HES 131 2023 EXERCISE PSYCHOLOGY
0.0(0)
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/185
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
186 Terms
1
New cards
Affect
To impact or change
Ask the question: What ‘__Affects__’ our exercise behaviour
Ask the question: What ‘__Affects__’ our exercise behaviour
2
New cards
Effect
The result of a change
Ask the question: What __Effect__does exercise have?
Ask the question: What __Effect__does exercise have?
3
New cards
Exercise Psychology studies
1. The psychological principles to the adoption and maintenance of exercise (Affect)
2. The psychological and emotional consequences of exercise (Effect)
2. The psychological and emotional consequences of exercise (Effect)
4
New cards
Exercise psychology focus:
-Non Elite Performance
-Non Competitive motives for participation
-Focus on enhancing participation
-Focus on psychological benefits of exercise
-Non Competitive motives for participation
-Focus on enhancing participation
-Focus on psychological benefits of exercise
5
New cards
Sport Psychology focus on:
-Elite Performance
-Competitive motives for performance
-Focus on enhancing performance
-Focus on psychological preparation for performance
-Competitive motives for performance
-Focus on enhancing performance
-Focus on psychological preparation for performance
6
New cards
Why is exercise psychology important
-Physical Inactivity is a problem
-Exercise behavior is complex
-Exercise psychology can help us understand this complex behavior
-Exercise behavior is complex
-Exercise psychology can help us understand this complex behavior
7
New cards
NEGATIVE IMPACT OF PHYSICAL INACTIVITY
•**Less-active people have a greater risk of developing high blood pressure.**
\
•**Physical inactivity increases your risk of type 2 diabetes.**
•**Physically inactive people are more likely to develop coronary heart disease.**
•**Physical inactivity can add to feelings of anxiety and depression.**
\
•**Physical inactivity increases your risk of type 2 diabetes.**
•**Physically inactive people are more likely to develop coronary heart disease.**
•**Physical inactivity can add to feelings of anxiety and depression.**
8
New cards
Why Study Exercise Psychology
-To understand the psychological antecedents (Affects) and consequences or results (Effects) of exercise behavior.
-To understand and promote exercise exercise adoption and adherence.
-To use exercise to reduce negative psychological/ emotional states and promote positive ones.
-To understand and promote exercise exercise adoption and adherence.
-To use exercise to reduce negative psychological/ emotional states and promote positive ones.
9
New cards
Exercise Adoption
-The beginning stage of an exercise regimen.
10
New cards
Exercise Adherence
-Maintaining an exercise regimen for a prolonged period of time following initial adoption phase.
11
New cards
Role of an exercise psychoIlogist
1. Identify: ;Current Behavior patterns ;Barriers to engaging in the behavior (exercise). (Person first, Exercise Experience, Current Lifestyle, Social Support, Potential Barriers)
2. Facilitate: ;Behavior change. With the information identified, making subtle, small changes to support exercise goals
3. Support: ;Individual in adoption and adherence of the behavior.
12
New cards
Work Opportunities
-Higher education
-Primary/ Secondary education
-Fitness and wellness
-Rehabilitation
-Business
-Primary/ Secondary education
-Fitness and wellness
-Rehabilitation
-Business
13
New cards
Business benefits to exercise
1. Reduced sickness 2 manage stress 3 improves mood and well being 4, better Employee output
14
New cards
EXERCISE PSYCHOLOGY CONCEPTS
Barriers and motives
Social influences and social support
Community
Self-esteem
Body image
Stress and coping
Quality of life
Social influences and social support
Community
Self-esteem
Body image
Stress and coping
Quality of life
15
New cards
Barriers and motives
Lack of time
Social Influence
Cultural Influences
Lack of energy
Fear of injury
Lack of resources
Social Influence
Cultural Influences
Lack of energy
Fear of injury
Lack of resources
16
New cards
Community, social influence and Support
•Shared interest
•Encouraging environment
•Social connection
Perceived motivations from social supports (can help or hinder motivation)
•Encouraging environment
•Social connection
Perceived motivations from social supports (can help or hinder motivation)
17
New cards
How is self esteem and body image influenced by exercise?
Attaining goals and accomplishments can increase self esteem and increase good feelings about physical acceptance.
18
New cards
Exercise and Stress and Coping
•Decreases cortisol
•Decreases tension
•Elevates mood
•Improve sleep
•Decreases tension
•Elevates mood
•Improve sleep
19
New cards
EFFECT OF EXERCISE
Regular exercise helps people become physically and mentally healthier.
