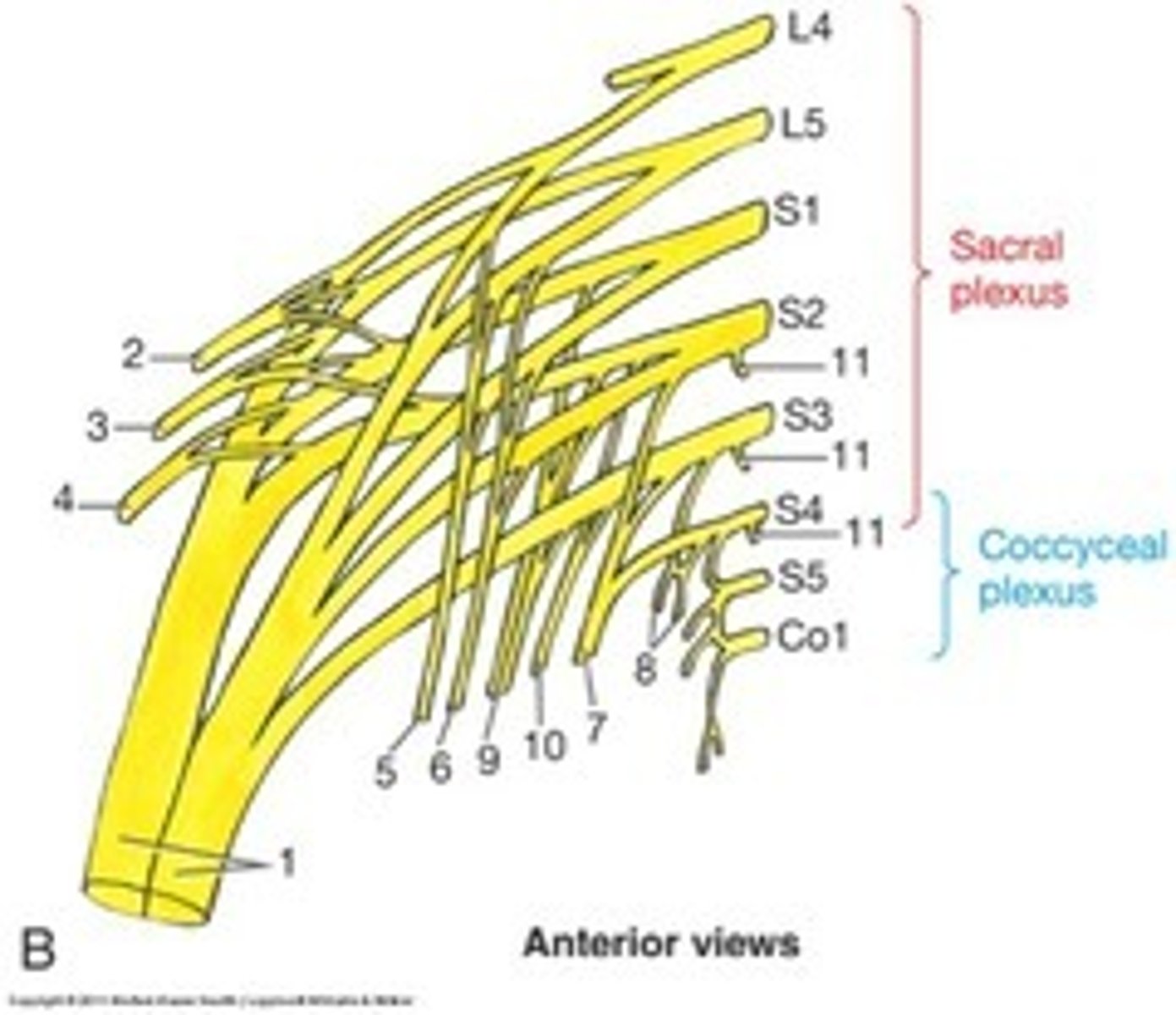
sacral plexus
Made up of nerves from L4-S4. Takes care the posterior thigh, most of the lower leg and foot, and part of the pelvis.
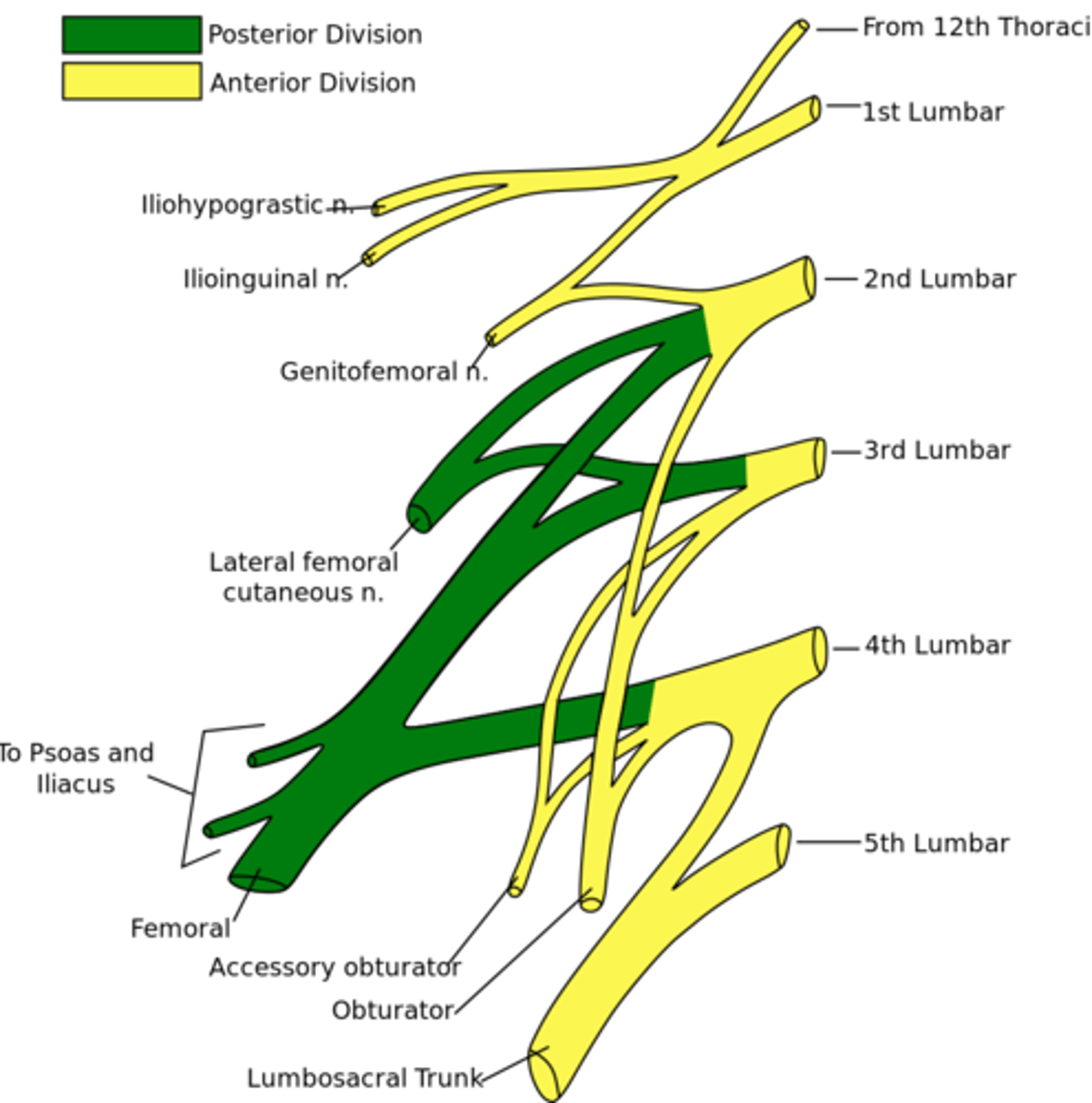
lumbar plexus
Made up of nerves from T12-L4. Innervates the skin and muscles of the abdominal wall, thigh, and external genitalia. Also innervates anterior thigh muscles and some of the skin distal to the inguinal ligament.
