Infection 2.2
1/76
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
77 Terms
Osteomyelitis
-Refers to the suppurative form of bone/marrow infection
What is the most common organism in osteomyelitis?
-Staphylococcus auerus
Can you tell the type of organism on imaging?
-No, but some are more common in certain scenarios (Salmonella in sickle cell anemia & Pseudomonas in intravenous drug users)
Population at risk for osteomyelitis?
-Immunocompromised
-Alcoholics
-Newborns
-Intravenous drug users
-Diabetics
-Patients on hemodialysis
-Post surgical patients
Osteomyelitis is common in what age of patients?
-2 to 12 years old (Males more than females)
Most common pathway of spread for osteomyelitis?
-Hematogenous spread
Clinically presentation of osteomyelitis
-Pediatric: acute systemic symptoms
-Adults: variable can be subtle
-Swelling
-Malaise
-Fever
-Elevated ESR, CRP, WBC
Common locations of Osteomyelitis
-Lower limb > Spine (lumbar most common) > Radius > SI
What part of the bone is most common in osteomyelitis?
-Metaphysis (unless under 1 then it’s epiphysis)
Latent period for Osteomyelitis visualization in extremities?
-7 to 10 days
Latent Period for Osteomyelitis visualization in spine?
-21 days
Acute/Early Imaging features of Osteomyelitis
-Soft tissue swelling
-Aggressive bone destruction
-Periosteal reaction (laminated or spiculated)
Laminated Periosteal reaction Indicating Osteomyelitis on X-ray (Acute)
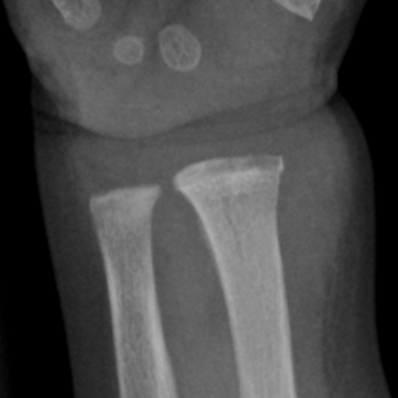
Acute Phase of Osteomyelitis on X-Ray
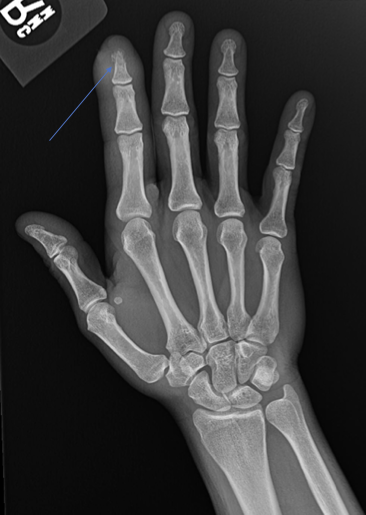