Improved sense
of well-being
Better sleep
Reduced stress
Stronger memory More energy
throughout the day Increased
self-confidence
Improved sense
of well-being
Better sleep
Reduced stress
Stronger memory More energy
throughout the day Increased
self-confidence
20
New cards
EFFECT OF EXERCISE ON THÉ BRAIN
Norepinephrine release improves attention, perception & motivation
Endorphin release dulling pain sensation
Serotonin release enhances mood
Brain-derived neurotrophic factor release.
Protect & repair neurons
Brain cells grow
Mood regulation
Mental clarity
Hippocampus grows over time with exercise. Improved learning ability & memory
Blood flow to the brain increases.
More oxygen & nutrients Dopamine release improves motivation focus & learning
Endorphin release dulling pain sensation
Serotonin release enhances mood
Brain-derived neurotrophic factor release.
Protect & repair neurons
Brain cells grow
Mood regulation
Mental clarity
Hippocampus grows over time with exercise. Improved learning ability & memory
Blood flow to the brain increases.
More oxygen & nutrients Dopamine release improves motivation focus & learning
21
New cards
SLOTH Model
-Categorizes 24 hours of the day into 5 domains:
1. Sleep
2. Leisure Time
3. Occupation
4. Transportation
5. Home-based Activities
1. Sleep
2. Leisure Time
3. Occupation
4. Transportation
5. Home-based Activities
22
New cards
Epidemiology
the method used to find the causes of health outcomes and diseases in populations
\
With the information gathered, scientists and health professionals can best inform specific populations on ways in which they can prevent and control health problems
\
With the information gathered, scientists and health professionals can best inform specific populations on ways in which they can prevent and control health problems
23
New cards
Examples of Epidemiology
* Environmental Exposures (eg. lead exposures)
* Infectious Diseases (eg. Covid)
* Injuries (Homicides in neighbourhood)
* Non-Infectious Disease (eg. Cancer)
* Infectious Diseases (eg. Covid)
* Injuries (Homicides in neighbourhood)
* Non-Infectious Disease (eg. Cancer)
24
New cards
Ways epidemiology is conducted
* Evidence Hierarchy of Epidemiological Study Designs
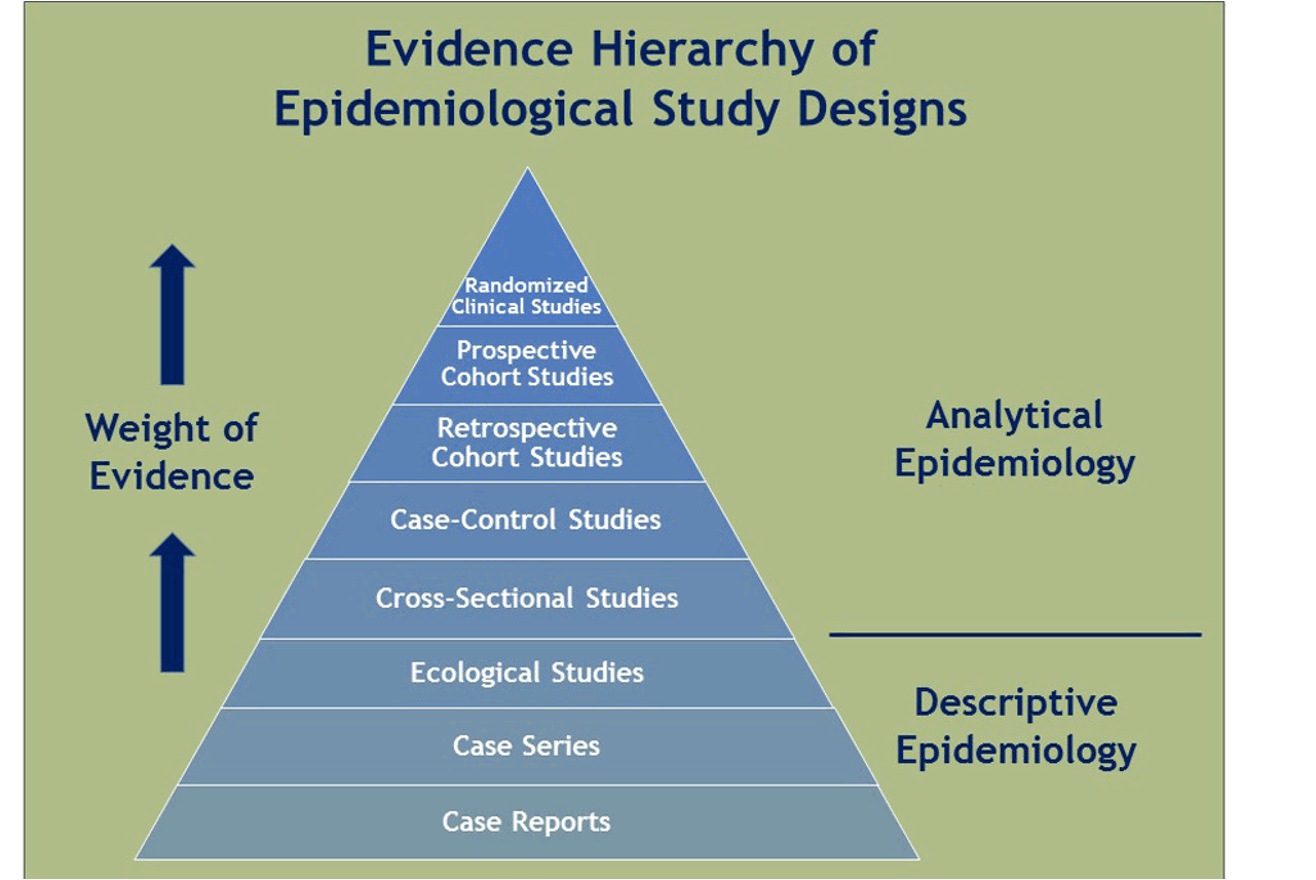
25
New cards
Types of Epidemiological Studies
