Microbiology exam 3
1/182
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
183 Terms
What is a chemoheterotroph?
Organisms that have to consume to get energy
What is a mass of hyphae called?
Mycelium
What are the jobs of vegetative hyphae and aerial hyphae?
Vegetative obtains nutrients
Aerial is involved in reproduction
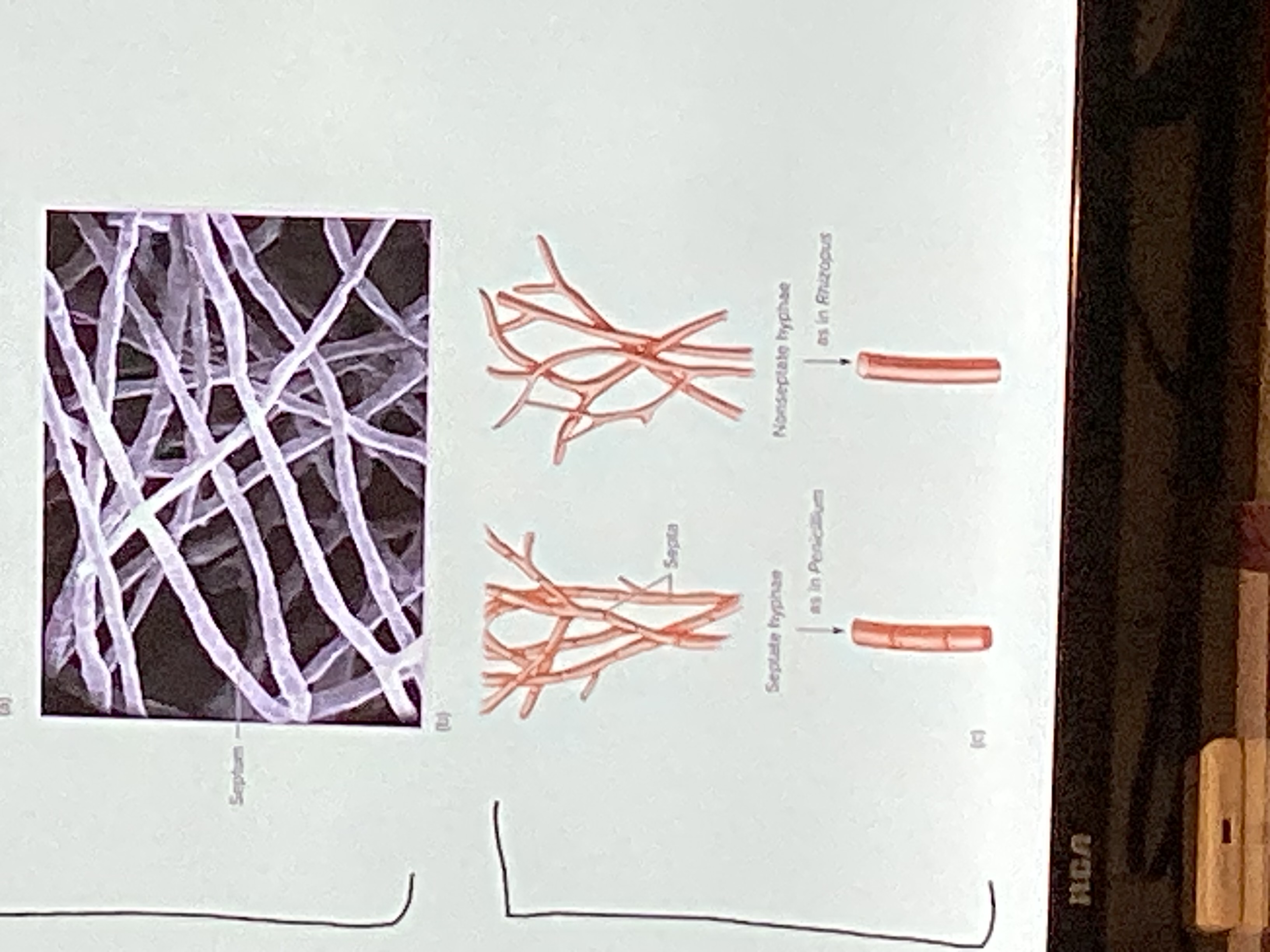
Coenocytic hyphae (non septate)
Does not contain septa (cross walls)
