Cellular Respiration: Pathways and Processes
1/46
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
47 Terms
Catabolic pathways
Breakdown molecules to harvest energy for ATP
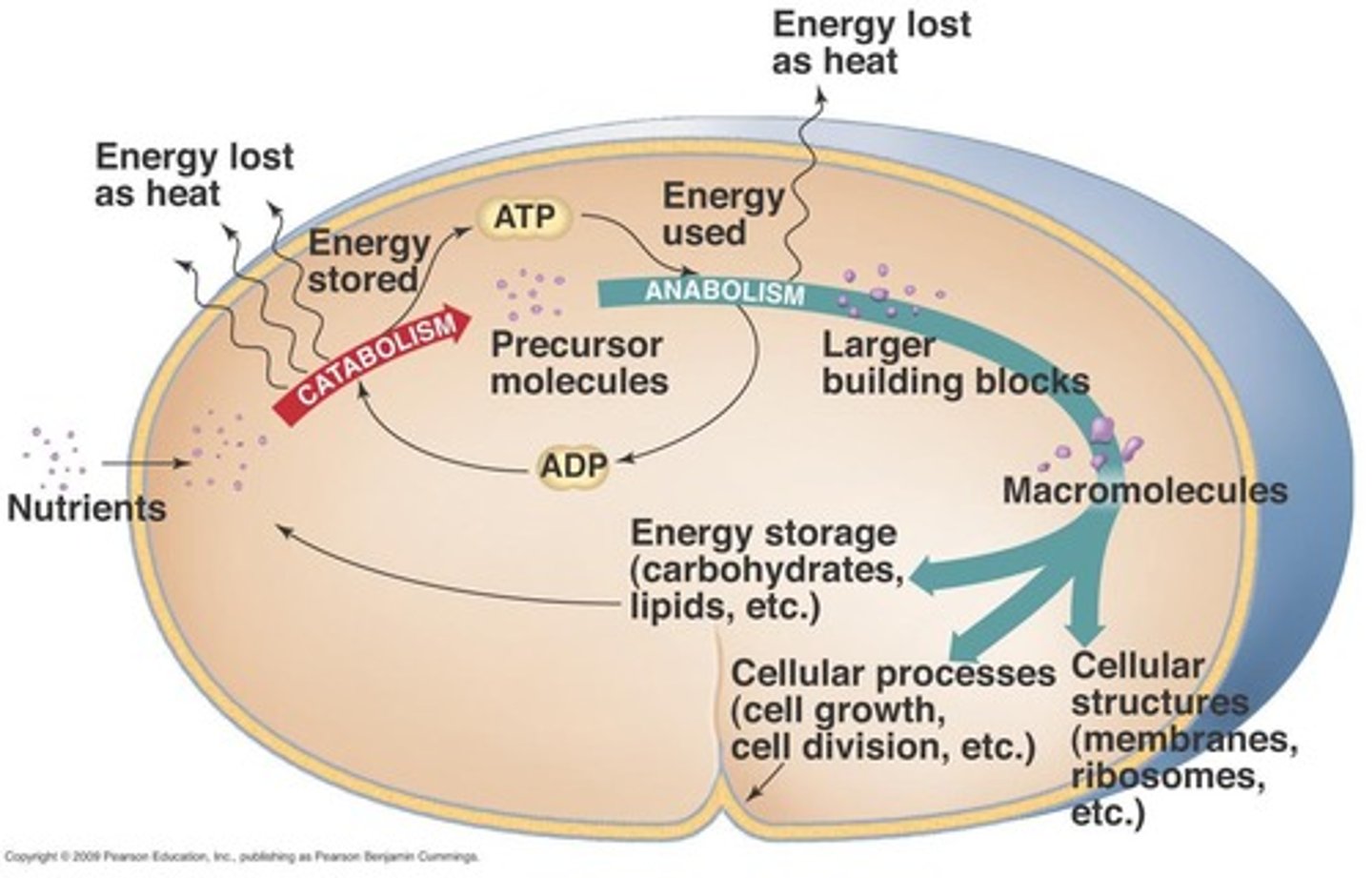
Anabolic pathways
Synthesize larger molecules using ATP energy
Cell respiration
Series of oxidation reactions producing ATP
Redox reactions