Non Experimental (Observational)
* Population Based (Descriptive survey, Analytic)
* Individual based
* Descriptive (case reports, case studies)
* Analytic (Cross-sectional study or Prevalence study, Case-control study or Case-reference, Cohort study or follow-up study)
\
Experimental (Interventional studies)
* Randomized (control or clinical trial)
* Non Randomized (Quasi-Experimental field trial Community Trial)
* Population Based (Descriptive survey, Analytic)
* Individual based
* Descriptive (case reports, case studies)
* Analytic (Cross-sectional study or Prevalence study, Case-control study or Case-reference, Cohort study or follow-up study)
\
Experimental (Interventional studies)
* Randomized (control or clinical trial)
* Non Randomized (Quasi-Experimental field trial Community Trial)
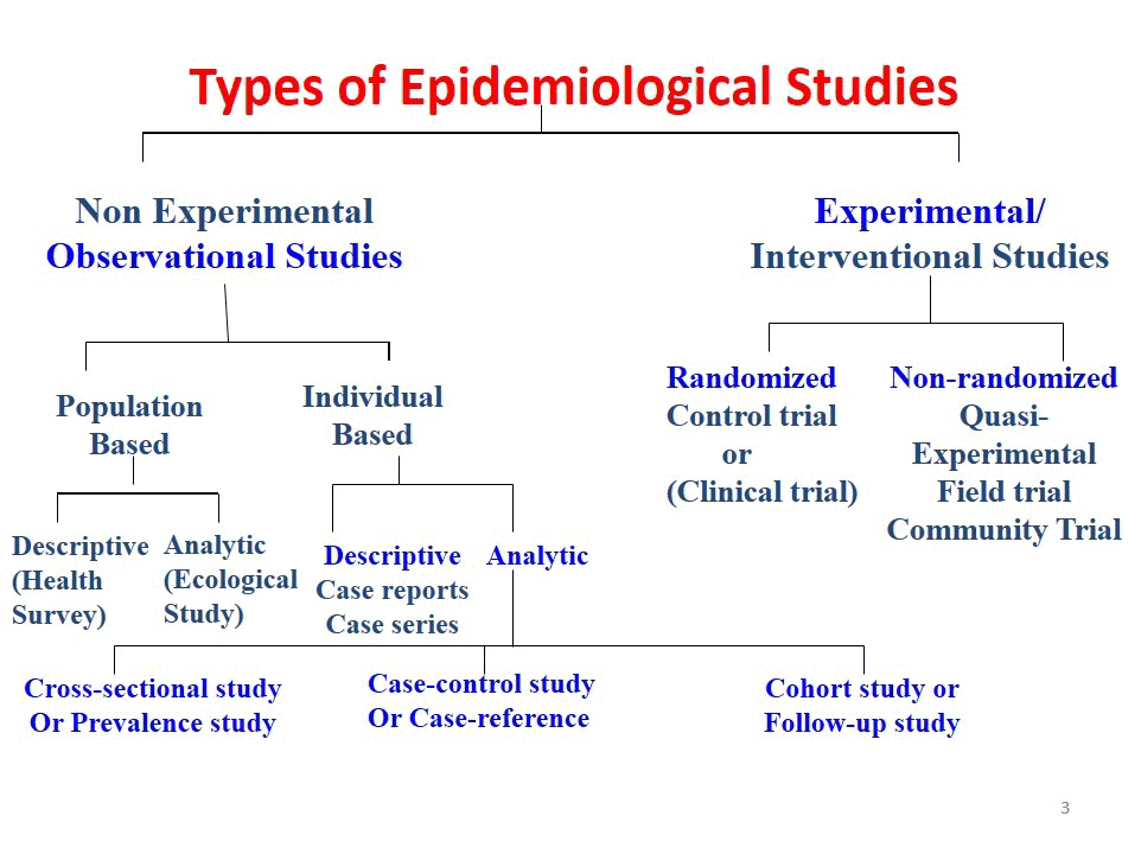
26
New cards
Non experimental: observational studies
In observational studies, the researcher observes and systematically collects information, but does not try to change the people (or animals) being observed
27
New cards
Population based Study example
**Observe Gym Behaviour**: Exercises chosen; Time spent in the gym
28
New cards
Individual based Epidemiological study example
**Observe the Gym Behaviour** __**of one person**__: Exercises chosen; Time spent in the gym
29
New cards
Experimental Epidemiological Study
* One or more variables are manipulated by the researcher (as treatments), subjects are randomly assigned to different treatment levels (random assignment), and the results of the treatments on outcomes are observed.
\
* In experimental research, some subjects are administered one or more experimental stimulus called a treatment (the treatment group ) while other subjects are not given such a stimulus (the control group )
\
* In experimental research, some subjects are administered one or more experimental stimulus called a treatment (the treatment group ) while other subjects are not given such a stimulus (the control group )
30
New cards
Experimental: Randomized (Epidemiological study)
In randomized control trials, the patients are randomly assigned to different groups (treatment and control groups). The resulting effect estimate is the difference between the mean response in the two groups