Ventral column
White matter
sensory to brain - temp and pain
from brain - motor information
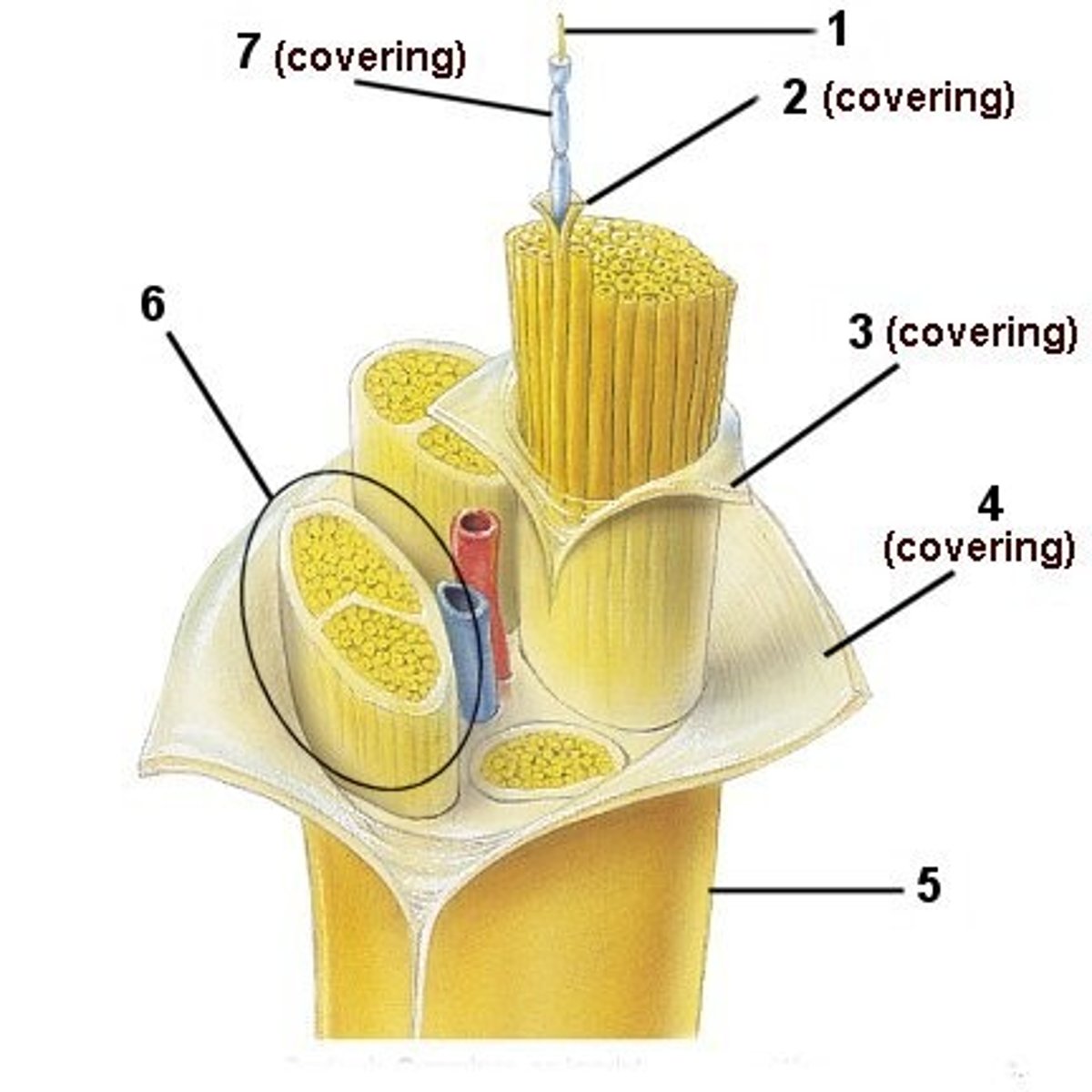
Nerve
Structure 5
A large bundle of neural axon fibers
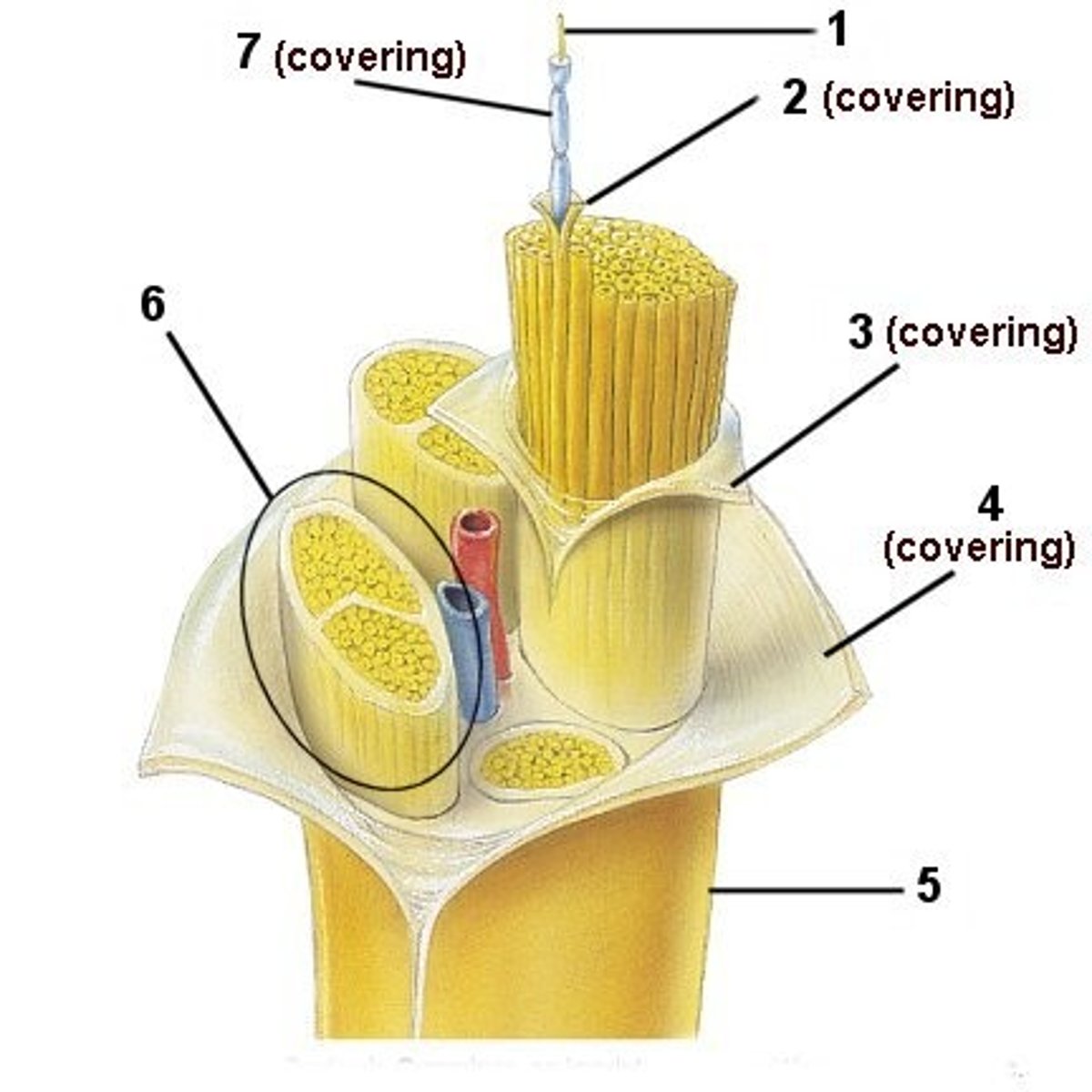
epineurium
Structure 4