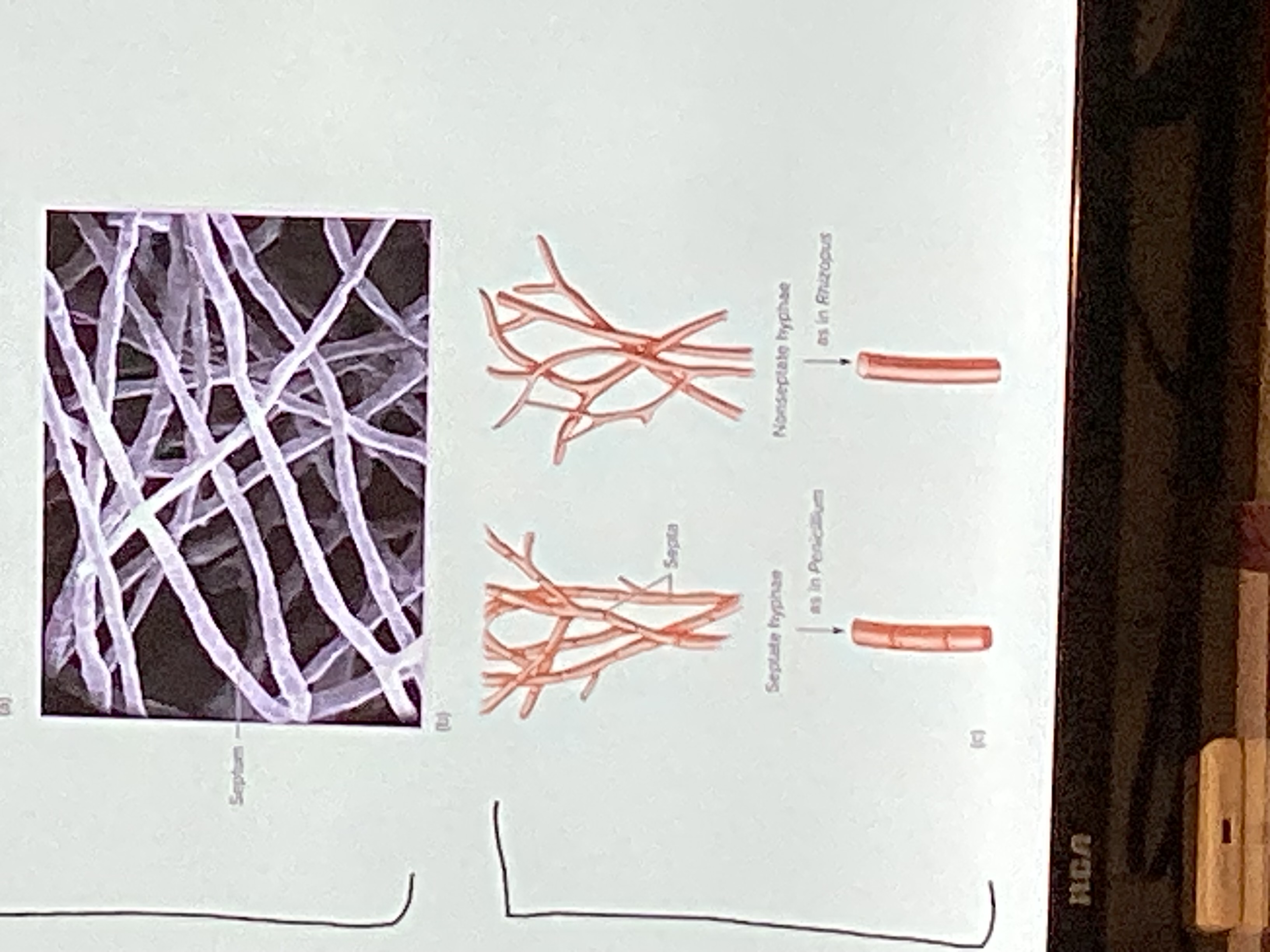
Septate hyphae
Contains cross walls
Features of yeasts
No filamentous and unicellular
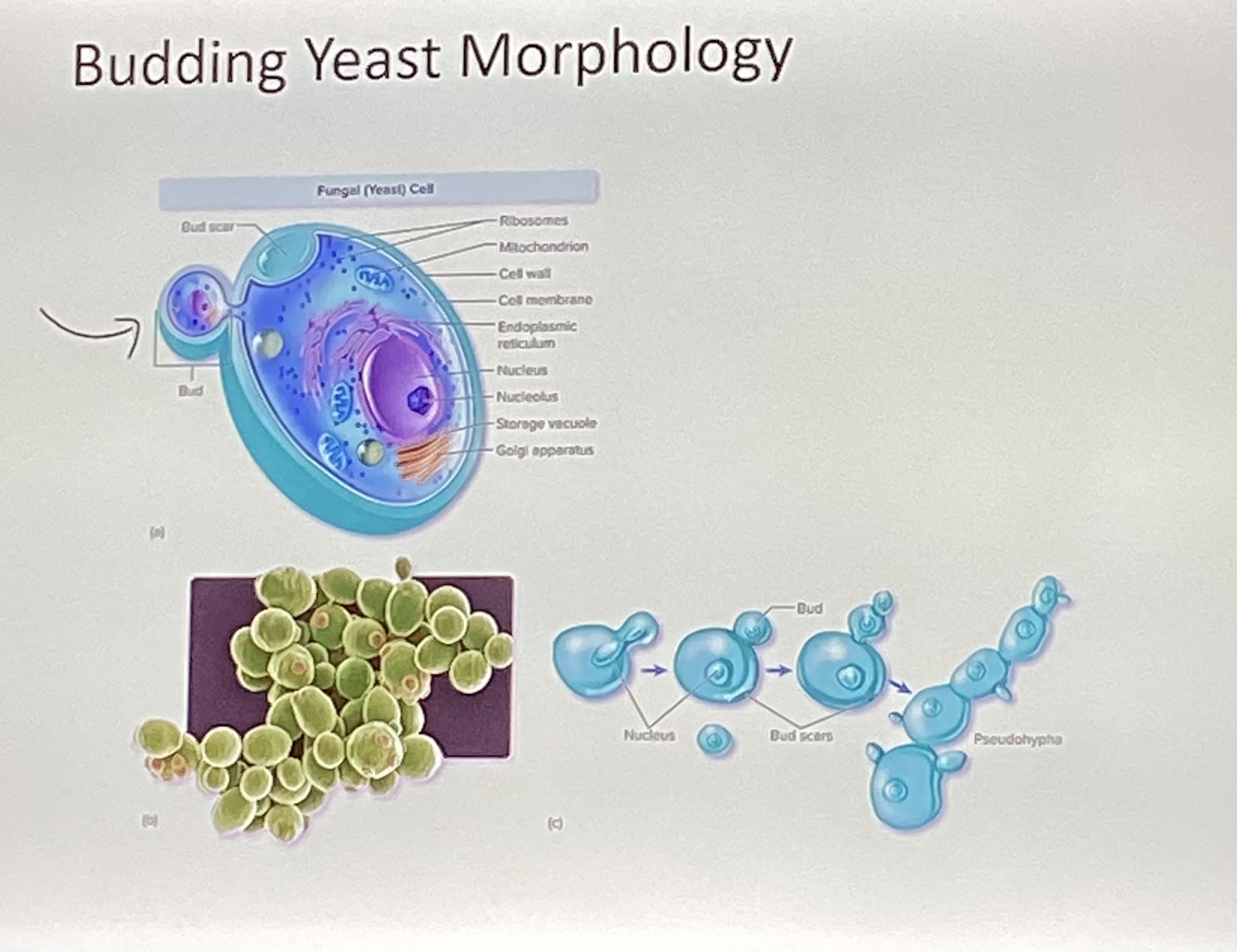
How do budding yeasts divide?