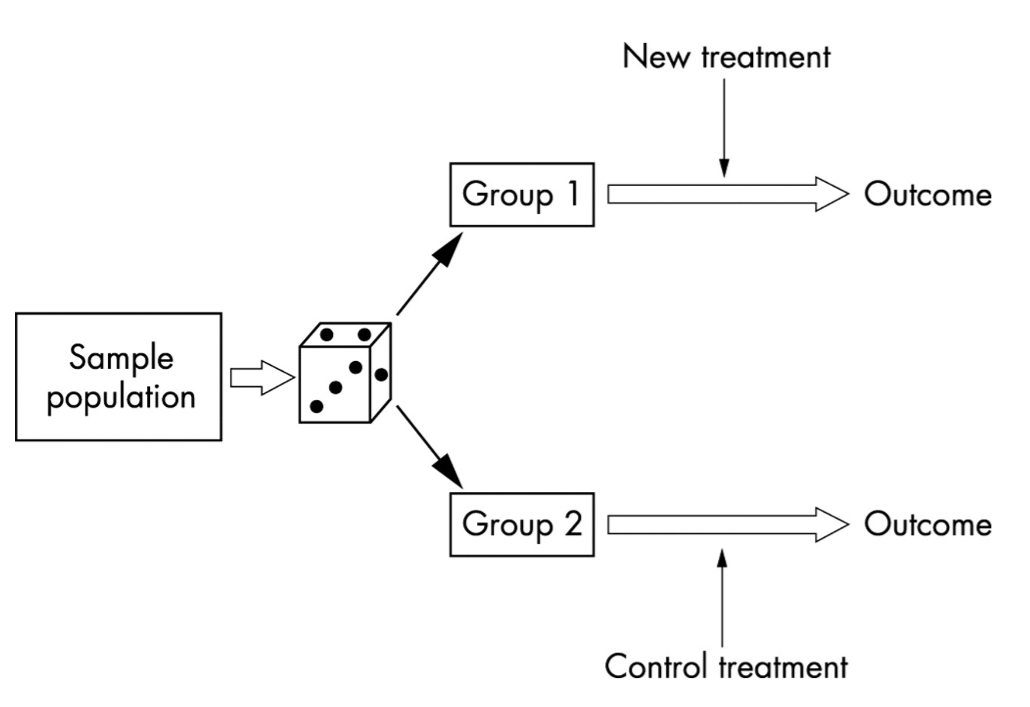
31
New cards
Experimental: non randomized (Epidemiological study)
**A** clinical trial in which the participants **are not** assigned by chance to different treatment groups. Participants may choose which group they want to be in, or they may be assigned to the groups by the researchers
32
New cards
Choosing the right study type
* Study design should be well thought out before initiating a research investigation. Choosing an inappropriate study design may undermine overall study validity. Critical thinking about the possible study design issues beforehand will ensure that the research question is adequately addressed
* Study design plays a major role in determining the scientific value of a research study. Understanding the basic study design concepts will aid clinicians in practicing evidence-based medicine
* Errors in study design are extremely difficult to correct after study completion. Thorough planning is required to avoid weak conclusions or unconvincing results
* Study design plays a major role in determining the scientific value of a research study. Understanding the basic study design concepts will aid clinicians in practicing evidence-based medicine
* Errors in study design are extremely difficult to correct after study completion. Thorough planning is required to avoid weak conclusions or unconvincing results
33
New cards
Physical Activity Epidemiology
Study and analysis of the frequency and distribution of PA in a defined population
34
New cards
Physical activity Epidemiology research trends
* Physical activity/Inactivity
* Obesity
* Fitness Levels
* Health Promotion
* Disease Prevention
* Obesity
* Fitness Levels
* Health Promotion
* Disease Prevention
35
New cards
Physical Activity Epidemiology (Helps to identify)
Study and analysis of the frequency and distribution of PA in a defined population
* Patterns of PA behavior
* Predictors (determinants) of PA behavior
* Individual, Interpersonal, social, environmental factors--> Determinants of health
* Outcomes of PA behavior (or inactivity)
* Patterns of PA behavior
* Predictors (determinants) of PA behavior
* Individual, Interpersonal, social, environmental factors--> Determinants of health
* Outcomes of PA behavior (or inactivity)
36
New cards
Five W's
