Bio 180 Exam1
1/258
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
259 Terms
What is the difference between a theory and a hypothesis?
Only scale--theories deal with "big ideas" that impact large parts of the physical or natural world; hypotheses are more focused or narrower in scope.
What is the difference between a hypothesis and a prediction?
A hypothesis is an idea--a testable explanation; a prediction is something that follows from a hypothesis and that you can measure
Which of the following is a prediction based on the cell theory that all organisms are made of cells, and all cells come from preexisting cells?
If you boil nutrient broth and place it in an air-tight flask, no cells will appear in the broth
What was important about the experimental design for Pasteur's flask experiment?
He compared results from two experimental setups which differed only in the type of flask in which the nutrient broth was placed
How do biologists test their ideas about the natural world?
Scientists make predictions based on hypotheses they have developed, and then design experiments or other types of studies to test those predictions.
Why is it important to perform multiple trials in an experiment -- meaning that you include many test individuals or samples?
To make it more likely that the results are not due to a few unusual individuals or circumstances
What does the p in "p-value" represent?
Probability (of getting the observed result, just by chance)
Suppose we run a statistical test, and learn that p = 0.01. What does this mean?
There is a 1 in 100 chance of observing a difference between treatment groups this extreme if the null hypothesis is correct.
If we want to plot the distribution of scores on Exam 1, we should use a...
Histogram
If we want to plot the exam scores of 1st-year students versus 2nd-year students, we would use a ...
Bar chart
If we want to compare the scores of 1st-year and 2nd-year students using a statistical test, our null hypothesis will be...
There is no difference in exam performance between students in year 1 and 2.
If we calculate means (averages) based on scores from 100 1st-year students and 400 2nd-year students, which is likely to have the smaller standard error?
2nd-year students, because we sampled more.
Which of the following statements is the best way to characterize the standard error?
A measure of how precise our estimate of the mean is.
When sample size increases ...
Rare events have less influence on the estimate of the average or slope.
If you are doing a linear regression, what is the slope of the line predicted by the null hypothesis?
0
What is the process component of the theory of special creation?
Species were created, instantaneously and independently of each other, by God.
What is the pattern component of the theory of special creation?
Species are recent, unrelated to each other, and do not change through time.
What is the pattern component of Lamarckian evolution?
Species change in a progressive manner--meaning that they get larger and more complex over time.
What is the relationship between the Great Chain of Being and the process component of Lamarck's theory of evolution?
Under Lamarkian evolution, species move up the Great Chain of Being over time.
What does it mean to claim that an acquired character is passed on to offspring?
If an individual's traits change during its lifetime, its offspring have the new version of trait.
The geologic record and radiometric dating are inconsistent with the theory of special creation. Why?
They support the hypothesis that Earth itself and life on Earth are ancient.
The "law of succession," the presence of vestigial traits, and the fact of extinction are all inconsistent with the theory of special creation. Why?
They support the hypothesis that the characteristics of species--and the collection of species present--has changed through time.
In response to studies on "evolution in action"--the observation that hundreds of populations have been observed to change in response to changes in their environments--proponents of the theory of special creation either 1) ignore the data, or 2) argue that they are irrelevant to the question of how large-scale differences among species arose (e.g. how bats came to have wings). As a scientist, how would you evaluate these objections?
There is no logical reason to suspect that the process that lead to changes being observed today didn't operate in the past, and that they would not lead to large changes over long time periods.
Genetic, developmental, and structural homologies are inconsistent with the theory of special creation. Why?
They support the hypothesis that species are related by common ancestry--meaning that they were not created independently of each other.
They support the hypothesis that species are related by common ancestry--meaning that they were not created independently of each other.
Why would an intelligent designer create traits that have reduced or no function?
Why is it considered important that there is "internally consistent" support for the theory of evolution by natural selection?
You can be more confident that an idea is correct if several different types of evidence support it.
What does the pattern component of the theory of evolution by natural selection state?
The characteristics of populations change over time, in response to changes in the environment.
What does the process component of the theory of natural selection state?
Evolution occurs because individuals with certain heritable characteristics produce the most offspring.
Today, biologists boil Darwin's four postulates down to two conditions that result in evolution. What are these conditions?