Chemical reactions involving electron transfer
Oxidation
Loss of electron(s) in a reaction
Reduction
Gain of electron(s) in a reaction
Electron carriers
Molecules that shuttle electrons in reactions
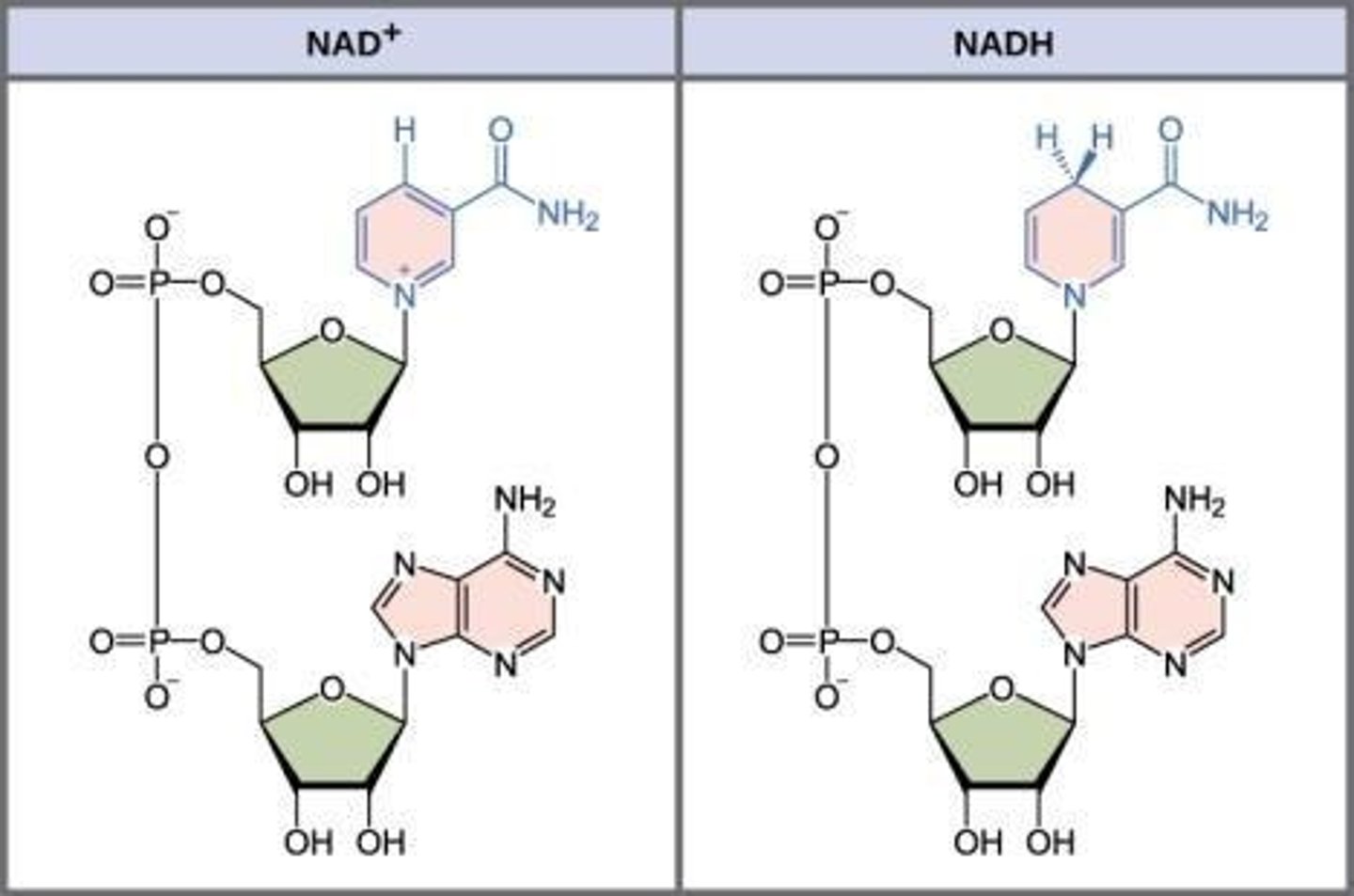
NAD+
Oxidized form of nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide
NADH
Reduced form of NAD+, carries electrons
Aerobic respiration