-Who exercises
-What do they do when they exercise
-Where do they exercise
-When do they exercise
-Why do they exercise
-What do they do when they exercise
-Where do they exercise
-When do they exercise
-Why do they exercise
37
New cards
Determinants of Health
Personal, social, economic, and environmental factors that determine individual and population health
\-Income and social status
\-Employment and working conditions
\-Education and literacy
\-Childhood experiences
\-Physical environments
\-Social supports and coping skills
\-Healthy behaviors -Access to health services -Biology and genetics -Gender -Culture -Race/Racism
\-Income and social status
\-Employment and working conditions
\-Education and literacy
\-Childhood experiences
\-Physical environments
\-Social supports and coping skills
\-Healthy behaviors -Access to health services -Biology and genetics -Gender -Culture -Race/Racism
38
New cards
Exercise Varies in:
-Frequency (Days/week)
-Intensity (% MAX HR)
-Time (Minutes/session)
-Type (Running, biking, weight training)
-Intensity (% MAX HR)
-Time (Minutes/session)
-Type (Running, biking, weight training)
39
New cards
Physical Activity
-Any body movement carried out by the skeletal muscles and requiring energy:
Light--\>Moderate--\>Vigorous
Light--\>Moderate--\>Vigorous
40
New cards
Exercise
Planned, structured, repetitive movement of the body designed to achieve a particular goal:
Light--\>Moderate--\>Vigorous
Light--\>Moderate--\>Vigorous
41
New cards
Sedentary Behavior
Any Waking Behavior with:
-An energy expenditure < 1.5 metabolic equivalents (METs)
-Performed while in a sitting, reclining, or lying posture
-Not all seated behaviors are sedentary
-An energy expenditure < 1.5 metabolic equivalents (METs)
-Performed while in a sitting, reclining, or lying posture
-Not all seated behaviors are sedentary
42
New cards
One Metabolic Equivalent (MET)
The amount of oxygen consumed while sitting at rest and is equal to 3.5 ml O2 per kg body weight x min.
Moderate Intensity\= 3-6 METs
Vigorous Intensity\> 6 METS
Moderate Intensity\= 3-6 METs
Vigorous Intensity\> 6 METS
43
New cards
Outcomes of Inactivity
PA, Morbidity, and Mortality
Morbidity (disease) rates can be directly and positively impacted by the adoption of a physically active lifestyle.