Sheath around entire nerve
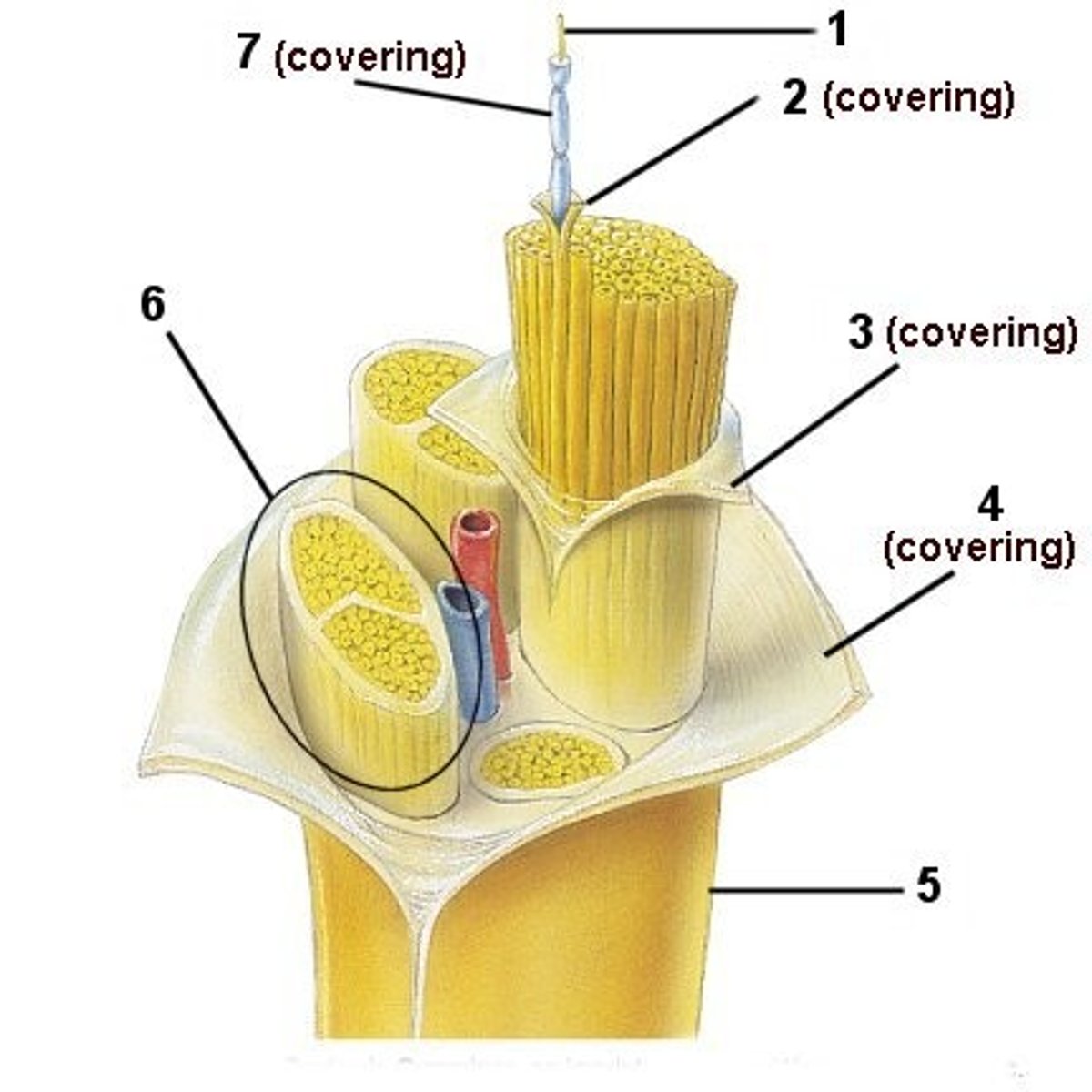
Fascicle
Structure 6
Bundle of axons in a nerve that is wrapped in perineurium
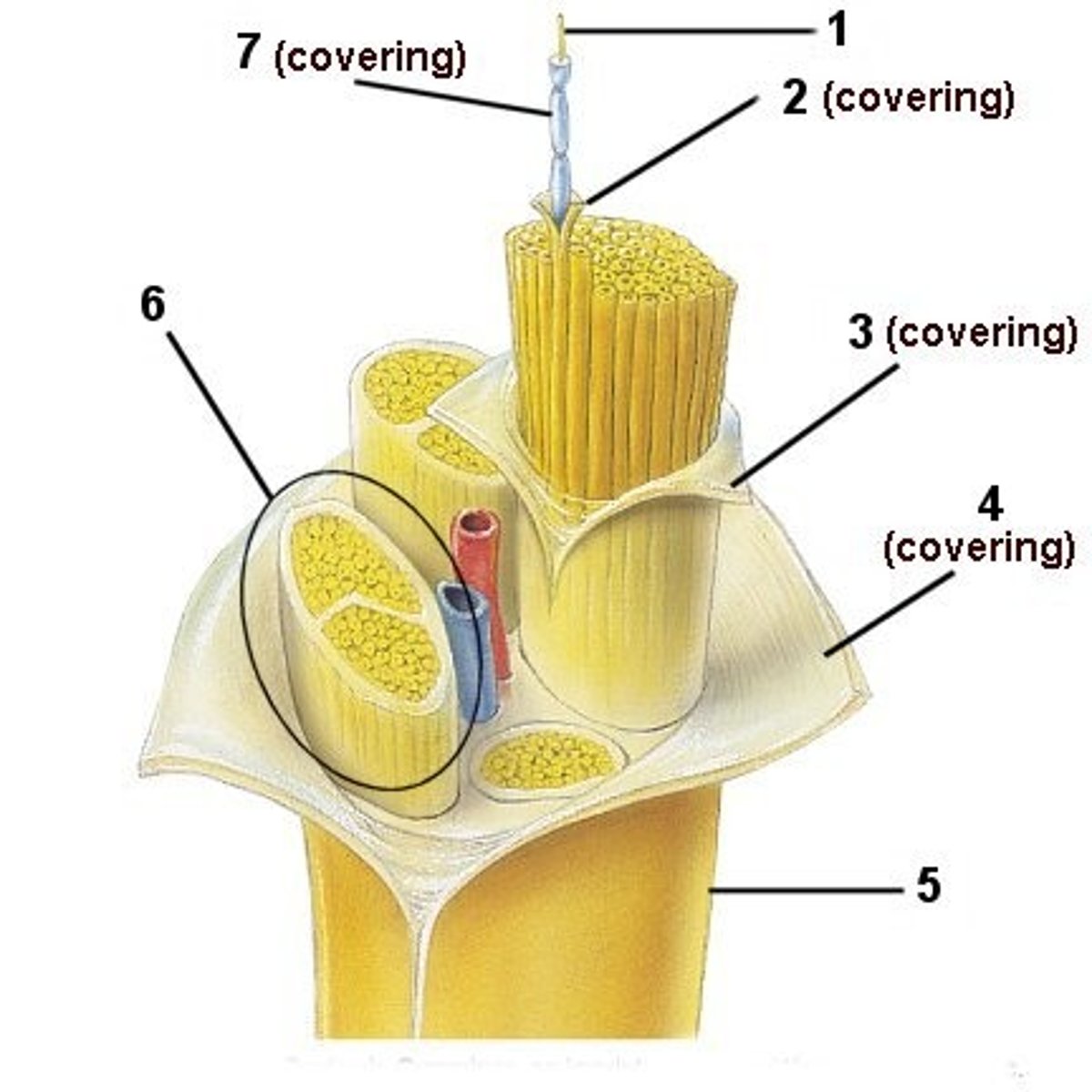
perineurium
Structure 3
Sheath around whole
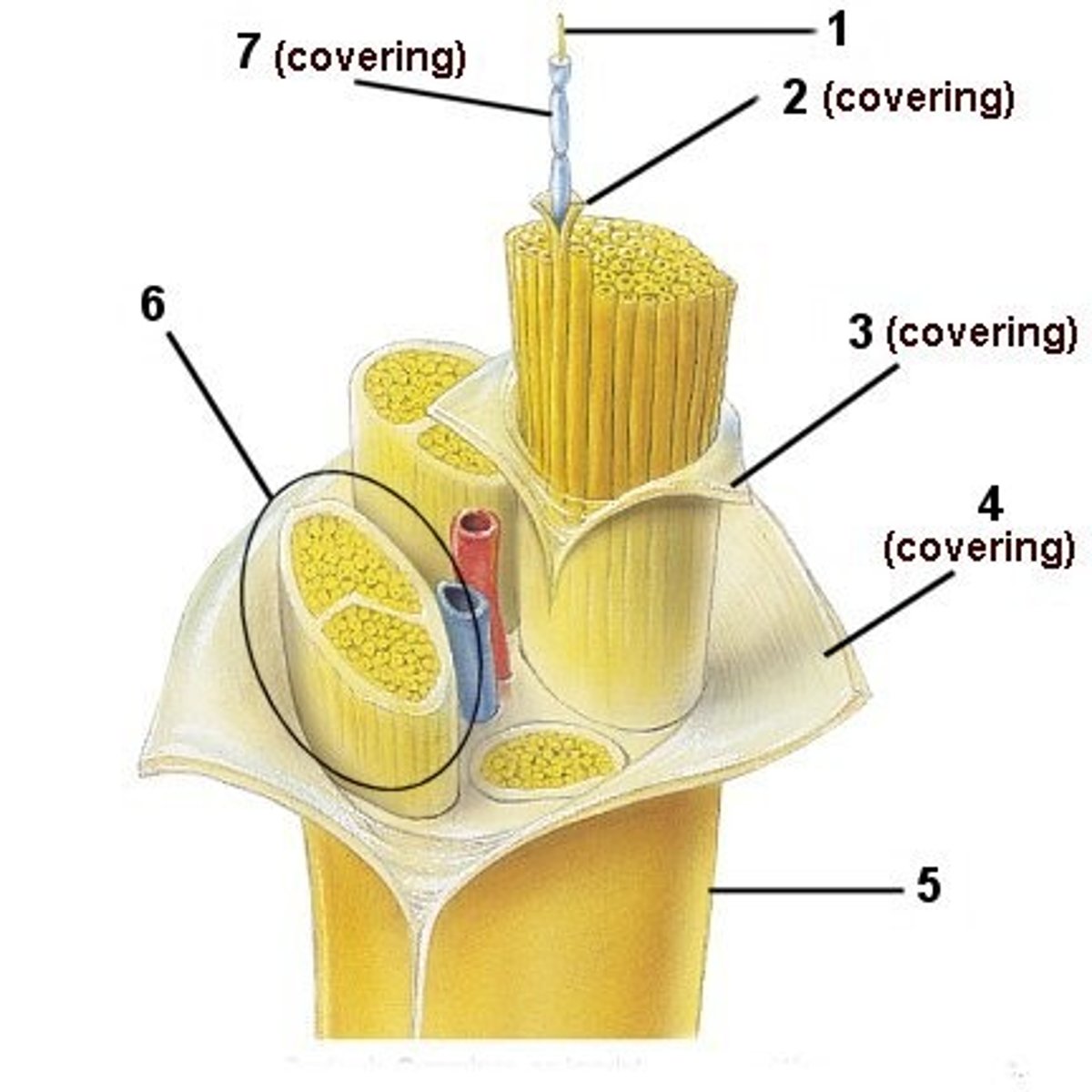