Brodie Abscess (Subacute Osteomyelitis)
-Localized, possible aborted form of suppurative osteomyelitis
-Staph is most common organism that causes this
-Most common in the tibia
-Geographic lucent lesion with variable sclerosis
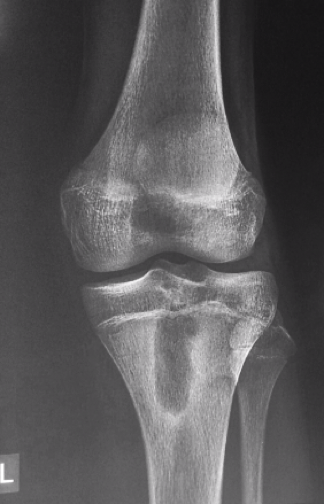
Clinical Presentation of Brodie Abscess
-Night pain relieved by aspirin (ddx w/ osteoid osteoma)
Brodie Abscess on X-ray
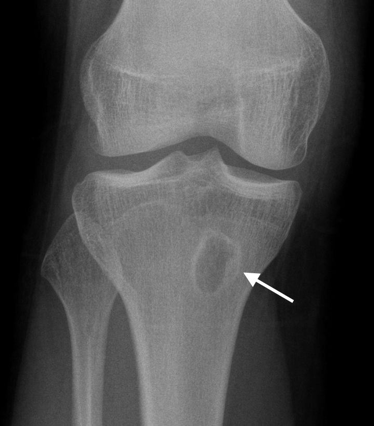
Brodie Abscess on X-ray #2
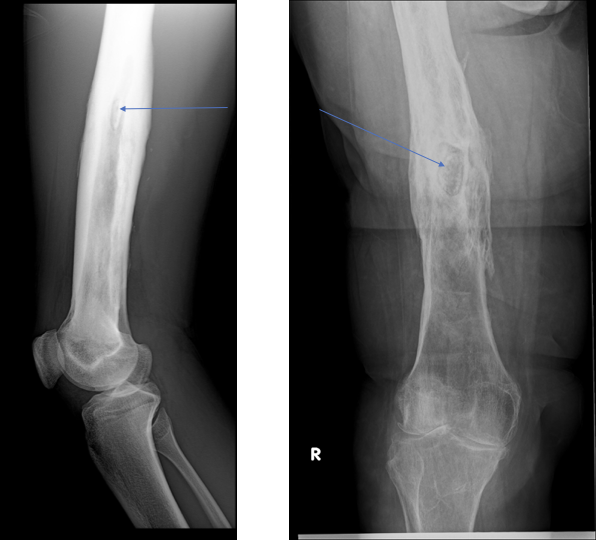
Sequestrum Formation in Chronic Osteomyelitis
-Necrotic infected bone surrounded by granulation tissue
-Harbors active infection and can cause recurrence of infection if not removed
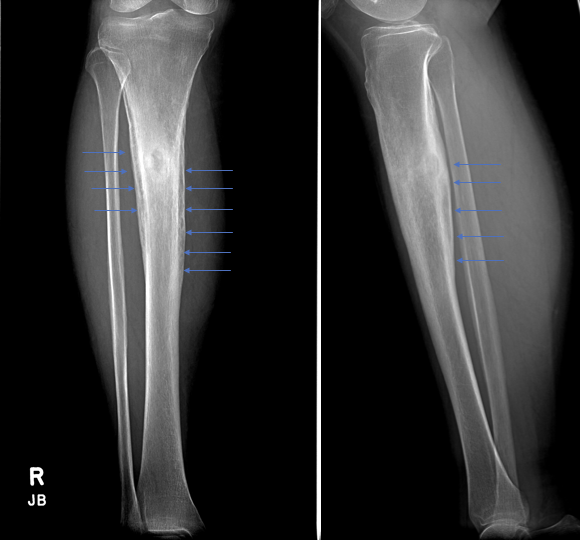
Involucrum in Chronic Osteomyelitis
-Periosteal envelop attempting to grow over the infection
Cloaca in Chronic Osteomyelitis
-Opening from the diseased bone into the soft tissues
Sinus Tract in Chronic Osteomyelitis
-Opening from the soft tissues to the hollow viscera or surface of the skin
Chronic Osteomyleitis general imaging features?
-Sclerosis
-Solids, wavy, irregular periosteal new bone formation
-Cortical thickening
-Possible superimposed osteolysis
Osteomyelitis showing malignant degeneration can lead to?
-Squamous cell carcinoma
Sequestrum (Chronic Osteomyelitis) on X-ray
Involucrum (chronic osteomyelitis)on X-ray
Septic Arthritis
-Most common in a single joint
-Most common due to hematogenous spread or direct extension
-Staphylococcus aureus most common organism
Where is direct extension in septic arthritis common in?