Morbidity (disease) rates can be directly and positively impacted by the adoption of a physically active lifestyle.
44
New cards
Sedentary Behavior, Morbidity, and Mortality
Increasing sedentary behavior increased risk of:
-All-cause mortality
-CV disease mortality
-Cancer mortality
-CV disease incidence
-Cancer incidence
-Type 2 diabetes incidence
-All-cause mortality
-CV disease mortality
-Cancer mortality
-CV disease incidence
-Cancer incidence
-Type 2 diabetes incidence
45
New cards
Intervention
-The process of intervening
-Action taken to improve something
-Action taken to improve something
46
New cards
Behavioral Intervention
the use of specific strategies to foster behavior change
47
New cards
Barrier
Any factor that prevents the behavior from occurring.
Can be actual or perceived.
Can be actual or perceived.
48
New cards
Facilitator
Any factor that helps the behavior occur
49
New cards
Actual Barriers
-Accessibility, resources
-Environmental factors
-Physical Limitations
-Environmental factors
-Physical Limitations
50
New cards
Perceived Barriers
-Lack of time
-Boredom/ lack of enjoyment
-Psychological or belief-based barriers
-Boredom/ lack of enjoyment
-Psychological or belief-based barriers
51
New cards
Common Barriers to Behavior Change
-Excuses
-Physical Barriers
-Procrastination
-Environmental
-Gratification
-Risk complacency
-Complexity
-Indifference and helplessness
-Rationalization
-Illusions of invincibility
-Physical Barriers
-Procrastination
-Environmental
-Gratification
-Risk complacency
-Complexity
-Indifference and helplessness
-Rationalization
-Illusions of invincibility
52
New cards
Theory
An attempt to explain a phenomenon (Or Behavior)A systematically organized body of knowledge applicable in a relatively wide variety of circumstances, especially a system of assumptions, accepted principles, and rules of procedure devised to analyze, predict, or otherwise explain the nature or behavior of a specified set of phenomena.
53
New cards
Theories of behavior are essential because they...
-Help us better understand and predict behavior (physical activity and exercise behavior)
-Provide a scientifically supported blueprint from which to form a hypothesis and design effective behavioral interventions
-Provide a scientifically supported blueprint from which to form a hypothesis and design effective behavioral interventions
54
New cards
Stimulus Response Theory (SRT)
-Predicts that peoples future behavior depends on the consequences of their past behavior
-Classical conditioning and instrumental conditioning
-Classical conditioning and instrumental conditioning
55
New cards
**Applying The Stimulus-response Theory to Exercise Behaviour**
1. Positive Reinforcement
2. Negative Reinforcement
3. Punishment
4. Extinction
56
New cards
Positive Reinforcement
Adding something positive to increase exercise
Praise from an external source (e.g., coach; social media)
Praise from an internal source (e.g., a goal; a purpose)
Praise from an external source (e.g., coach; social media)
Praise from an internal source (e.g., a goal; a purpose)
57
New cards
Negative Reinforcement
Taking something away that is negative to increase exercise
Ex: Alleviating symptoms of psychological or physical distress
**Psychological**: Anxiety; Depression; Energy
**Physical**: Arthritis; Pain
Ex: Alleviating symptoms of psychological or physical distress
**Psychological**: Anxiety; Depression; Energy
**Physical**: Arthritis; Pain
58
New cards
Punishment
Adding something negative (decreases exercise)
Example = injury or embarrassment
Example = injury or embarrassment
59
New cards
Extinction
Taking away reinforcement
Decrease exercise
Eg: rewards, reductions in pain
Decrease exercise
Eg: rewards, reductions in pain
60
New cards
ABCs of psychology
Activating Event
Belief
Consequences
Belief
Consequences
61
New cards
Self-Efficacy Theory or Social Cognitive Theory (Albert Bandura)
If people believe that they can execute a particular course of action, they become more motivated to do so, and are more inclined to take action.
(Situation-specific form of self-confidence)
\
Social Cognitive Theory (SCT):
is an interpersonal-level theory developed that emphasizes the dynamic interaction between people (personal factors), their behavior, and their environments.
(Situation-specific form of self-confidence)
\
Social Cognitive Theory (SCT):
is an interpersonal-level theory developed that emphasizes the dynamic interaction between people (personal factors), their behavior, and their environments.