endoneurium
Structure 2
Sheath around each axon in a nerve
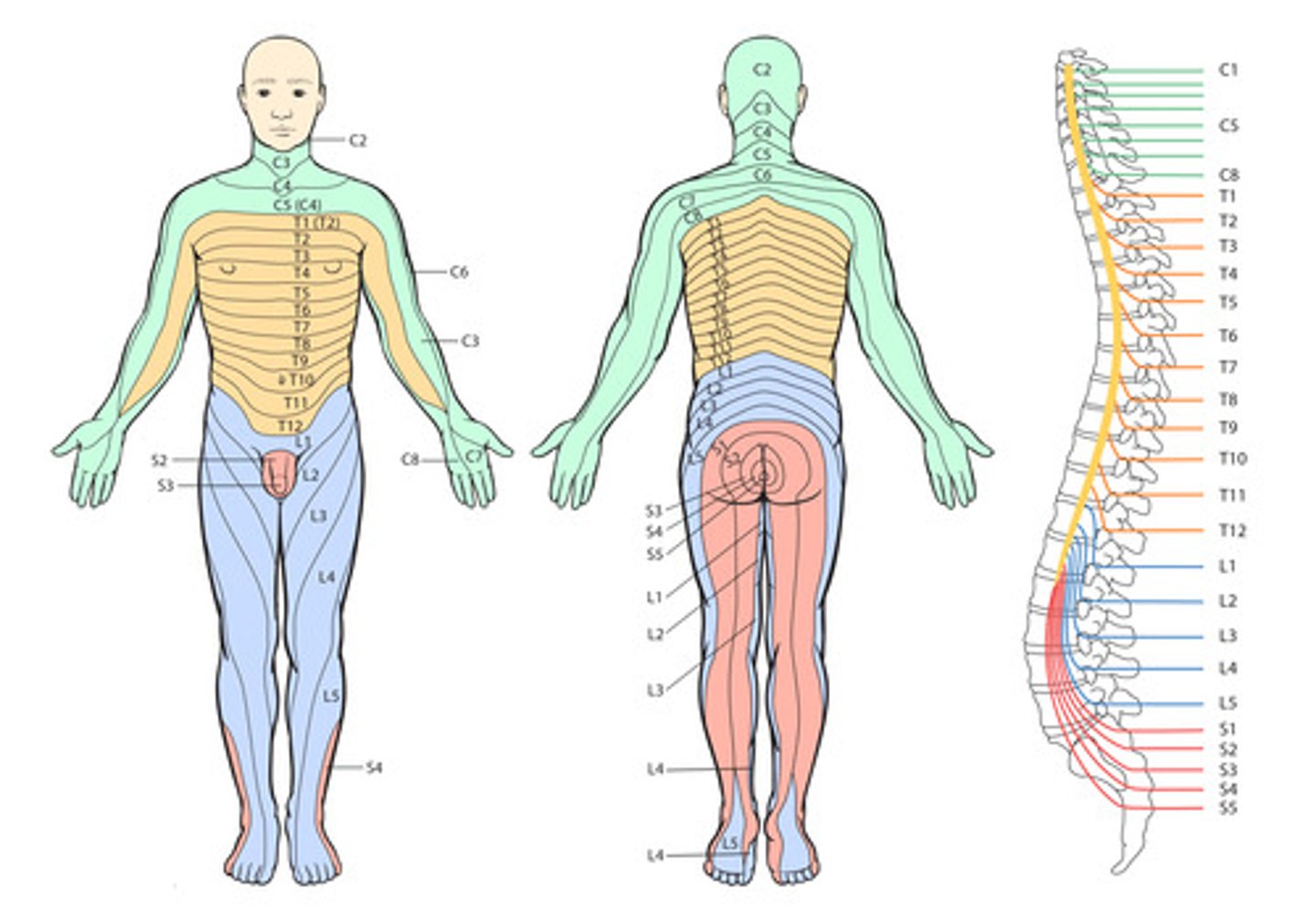
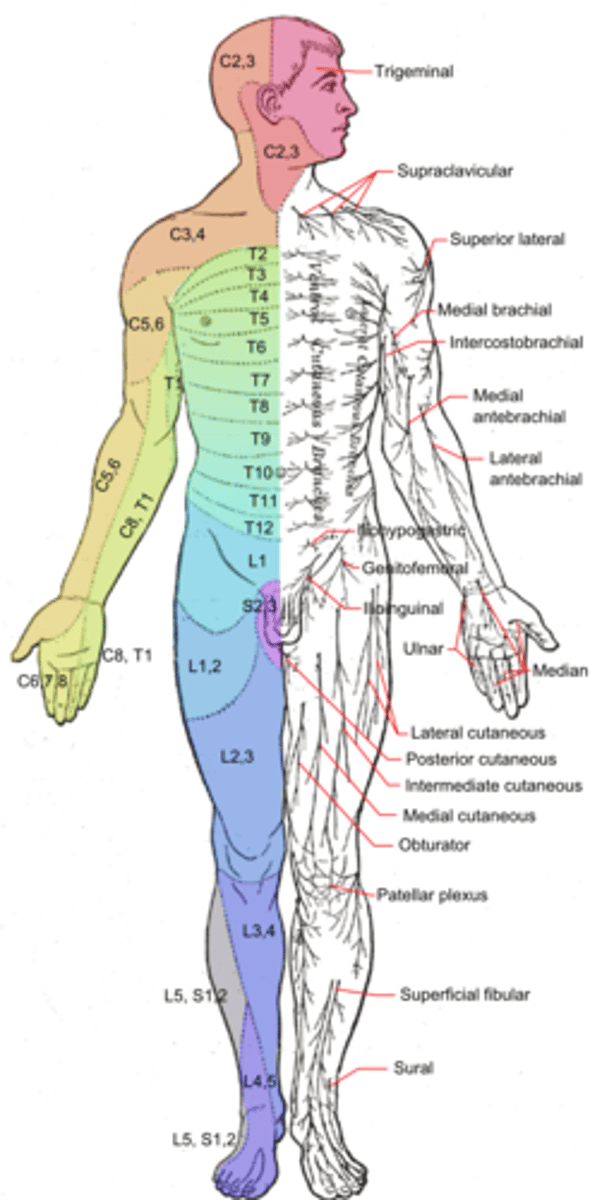
Dermatome
an area of the skin supplied by nerves from a single spinal root.
Myotome
