Pre-AP Unit 4: Classical China & India
1/19
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
20 Terms
feudal
a peasant or worker received a piece of land in exchange for serving a lord or king
authoritarian
expecting unquestioning obedience

imperial
relating to or associated with an empire
aristocratic
belonging to or characteristic of the nobility
urbanization
the condition of being transformed into a city

sovereign
a nation's ruler usually by hereditary right

filial
relating to or characteristic of or befitting an offspring

magistrate
a lay judge or civil authority who administers the law

geographic context
where a historical event took place and why it took place there; includes location, location relative to other places, geographic features, and climate
historical circumstances
the events that led to an event; includes the time period and larger historical trends as well as causes
legalism
philosophy that proposes humans are evil and must have harsh laws to keep them in order

civil service
government jobs that civilians obtained by taking examinations about Confucianism

centralized government
Central authority controls the running of a state. Complex, organized bureaucracy
Han Dynasty
(202 BCE-220 CE) This dynasty continued the centralization of the Qin Dynasty, but focused on Confucianism and education instead of Legalism. *GOLDEN AGE*

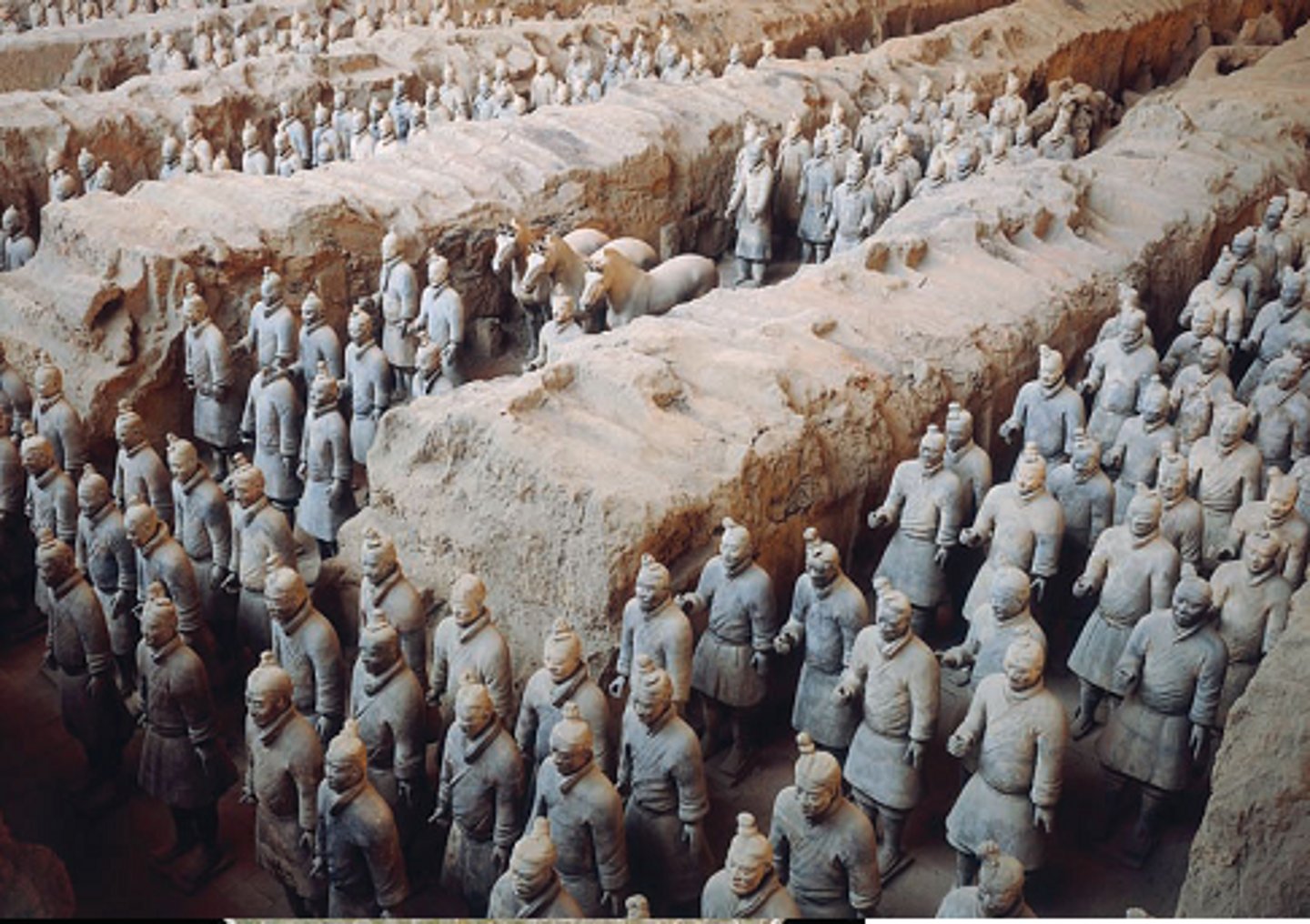
Terracotta Army
a 6,000 man fully armed army made out of clay that guards Emperor Qin Shi Huang's imperial tomb