Unevenly
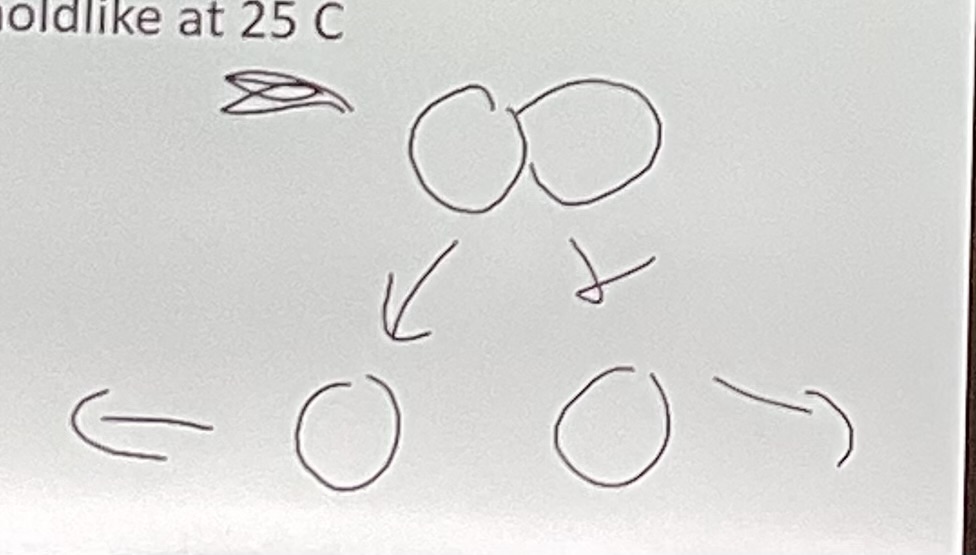
How do fission yeasts divide?
Evenly
What is dimorphic fungi?
Yeast like at 37*C and moldlike at 25*C
Are fungi haploid or diploid?
Haploid
Is mitosis or meiosis responsible for asexual fungi reproduction?
Mitosis
Is mitosis or meiosis responsible for sexual fungi reproduction?
Meiosis
What are anamorphs?
FunginOnly capable of asexual reproduction.
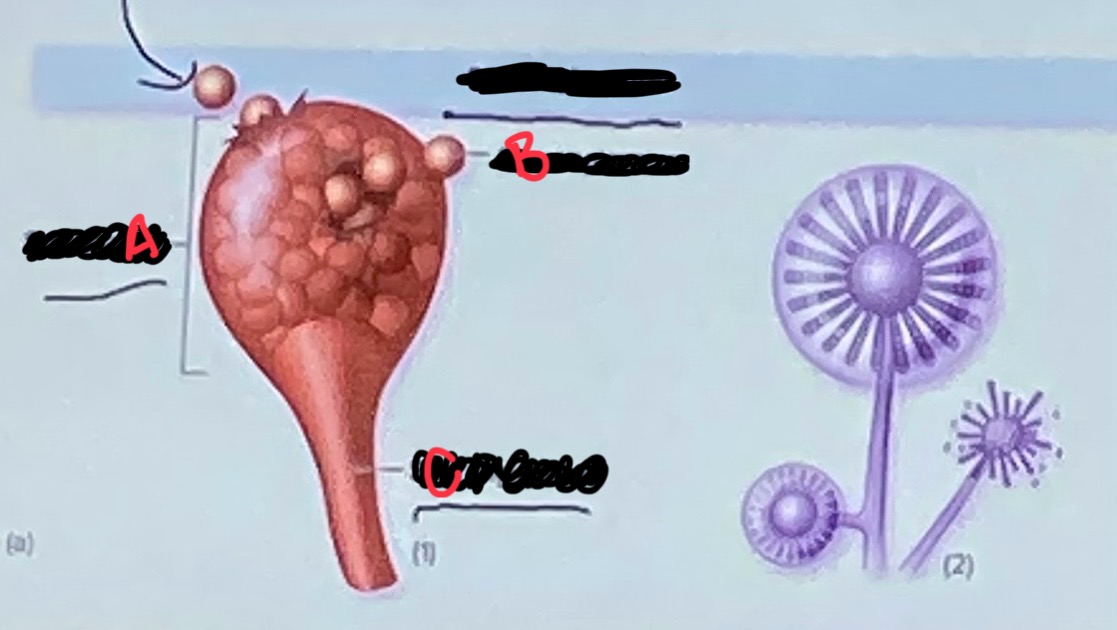
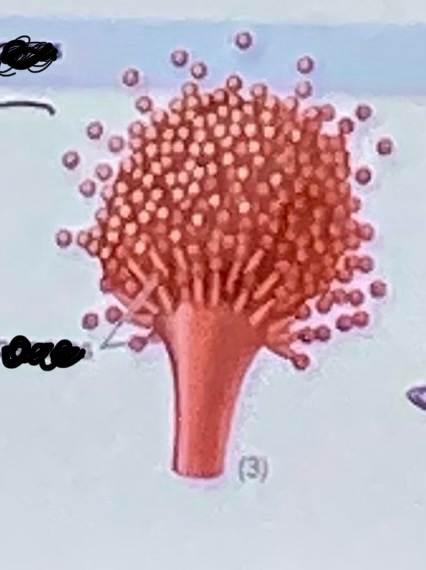