62
New cards
\
Social Cognitive Theory (SCT) Factors
Social Cognitive Theory (SCT) Factors
Cognitive Factors
(Knowledge, expectations, attitudes)
Behavioural Factors
(Skills, practice, self-efficacy)
Environmental Factors
(Social norms, access in community, Influence on others)
(Knowledge, expectations, attitudes)
Behavioural Factors
(Skills, practice, self-efficacy)
Environmental Factors
(Social norms, access in community, Influence on others)
63
New cards
Self-Efficacy
Self-efficacy is a person’s particular set of beliefs that determine how well one can execute a plan of action in prospective situations.
\
Self-efficacy is a person’s belief in their ability to succeed in a particular situation.
\
Often used synonymously with confidence
\-Past performance (strongest)
-Vicarious experiences
\-Social persuasion
\-Physiological/ affective states
Outcome:
\-Behaviour -Cognitions -Affect
\
Self-efficacy is a person’s belief in their ability to succeed in a particular situation.
\
Often used synonymously with confidence
\-Past performance (strongest)
-Vicarious experiences
\-Social persuasion
\-Physiological/ affective states
Outcome:
\-Behaviour -Cognitions -Affect
64
New cards
Applying Self-Efficacy Theory to Exercise Behaviour
If people **believe** that they can execute a particular course of action, they become **more motivated** to do so, and are more inclined to **take action**.
Self-efficacy is a **situation-specific** form of self-confidence
Self-efficacy is a **situation-specific** form of self-confidence
65
New cards
Domains of Self-Efficacy
General Self Efficacy
Exercise Self Efficacy
Sports Self Efficacy
Academic Self Efficacy
Exercise Self Efficacy
Sports Self Efficacy
Academic Self Efficacy
66
New cards
Measuring Self-efficacy
**Strength**: involves measuring the strength of the individual’s belief in his or her ability to successfully accomplish a specific task
**Level of Difficulty or Challenge:** measuring the individual’s self-efficacy for successfully performing the task at varying degrees of difficulty
**Generality**: extent of SE transfer from one task to another
**Specificity**: Task SE, barrier SE, scheduling SE
**Level of Difficulty or Challenge:** measuring the individual’s self-efficacy for successfully performing the task at varying degrees of difficulty
**Generality**: extent of SE transfer from one task to another
**Specificity**: Task SE, barrier SE, scheduling SE
67
New cards
Strength
-Involves measuring the strength of the individuals belief in their ability to successfully accomplish a specific task
68
New cards
Level of difficulty or challenge
Measuring the individuals self-efficacy for successfully performing the task at varying degrees of difficulty
69
New cards
Generality
Extent of SE transfer from one task to another
70
New cards
Specificity
Task SE, Barrier SE, Scheduling SE
71
New cards
Theory of Planned Behaviour
The Theory of Planned Behavior assumes that individuals act rationally, according to their attitudes, subjective norms, and perceived behavioral control. These factors are not necessarily actively or consciously considered during decision-making, but form the backdrop for the decision-making process.
72
New cards
Beliefs
If you believe exercise is fun, you will partake
If you believe exercise is important for mental health, you will partake
If you believe exercise improves physical health, you will partake
\
If you DON’T think the above, your beliefs and motivations surrounding exercise participation will impact your action, and will most often than not, lead to inaction
\
NORMATIVE- Social norms; Family norms etc
CONTROL BELIEFS –The ease or difficulty of performing the behavior
If you believe exercise is important for mental health, you will partake
If you believe exercise improves physical health, you will partake
\
If you DON’T think the above, your beliefs and motivations surrounding exercise participation will impact your action, and will most often than not, lead to inaction
\
NORMATIVE- Social norms; Family norms etc
CONTROL BELIEFS –The ease or difficulty of performing the behavior
73
New cards
Attitudes
Our attitude and perception towards exercise and the domain of exercise, can contribute to our current and future physical activity levels
74
New cards
SUBJECTIVE NORMS
Normative language with family, friends, and peers
75
New cards
INTENTION
Based on attitudes and beliefs, one will either engage or disengage in exercise and physical activity
76
New cards
Self-determination Theory (SDT)
Provides an understanding of what keeps people focused and motivated to pursue desired behaviors
3 Key Concepts:
1. Types of motivation
2. Basic psychological needs
3. The social context
3 Key Concepts:
1. Types of motivation
2. Basic psychological needs
3. The social context
77
New cards
Types of motivation
-Amotivation
-Extrinsic Motivation
-Intrinsic Motivation
