Chemistry - Introduction 1
1/16
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
17 Terms
Very reactive, especially near water
Malleable, ductile, and good conductors
One Valence electron
Typically extracted from compounds
What are the properties of alkali metals (1A)?
Low electron affiliates and electromagnetism
Two valence electrons
Form divalent anions
Have smaller atomic radii than alkali metals
What are the properties of Alkaline Earth metals (2A)?
Fairly nonreactive—malleable
High melting and boiling points
Good for electrical conductivity
Low ionization energies and very similar to one another
Exhibit wide ranges of oxidation states
What are the properties of transition metals?
High electronegatives
Highly reactive with alkali and alkaline Earth metals
Low ionization energies
Form anions with one (-1) negative charge
What are the properties of Halogens?
Solid at room temp (except mercury)
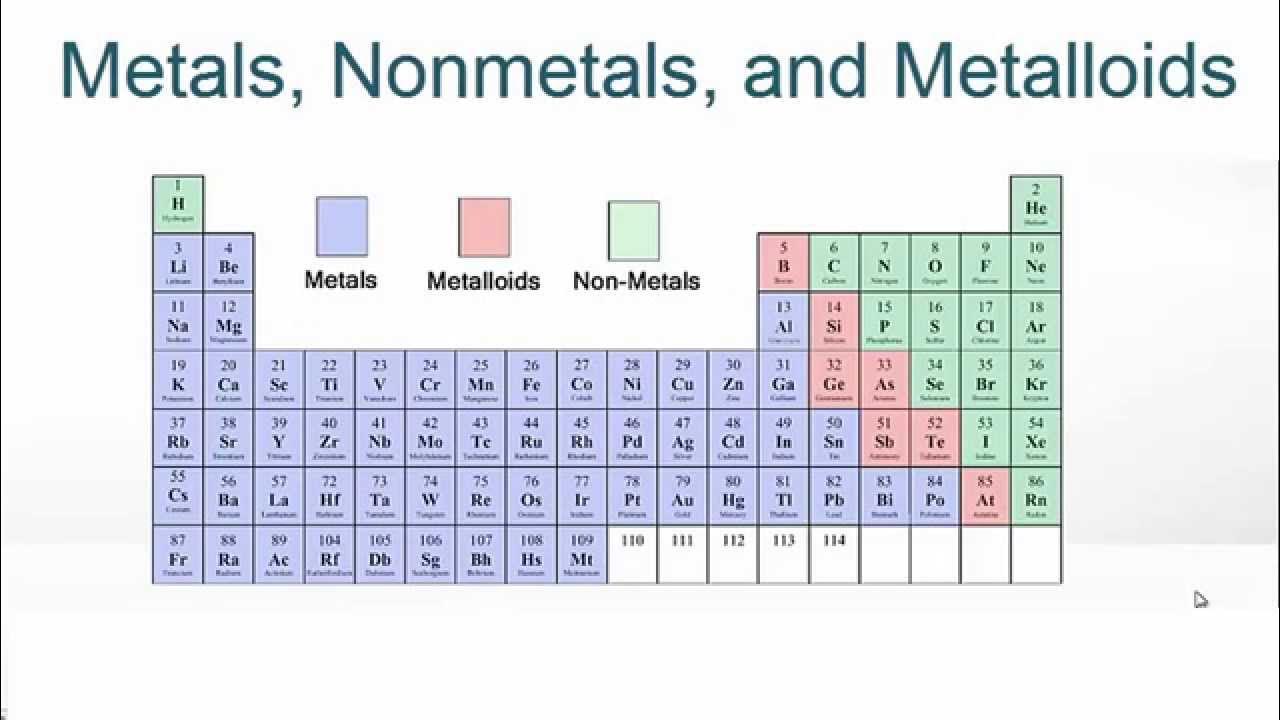
Metalloids have both metal and nonmetal characteristics (brittle solids and gain elections easily)
What are the properties of metals, metalloids, gases, and nonmetals?
Sliver-white metals
Tarnish when exposed to air
High melting and boiling points
Highly reactive
Strong reducing agents
What are the properties of lanthanides?

Radioactive
Highly electropositive
Dense metals with distinctive structure
Combine directly with most nonmetals
What are the properties of Actinides?
Fairly nonreactive!
Complete valence shell (8 electrons; depends on size of atom)
Very low electronegatives
Low boiling points
gases at room temp.
What are the properties of noble gases?
Ion
An atom/molecule with a net electrical charge
Created by the loss or gain of one or more electrons, resulting in an imbalance.
Cation
The loss of electrons in an ion
Anion
The gain of electrons in an ion
Net Electrical Charge
The total and overall change of an object or system
The sum of all protons and electron changes
Ionization
The process of gaining or losing electrons to create a net electric charge
Electronegativity
An atom’s ability to attract electrons in a chemical bond
Fluorine is the most electronegative element
Valence Electron
The atom’s outermost shell
Responsible for chemical bonding and determining an element’s reactivity
Influences the electronegativity and the type of bond formed (Ionic or covalent)
divalent anions
Ngeativiely charged ions that carry and -2 charge
Gained two extra electrons (also called bivalent anions
EX: Sulfate (SO) and Carbonate (CO)
oxidation states
The hypothetical charge an atom would have if all bonds were 100% Ionic, indicating electron loss (+state) or gain (-state)
Oxidation number