Name these parts
A - sporangium
B - sporangiospore
C - sporangiophore
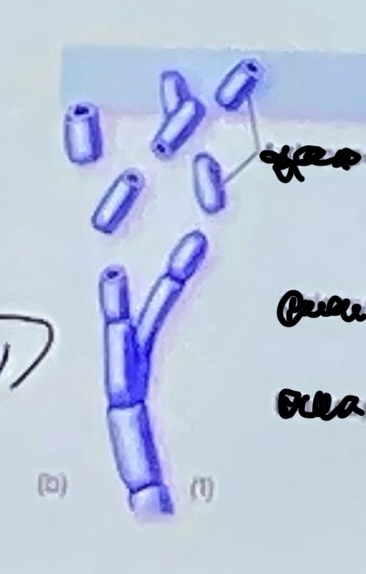
Arthrospores
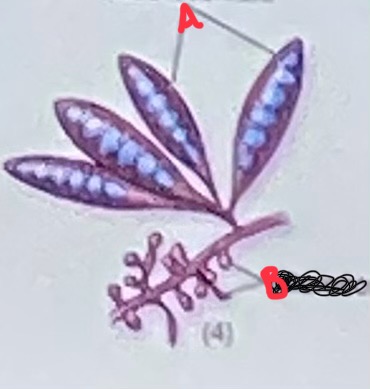
A - macroconidia
B- microconidia
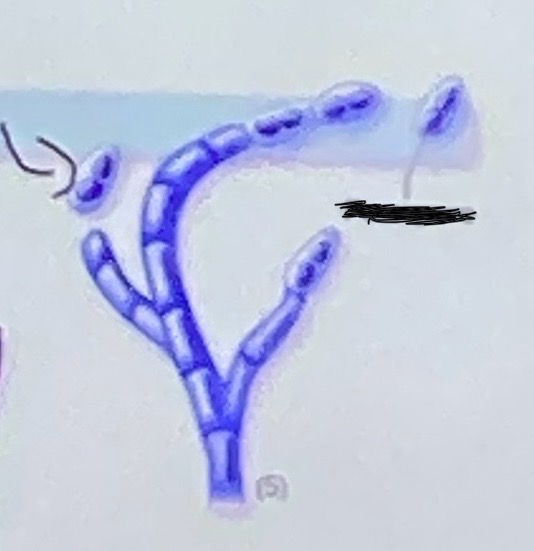
Porospores
Phialospore
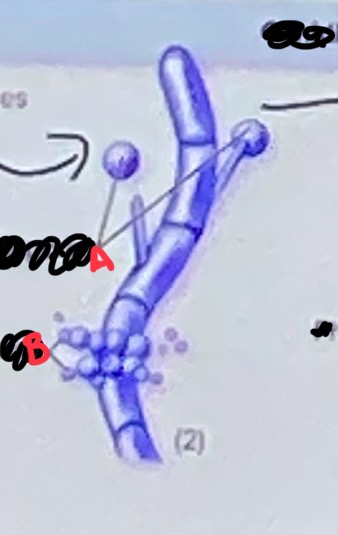
A - chlamydospores
B - blastospores
What are telomorphs
Sexual spores by fusion of two nuclei from opposite mating strains
What are the 3 phases of sexual reproduction of telomorphs?
