UC Berkeley PH 162A Midterm 1
1/131
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
132 Terms
Characteristics of Prokaryotes
no nucleus, no membrane bound organelles
examples of prokaryotes
bacteria and archaea
Characteristics of Eukaryotes
nucleus and membrane bound organelles
examples of eukaryotes
plants, animals, fungi, protists
Purpose of Koch's Postulates
series of guidelines used to identify the microorganism that causes a specific disease
What are Koch's Postulates?
1. The same pathogen must be present in every case of the disease.
2. The pathogen must be isolated from the diseased host and grown in pure culture.
3. The pathogen from the pure culture must cause the disease when it is inoculated into a healthy, susceptible laboratory animal.
4. The pathogen must be isolated from the inoculated animal and must be shown to be the original organism.
What are the three kinds of horizontal gene transfer?
transduction, conjugation, transformation
How does specialized transduction work?
Phage DNA is integrated into plasmid of bacteria; bacteria reproduces, allowing phage DNA to replicate
How does generalized transduction work?
Any section of bacterial DNA is transferred; random bacterial DNA is included in new virions and introduced to new bacteria upon infection
What is conjugation?
transfer of DNA between bacteria using a pilus; involves plasmids
What's a plasmid?
Tiny circles of DNA found in bacteria, non-chromosomal
What is transformation in horizontal gene transfer?
uptake of new, random genes from environment; "competence" is required
What is competence in transformation?
bacteria needs to be in a state where it can be transformed; sometimes in lab they are electrocuted
What is the importance of ribosomes in taxonomy?
bacterial ribosomes remain consistent among all living things; slight differences allows us to determine common ancestors
What size ribosome do we sequence for taxonomy?
16S
How much similarity do the ribosomes in bacteria need to have to be the same species?
97% or greater
What's a silent mutation?
a base change mutation where it doesn't effect the amino acid produced
What's a missense mutation?
a base change mutation changes the amino acid produced
What's a nonsense mutation?
a base change mutation prematurely introduces stop codon, shortening the protein
What's a frameshift mutation?
insertion/deletion of a base which shifts the ribosome's reading frame; can result in premature stop codons or affect the folding of protein entirely
What are characteristics of gram-positive bacteria?
thick peptidoglycan layer, one membrane, techoic acid, stains purple
A bacteria is stained purple. Is it gram-positive or gram-negative?
gram-positive
What are characteristics of gram-negative bacteria?
thinner peptidoglycan layer, two membranes, outer membrane has lipopolysaccharides (LPS)
What kind of cell shape is this?
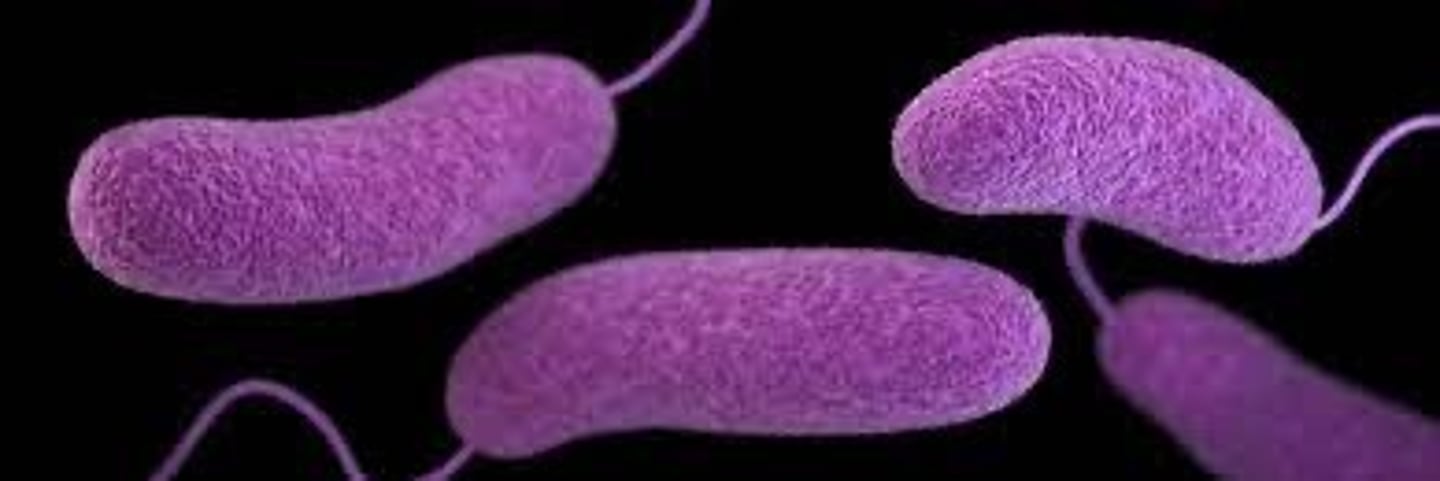
What kind of cell shape is this?