Respiration using oxygen to produce ATP
Anaerobic respiration
Respiration that does not require oxygen
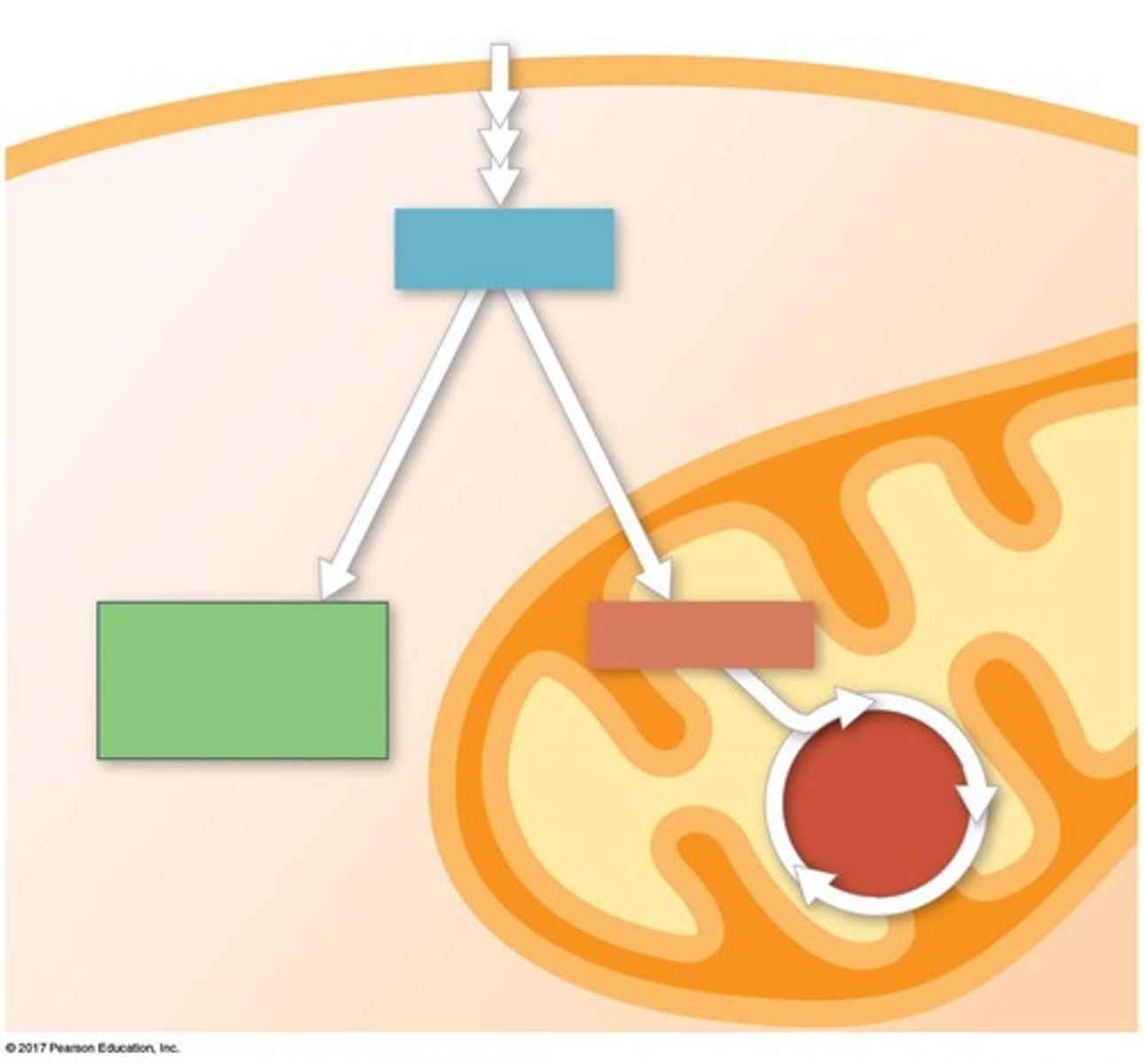
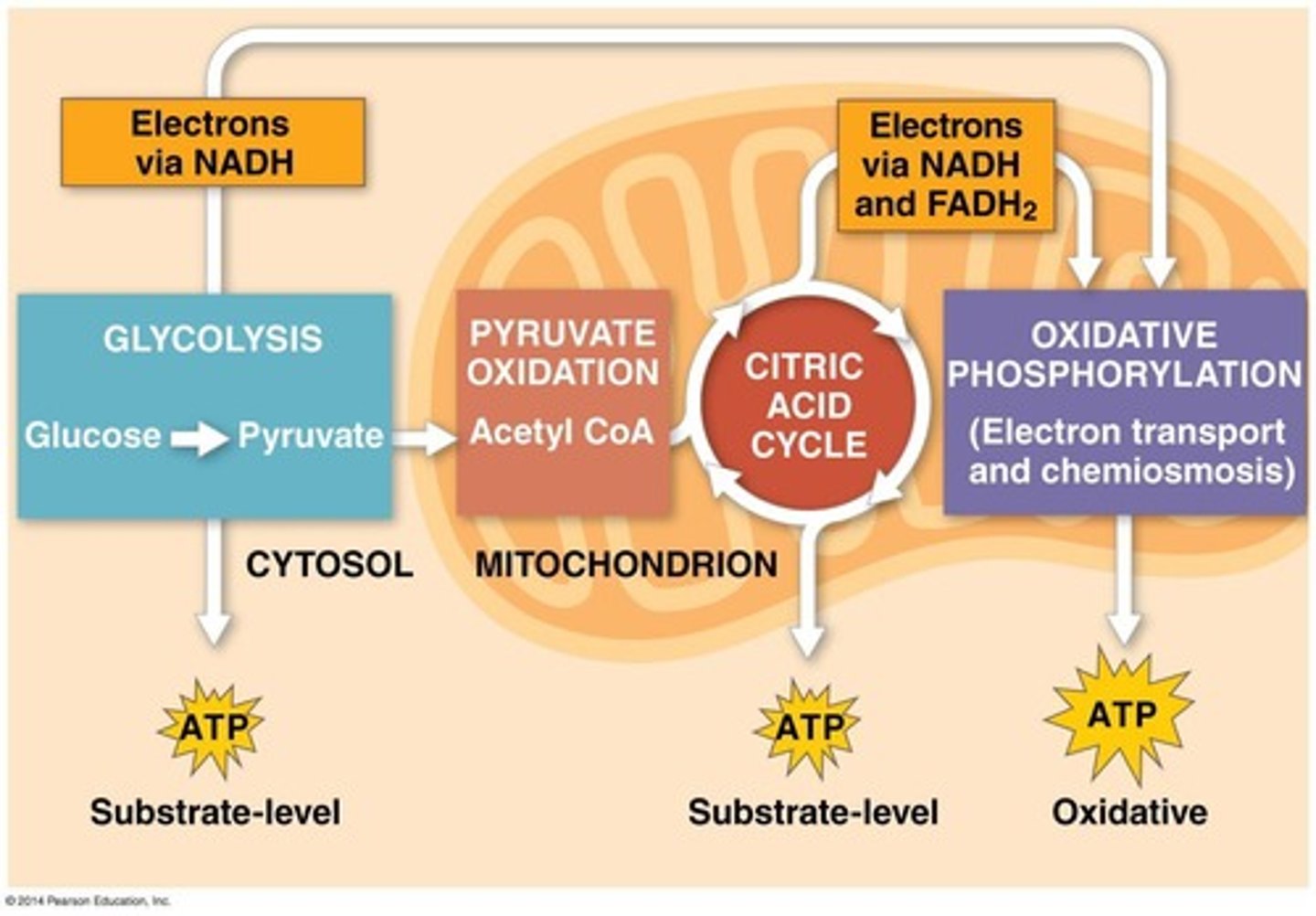
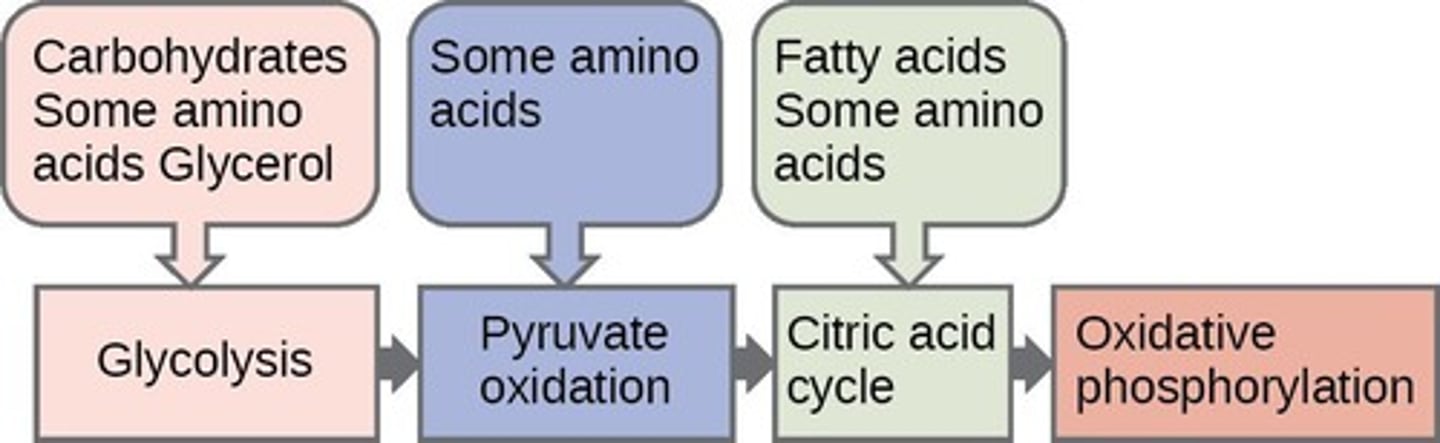
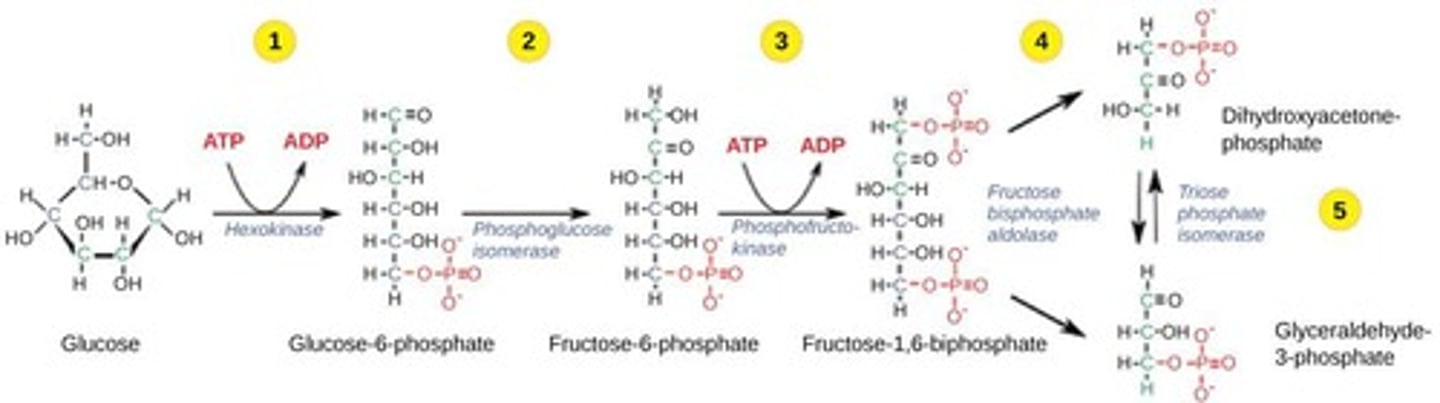
Glycolysis
Splitting glucose into two pyruvate molecules
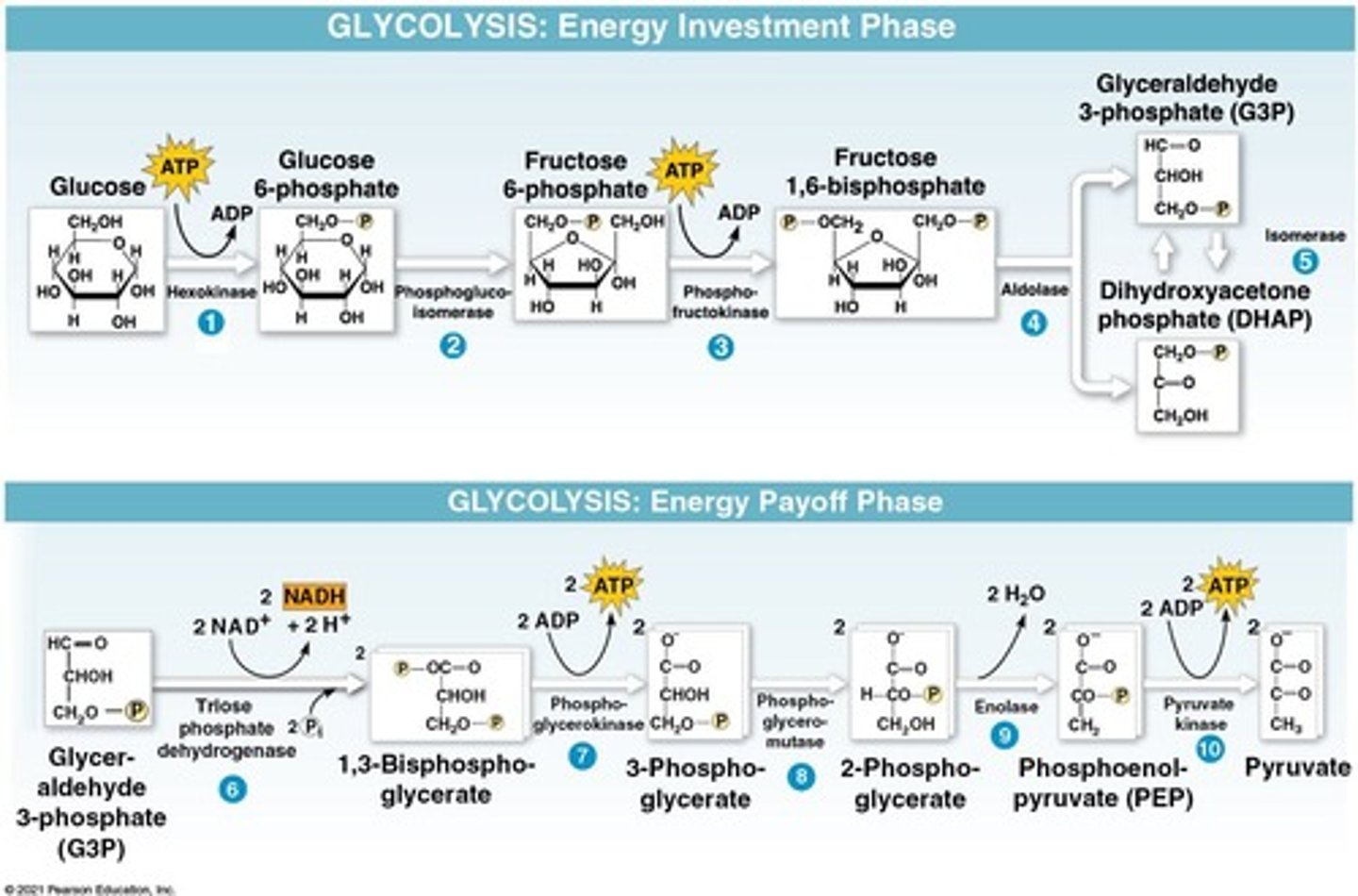