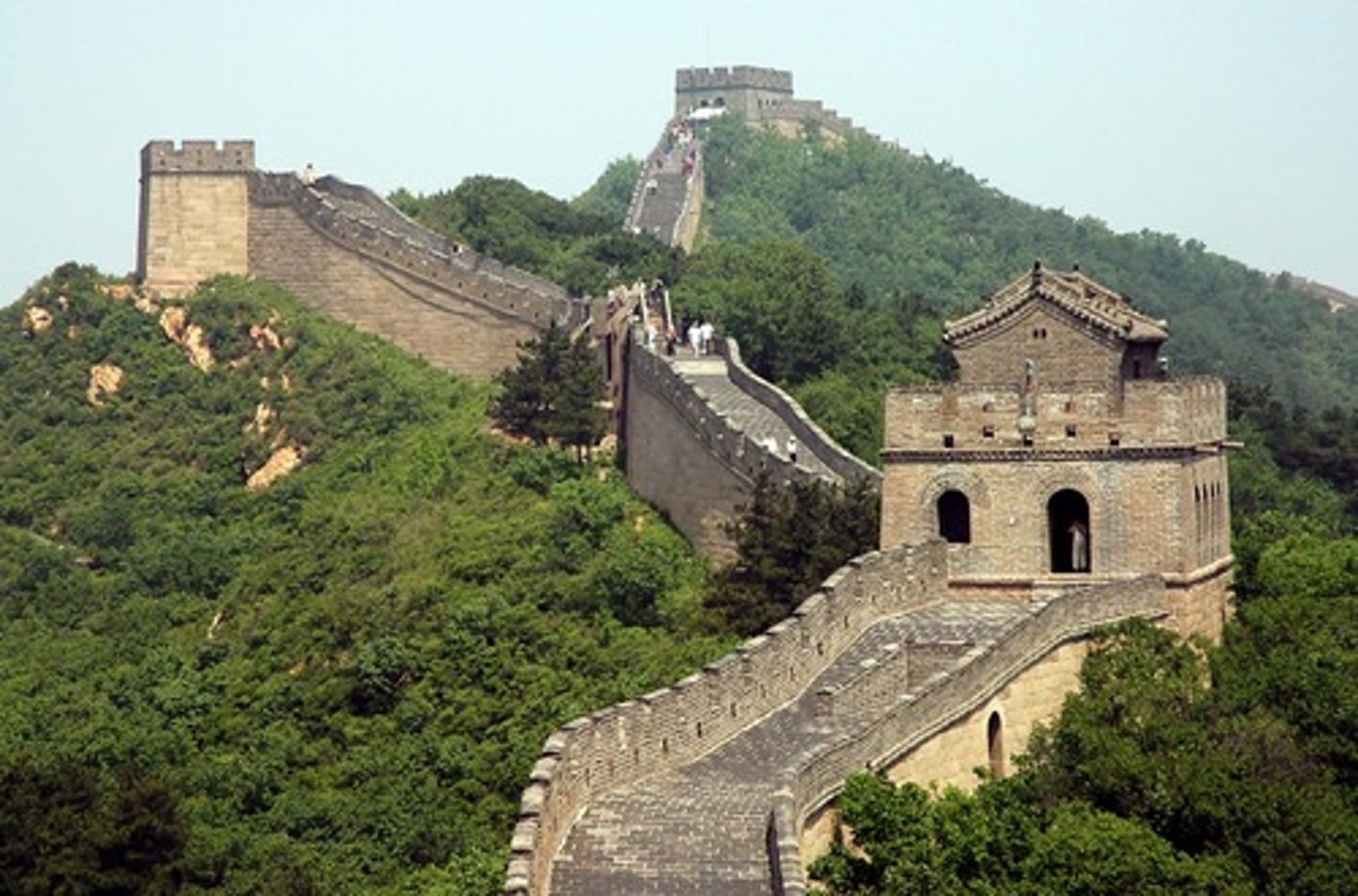
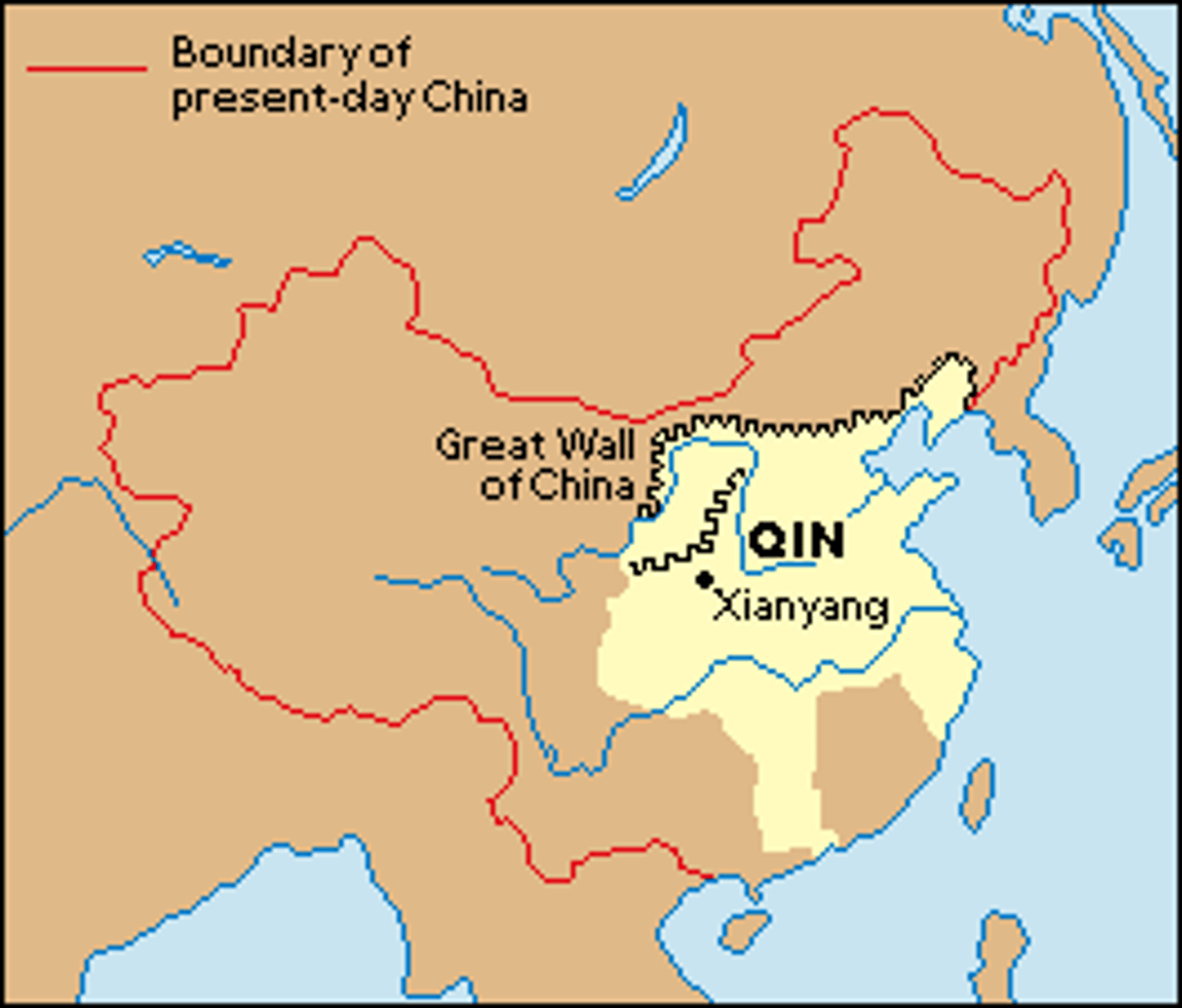
Great Wall of China
Northern wall facing the Gobi desert, built to keep out Mongol invaders (Can be seen from space!)