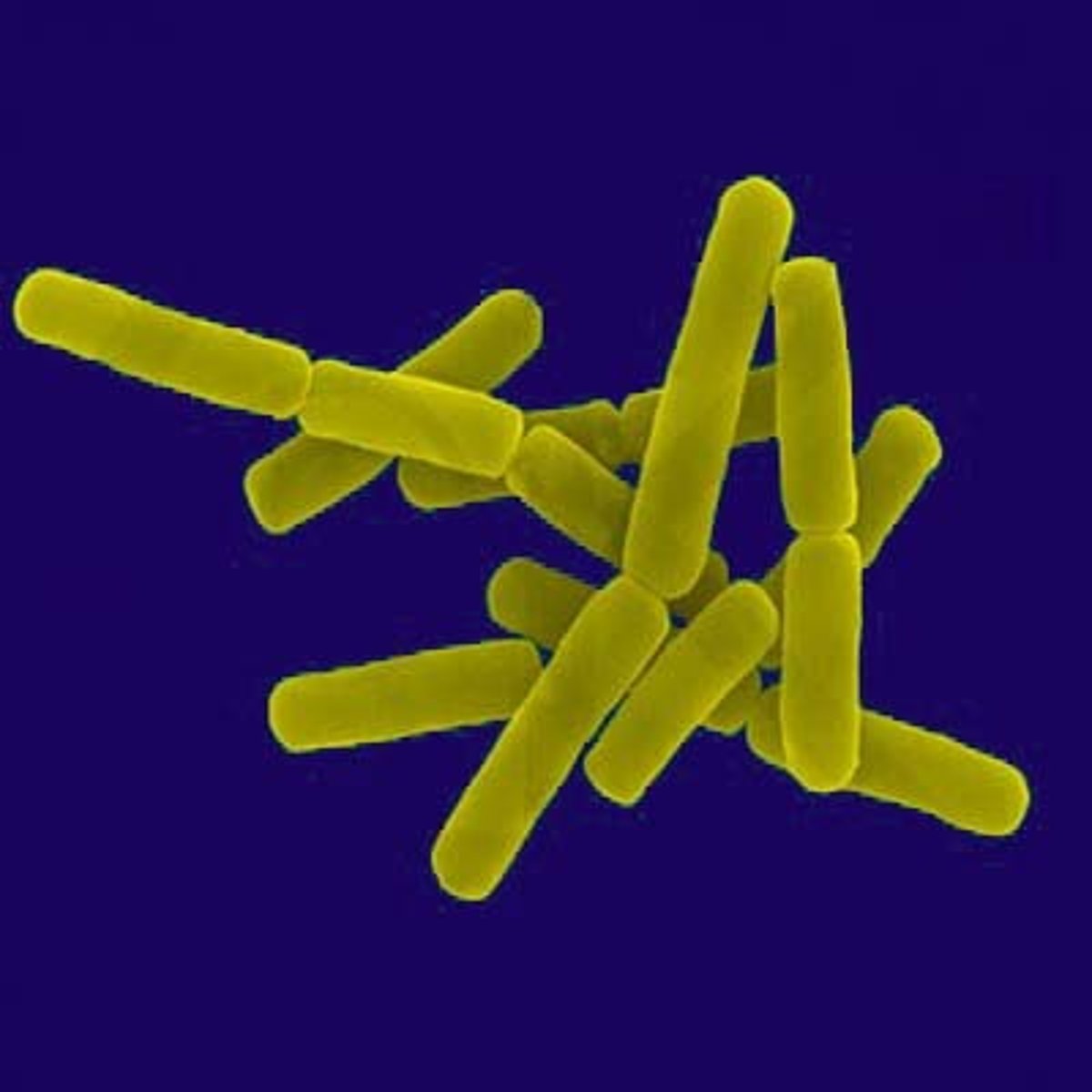
What kind of cell shape is this?