-The foot
Clinical Presentation of Septic Arthritis
-Chills
-Fever
-Edema
-Pain
-Erythema
-Elevated ESR, CRP, and WBC
Most common places for Septic arthritis
-Knee and hip
Imaging Features of Septic Arthritis
-Joint effusion
-Displaced fat pads and distention
-At hip, waldenstrom’s sign (>11mm total or 2.0mm difference between sides)
-Rapid loss of joint space and destruction of subarticular cortex (white line at joint margin will disappear)
-Can show osteomyelitis
-Bony ankylosis and growth disturbances possible
Septic arthritis on X-ray
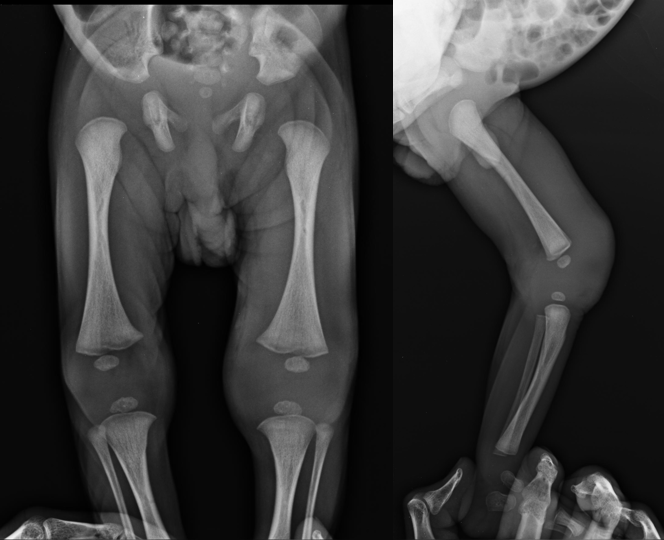
Fight Bite on X-ray (Septic arthrtitis)
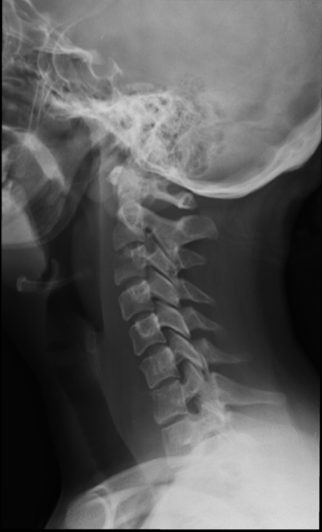
TB Spondylodiscitis on X-ray
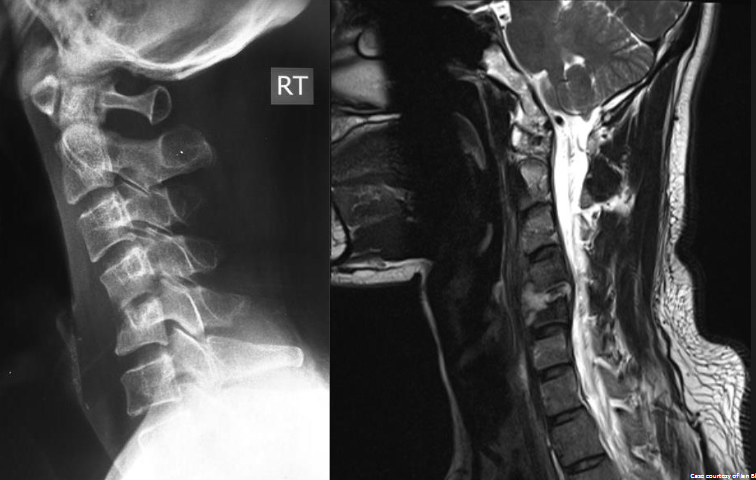
Pyogenic Spondylodiscitis
-Acute suppurative infection of the spine
-Almost always involves a disc and 2 adjacent vertebra
-Pediatric: Implants in the disc and moves into the vertebra
-Adult: begins in the anterior superior/inferior corner at the endplate and invades the disc
-Most common in lumbar
-Staphylococcus aureus organism is most common
Clinical Signs of Pyogenic Spondylodiscitis
-Signs of systemic infection
-Pinpoint tenderness or dull ache throughout region
-Elevated ESR,CRP, WBC
Imaging Features of Spondylodiscitis
-21 day radiograph period
-Early destruction of endplate and loss of disc height
-Progression to destruction of anterior vertebral body
-Paraspinal abscess or phlegmon possible
-Does not often show subligamentous spread
Pyogenic Spondylodiscitis on X-ray
Tuberculosis
-Caused by mycobacterium tuberculosis
-Has primary and secondary stages
-Hematogenous is the most common form of spread (batson’s venious plexus)
Primary Tuberculosis
-Pulmonary infection that resembles lower respiratory infection/pneumonia
-may remain silent for remainder of patient’s life
Secondary Tuberculosis
-AKA post-primary
-Reactivation of organism, typically in immunocompromised, causes severe pulmonary destruction and may spread to other organ system
Osseous Involvement in tuberculosis is in what population?
-2 to 30 years of age
Most common location of Tuberculosis Spondylodiscitis (Potts disease)
-Spine (Thoracolumbar mainly)
Septic Tuberculosis is most common in?