When 1) certain heritable traits are associated with 2) higher numbers of offspring produced.
What observations suggest that in M. tuberculosis, antibiotic resistance is a trait with heritable variation?
Some individuals are more resistant to antibiotics than others, and pass this trait on to offspring.
What observations suggest that in environments containing antibiotics, M. tuberculosis individuals experience differential reproductive success based on their degree of resistance?
Over time, the frequency of resistant individuals increases when patients take antibiotics.
The top graph in Figure 22.13 (5th edition: 25.16) indicates that beak depth is variable in this population. What evidence did the researchers have that at least some of this variation was heritable?
In the next generation (in offspring of individuals who survived), average beak size was larger.
Look at the middle graph in Figure 22.14 (5th edition: 25.17). Why didn't beak size continue to increase, after the 1978 drought?
The environment changed, and large-beaked individuals no longer had highest fitness.
In biology, what does the word fitness mean?
The ability to survive and reproduce.
In biology, what does the word adaptation mean?
A trait that increases fitness in a certain environment.
What was the central claim of the theory of blending inheritance?
The physical matter responsible for traits blends within individuals, like pigments in paint.
What does it mean to say that an acquired character can be inherited?
If an individual's traits change over the course of its lifetime, those changes will be passed on to offspring.
What is a model organism?
A species that is easy to work on. Also, results from this species are relevant to many other species.
What is another name for a pure-breeding line or population?
homozygous
Which of the following is correct about F1s and F2s?
F1s are the first generation in an experimental cross; F2s are the second.
What is the difference between an individual's phenotype and genotype?
phenotype is appearance; genotype is the alleles present
What is "particulate" about particulate inheritance?
Genes retain their physical integrity over time, like particles--they don't blend together.
Which of the following characterizes a dominant allele?
Heterozygotes show its phenotype.
Which of the following characterizes a recessive allele?
Heterozygotes don't show its phenotype.
What's the difference between a gene and an allele?
An allele is a version of a gene.
What's a gamete? (Note that this term is used in the reading but not explicitly defined. If you need to, you can look it up in the glossary--the green-tipped pages (tan colored pages in the 5th edition) in the back of the book.)
A reproductive cell (sperm or egg).
What does it mean to say that something--like a gene--"segregates"?
It separates. In the case of a gene, the two alleles present in a parent separate and go into different gametes.
If "dependent assortment" occurs, how do alleles of different genes behave?
They "stick together" (they are transmitted together--as if they were a single gene).
What does a ratio report?
The relationship between numbers of the same kind (so it is unitless).
A F1's genotype is PpTt. Its parents had the genotypes PPTT and pptt. What are the gamete genotypes that the F1 produces under the hypothesis of independent assortment?
PT, Pt, pT, pt (in equal proportions)
A F1's genotype is PpTt. Its parents had the genotypes PPTT and pptt. What are the gamete genotypes that the F1 produces under the hypothesis of dependent assortment?
PT, pt (in equal proportions)
If a parent's genotype is PpTtLl, what are the gamete genotypes it produces under the hypothesis of independent assortment?
PTL, PTl, pTL, pTl, ptL, ptl, PtL, Ptl (in equal proportions)
What's the difference between a chromosome and a chromatid?
After replication, a chromosome consists of two chromatids.
When you look at a drawing or photograph of chromosomes, how can you tell if they are replicated or unreplicated?
Unreplicated chromosomes consist of a single "thread"; replicated chromosomes have two "threads."
What's the difference between a haploid cell and a diploid cell?
Haploids have one of each type of chromosome; diploids have two of each type.
What does it mean to say that two chromosomes are homologous?
They are the same size and contain the same genes.
Which of the following is the correct definition of haploid number?
The number of different types of chromosomes present.
Which of the following is the correct definition of ploidy?
The number of each type of chromosome present.
What does it mean to say that "homologs synapse?"
Pairs of homologous chromosomes physically come together.
The chromosome theory of inheritance is based on the claim that genes are found on chromosomes. If you were going to build a physical model of a chromosome from everyday materials to demonstrate meiosis (including crossing over), which of the following would work best?
strings of pop beads (each bead is a gene)
What is a genetic locus?
A particular position on a chromosome.
What's the pattern component of the chromosome theory of inheritance?