A _________ is the group of muscles that a single spinal nerve root innervates.
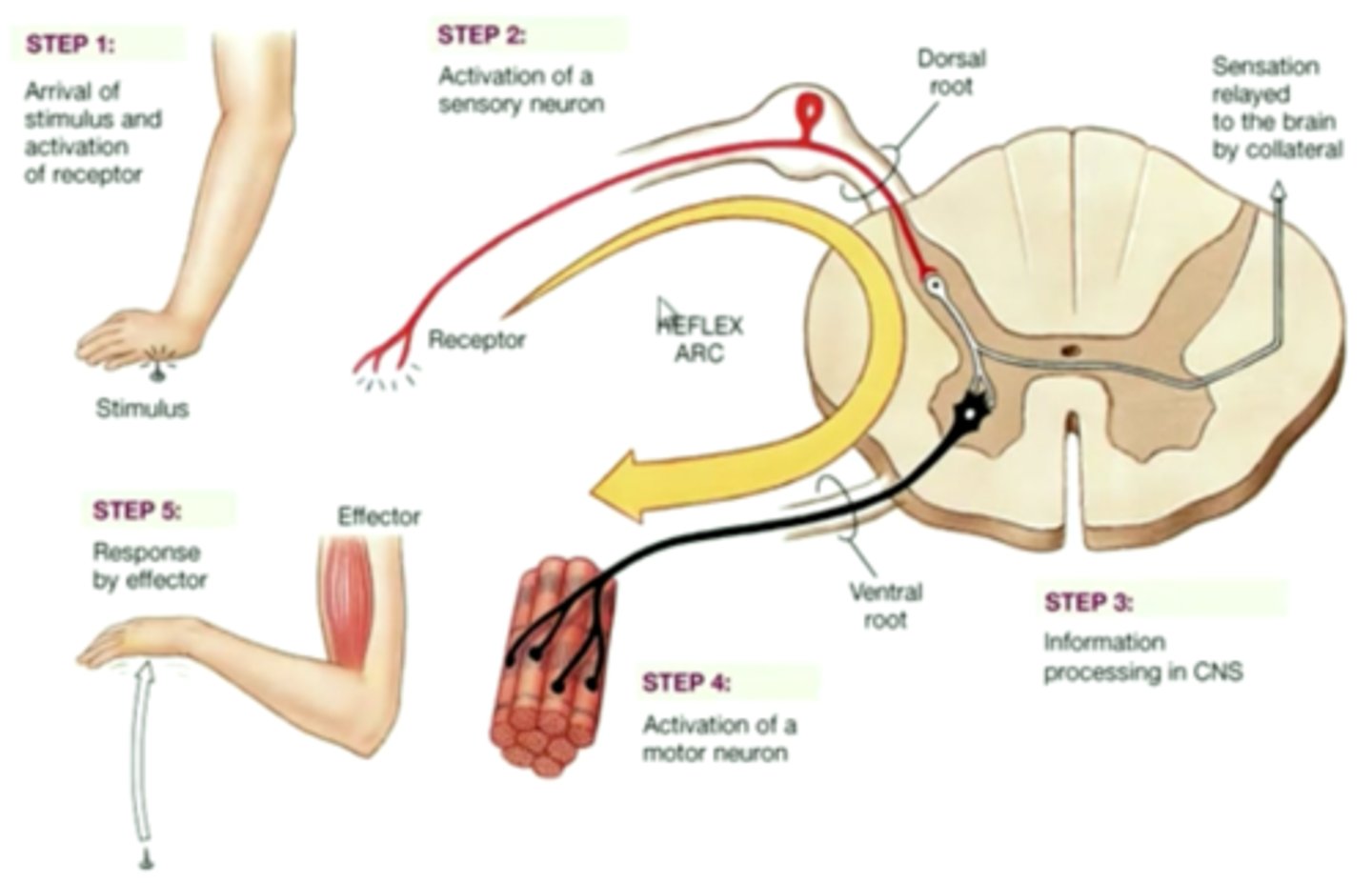
Reflex arc
The nerve pathway involved in a reflex action including at its simplest a sensory nerve and a motor nerve with a synapse between.
