Disorders of the Parathyroid
1/41
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
42 Terms
Ca2+ and phosphates
What does parathyroid hormone regulate?
bones, intestine, kidneys
What organs does PTH act on?
stimulates osteoclast
PTH action at the bones
increases calcium reabsorption (also needs calcitriol)
PTH action on the intestines
Ca2+ conservation, calcitriol release
PTH action on the the kidneys
hypoparathyroidism
An endocrine disorder characterized by low serum PTH leading to hypocalcemia
post-surgical (most common), autoimmune, functional
Acquired causes of hypoparathyroidism
polyglandular autoimmune syndrome, systemic lupus erythematosus
Common autoimmune causes of hypoparathyroidism
low Mg (parathyroids need mag to function)
Functional causes of hypoparathyroidism
tetany (hypocalcemia)
What is the hallmark of acute hypoparathyroidism?
chvostek (facial twitch), trousseau (arm spasm), muscle cramps, stridor, carpopedal spasm, seizures, hyperactive deep tendon reflexes, prolonged QT
Signs of severe hypoparathyroidism
Increased bone density, osteosclerosis, craniofacial abnormalities, dental abnormalites, cataracts (irreversible)
Signs of chronic hypoparathyroidism
Anything that has hypocalcemia (resp alkaosis, epilepsy, loop diuretics, phenytoin, alndronate, pancreatitis)
DDX for hypoparathyroidism
Serum Ca + (0.8 x (4 - albumin))
Formula for corrected Ca2+
45% of calcium binds albumin so low serum may be due to hypoalbuminemia
Why do we need to “correct” ca levels when looking at lab work?
PTH (low), Serum Ca (low), Serum phosphate (high), urinary Ca (low), EKG (Qt prolongation), Mg (maybe low)
