MCDB Day 4
1/50
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
51 Terms

What direction does DNA pol III move along the red (top) parental template strand? – slide 6
right to left, this is the template for leading strand
Imagine a bacterial replication fork. Synthesis of which new strand(s) of the DNA backbone would be affected by mutations in the enzyme primase?
both leading and lagging strands
What is the importance of telomeres?
these repeating DNA sequences (TTAGGG) at the ends of chromosomes PROTECT dna from getting lost/shorter (allows cell to keep dividing and not age)
Central Dogma: Transcription
dna to rna
What is the central dogma of molecular biology?
dna to rna (transcription) then rna to polypeptide (translation)
What do DNA, RNA, and polypeptide represent in baking terms?
DNA = master recipe book (cookbook)
RNA = handwritten copy of one recipe (messenger RNA/mRNA)
polypeptide = finished cake
What happens from DNA to RNA?
transcription
What happens from RNA to the polypeptide?
translation
What dramatically changes a protein’s form/function?
3D structure — Small mutations in DNA/gene sequence can cause big changes in amino acid sequence, and that changes protein shape and function
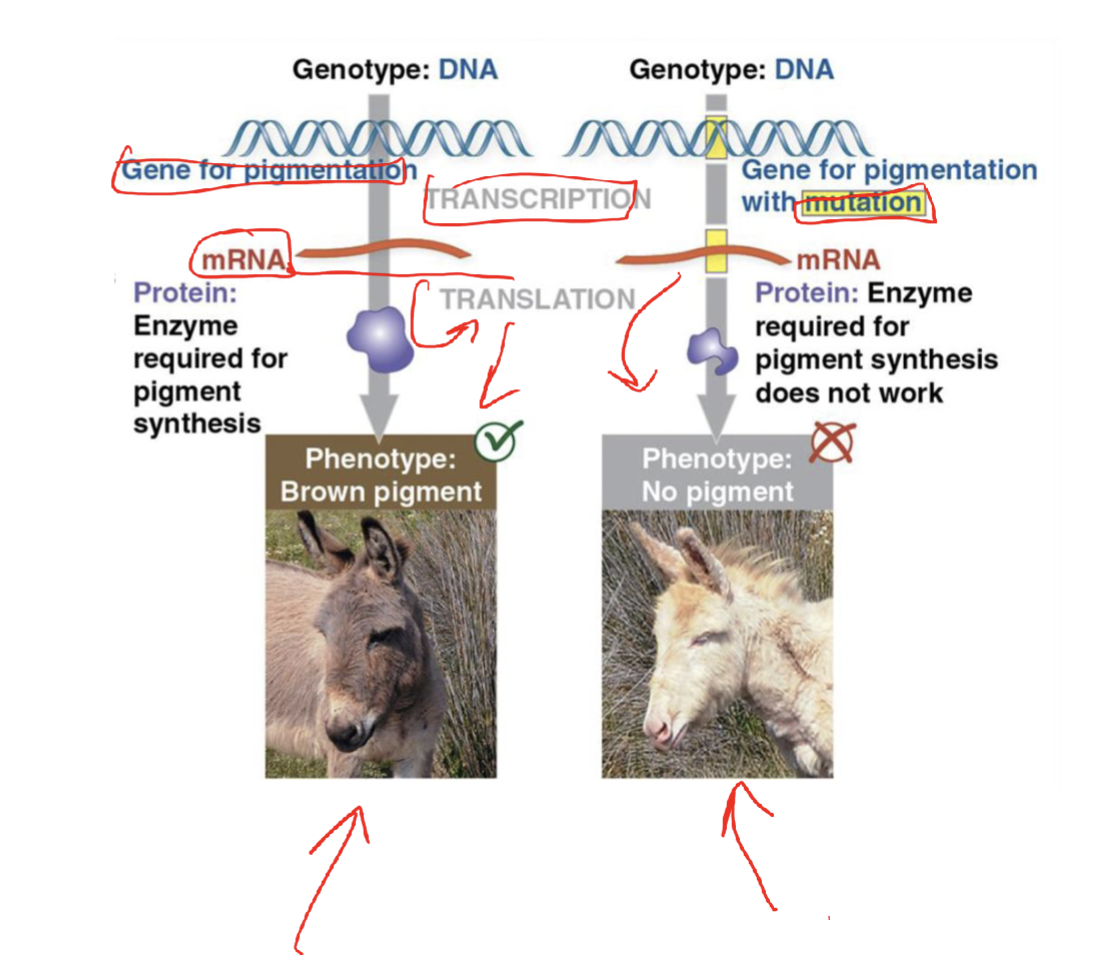
What directs the making of a protein?
gene expression -
How are proteins a direct link to an organism’s genotype and phenotype? (Genotype to Gene to mRNA, transcription, to protein to the phenotype, translation)
genotype (dna) → mRNA → protein →phentype (physical traits)
Proteins made from gene instructions determine traits
What is mRNA? – messenger RNA – message you copy from computer at library to make cake
messenger RNA – a copy of a gene/DNA that tells the ribosome what protein to make
How do you make a mature mRNA molecule? (two steps) – slide 16
DNA RNA transcription
RNA processing (splicing)
Where do both of these steps of making an mRNA molecule occur?
inside the nucleus (before translation)
What direction is the template strand considered?
