Series 65: Unit 1
1/37
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
38 Terms
What is a security?
A security is a tradable investment that represents ownership (like stocks) or debt (like bonds).
What is common stock?
equity (ownership) in a corporation
What is preferred stock?
Equity that pays fixed dividends, has priority over common stock in bankruptcy, and usually lacks voting rights
True/False: All stockholders are owners of a corporation and all bondholders are creditors.
True
What is capital appreciation
An increase in the market price of securities
What is a property dividend?
An alternative to cash or stock dividends, where a company gives shareholders property in lieu of cash or cash equivalents.
What is a stock split?
When a company increases the number of its outstanding shares to boost the stock's liquidity.
What is liquidity?
How easily assets can be converted into cash.
What is limited liability?
Business owners (e.g., of a corporation or LLC) aren't personally liable for debts beyond their investment.
What is market risk?
The chance that a stock price will decline from fluctuations in the market.
What is business risk?
The chance that a stock price will decline from company earnings/news.
What are senior securities?
A company’s debt and preferred shares
Why is it called senior securities?
If a company enters bankruptcy, the holders of its bonds and preferred stock have priority over common stockholders.
What are residual rights?
Right of the company owners to claim the remaining assets. Common stockholders have residual rights.
Why would you include common stock in a client’s portfolio?
Potential capital appreciation
Income from dividends
Hedge against inflation
Common stock in a portfolio would incur what potential risks?
Market Risk
Business Risk
Low Priority at Dissolution
What are dividends in arrears?
Unpaid dividends on cumulative preferred stock that have not been paid in past periods and must be paid out before any dividends can be given to common shareholders.
For investors looking for fixed income through preferred stocks, what would be the least appropriate choice of preferred stock.
Adjustable-Rate Preferred, because the dividend will likely fluctuate.
Why would you include preferred stock in a client’s portfolio?
Fixed income from dividends
Prior claim ahead of common stock
Convertible preferred sacrifices income in exchange for potential appreciation
Preferred stock in a portfolio would incur what potential risks?
Market Risk - fear of maintaining dividend
Possible loss of purchasing power
Interest rate (money rate) risk
Business difficulties leading to possible reduction or elimination of the dividend and even bankrupty leading to loss of principal.
What are the different types of preferred stock?
Straight preferred stock
Cumulative preferred stock
Callable preferred stock
Convertible preferred stock
Adjustable-Rate preferred stock
Straight preferred stock
Has no special features beyond the stated dividend payment. Missed dividends are not paid to the stockholder.
Cumulative preferred stock
Accrues payments to shareholders if dividends are reduced or suspended.
Callable (redeemed) preferred stock
Generally higher dividends, but company can buy back from investors at a stated price after a specified date.
Convertible preferred stock
Owner can exchange their shares for a fixed number of shares of common stock of the issuing corporation. Often has lower dividend rate than non-convertible.
Adjustable-Rate preferred stock
Preferred stock with floating dividend rates. Stock price remains stable in exchange.
Restricted Securities
Securities that cannot be sold until having them for a certain period of time. (generally 6 months and sometimes volume restrictions as well).
Control person
A corporate director, an officer, a large stockholder, or the immediate family of any of the preceding residing in the same home.
Control stock
Stock held by a control person.
American depositary share (ADR)
A negotiable security that represents a receipt for shares of stock in a non-U.S. corporation. ADRs are bought and sold in the U.S. securities markets like any domestic stock.