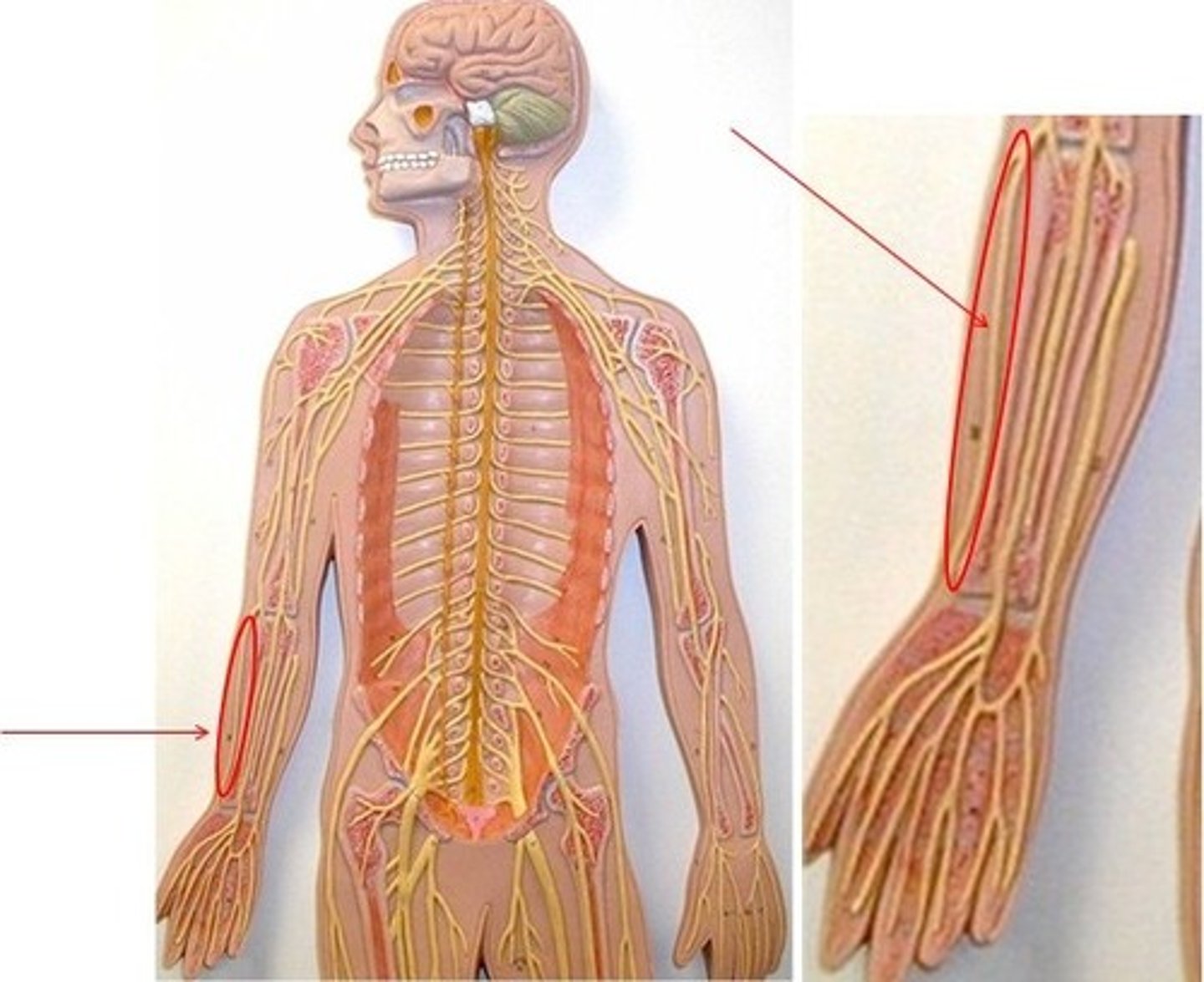
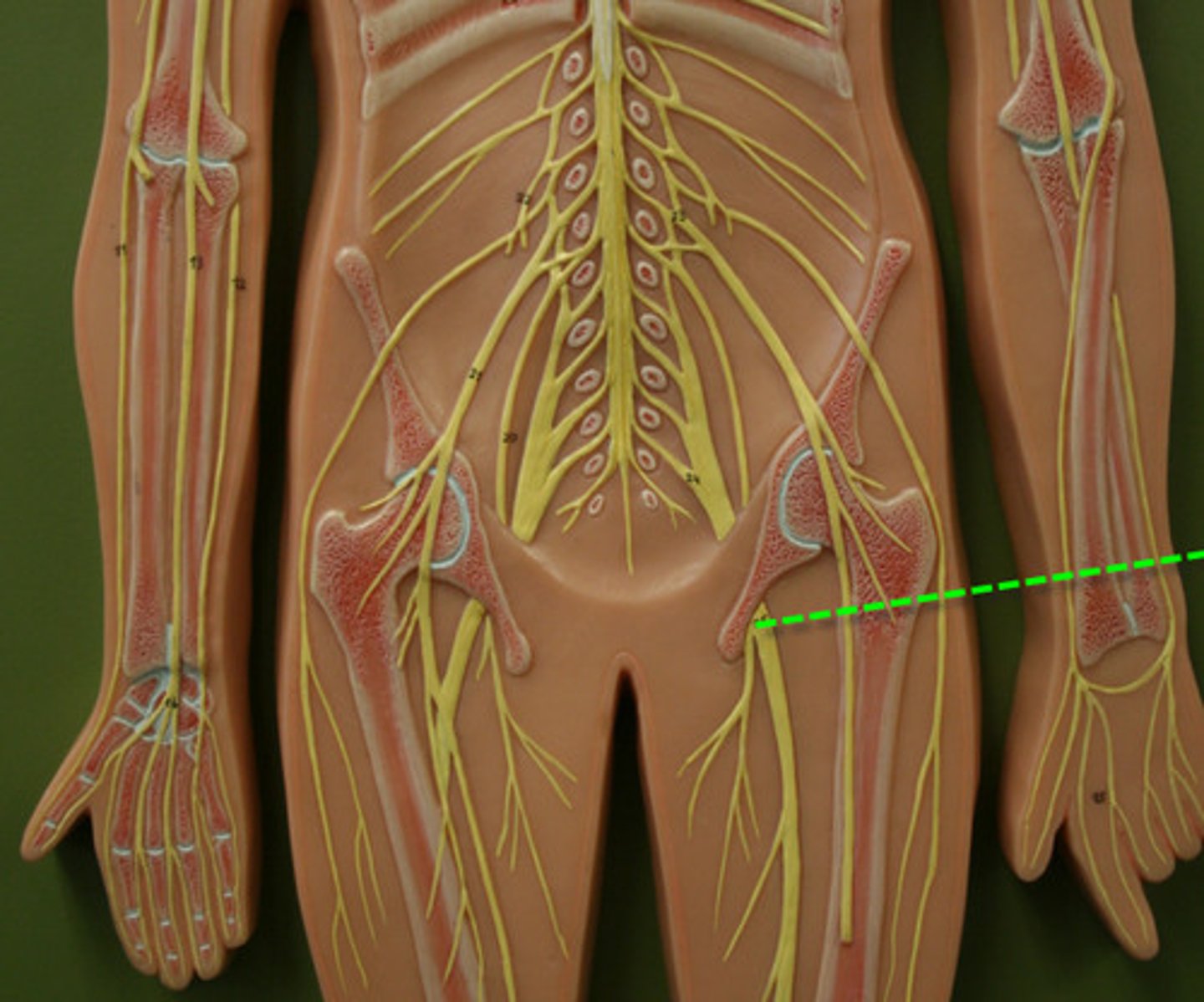
sciatic nerve
Largest and longest nerve in the body
motor - flexes knee joint
sensation - branches to innervate skin of lateral leg and all of the foot.