-Extrinsic Motivation
-Intrinsic Motivation
78
New cards
4 Types of Extrinsic Motivation
**External regulation**: e.g. motivated by the prize for accomplishing your exercise goal
**Introjected regulation**: e.g. motivate by family pressure that you need to lose weight
**Identified regulation:** e.g. motivated to beat your last time in the next race
**Integrated regulation:** e.g. motivated by the fact that everyone knows you as the ‘fit’ one
**Introjected regulation**: e.g. motivate by family pressure that you need to lose weight
**Identified regulation:** e.g. motivated to beat your last time in the next race
**Integrated regulation:** e.g. motivated by the fact that everyone knows you as the ‘fit’ one
79
New cards
Intrinsic Motivation
-Intrinsic Regulation
-Ideal form of motivation
-Ideal form of motivation
80
New cards
Basic Psychological Needs (SDT)
The satisfaction of three basic psychological needs leads to the development of more internally regulated forms of motivation:
1. Autonomy
2. Competence
3. Relatedness
1. Autonomy
2. Competence
3. Relatedness
81
New cards
Autonomy
Having the choice to decide what you want to do and how you will do it
People like to have a choice in their behaviours and goals
Allow people to take turns choosing and running the drills
People like to have a choice in their behaviours and goals
Allow people to take turns choosing and running the drills
82
New cards
Competence
Feeling like you have the skills and requirements to meet the demands of the environment
Feeling like you have mastery and control
Opportunities to display strengths during practice or games
Feeling like you have mastery and control
Opportunities to display strengths during practice or games
83
New cards
Relatedness
Feeling a sense of belonging and closeness to others
We like to feel connected to other people
Importance of relationships
Team bonding activities, hang outs
We like to feel connected to other people
Importance of relationships
Team bonding activities, hang outs
84
New cards
Social Context
Fulfilment of BPN depends on characteristics of the social environment in which exercise takes place.
85
New cards
The Social Ecological Model
-Recognizes that individual-level factors are only one of the multiple levels of influence on behavior.
86
New cards
Individual Level Factors
Biological, Psychological, Skills
87
New cards
Social Ecological Model of Physical Activity
-Individual
-Physical Activity Domains
-Interpersonal
-Physical Environment
-Policy
-Physical Activity Domains
-Interpersonal
-Physical Environment
-Policy
88
New cards
Influence of the interpersonal environment on PA behavior
-How individuals and groups exert social influence over others exercise behavior
89
New cards
Social Influence
Real or imagined pressure to change ones behavior, attitudes, or beliefs.
90
New cards
Social Support
Refers to the perceived comfort, caring, assistance and information that a person receives from others.
91
New cards
Social influences and support on PA behavior can come from:
-Family
-Friends, School teachers, Coworkers
-Health-care providers
-Exercise leader/instructor, exercise group, Co-exercisers and observers
-Friends, School teachers, Coworkers
-Health-care providers
-Exercise leader/instructor, exercise group, Co-exercisers and observers
92
New cards
Types of Social Support
-Instrumental Support
-Emotional Support
-Informational Support
-Appraisal (Validation) Support
-Emotional Support
-Informational Support
-Appraisal (Validation) Support
93
New cards
Instrumental Support
-Tangible, practical assistance that will help a person achieve their exercise goals
94
New cards
Emotional Support
-Expressing encouragement, caring, empathy, and concern toward a person
95
New cards
Informational Support
-Providing instructions, directions, advice, suggestions about how to exercise
96
New cards
Appraisal (Validation) Support
Feedback that can be used to gauge progress or validate that ones thoughts, feelings, problems, experiences are normal.
97
New cards
Social Influences on exercise: The Family
-Children and youth: Parents have a strong influence on PA participation
-Parents can provide many different types of support and establish social norms for an active lifestyle
-Parents can provide many different types of support and establish social norms for an active lifestyle
98
New cards
Downside of Family support
-Behavioral reactance:
Responding in the opposite direction to the direction being advocated
-Fine line between feeling supported and feeling controlled
Responding in the opposite direction to the direction being advocated
-Fine line between feeling supported and feeling controlled
99
New cards
Spouse/partner
-Positive relationship between PA levels and amount of social support that partner provides
100
New cards
Health Care Providers
-Potential source of informational support for individuals