Mendel's rules: the principle of segregation and the principle of independent assortment, because genes are found on chromosomes.
What's the process component of the chromosome theory of inheritance?
The behavior of chromosomes during meiosis I.
What is sex-linkage, X-linkage, and Y-linkage?
X-linked alleles are on the X chromosome; Y-linked alleles are on the Y chromosome; both are sex-linked.
What is an autosomal trait?
A trait associated with a gene on a non-sex chromosome.
X and Y chromosomes follow the principle of segregation. What does this mean?
If an individual is XY, then each gamete gets one X or one Y.
In this class and other classes at UDub, you'll write X-linked alleles as XR and Xr. If you're keeping track of more than one X-linked allele at a time, you'd write the chromosomes as XRB and Xrb (or whatever the genotype actually is for the R and B genes). Suppose a male carries an X chromosome with the R allele and the b allele. How would you write his genotype?
XRb Y
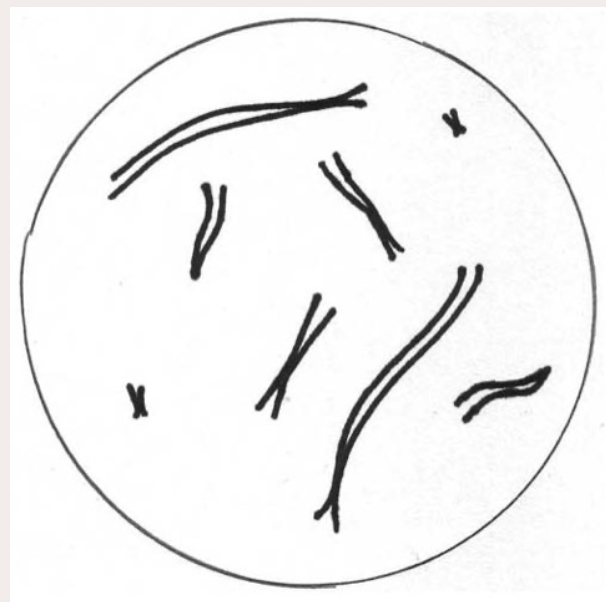
How many chromosomes are in this cell? Are they replicated or unreplicated?
8 replicated
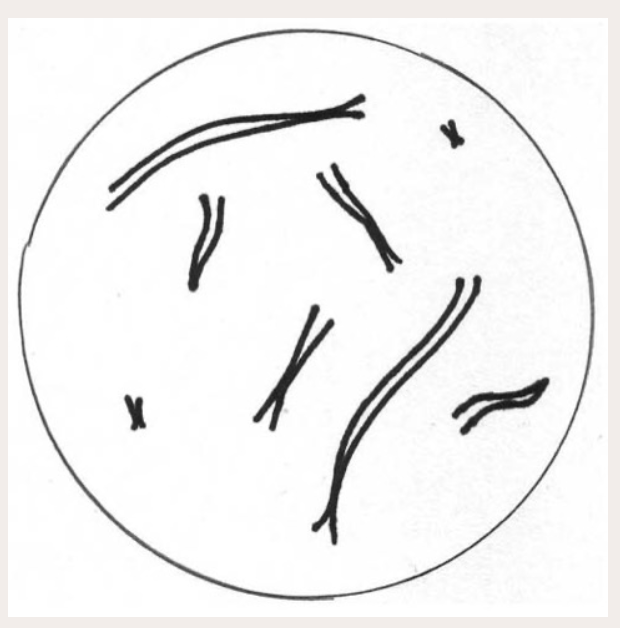
What is the haploid number of this cell? Is it haploid or diploid?