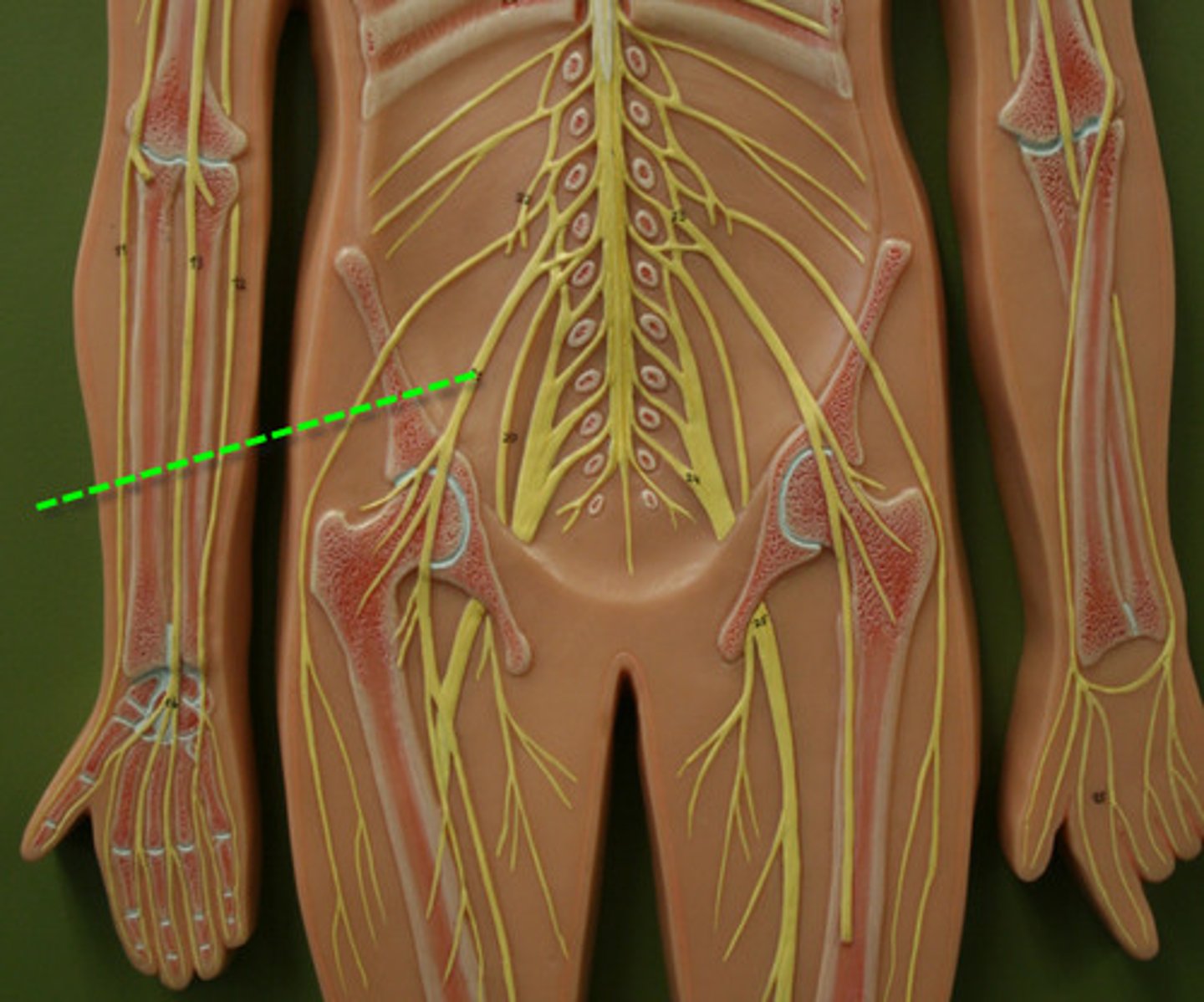
Femoral nerve
motor - flexes him and knee
sensory - sensation of the anterior and medial thigh, as well as medial foot and lower leg
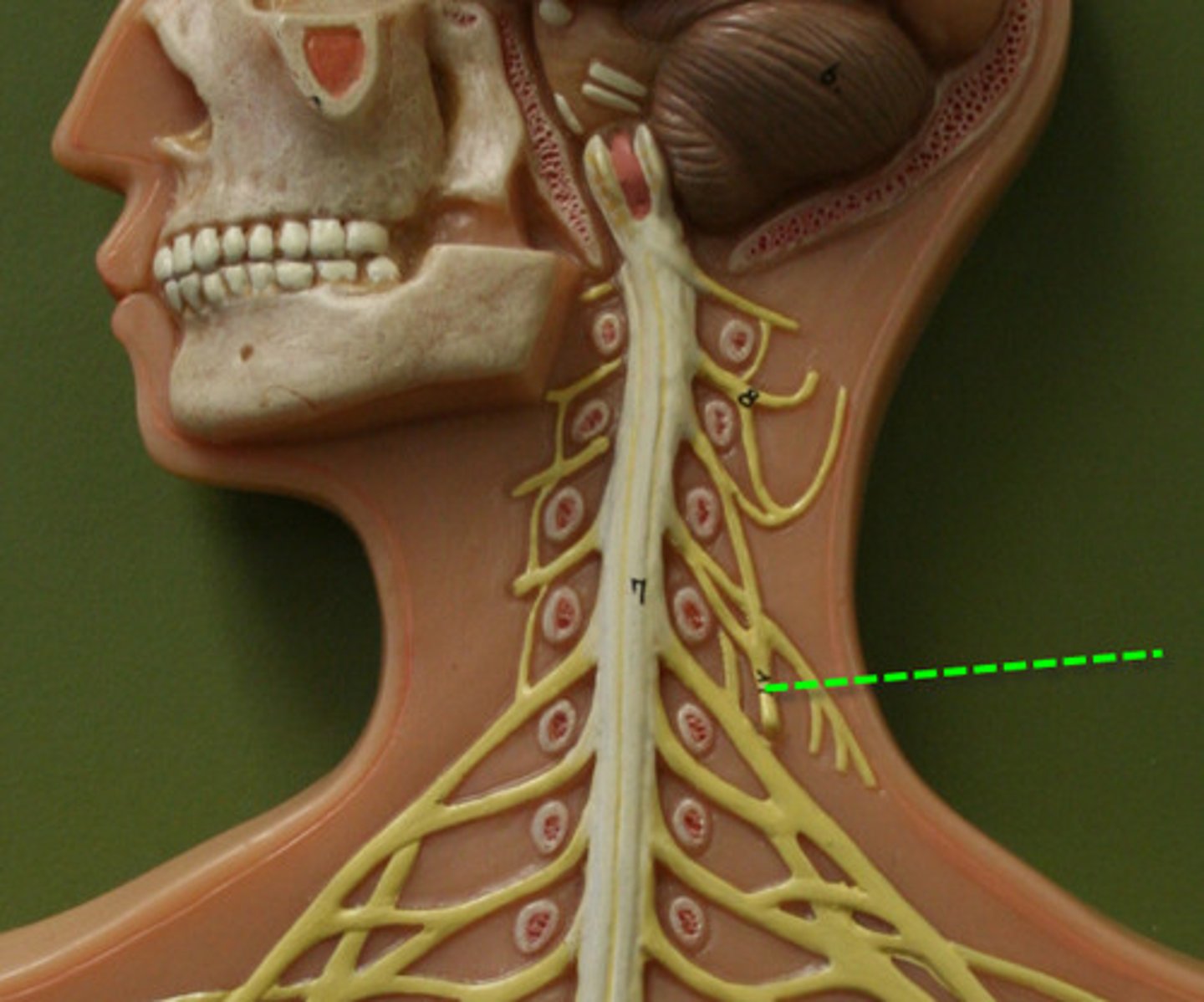