-Hip
Tuberculosis Spondylodiscitis Imaging Features
-Radiographic latent period of 21 days
-Early:
-Disc space loss occurs but is minimal
-Anterior vertebral body/endplate destruction
-Subligamentous spread
-Propensity to skip levels
Late:
-Pathologic vertebral collapse (gibbus deformity)
-Retorpharyngeal, paravertebral, psoas abscess (cold abscess & Snowflake sign)
Phemister’s Triad
-Progressive slow joint space narrowing
-Juxta-articular osteopenia
-Peripheral erosions of the articular surface
Tuberculosis Arthritis
-Phemister’s Triad
-Rice bodies (chronic synovitis causes shedding of synovium with relatively uniform size/shape loose bodies)
-Loss of subchondral bone and lytic destruction
-In the knee can show a widened intercondylar notch, enlarged condyle, and osteopenia
Scrofula
-Lymph node involvement, often in cervical lymph nodes (tubeculosis)
Cold Abscess
-Large abscess without classic severe inflammation (tuberculosis)
Snowflake Sign
-Calcification throughout a cold abscess (tuberculosis)
Pott Disease
-Spinal involvement in tuberculosis
Gibbus Deformity
-Acute angulation of the spine due to collapse
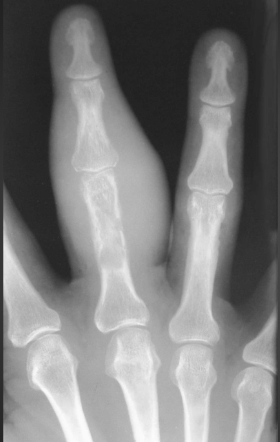
Spina ventosa
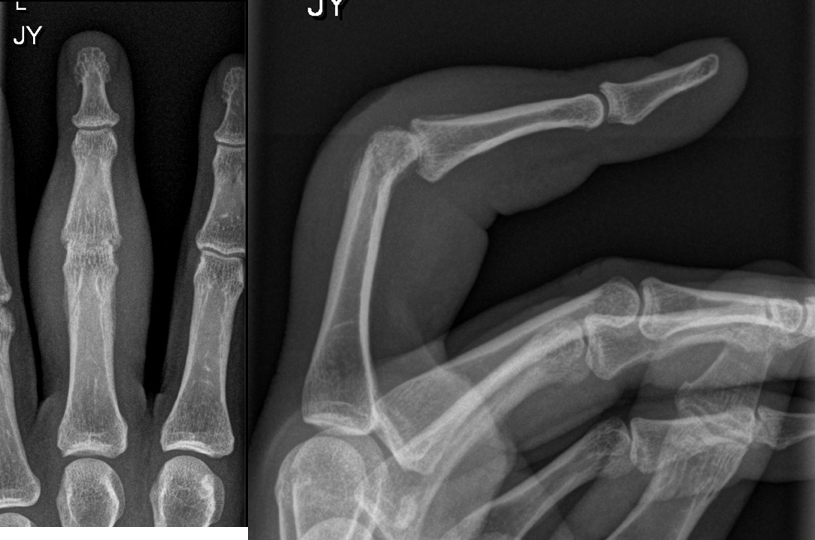
-Tuberculosis dactylitis with expansile osseous lesion
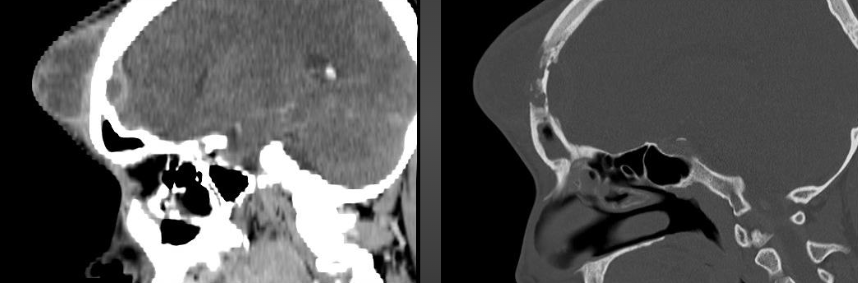
Pott Puffy Tumor
-TB of the skull (frontal bone) with scalp abscess
Weaver Bottom
-Subgluteal tuberculous bursitis with direct extension into the ischium
Classic TB Spondylodiscitis
-Lytic destruction and osteopenia in the anterior vertebral body adjacent to the endplate with early sparing of the disc and subligamentous spread to multiple levels
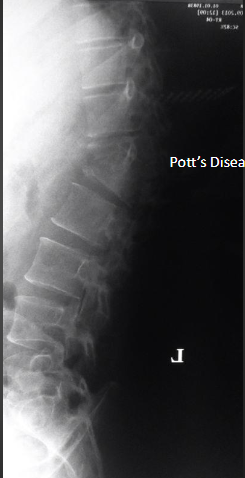
Pott’s Disease on X-ray
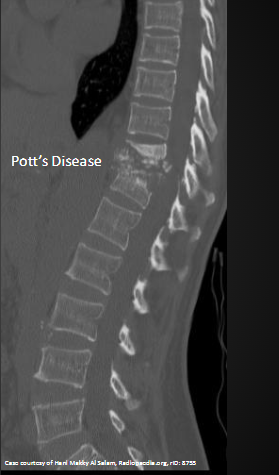
Pott’s Disease w/Gibbus deformity on X-ray
Tuberculosis Dactylitis on X-ray
Pott Puffy Tumor on Imaging
Mycotic Osteomyelitis
-non-suppurative
-Very similar to tuberculosis in clinical and radiographic manifestation
Most common Mycotic INfections
-Coccidiomycosis
-Actinomycosis
-Candida albicans
-Aspergillosis
-Blastomycosis
