ap precalc is my 13th reason
1/45
Earn XP
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
46 Terms
RECOGNIZING CHANGE PATTERNS IN FUNCTIONS (starts on next card)
linear
rate of change is constant on any interval
quadratic
2nd differences of output values are constant over consecutive equal-length input value intervals
polynomial (degree n)
nth differences of output values are constant over consecutive equal-length input value intervals
exponential
output values are proportional over equal-length input value intervals
logarithmic
proportional input values result in constant change in output values
RATES OF CHANGE (starts on next card)
average rate of change (AROC)
the aroc of f(x) over the interval [a, b] is the slope of the line between the points
rate of change (ROC)
roc of f at a point refers to the slope of the graph at that point
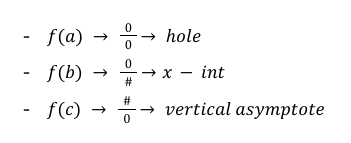
BEHAVIOR OF RATIONAL FUNCTIONS (starts on next card)
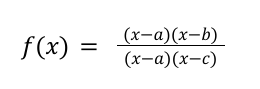
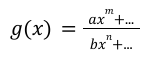
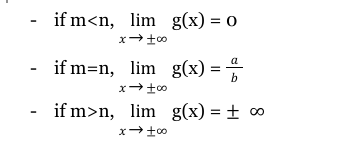
SEQUENCE FORMULAS (starts on next card)
arithmetic
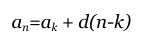
geometric
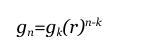
PROPERTIES OF EXPONENTS (flip this card)
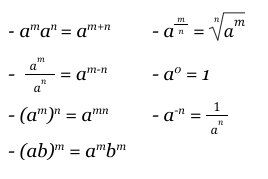
PROPERTIES OF LOGARITHMS (flip this card)
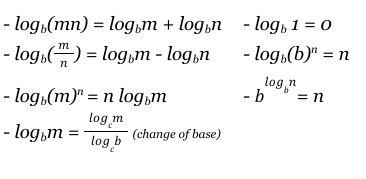
TRANSFORMATIONS (starts on next card)
g(x) = a f(b(x+h))+k
(vertical changes)
stretch if |a|>1
compression if |a|<1
reflection if a is negative
g(x) = a f(b(x+h))+k
(horizontal changes)
stretch if |b|>1
compression if |b|<1
reflection if b is negative
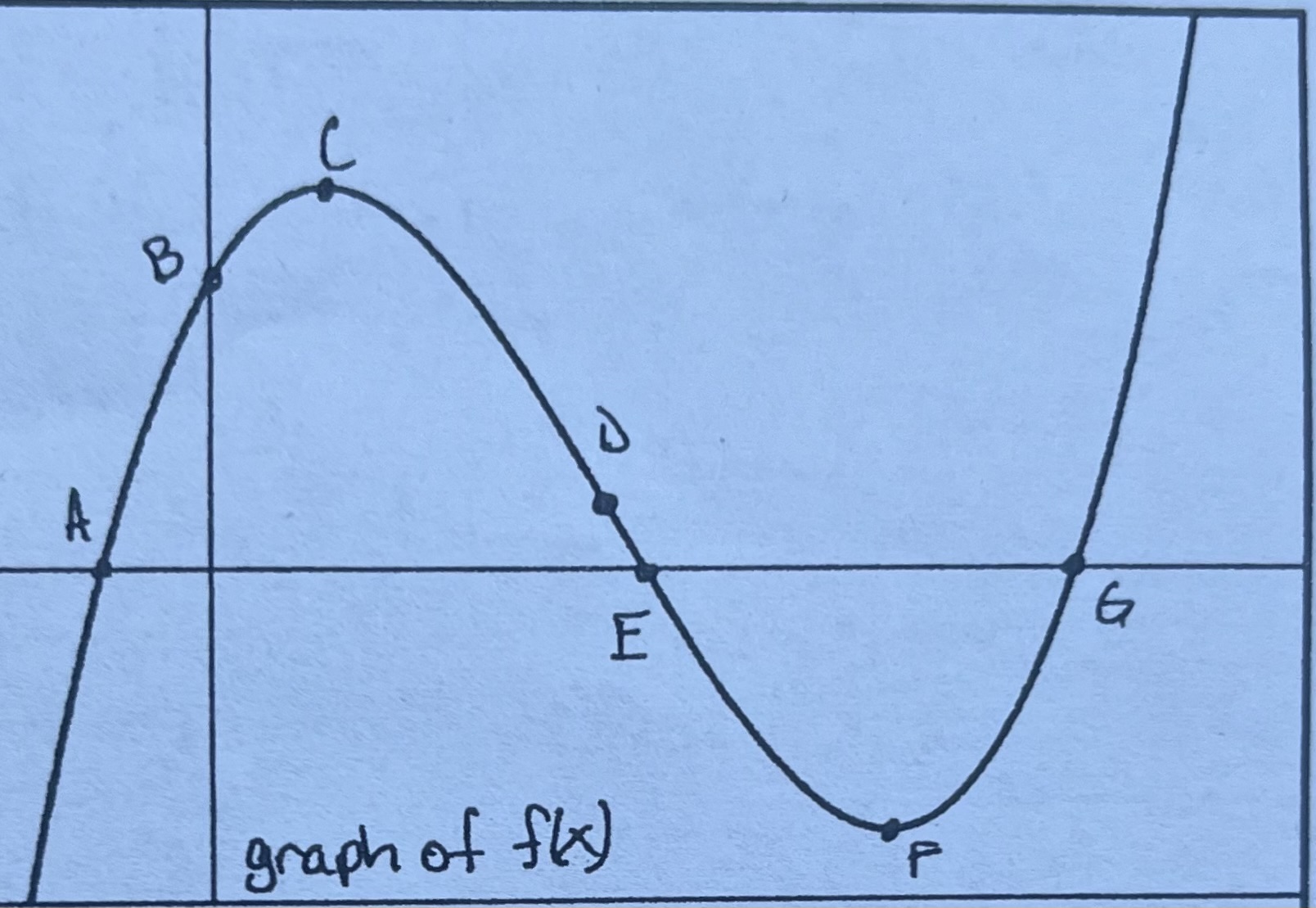
FUNCTION BEHAVIORS (flip this card)
-∞ to D: f(x) is concave down. roc is decreasing.
