
Looks like no one added any tags here yet for you.
What is complete market failure?
Complete market failure occurs when a market is unable to allocate resources efficiently, resulting in a total lack of goods or services for consumers. This can happen due to extreme externalities, public goods, or information asymmetries.
What is partial market failure?
Partial market failure occurs when a market allocates resources inefficiently, leading to some goods or services being underproduced or overproduced, often due to externalities or imperfect competition.
What are externalises?
Externalities are costs or benefits that affect third parties not directly involved in a transaction, leading to market inefficiencies. Leading to under or over consumption
What are information asymmetries?
lacks of complete knowledge of one party, which can lead to adverse selection or moral hazard in transactions.
What is monopoly?
when a firm has market power and can set high prices. Monopolies may also be more inefficient because they face less competitive pressures.
What are immobilities?
geographical immobilities occur when its difficult for people or firms to move to another area
occupation immobilities cocue when it is difficult for people to retain and get skills in new high tech industries
What are public goods?
goods that are non-excludable and non-rivalrous in consumption.
What is inequality in market failure?
unequal distribution of resources and opportunities that can arise when markets do not operate efficiently.
What are the different reasons for market failure?
externalities
information asymmetries
monopoly
immobilities
public goods
inequality
What does non-rivalry mean?
when a good is consumed, it doesn’t reduce the amount available for others.
What does non- excludability mean?
this occurs when its not possible to provide a good without it being possible for other to enjoy
What does non-rejectability mean?
With a public good once provided you have no choice but to experience it
What does zero marginal cost mean?
it costs nothing for more consumers to enjoy it
what do public goods suffer form?
free rider problem
What is the free rider problem?
when individuals benefit from a public good for free, leading to underproduction of the good as producers cannot cover costs.
public good - what is the Quasi-public good?
A good that is partially non-excludable and non-rivalrous, allowing for some level of public access while still enabling private consumption.
public good - what is a pure public good?
A public good with 100% non-excludability and non-rivalry
public good - what’s a private good?
A private good is rivalrous and excludable, others are prevented from using it
Externalities - what are social benefits?
the total benefit to society
externalities - what’s the social benefit equation?
social benefit = private benefit + external benefits
externalities - what’s the social marginal benefit?
the additional benefit to society of producing an extra unit
externalities - what is social cost?
the total cost to society
externalises - what’s the social cost equation?
social cost = private cost + external costs
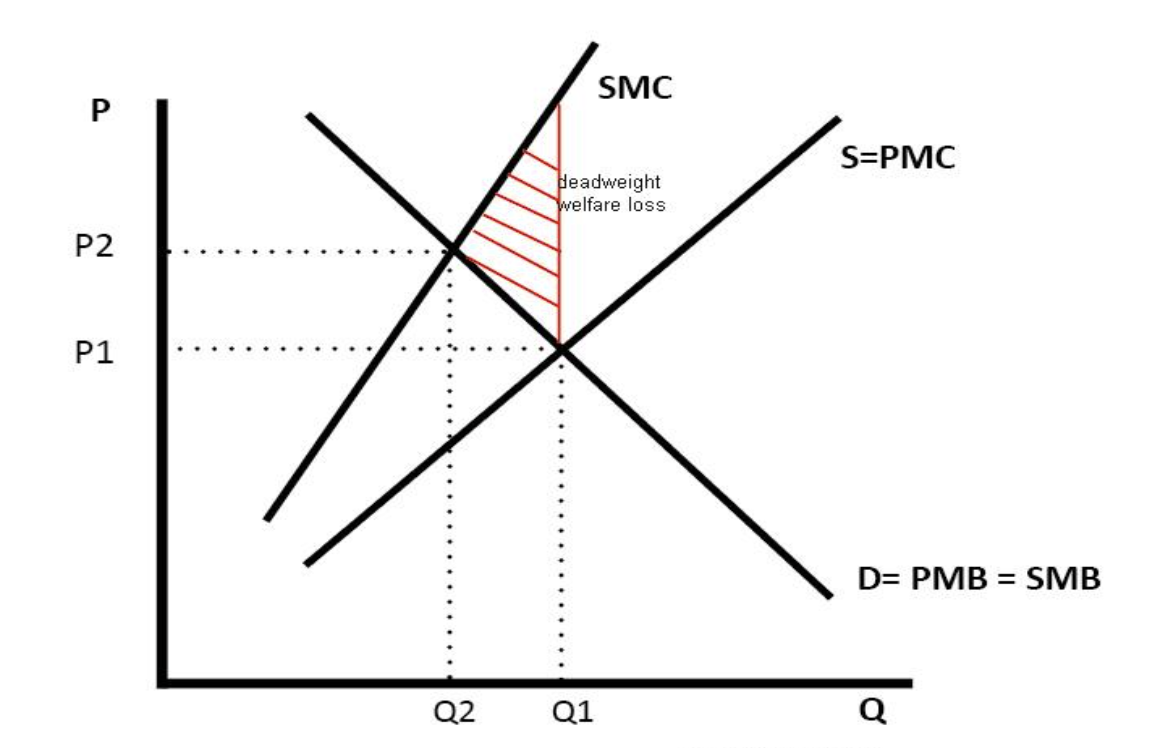
Whats negative externality?
occurs when there’s a cost imposed on a third party
Whats negative eternality of consumption?
occurs when consumer enjoys a good but causes a cost on the third party.