Plasmogamy
Karyogamy
Meiosis
Plasmogamy
Haploid donor cell nucleus (+) penetrates cytoplasm of recipient cell (-)
Karyogamy
(+) and (-) nuclei fuse and form diploid zygote
Meiosis in telomorphs
Diploid nucleus produces haploid nuclei (sexual spores)
Which fungi are known as the sac fungi?
Ascomycota
Define mycosis (mycoses).
Fungal infection singular or plural
Systemic mycosis
all throughout/deep within the body.
Subcutaneous mycoces
Beneath the skin
Cutaneous mycoses
Affects hair, skin and nails.
Superficial mycoses
Localized and non-destructive. Typically cosmetic affects
Opportunistic mycoses
Fungi is harmless in normal habitat but pathogenic in compromised hosts. Can be introduced with things like implanted prosthetic devices and catheters.
What pathogen causes yeast infections? What type of pathogen is it?
Candida. Opportunistic pathogen.
What are the 3 types of organisms can cause dermatophytoses (infections of skin, hair and nails)?
Dermatophytes:
Geophilic (found in soil, ocassional pathogens)
Zoophilic (animal parasites transferred to humans)
Anthropophilic (human to human)
What kind of fungi causes coccidioidomycosis?
Ascomycota.
Which fungi is dimorphic encouraged by the nitrogen in bird and bat droppings?
Coccidiodes immitis and coccidiodes posadasii
Which phylum is Aspergillus in?
Ascomycota.
What are included in Kingdom Protista?
Algae and protozoans.
Protist
any eukaryotic unicellular or colonial organism that lacks true tissues
Features of protozoa
Habitats are mostly fresh and marine water, soil, plants and animals
Unicellular with some complex life cycles
Most are harmless but a few species are responsible for disease
What is a free-living protozoa?
Scavenge dead plant or animal debris or graze on live cells of bacteria and algae
What is a parasitic protozoa?
Lives on the fluids of the host such as plasma and digestive juices. May actively feed on tissues.
Trophozoite
Motile feeding stage of a protozoan. Requires ample food and moisture to remain active.
Cyst (protozoa)
Dormant resting stage. Formed when conditions become unfavorable for growth and feeding.
Conjugation
Form of genetic exchange between two cells
Classification of Protozoans that use flagella to move
Flagella alone or flagella and amoeboid motion
Single nucleus
Sexual reproduction by syngamy
Form cysts and are free-living
Classification of Protozoans that use amoeboid motion to move
Primarily amoeba
Use pseudopods for locomotion
Asexual reproduction by fission
Mostly uninucleate
Usually encyst
Free-living and not infectious
Classification of protozoans that use cilia to move
Have cilia in tufts for feeding and attachment
Most develop cysts
Have macro and micronuclei
Division by transverse fission
Most have definite mouth and feeding organelle
Free-living and harmless
Classification of protozoan that have no motility (sporozoa)
Motility absent
Complex life cycles with well-developed asexual and sexual stages
Special spore-like cells (sporozoites)
Entire group is parasitic
What is the only human parasite? What does it cause?
Balantidium coli (causes dysentery)
How is toxoplasmosis transmitted? What type of infections can it cause?
By cats. Can cause fetal infections.
What is the definitive host of toxoplasmosis and what is the intermediate host
Definitive = cat
Intermediate = prey animals (birds, rodents etc)
Intermediate Host
Host where sexual reproduction does not occur.
Definitive host
Where sexual reproduction occurs.
Dead-end host
A host that harbors a pathogen but does not transmit it to another host, often limiting the spread of the disease.
What is the organism that causes malaria?
Plasmodium
What 2 hosts are requires for malaria transmission?
Mosquito and human
Which host is definitive and which is intermediate in malaria transmission?
Definitive = mosquito
Intermediate = human
What kingdom are helminths in?
Kingdom Animalia
What two categories are helminths divided into?
Flatworms (thin, segmented bodies) like flukes
Roundworms (long and round, unsegmented bodies) like nematodes
4 features of helminths
Reproductive tract is most developed
Primitive digestive, excretory, nervous and muscular systems
Thick cuticles for protection
Mouth glands for breaking down the host’s tissue
3 stage life cycle of helminth
Fertilized egg (embryo)
Transmission of egg or larva to the body of another host, either a different or the same speciesLarval stage
Intermediate (secondary) host is where the larval development occursAdult Stage
The final mating and adulthood is done in the definitive (final) host.
