Leadership
1/23
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
24 Terms
Why is understanding leadership theories important for pharmacists?
-can help with assist in the leadership development of process, therefore improving quality of care
What are leadership theories?
-explanations of how and why certain people become leaders. They focus on the traits and behaviours that people can adopt to increase their leadership capabilities
What are the 6 main theories on leadership?
Great man theories (you’re born to lead)
Trait theories
Behavioural theories (what do they do?)
Contingency theories (how does the situation influence good leadership?)
Power and influence theories (what is the source of the leader’s power?
Other theories
What is the great man theory?
-great leaders are born and not made
Explain what the trait theory is?
-Trait leadership
-personal characteristics that foster consistent leader effectiveness across a variety of group and organizational situations.
-how you respond depends on the situation that you’re placed in and the traits/characteristics you develop as a result of it (stress tolerant, persistent etc)
Explain the behavioural theory
-this theory doesn’t take environment into account
-Behaviorists view leadership as a key set of actions instead of as personal characteristics. To determine these behaviors, researchers evaluated what successful leaders did, developed a taxonomy, and identified broad patterns.
-A leader’s behaviour can be changed and adapted
Give 2 models that explain the behavioural theory of leadership
-Lewin’s leadership styles of decision making
-Likert’s leadership styles
Explain Lewin’s leadership styles of decision making
-divided into 3 parts: authoritarian leaders, participative leaders, delegative leaders
1. Authoritarian leaders make decisions, instructions and direct activities without any participation from others. (good for when in a rush but participants may feel like they’re being controlled)
2. Participative leaders, also known as democratic leaders, involve their peers, team, co-workers in the decision-making process (slower because you’re taking every person’s opinion into account)
3. Delegative leaders give full autonomy to make decisions to their teams. (only good for self-motivating team)
Explain Likert’s leadership styles as a behavioural theory model
-split into 4:
exploitative authoritative
benevolent authoritative
consultative
participative
-Exploitative Authoritative=The leader has a low concern for people, using fear and threats to achieve outcomes.
-Benevolent Authoritative=The leader is authoritative but has concern for people, using reward to encourage performance.
-Consultative=The leader makes an effort to listen to others; however, many decisions are still made at the top and the upward flow of information is still somewhat idealized
-Participative=The leader engages in participative methods, engaging all members of the team in decision-making. Communication flows both ways. Trust required. Considered to be the most effective.
Explain the contingency theory. Give 5 examples of this theory
• There’s no one leadership style, rather the uniqueness of each situation requires a different approach.
– Fiedler’s Least Preferred Co-worker Theory
– Cognitive Resource Theory
– Strategic Contingencies Theory
– Path Goal Theory
– Hersey-Blanchard Leadership Theory
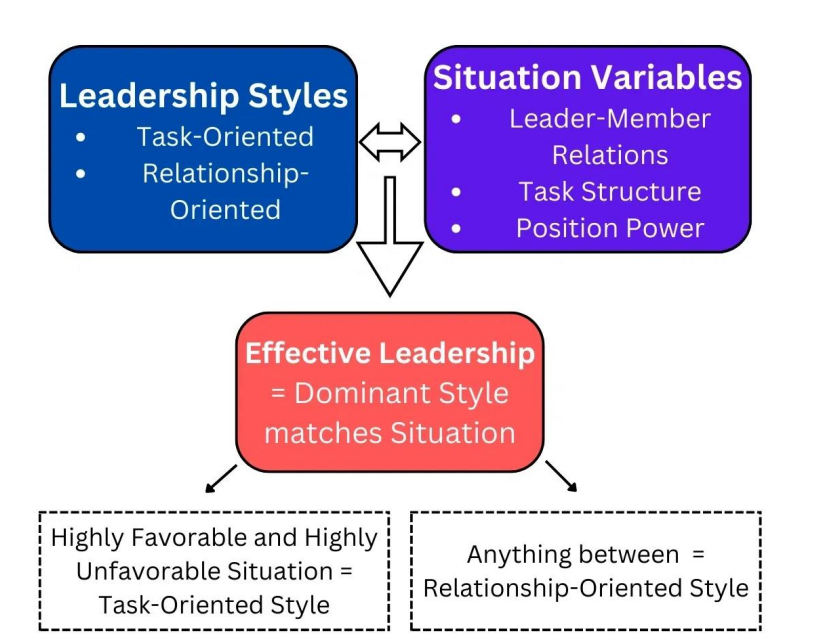
Explain Fiedler’s Contingency Model of Leadership
-an example of the contingency theory
🔹 Core Concept:
-Effective Leadership happens when a leader’s dominant style fits the situation. Requires use of correct leadership styles in the correct situation
🔹 Leadership Styles:
Task-Oriented: Focused on getting the job done.
OR
Relationship-Oriented: Focused on maintaining good interpersonal relationships.
-so 1 or the other should be used depending on situation e.g. good relationship, than task-orientated style is better
🔹 Situation Variables:
Leader-Member Relations – Trust and respect between leader and team.
Task Structure – How clearly defined the tasks are.
Position Power – The authority the leader has to reward or punish.