Coccidiomycosis
-Most common in San Joaquin valley(California, Nevada, and Mexico)
-Typically a respiratory infection nearly identical to TB
-Predilection for boney prominences
-Associated with desert rheumatism
Desert Rheumatism
-Erythema nodosum
-Polyarthritis
-Fever
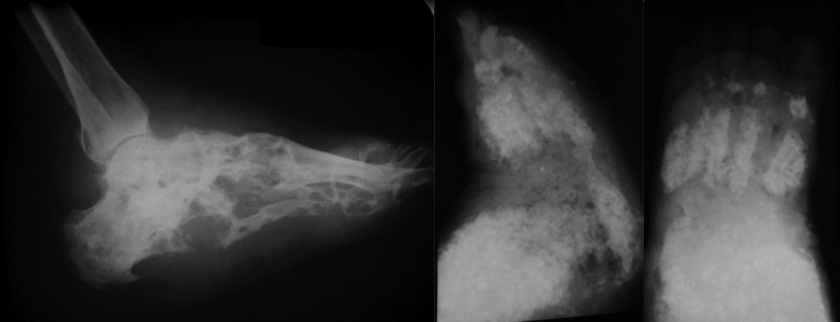
Maduramycosis
-Most common fungal osteomyelitis
-Chronic fungal infection of the foot (madura foot)
-Melting snow appearance
Madura Foot on X-ray
Syphilitic Osteomyelitis
-Caused by Treponema pallidum
-Presents a congenital or acquired (part of Torch)
Congenital Syphilis
-Transmitted to fetus via the placenta after the 4th month of gestation
-symptoms usually manifest in the first 4 months of life but often not diagnosed until >10 years of age
-Osseous most common at knees, shoulders, and wrist
Hutchinson Triad
-Hutchinson’s teeth
-Interstitial keratitis
-Deafness
Imaging Features of Congenital syphilis Metaphysisitis
-Bilateral symmetric
-Lucent metaphyseal bands similar to leukemia and neuroblastoma metastasis
-Irregular fragmented (sawtooth) metaphysis at growth plate
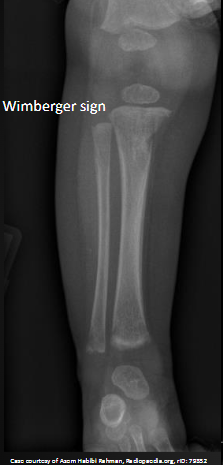
-Wimberger’s sign (Eccentric erosive change at the proximal medial tibia bilaterally
Imaging Features of Congenital Syphilis Periostitis
-Symmetric laminated periostitis that is often widespread (DDX with HOA and hypervitaminosis A)
Imaging Features of Congenital Syphilis Osteitis
-Extension of metaphysitis into the diaphysis, reactive sclerosis, and asymmetric overgrowth of involved bone (can cause saber shin)
-Regions of focal or poorly defined lysis
Clutton’s Joints
-Painless swelling of a joint (knees most common)
Syphilitic Dactylitis
-Swelling in digits resembling spina ventosa of TB
Acquired Syphilis
-Most common in skull, tibia, and clavicles (frontal bone)
-Osseous manifestations seen in tertiary syphilis
Imaging features of Acquired Syphilis
-Diffuse periostitis that may lead to increased thickness and altered contour of bones
-Lytic destruction that may be focal and well-circumscribed or permeative
Wimberger Sign on X-ray (Syphilis)