How can male and female nematodes be told apart?
They have different morphologies
Trematodes
Sexes are separate or male/female organs are in the same worm (hermaphroditic)
Cestodes
generally hermaphroditic
What is the most common route of transmission for helminths?
Fecal-oral but can also be picked up by them burrowing into your feet from walking barefoot and picking one up.
What are the main biological reservoir for helminths?
Humans. Also sometimes animal or insect vectors.
Features of trematodes (flukes)
Flat, leaf shape
Ventral/oral sucker
Absorb food through cuticle on the outside
Monoecious
Having both male and female reproductive organs in the same organism, allowing for self-fertilization.
Dioecious
Having distinct male and female individuals within a species, requiring cross-fertilization.
Scolex
The highly specialized anterior end of a tapeworm, equipped with hooks and suckers for attachment to the host's intestine.
Proglttids
Segments of a tapeworm that contain both male and female reproductive structures, allowing for reproduction.
What are the definitive hosts for cestodes (tapeworms)?
Humans.
Cycticerci
The larval form of tapeworms that develop in the tissues of intermediate hosts, often causing cysticercosis in humans.
What kinds of cells do the planaria have?
Entire body is stem-cells that can differentiate into other cells.
Are roundworms monoecious or dioecious?
Dioecious
Where is the infection infestation of pinworms located?
Large intestines
What is the transmission mode for pinworms?
Fecal-oral/fomites
What are the cell walls of fungi made of?
Chitin
Features of fungi (6)
-Unicellular or multicellular
-Haploid
-Eukaryotes
-Chitin cell walls
-Heterotrophs
-Can reproduce sexually or asexually
General Characteristics of Viruses (8)
-Obligatory intracellular parasites
-Small
-Ubiquitous
-Contain DNA or RNA (never both)
-No ribosomes
-No ATP-generating mechanism
-Contain a protein coat (capsid)
-Resistant to antibiotics
-Some viruses enclosed by an envelope
-Some viruses have spikes
-Host specificity
Virus Host range
The spectrum of cells a virus can infect, which can vary from a single species to multiple species within a family.
Virion Structure
-Nucleic acid
-Capsid
RNA Plus (sense)
makes sense to the ribosome so it can be translated
5’ to 3’
RNA minus (antisense)
Doesn’t make sense to the ribosome so it must be transcribed firstinto a complementary strand before translation.
3’ to 5’
Types of virus DNA
Double stranded (dsDNA) - can be read directly
Single stranded (ssDNA) - often requires second strand to be synthesized
What is the name of the System used for viral classification?
The Baltimore System
Function and Structure of Capsid (protein coat)
-Prevents degradation and helps with transmission
-Capsomeres (protein unit)
-Nucleic acid + capsid protein= nucleocapsid that protects viral genetic material
Virus envelope
Enveloped versus nonenveloped (can come from other membranes)
Spikes (virus)
Can be used for attachment (both to the capsid and the host cell)
Polyhedral virus shape
Viruses with symmetrical geometry include those with icosahedral and helical structures, characterized by a uniform arrangement of proteins that form their capsid.
Icosahedral virus
A type of virus shape characterized by a polyhedral structure with 20 equilateral triangular faces. This arrangement provides a highly symmetrical and stable configuration for the viral capsid.
Helical virus shape
Aka filamentour
Capsid monomers form a helical tube around helical nucleic acid
Can be very long
Complex virus shape
Combination of polyhedral and helical structures (like bacteriophage)
Unusual arrangements
5 Steps of Lytic Cycle
Attachment
Penetration (entry)
Biosynthesis (makes viral proteins)
Maturation (assembles viruses)
Release (cell bursts = lysis)
5 steps of lysogenic cycle
Attachment
Penetration (entry)
Integration of viral DNA into host (becomes prophage)
Replication with host DNA
Can later enter lytic cycle
Prophage
Viral DNA inside host’s genome
6 steps of replication of an animal virus
Attachment
Entry
Uncoating
Biosynthesis
Assembly
Release
Acute viral infection
Quick illness, virus cleared (like the flu)
Latent viral infection
Virus hides in host cells and can reactivate later.