phrenic nerve
controls the diaphragm
axillary nerve
controls movement and sensation of shoulder
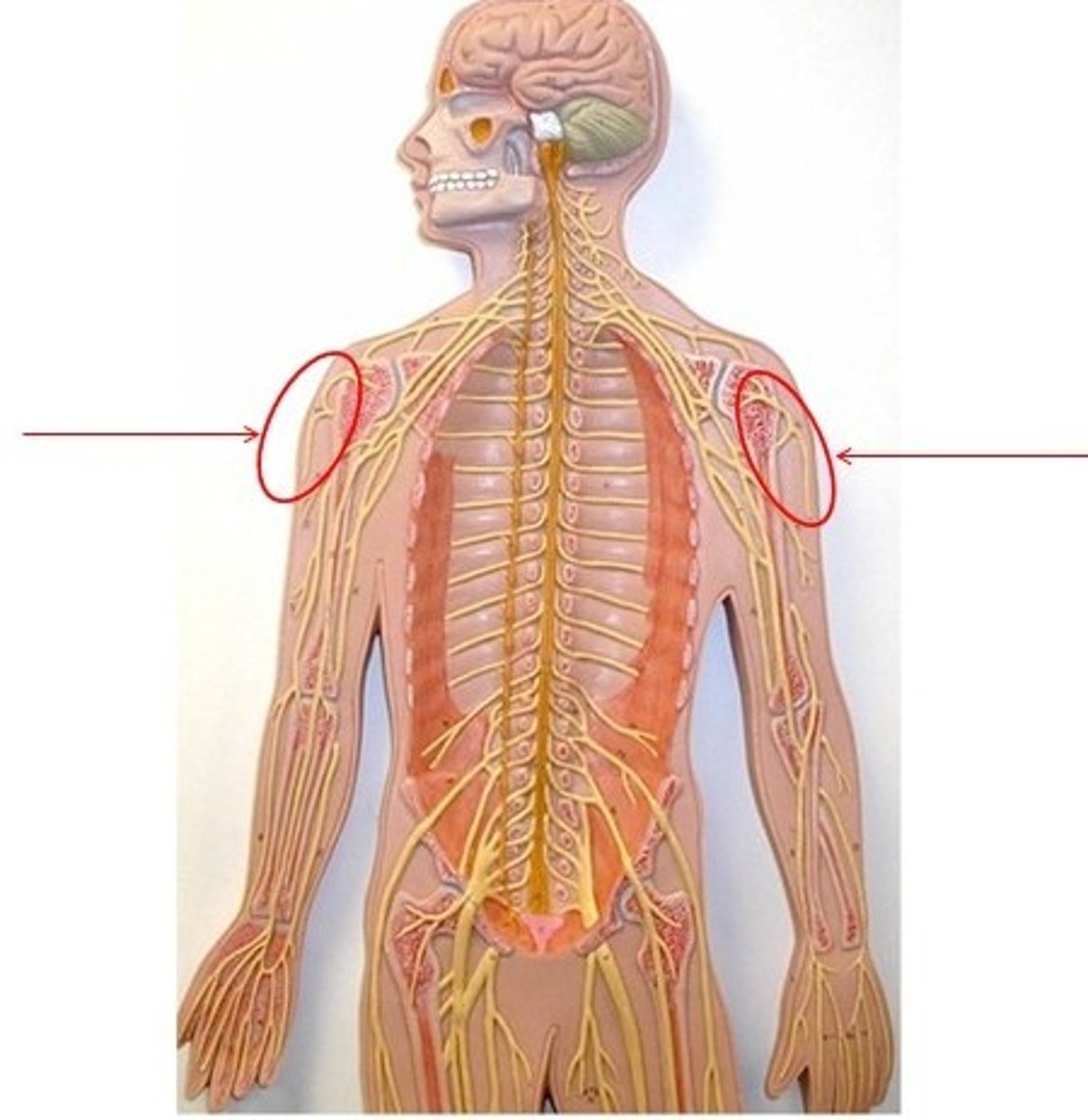
radial nerve
motor - extends elbow and hand,
sensory - feeling in hand and wrist