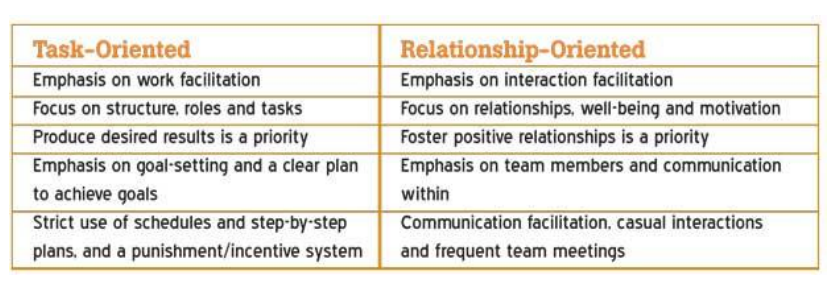
Explain the cognitive resource theory
-example of the contingency theory
-extension of Fiedler’s leadership theories
-explains what characteristics leaders show when their leadership is task-orientated vs relationship-orientated (give examples using image)
Explain the strategic contingency theory
-example of contingency theory
-focuses on how leaders gain power. e.g.:
problem-solving ability= people trust you more and listen to you
control of information= knowing what to tell and what not to tell
being irreplaceable
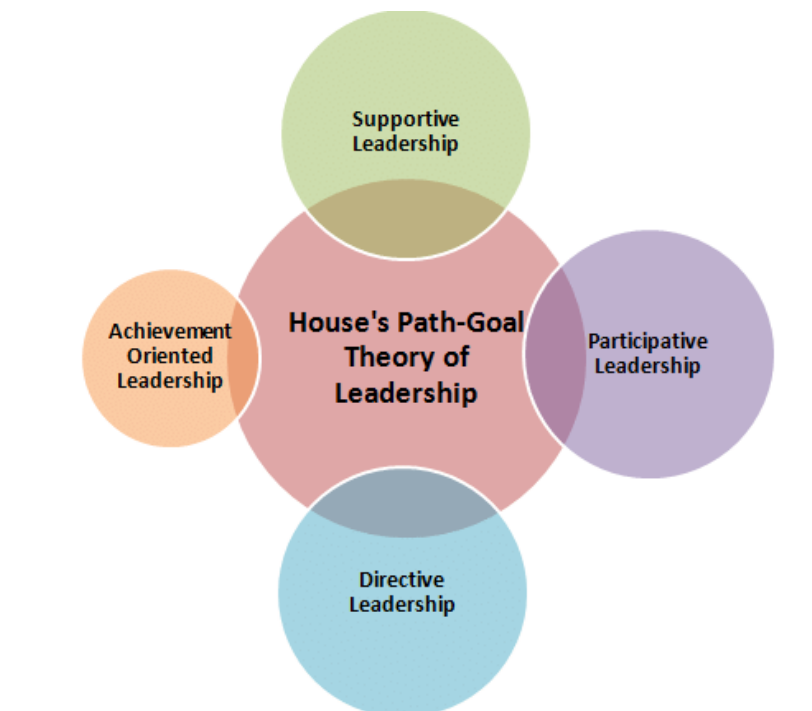
Explain House’s Path-Goal Theory of Leadership
4 different qualities that make a good leader, adapted based on the situation:
-supportive leadership= encouraging the team
-participative leadership= taking the team’s thoughts and opinions into account
-directive leadership= clear goals made. Clear instructions and communication
-Achievement-oriented leadership= efficiency leading to reward. Make new goals and ensure they are being rewarded
What is the power and influence theory?
Power and therefore leadership involves influencing people via authority. This influence can manifest in the form of rewards or punishments and/or through personal and positional power i.e. :
– Transactional
– Transformational
Explain the transactional leadership (part of the power and influence theory)
-Transactional leadership occurs when there’s an exchange of performance for either reward or penalty.
-Transactional leaders give followers something they want in exchange for something the leaders want - Transactional leadership is task-oriented, works within set organizational boundaries, and suggests a management focus for the leader
e.g. if you work an extra night, I will give you an extra day off
Explain the transformational leadership (part of the power and influence theory)
-transformational leadership=“the relationship of mutual stimulation and elevation that converts followers into leaders and may convert leaders into moral agents.”
• “the goal of transformational leadership is to transform people and organisations in a literal sense – to change them in mind and heart. Empower and motivate team so that they can be like you
What is servant leadership?
-the desire to serve the needs of others even before aspiring to lead them.
-characteristics of a servant leader:
listening
persuasion
empathy
person-centred care
What is the definition of professionalism?
-specialised knowledge etc (just mention qualities of a professional)
What is the Francis report?
-a report published in 2013 on the causes of the failings in care at Mid Staffordshire NHS foundation trust 2005-2009nthat lead to hundreds of deaths exposed
How many recommendations did the Francis report make?
290
What occurred in the hospital that the Francis report was based on?
-basic rights of pts weren’t upheld
-pts’ complaints ignored
-beds not changed for days
-managers obsessed with meeting targets rather than the pts
-staff lacked compassion
-a culture of bullying and fear led to many staff from speaking up
What were the recommendations from the Francis report?
-whistleblowing (the act of a worker reporting wrongdoing or malpractice in the workplace that affects others, often to an authority or the public)
-transparency and openness throughout the healthcare system with no consequences
What does fitness to practise mean?
-pharmacists and technicians must be registered with the GPhC
-have the skills, knowledge and health required to do job safely and effectively
e.g. convicted for criminal offence= not FTP