D to ∞: f(x) is concave up. roc is increasing.
C to F: f(x) is decreasing. roc is negative.
F to ∞: f(x) is increasing. roc is positive.
A to E: f(x) is positive
E to G: f(x) is negative
C and F: extrema (C - relative max; F - relative min)
D: point of inflection (change in concavity)
INVERSE FUNCTIONS (starts on next card)
numerically
if f(a) = b then f-1(b)=a
graphically
f-1(x) is the reflection of f(x) over the y=x
algebraically
to find f-1(x), switch x and y on f(x) and solve for x
verbally
f-1(x) uses the opposite operations of f(x) in the reverse order
f-1(x) is a function if every output value of f(x) comes from a unique input value
a function that is either strictly increasing or strictly decreasing is invertible
the domain of f-1(x) is the range of f(x) and vice versa
extra note?? or smth ig??? idk atp
f-1(f(x)) = f(f-1(x)) = x
for all x in the domain of either function
IDENTITIES (starts on next card)
pythagorean
sin²θ + cos²θ = 1
tan²θ + 1 = sec²θ
cot²θ + 1 = csc²θ
reciprocals (pythagorean)
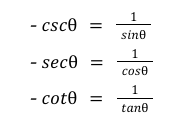
quotients (pythagorean)
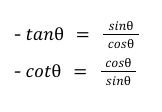
angle sum/difference
sin (a+b) = (sin a)(cos b) + (cos a)(sin b)
sin (a-b) = (sin a)(cos b) - (cos a)(sin b)
cos (a+b) = (cos a)(cos b) - (sin a)(sin b)
cos (a-b) = (cos a)(cos b) + (sin a)(sin b)
SINE COSINE COSINE SINE COSINE COSINE SINE SINE AHHAHAHHHHHHHHH ok sorry
double angle
sin 2θ = 2 sinθ cosθ
cos 2θ = cos²θ - sin²θ
= 2 cos²θ - 1
= 1 - 2 sin²θ
SINE/COSINE GRAPH PROPERTIES (starts on next card)
f(x) = a sin (b(x+c)) + d
y = sinx: starts at midline and does upward
y = cosx: starts at maximum and goes downward
|a| = amplitude d = midline
|a| + d = maximum -e = phase shift
|a| - d = minimum (2π)/b = period
SPECIAL RIGHT TRIANGLES (flip this card)
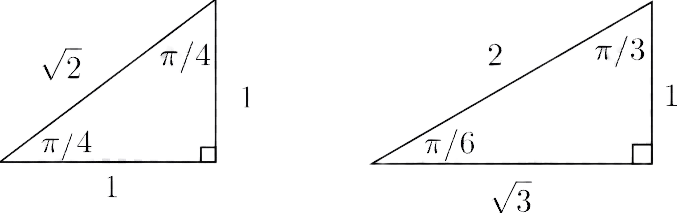
INVERSE TRIG FUNCTIONS (can be written as sin-1(x) or arcsin(x) (flip this card)
f(x) = sin-1x | g(x) = cos-1x | h(x) = tan-1x | |
|---|---|---|---|
input | ratio of sides or y-coordinate on unit circle | ratio of sides or x-coordinate on unit circle | ratio of sides or slope of terminal side of θ |
output | standard position angle | standard position angle | standard position angle |
domain | x→[-1,1] | x→[-1,1] | x→[-∞,∞] |
range | y→[(-π/2), (π/2)] (quad 1 and 4) | y→[0, π] (quad 2 and 3) | y→[(-π/2), (π/2)] (quad 1 and 4) |
POLAR COORDINATES (starts on next card)
rectangular (x,y) → polar (r,θ)
r = √x² + y²
tan-1(|y/x|) = reference angle (use quadrant and reference angle to find θ)
polar (r,θ) → rectangular (x,y)
x = r cosθ
y = r sinθ
polar form of a complex number
a + bi = r(cosθ + isinθ)
PASCAL’S TRIANGLE (flip this card)
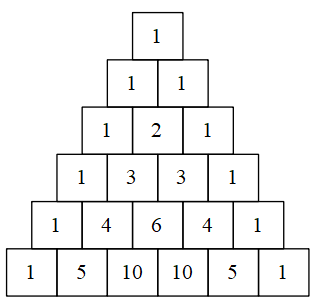
JUSTIFICATIONS/FRQ TERMINOLOGY (starts on next card)
a function is increasing over an interval of its domain if:
for all a and b in the interval, if a < b, then f(a) < f(b)
a function is decreasing over an interval of its domain if:
for all a and b in the interval, if a < b, then f(a) > f(b)
YOU GOT THIS WOOOOOO!!!!!!