4; is is diploid
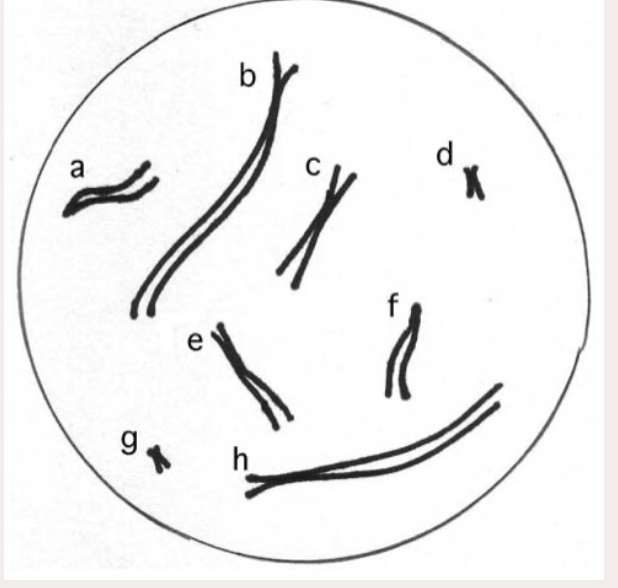
Which pairs of chromosomes in this cell are homologous? (In this drawing, the letters don't refer to alleles--they are just labels for the chromosomes that are shown.)
a-f, b-h, c-e, d-g
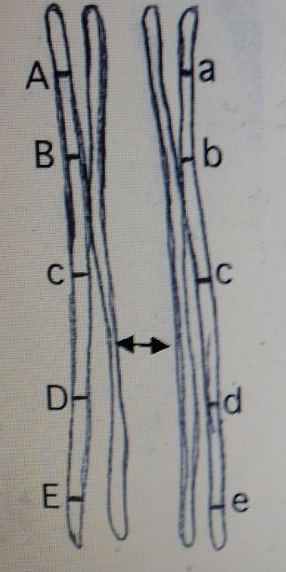
If crossing over occurred at the point indicated, what would the genotypes of the resulting chromosomes be? (The double arrow indicates the precise point where the strands of the non-sister chromatids break and exchange.)
ABcde, abcDE
Which of the following happens during interphase, before mitosis or meiosis?
Chromosomes replicate (each consists of two sister chromatids).
Which of the following is the most important difference between the events of prophase in mitosis versus meiosis I?
In meiosis I, homologs synapse.
What is "meta" about metaphase?
Meta means "between"; chromosomes move to the middle of the cell--between the two poles.
Why don't alleles from linked genes assort independently, if no crossing over occurs?
They are transmitted together (on the same chromosome), instead of being transmitted independently of each other.
Why do alleles from linked genes assort independently, if crossing over DOES occur?
They end up on different chromosomes, so are then transmitted independently of each other.
Autosomal Inheritance
The patterns of inheritance of any genes not on a sex chromosome. These are the “standard” patterns of inheritance
Autosomal Inheritance Example/Comment
Mendel only studied this one
Gene
A hereditary factor that influences a particular trait
Gene Example/Comment
This is the earliest definition. A more modern definition of a gene is the region of DNA in a chromosome that codes for a particular protein or RNA
Allele
A particular form of a gene
Allele Example/Comment
The two alleles in a diploid may be the same or different
Homozygous
Having two of the same allele
Homozygous Example/Comment
Refers to a particular gene
Heterozygous
Having two different alleles
Heterozygous Example/Comment
Refers to a particular gene
Dominant Allele
An allele that produces the same phenotype in heterozygous and homozygous genotypes
Dominant Allele Example/Comment
Dominance does not imply high frequency or high fitness
Recessive Allele
An allele that produces its phenotype only in homozygous genotypes
Recessive Allele Example/Comment
Phenotype “recedes” or disappears in heterozygous individuals; recessive does not imply low frequency or low fitness
Pure line
Individuals identical in phenotype that, when crossed, produce offspring that all have the same phenotype
Pure line Example/Comment
Pure line individuals are homozygous for the gene in question
Hybrid
Offspring from crosses between homozygous parents with different genotypes
Hybrid Example/Comment
Hybrids are homozygous
Polymorphic trait
A trait that appears commonly in two or more different forms
Polymorphic trait Example/Comment
Flower color in pea plants, which is commonly purple or white, is a polymorphic trait
Reciprocal Cross
A cross in which the phenotypes of the male and female are reversed compared with a prior cross
Reciprocal Cross Example/Comment
Used to test if the sex of the parent influences transmission of the trait
Testcross
A cross of a homozygous recessive individual and an individual with the dominant phenotype but unknown genotype
Testcross Example/Comment
Usually used to determine whether a parent with a dominant phenotype is homozygous or heterozygous