3’ to 5’
What direction is the non-template strand or coding strand considered?
5’ to 3’
After transcription, what is created from the template strand? (hint: it is complementary to the template strand)
mRNA strand (5’ to 3’)
What makes the coding strand(DNA non template strand) and mRNA strand different?
URACIL base
What is RNA polymerase?
enzyme that binds once to RNA and catalyzes polymerization of hundreds of RNA bases
What does RNA polymerase do? – Slide 19
Reads template DNA strand 3’-to-5’
• Catalyze addition of nucleotides in a
5′-to-3′ direction
How much RNA polymerase is found in bacteria and eukaryotes?
bacteria/prokaryotes - 1
eukaryotes - 3 (I, II, III)
What makes RNA polymerase different from in DNA replication?
don’t need primers and dont need help unwinding bc its only one strand
What are the 4 components needed to make mRNA from DNA during transcription?
a DNA template
4 ribonucleoside triphosphates (ATP, GTP, CTP, UTP)
RNA polymerase
salts and pH buffer, if done in a test tube
What directs transcription initiation?
gene sequence
What indicates the transcription start point? What does it tell the RNA polymerase to do?
promoter sequence show start point
tells RNA polymerase where to start transcription and which is the DNA template strand
What is the TATA box?
beginning of promoter sequence
A DNA sequence in the promoter that helps RNA pol know where to start
What are transcription factors?
help guide RNA polymerase to the promoter site
Proteins in eukaryotes that help RNA polymerase bind to the promoter
What is the transcription initiation complex?
RNA pol + transcription factors + promoter DNA = the setup for transcription to begin
What are the 3 steps to transcription?
initiation, elongation, termination
In what direction does RNA polymerase READ?
3’ to 5’ -
In what direction does RNA polymerase BUILD?
5’ to 3’
Does the RNA polymerase unwind the DNA on its own?
yes it does
How is atp, adp, RNA, ntps, dnTPs, involved? How is energy added from removing phosphates?
RNA and DNA are built from NTPs and dNTPs.
These molecules provide both the base and the energy to add it to the chain by releasing two phosphates.
What happens initiation?
RNA polymerase finds the promoter (TATA box) on DNA.
It unwinds the DNA at the start site.
No primer is needed.
RNA polymerase knows which strand to read based on the promoter's orientation.
What happens in elongation?
RNA polymerase reads the template strand in the 3' → 5'
It builds the RNA strand in 5' → 3'
uses NTPs (A, U, C, G with three phosphates).
It removes 2 phosphates from each NTP to release energy and connect the base (powers the formation of phosphodiester bonds)
ATP is one of the NTPs—it gets used both as a base and as a source of energy.
What happens in termination?
RNA polymerase stops when it reaches a termination signal (a specific DNA sequence).
The RNA strand is released.
DNA rewinds.
How does the mRNA transcript get modified BEFORE exiting the nucleus? (2 ways)
- pre-mrna modification and intron splicing
What is the 5’ end of the pre-mRNA modified with? – sign to not digest
nucleotide 5’ cap
What is the 3’ end of the pre-mRNA modified with? –
poly A tail
**transcription does NOT have a stop codon
ok - true
What do the nucleotide 5’ cap and poly-A tail modification protect the mRNA from?
hydrolytic enzymes and also facilitate ribosome attachment to the 5’ end for protein synthesis
What is splicing?
removal of intron sequences
What is an exon?
coding part of mRNA
What is an intron?
noncoding part of mRNA
How are the introns exactly removed from the pre-mRNA? –
splicosomes
What makes up spliceosomes
(protein and small RNA/ribozymes that recognize the splice sites) –
poly A signal + consensus sequence (important for function but not protein coding)
What are ribozymes?-- RNA function as an enzyme by itself?
catalytic RNA molecules thatfunction as enzymes and can splice RNA
What do exons essentially code for?
Why can RNA function as an enzyme?
it can form a three-dimensional structure
because of its ability to base-pair with itself
Some bases in RNA contain
functional groups that can
participate in catalysis
● RNA may hydrogen-bond with
other nucleic acid molecules