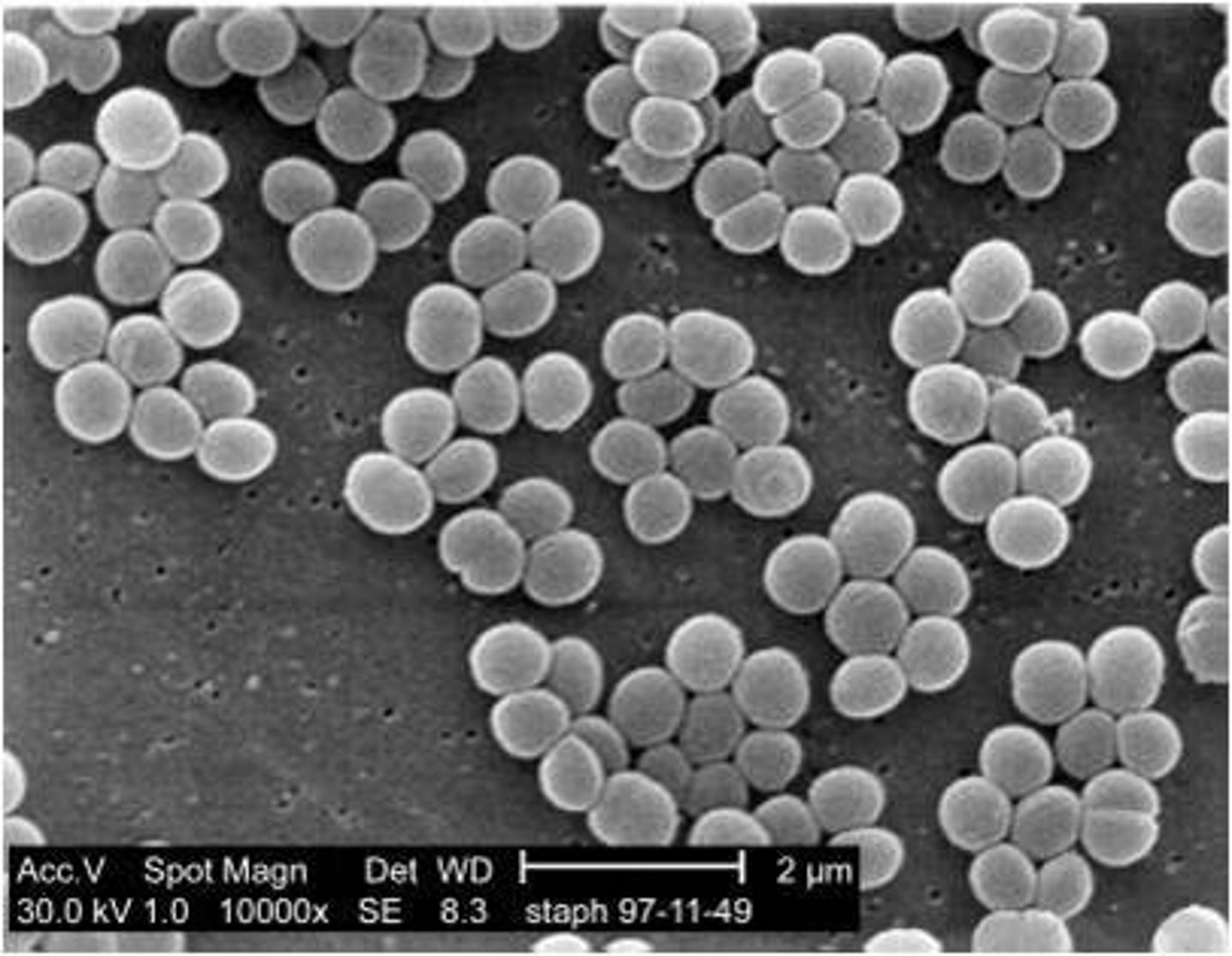
What does a Zeihl-Neelsen acid fast stain do?
detects high lipid content in cell walls for non- gram-pos or gram-neg bacteria
What are exotoxins?
proteins secreted by certain bacteria and other organisms into host cell
What kind of toxin is an A-B toxin?
exotoxin
What are some endotoxins?
lipopolysaccharides from the cell wall of gram-negative cells; contains lipid A;
What are endotoxins?
Lipid A released, can cause systemic shock and other fatal effects.
How do A-B toxins work?
work by binding to host cell receptor (B part) and transferring damaging agent (A part) cross the membrane
What's a Type III secretion system?
in gram-negative bacteria; shoot "conjugation pilus" into host cell to secrete virulence factors
Name the steps for diagnosis and identification of bacteria.
1. culture
2. gram stain
3.. selective media (blood agar, for example, to see hemolysis)
4. serological and biochemical (like the COVID rapid test)
5. antibiotic test
6. MALDI-TOF mass spectrometry (ionizes sample)
7. sequencing
What are membrane-disrupting toxins?
exotoxins that lyse host cells by disrupting plasma membranes
Antibiotic type that does inhibition of cell wall synthesis
beta-lactams
Name a beta-lactam
penicillin
Antibiotic that inhibits protein synthesis
tetracycline
Antibiotic type that inhibits nucleic acid synthesis
quinolones
Name a quinolone
ciprofloxacin
Antibiotic type that acts as antimetabolites, inhibits folic acid synthesis pathway
sulfonamides
What are some kinds of antibiotic resistance?
efflux pumps, inactivating enzymes, decreased uptake, target alterations
Name two antivirals.
acyclovir, AZT
What is acyclovir an analog for?
nucleotide base guanine
What antiviral treats herpesvirus?
acyclovir
What is AZT an analog for?
nucleotide base thymine
What antiviral treats HIV? How?