Qin Dynasty
(221-206 BCE) Origin of modern name of China comes from this "Legalist" regime ruled by Qin Shi Huang
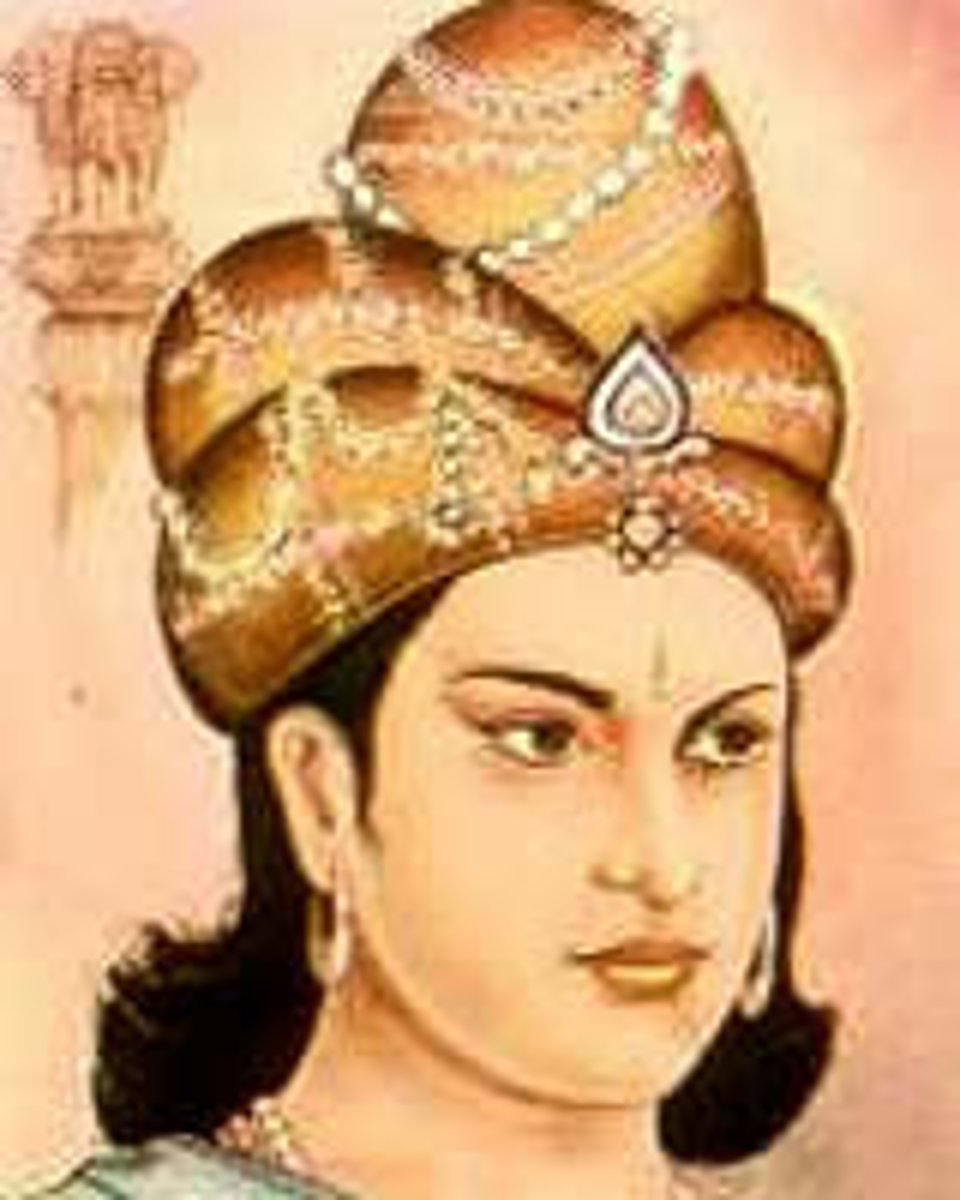
Ashoka the Great
King who builds Buddhist pillars throughout his empire - Laws for all to see & spread of Buddhism