Diagnostics for hypoparathyroidism
ABCs, IV calcium (Ca Glutamate OR CaCl), vitamin D, Mg
45 y/o male patient presents to the ER after a seizure. Past medical hx is positive for thyroid cancer which was removed via complete thyroidectomy 1 week ago. Physical exam shows a positive chvostek and trousseaus sign. Vitals WNL. Lab work is as follows PTH low, corrected calcium under 7.5 mg/dl, high serum phosphate, low Mg. What is your treatment plan?
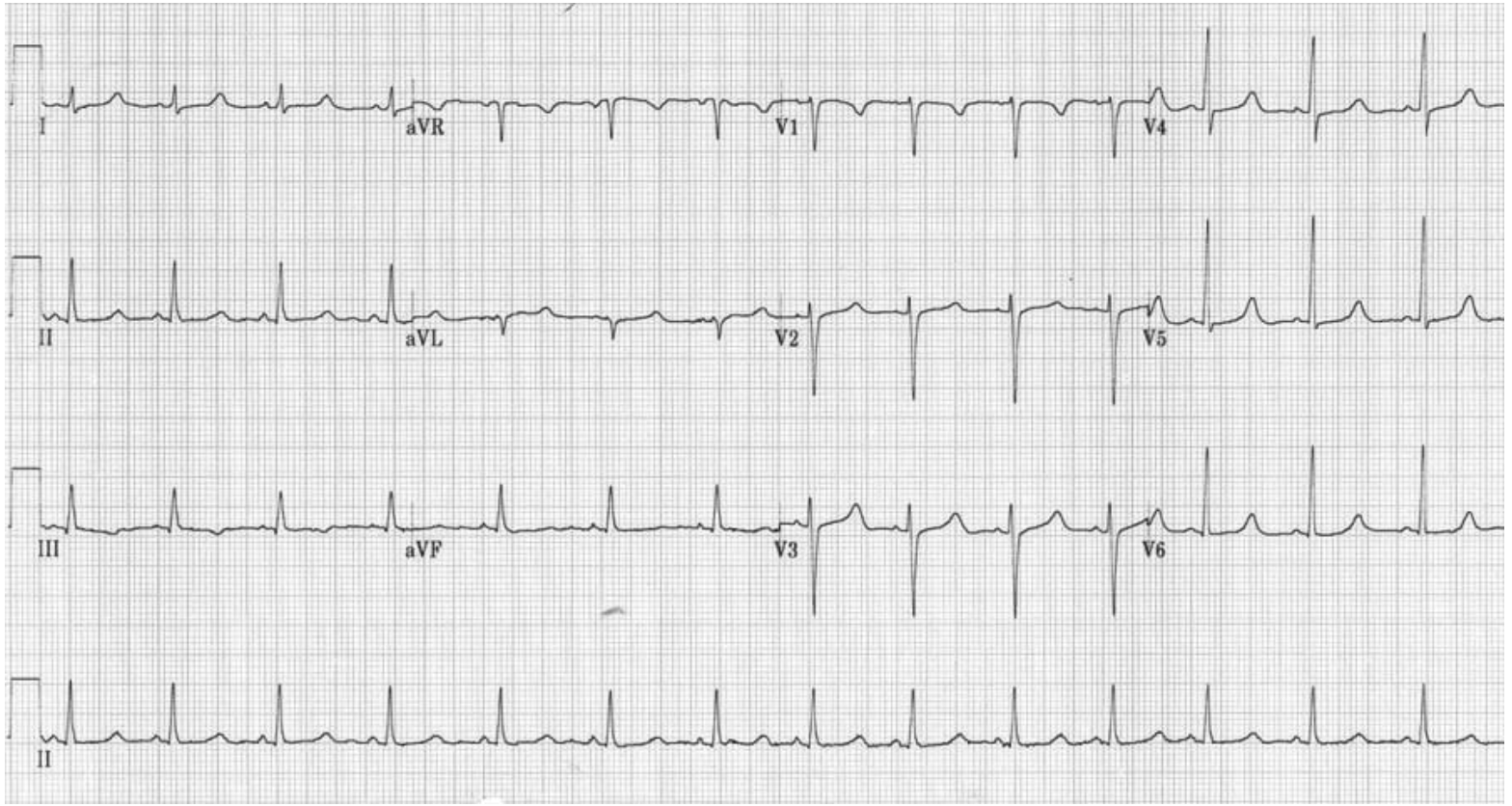
Oral calcium, oral vitamin D (taper after 3 weeks), oral Mg (taper after 3 weeks), Human PTH (teriparatide - severe cases)
45 y/o male patient presents to the clinic for numbness of the hands and feet. Past medical hx is positive for thyroid cancer which was removed via complete thyroidectomy 1 week ago. Vitals WNL. Lab work is as follows PTH low, corrected calcium low, high serum phosphate, low Mg. What is your treatment plan?
increased risk of osteosarcoma
BBW for teriparatide (human PTH)
urinary/serum calcium, serum phosphate weekly until stable then q3-6 months
Monitoring plan for hypoparathyroidism
hypercalcemia, nephrolithiasis, nephrocalcinosis, renal failures
Side effects of hypoparathyroidism treatments
Primary hyperparathyroidism
increase in the secretion of the parathyroids, causing elevated serum calcium, decreased serum phosphorus, and increased excretion of both calcium and phosphorus
Single parathyroid adenoma (most common), hyperplasia of 2+ parathyroid gland, MEN association, carcinoma
What are some causes of primary hyperparathyroidism?