Energy investment phase
Initial phase using 2 ATP in glycolysis
Energy payoff phase
Phase producing 4 ATP and NADH in glycolysis
Substrate-level phosphorylation
Direct transfer of phosphate to ADP for ATP
NET yield from glycolysis
2 ATP, 2 NADH, 2 pyruvate produced
Pyruvate oxidation
Conversion of pyruvate to Acetyl CoA
Citric acid cycle
Cycle occurring in mitochondrial matrix for ATP
Acetyl CoA
Key molecule entering the citric acid cycle
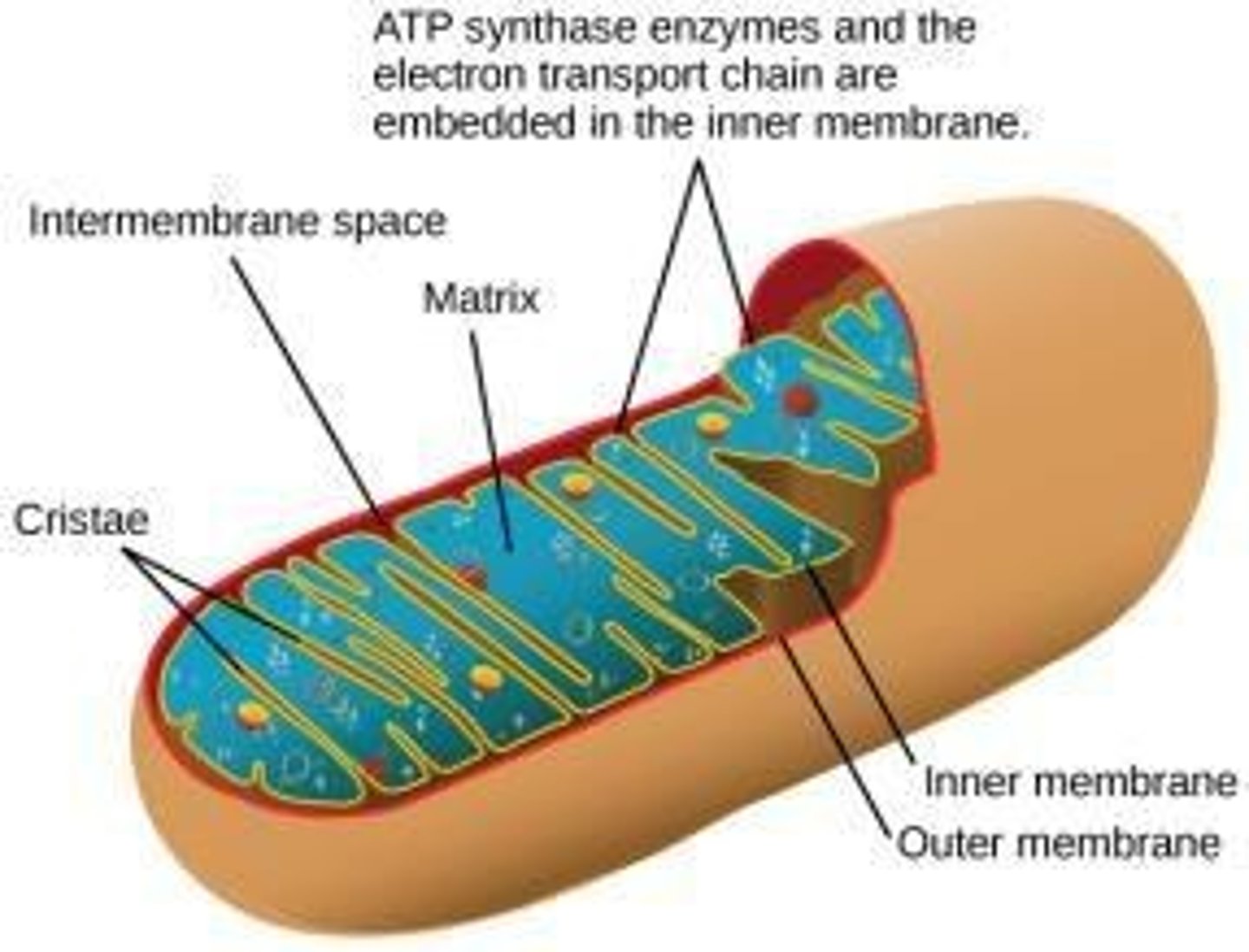
ATP synthase
Enzyme using proton gradient to produce ATP
Oxaloacetate
Molecule that combines with Acetyl CoA in cycle
Free energy
Energy released during glucose oxidation process
C6H12O6 + 6 O2
Glucose and oxygen reactants in aerobic respiration
2 CO2
Waste product from pyruvate oxidation
2 NADH (from pyruvate)
Electrons carried to ETC from pyruvate conversion
Citric Acid Cycle
Series of reactions producing energy carriers.
FADH2
Another electron carrier produced in the cycle.
GTP
Energy molecule produced in the citric acid cycle.
ATP Yield
2 ATP produced per acetyl CoA in cycle.
Electron Transport Chain
Membrane proteins transferring electrons to O2.
Chemiosmosis
Process using H+ gradient to synthesize ATP.
Proton Gradient
Difference in H+ concentration across membranes.
Oxidative Phosphorylation
Major ATP production phase in cellular respiration.
Anaerobic Respiration
Uses non-oxygen molecules as electron acceptors.
Fermentation
Process generating ATP without oxygen present.