Mauryan Empire
(321-185 BCE) This was the first centralized empire of India whose founder was Chandragupta Maurya.

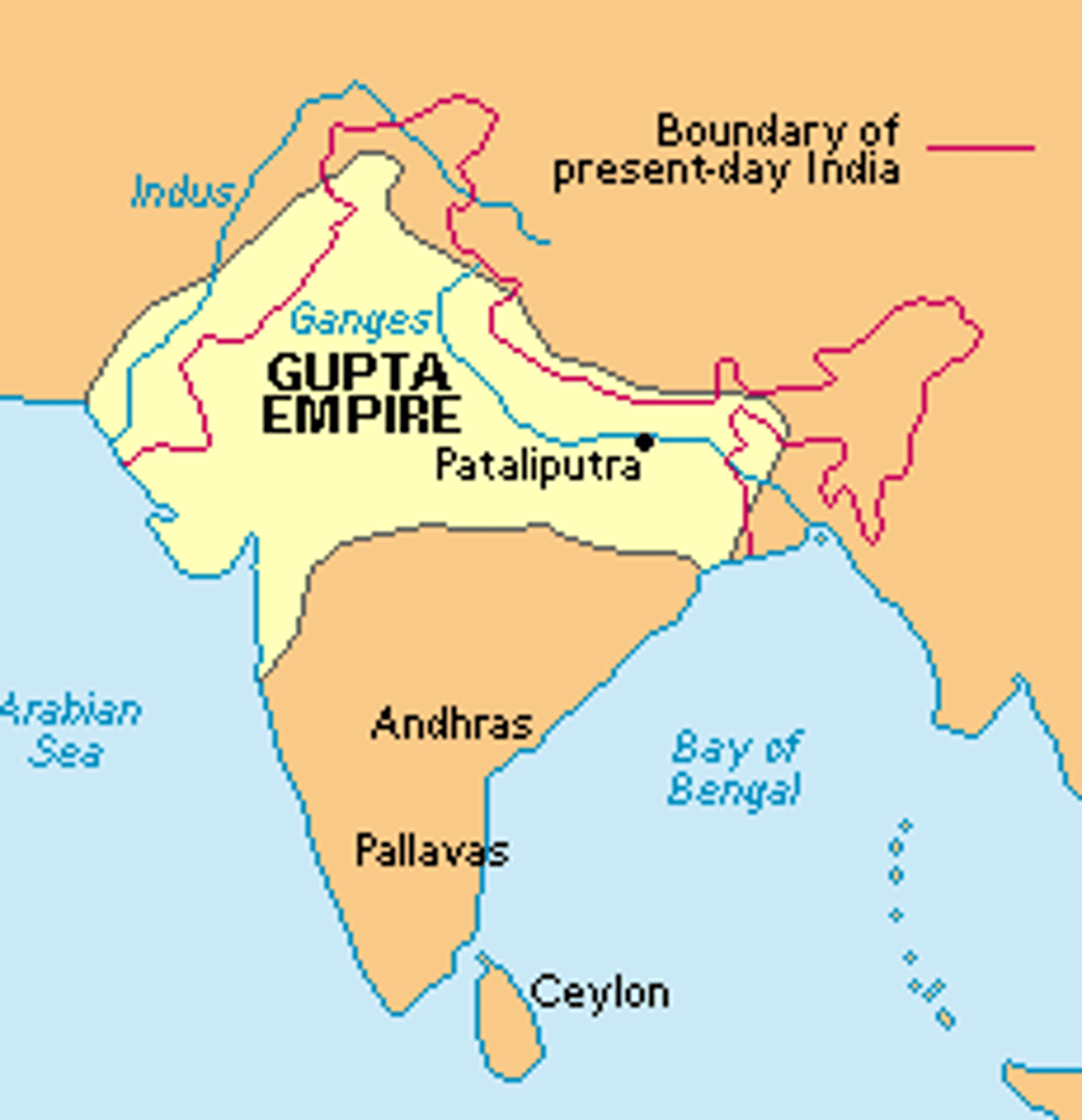
Gupta Empire
Powerful Indian state based in the Ganges Valley. It controlled most of the Indian subcontinent through a combination of military force and its prestige as a center of sophisticated culture. Often associated with a Golden Age of classical India.