Accounting Information Systems Flashcards - Exam 1
1/93
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
94 Terms
Access restricted
Able to limit access to authorized parties |
Available
Available to users when needed in a format that can easily and quickly used
Complete
Does not omit aspects of events or activities.
Concise
Clear and to the point; free of unnecessary detail.
Consistent
Presented in the same format over time
Current
Includes event and activity data ip to the present
Objective
Unbiased
Relevant
Reduces uncertainty and improves decision making
Reputable
Perceived as true and credible to to a trusted source
Timely
Provided in time for decision makers to make informed choices.
Understandable
Presented in a useful and intelligible format
Usable
Easy to use for different tasks by humans or machines
Verifiable
Same information produced by two independent knowledgable people
AIS components
People
Procedures
Data
Software
IT
Internal controls
Value of an AIS
Improves…
Quality
Efficiency
Internal controls
Decision making
Sharing Knowledge
Factors influencing an AIS
Organizational structure
Business strategy
IT
Value Chain
Inbound Logistics
Operations
Outbound Logistics
Firm Infrastructure (Administrative Roles)
HR
Technology
Purchasing
Marketing and Sales
Service
Data input
Data input → Data Processing → Data Storage → Information Output
Turnaround Documents
output documents generated by the company & sent to an external party
General Ledger
summary level data for every asset, liability, and equity
Subsidiary Ledger
detailed data for any general ledger account with many individual sub-accounts
Control account
General Ledger account corresponding to a subsidiary ledger
sequence codes
items are numbered consecutively for accounts of all items
block code
blocks of numbers are reserved for categories of data
group codes
subgroups of digits used to code items
mnemonic coding
letter and numbers are interspersed to identify an item
Chart of accounts
list of numbers assigned to each general ledger account
General journal
used to record infrequent or nonroutine transactions
Specialized journal
records repetitive transactions
Audit trail
traceable path of a transaction through a data processing system
Entity
something about which information is stored
Attributes
characteristics of interest that are stored
Fields
data about entity attributes
Record
input within a field
Data Value
content within a record
File
group of related records
Master file
stores cumulative information about an organization
Transaction file
records of individual business interactions that occur during a specific time
Database
set of interrelated, centrally coordinated files
CRUD acronym for data
Create
Read
Update
Delete
Batch processing
Updating done periodically
Real time processing
Updates each transaction as it occurs
Documents
records of transaction or other company data
ERP
integrates all aspects of a company’s operations with a traditional AIS
Database: several entities about which the company wants to store data about
several entities about which the company wants to store data about
Database management system
software program that manages the data.
Database system
combo of the data, database, dbms, and applications
Online transaction processing database
used to process normal business transactions.
Data warehouse
one or more very large databases containing detailed and summarized data for analytical processing.
Advantages of Database systems
Data integration
Data sharing
Minimal data redundancy and data inconsistencies
Data independence
Cross functional analysis
Logical View
How people conceptually organize and understand among data items
Physical View
The way data is physically arranged and stored in the computer system
Record layout
documents the structure of the data items stored in a file
Schema View
description of the data elements in a database, relationships among them, and the logical model used to organize them
external level
user’s logical view of their portion
subschema
each user’s logical view of their database
conceptual-level schema
org-wide view of the entire database
internal level schema
low level view of the database
access rights
portions of the database the user needs to perform their duties
data dictionary
information about the structure of the database
normalization
assuming everything is stored in one large table and then decomposed into smaller ones
semantic data modeling
designer uses the knowledge of business processes and information needs to create a diagram that shows what to include in the database
Relational Database Management System Requirements
Every column must be single valued
Entity Integrity Rule: Primary keys cannot be null
Foreign keys if not null must have values the respond to the value of a primary key in another table
All non-key attributes in a table must describe a characteristic of the object identified by the primary key
relational data model
conceptual and external-level schemas as if data are stored in 2-D tables
primary key
database attribute that uniquely identifies a specific row
foreign key
an attribute in one table that is a primary key in another table and used to link 2 tables.
Four V’s of Data
volume: amount of data created and stored
variety: different forms data can take
veracity: quality of data
velocity speed at which data is created and stored
SMART questions
Specific
Measurable
Achievable
Relevant
Timely
Data Extraction Requirements
understand the data needs and available data
performing the data extraction
verify the data extraction quality and what was done
Structured data
highly organized and fit into fixed fields
Unstructured data
no uniform structure and include items as images, vid, etc.
Semi-structured data
organized to some extent but not enough to be inserted into a RDMS
Data marts
smaller data repositories that hold structured data
Data lake
collection of structured, semi-structured, and unstructured data in a single place
Dark data
data that an organization stores but isn’t analyzed and is ignored
Data swamp
data lakes that aren’t accurately documented and cannot be used
data about the data dictionary
data about the data dictionary
Flat file
text file that consolidates data from multiple tables into a single row
Delimiter
a character that separates one field from another
Text qualifier
two characters that indicate the start and end of a field
Transforming Data Requirements
Understand the data and the desired outcome
Standardize, structure, and clean the data
Validate data quality and verify that data meets the data requirements
Document the transformation process
Load the data
in the name
Descriptive Analytics
asks what happened.
Diagnostic Analytics
asks why did this happen.
Prescriptive Analytics
asks what should be done.
Predictive Analytics
answer the question “why might this happen in the future”
Data storytelling
process of translating complex data into simpler terms
Data visualization
use of graphs to show data
Data dashboard
collection of key metrics and data points
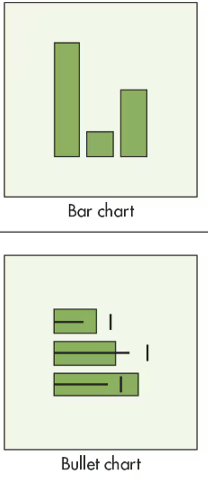
What graph is used for Comparison?
Bar Chart or Bullet Chart
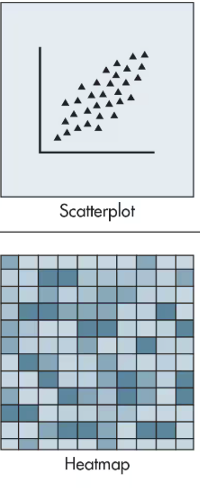
What graph is used for Correlation?
Scatter Plot or Heatmaps
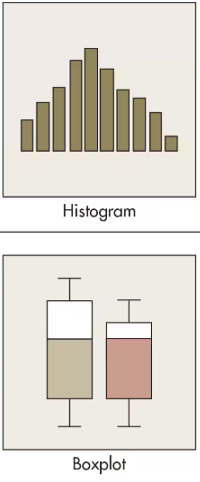
What graph is used for Distribution?
Histogram or Box Plot
What graph is used for Trend Evaluation?
Line Chart or Area Chart
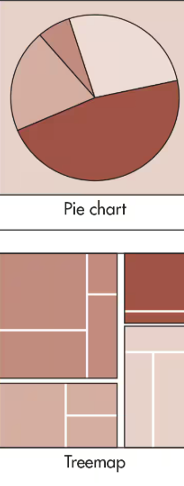
What graph is used for Part-to-Whole?
Pie Chart or Treemap