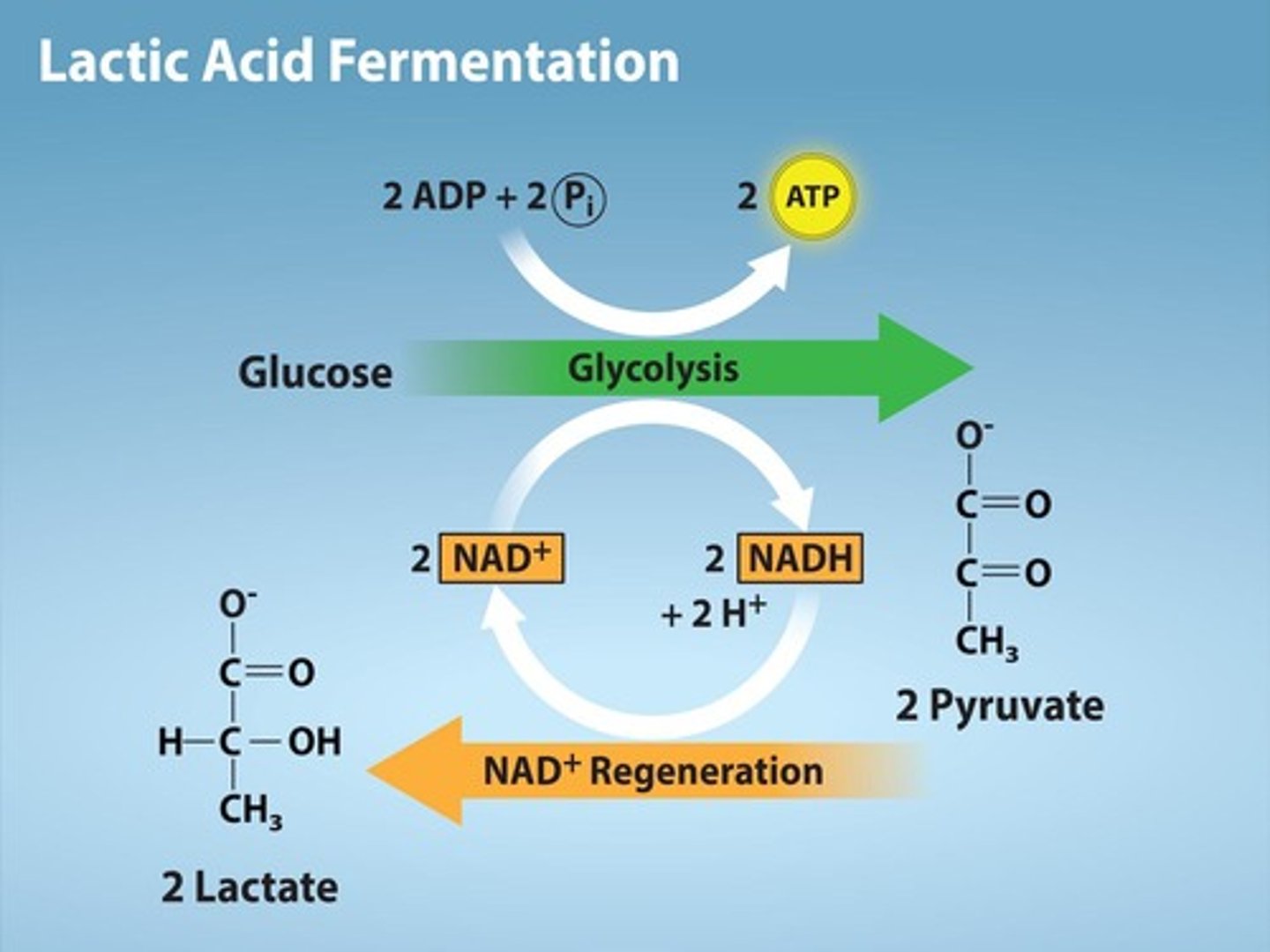
Lactic Acid Fermentation
Occurs in muscle cells under low oxygen.
Alcohol Fermentation
Occurs in yeast, producing ethanol and CO2.

Feedback Inhibition
Regulation mechanism by NADH and ATP levels.
ATP Synthase
Enzyme converting ADP to ATP using H+ flow.
Energy Yield
Theoretical 36 ATP for eukaryotes per glucose.
Methanogens
Archaea using CO2 as electron acceptor.
Sulfur Bacteria
Reduce sulfate to hydrogen sulfide.
Glucose Oxidation
Complete breakdown of glucose to CO2.
NAD+ Regeneration
Essential for continuing glycolysis and respiration.
Proton-Motive Force
Energy stored in H+ gradient for ATP synthesis.
Actual ATP Yield
~30 ATP per glucose for eukaryotes.
Leaky Membrane
Causes reduced ATP yield in eukaryotes.