Whats negative eternality of production?
occurs when a firm produces a good and the production process harms third parties
Negative production externality diagram -
a positive externality in consumption
occurs when there is a benefit to a third party for your consumption
a positive externality in production
occurs when you produce a good that benefits the third party
positive consumption externality diagram
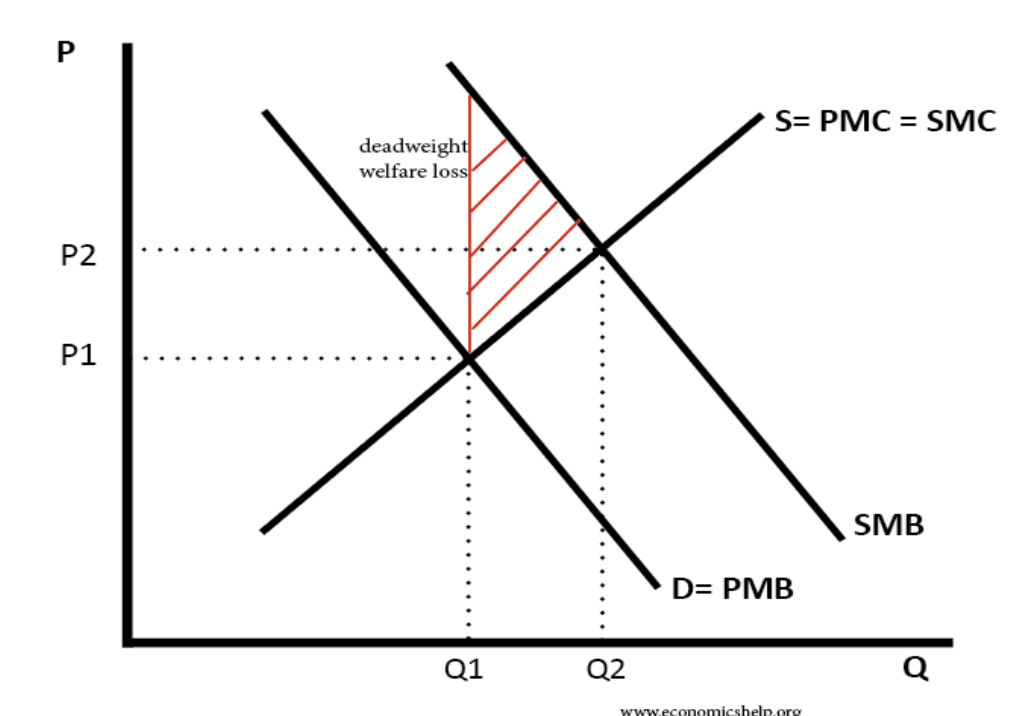
What are merit goods?
occur where people may be unaware of the benefits of consuming a good
what externalities for merit goods have?
positive
what happens to merit goods in a free market?
they are under consumed
What are demerit goods?
occurs where people ignore the cost of consuming a good
What externalises do demerit goods have?
negative
What happens to demerit goods in a free market?
they are over consumed
Whats symmetric information?
both parties share the same knowledge
Whats asymmetric information?
when one party has more information than the other parties
Whats imperfect information?
when all parties lack complete knowledge/awareness
what’s geographical immobility?
when its difficult for labour and capital to move to different areas
Whats occupational immobilities?
when labour lacks the relevant skills for a particular job
What are moral hazards?
occurs when financial guarantees alter economic behaviour and increase risk taking
negative consumption externality diagram -
What does tax do?
shifts supply curve to the left, makes good more expensive, reduces demand
What are taxes typically used for?
demerit goods with negative externalities
specific tax diagram -
What does specific tax do?
places a certain per unit tax on the good, same whatever the price
Ad valorem tax diagram -
What does ad valorem tax do?
places a certain percentage on the good, usually 20%. The higher the price of the good, the more tax is paid
What should the ideal tax be equal to?
external marginal cost, which makes consumers pay the full social marginal cost
advantages of taxes:
raised revenues for government to spend on alternatives
encourages firms to reduce pollution
What are subsidies?
grant given by the government to encourage production or consumption of a good
Whats the aim of a subsidy?
to encourage consumption of goods which are under consumed in a free market
What are tradable pollution permits?
giving firms a legal right to pollute a certain amount
What happens if a firm produces less pollution?
the firm can sell its permit to other firms
What happens to firms when they produce more pollution?
firms have to buy permits from other firms
problems of pollution permits:
difficult to measure pollution levels, incentive for firms to hide pollution