asymptomatic hypercalcemia, hypercalcuria, possible kidney stones, cortical demineralization (excess PTH), pathological fractures, cystic bone lesion
Signs of primary hyperparathyroidism
secondary hyperparathyroidism
hypocalcemia due to non-parathyroid disorder (probs the kidneys) leads to chronic PTH hypersecretion
Tertiary hyperparathyroidism
Parathyroids are autonomous in their secretion of PTH - unrelated to serum calcium concentration in patients with long-standing secondary hyperparathyroidism

CKD (kidneys start throwing out everything (including calcium - loss of feedback, more PTH)), vitamin D deficiency
Causes of secondary/tertiary hyperparathyroidism
Asymptomatic or mild, symptoms may arise due to hypercalcemia (bones, stones, groans, psychic moans, fatigue overtones)
Presentation of Hyperparathyroidism
low bone density, arthralgia, pathologic fracture (loss of cortical bone loss)
Skeletal symptoms of hyperparathyroidism - hypercalcemia
Nephrogenic DI (polyuria, polydipsia), nephrolithiasis
Renal symptoms of hyperparathyroidism - hypercalcemia
N/V, constipation, weight loss
GI symptoms of hyperparathyroidism - hypercalcemia
fatigue, HA, insomnia, irritability, depression
Neuropsychiatric symptoms of hyperparathyroidism - hypercalcemia
hypertension, brady, shortened QT
Cardiovascular symptoms of hyperparathyroidism - hypercalcemia
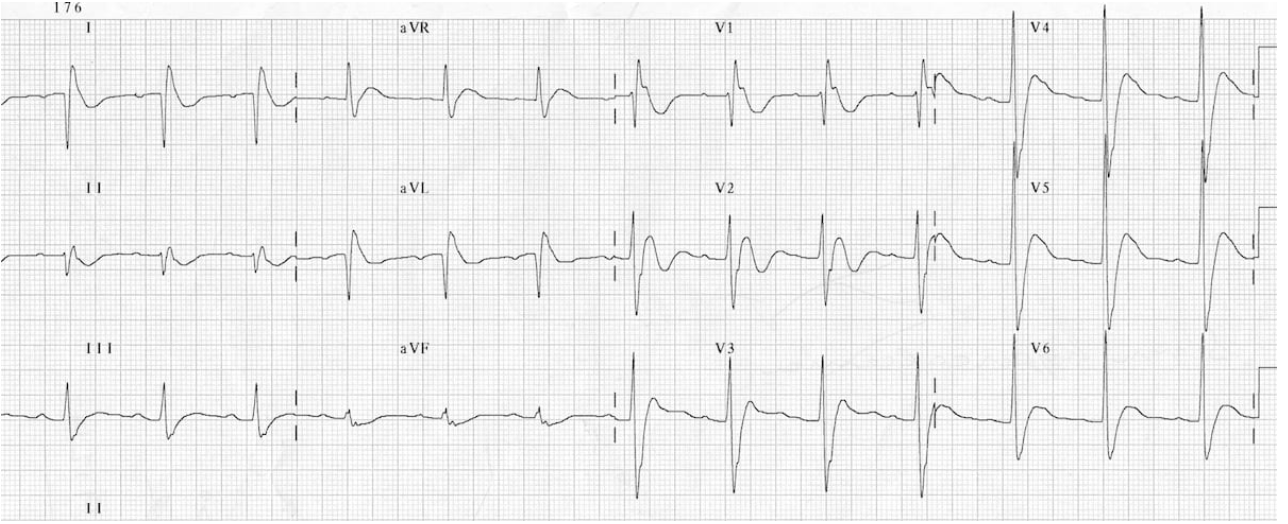
elevated serum and/or urine calcium (usually above 10.5), elevated PTH, low/normal serum phosphate, ALP normal/elevated
*Labs for primary hyperparathyroidism
Look for underlying (probably kidney labs BUN/Creat), elevated PTH, serum calcium may be normal
*Labs for secondary hyperparathyroidism
Xray, U/S (kidney stones), DXA (determine bone density)
What imaging would you get for pre-op hyperparathyroidism
salt and pepper skull, brown tumor (cystic lesion), osteopenia
XRAY red flags for calcium disorders

lab error, dehydration, malignancy, multiple myeloma, sarcoidosis, Supplementation (Vitamin D and calcium), prolonged physical immobilization (Wolff's Law)
DDX for hyperparathyroidism
parathyroidectomy
Definitive treatment plan for symptomatic/meets asymptomatic guidelines hyperparathyroidism
Cinacalet (severe hypercalcemia - inhibit PTH secretion), bisphosphanates (osteoporosis)
For nonsurgical candidates, what is the treatment plan for hyperparathyroidism
thiazide diuretics (increase Ca reabsorption), calcium containing antacids, immobilization/bed rest
What are we avoiding with hyperparathyroidism peeps?
osteoporosis, osteopenia
What may be able to be reversed if primary hyperparathyroidism is cured?