AZT; blocks reverse transcriptase which HIV creates
What fungal cell component does antifungals target?
Ergosterole
What are prions?
misfolded proteins
Name four diseases related to prions.
scrapie, mad-cow, kuru, creuzfeldt-jacob
What kind of cancer can HPV cause?
cervical cancer
What kind of cancer can Hep B and C cause?
liver cancer
What kind of cancer does Epstein Barr cause?
Burkitt's lymphoma, nasopharyngeal carcinoma
Baltimore
Anopheles mosquito causes what disease?
malaria
Malaria affects which parts of the body?
blood and liver, in a cycle
What are the two types of trypanosoma spp.?
African and American trypanosomiasis
What's another name for African trypanosomiasis?
sleeping sickness
What's another name for American trypanosomiasis?
Chaga's disease
African trypanosomiasis is caused by what? Where in the body does it affect?
Tsete fly, from cattle reservoir; extracellular in blood, lymph, cerebrospinal fluid
American trypanosomiasis is caused by what? Where in the body does it affect?
can be eaten or given by Triatome bug ("kissing bug") from a mammalian reservoir; infects smooth muscle (heart)
Why is it hard to diagnose Chaga's disease?
mostly flu-like symptoms early on
Leishmaniasis is cause by what? Where in the body does it affect?
Sandflies, varying based on subspecies; affects skin, nose, mouth, and internal organs
What's another name for cestodes?
tapeworms
How do you get tapeworms?
Red meat, fish, water
Are humans definitive or intermediate hosts for cestodes?
both
How does the life cycle of a tapeworm work?
Animal eats egg; larvae form cysts; human eats animal; larvae matures into adulthood
What are the two kinds of African trypanosomiasis?
T. brucei gambiense and T. brucei rhodesiense
Name an American trypanosomiasis strain?
T. cruzi
What disease do trematodes cause?
Schistosoma spp.
What's an intermediate host for trematodes?
freshwater snails, fish
How do trematodes get to their definitive host?
They're attracted to lipids in skin; humans swimming have a chance of being penetrated through the skin by trematodes
Schistosoma haematobium affects what?
urinary tract, bladder
Schistosoma japonicum affects what?
intestinal wall, liver
Schistosoma mansomi affects what?
colon, rectum, liver
What are some of the symptoms of schistosoma spp.?
bloody urine, dermatitis, hypertension, granuloma formation creating swelling
What's another name for onchocerciasis?
river blindness
What causes the blindness in river blindness?
adult worm makes microfilariae, which can travel to the eye, with Wolbachia in them which triggers immune response
How is river blindness transmitted?
black fly injects larvae during blood meal
How are hookworms transmitted?
penetration of skin by larvae found in the soil; get to lungs, coughed up, go down to small intestine
What are some symptoms of hookworms?
worm burden can cause anemia and iron deficiency, stunting growth in children
What is the transmission of ascaris? What is it similar to?
orally ingested; similar to hookworms
What is the species name for the parasite that causes malaria?
Plasmodium spp.
What is the envelope and capsid shape of picornaviridae?
naked, polyhedral
What is the envelope and capsid shape of togaviridae?
enveloped, polyhedral
What is the envelope and capsid shape of retroviridae?
enveloped, spherical
What is the envelope and capsid shape of coronaviridae?
enveloped
What's a disease associated with picornaviridae?
Enterovirus; Polio
What's a disease associated with togaviridae?
Rubella virus
What's a disease associated with flaviviridae?
flavivirus; yellow fever
What's a disease associated with retroviridae?
HIV; AIDS
What is the envelope and capsid shape of paramyxoviridae?
enveloped, helical
What is the envelope and capsid shape of rhabdoviridae?
enveloped, helical
What is the envelope and capsid shape of orthomyxoviridae?
enveloped, helical
What is the envelope and capsid shape of filoviridae?
enveloped, filamentous
What is the envelope and capsid shape of bunyaviridae?
enveloped, spherical
What is the envelope and capsid shape of reoviridae?
naked, polyhedral
What's a disease associated with paramyxoviridae?
morbillivirus; measles
What's a disease associated with rhabdoviridae?
lyssavirus; rabies
What's a disease associated with orthomyxoviridae?
influenza