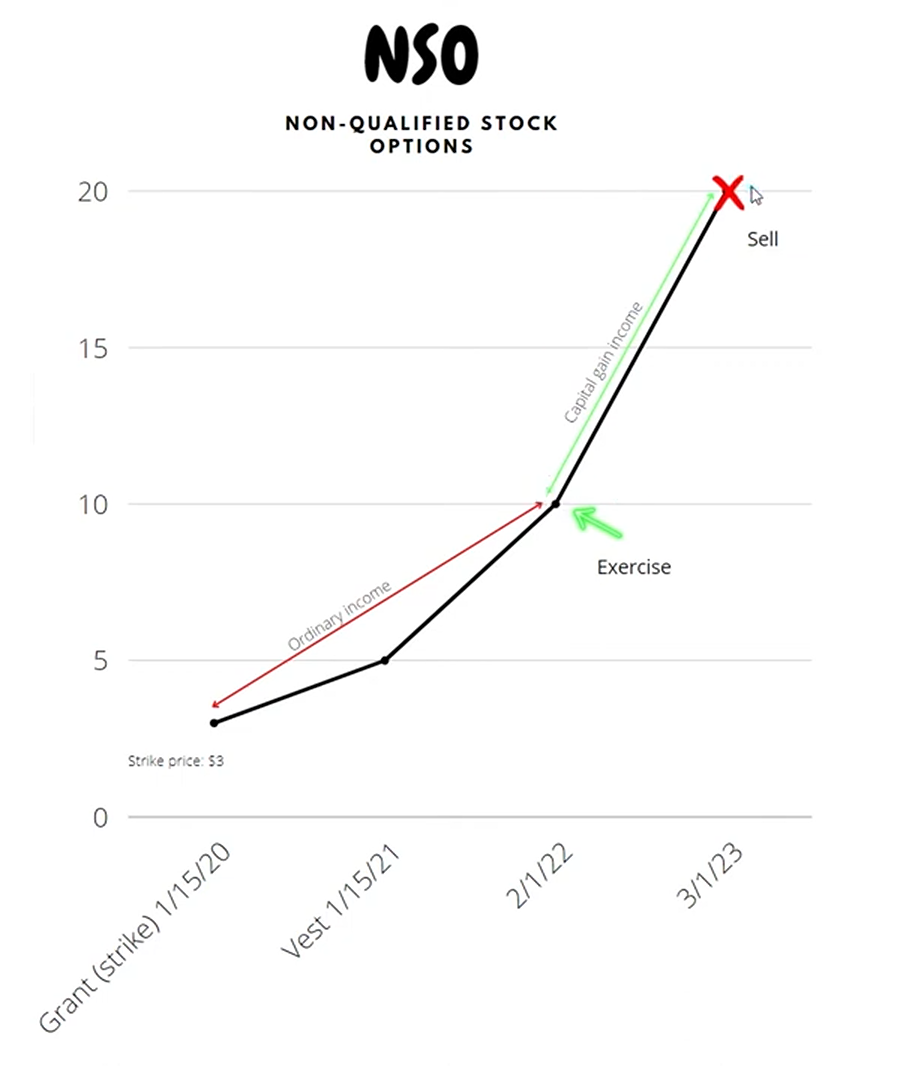
Nonqualified Stock Options (NSOs)
lets an employee buy company shares at a set (grant) price within a specific period. Upon exercise, the difference between the grant price and market price is taxed as ordinary income.
Incentive Stock Options (ISOs)
If ISO shares are held at least two years from grant and one year from exercise, profits are taxed as long-term capital gains. Otherwise, they’re taxed like NSOs as ordinary income.
ISOs must be exercised within 10 years. However, the difference between the market price at exercise and the strike price is a preference item for calculating the Alternative Minimum Tax (AMT).
Currency Risk
the chance that an investment in a foreign currency loses value if that currency weakens against the U.S. dollar.
Emerging Markets
Emerging markets typically have:
Low income levels (measured by GDP)
Low equity market capitalization
Limited market liquidity
Restrictions on foreign ownership and currency conversion
High volatility
Potential for economic growth and development
Stabilizing political and social institutions
High taxes and commission costs for foreign investors
Lower regulatory standards and reduced transparency
Developed Markets
Developed markets typically have:
Highly developed economies
Stable political and social institutions
Large equity market capitalization
Low commission rates
Few or no currency conversion restrictions
Highly liquid markets with many brokers and market makers
Many large-cap securities
Strong regulatory frameworks ensuring high transparency
Why would you include foreign securities in a client’s portfolio?
You’ve broadened the investment universe, allowing for greater diversification.
Foreign securities sometimes outperform domestic ones.
Foreign securities are usually not highly correlated with domestic ones, leading to reduced overall portfolio risk.
Risks of Investing in Foreign Markets
Country risk
Exchange controls
Currency risk
Withholding taxes and fees
Country Risk
the overall risk of investing in a specific country, including political instability, restrictive economic policies, and factors like interest rates and inflation.